Topic sahara desert on map of egypt: Explore the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert in Egypt, a mesmerizing blend of history, culture, and breathtaking landscapes awaiting discovery.
Table of Content
- Where can I find the Sahara Desert on a map of Egypt?
- Geographical Location of the Sahara in Egypt
- Size and Extent of the Sahara Desert in Egypt
- Major Landmarks and Features in the Egyptian Sahara
- Climate and Weather Patterns in the Sahara of Egypt
- Flora and Fauna Unique to the Egyptian Sahara
- YOUTUBE: Explaining Egypt\'s Geography in Under 3 Minutes
- Historical Significance of the Sahara in Egyptian History
- Impact of the Sahara on Egyptian Culture and Society
- Navigation and Travel Routes Through the Egyptian Sahara
- Conservation Efforts in the Sahara Desert of Egypt
- Future Challenges and Opportunities in the Egyptian Sahara
Where can I find the Sahara Desert on a map of Egypt?
To find the Sahara Desert on a map of Egypt, you can follow these steps:
- Get a map of Egypt.
- Locate the western side of Egypt.
- Identify the vast expanse of desert in this region.
- This area is part of the Sahara Desert.
Alternatively, you can use online mapping services like Google Maps or OpenStreetMap to search for the Sahara Desert in Egypt. Simply enter \"Sahara Desert\" or \"Western Egypt\" in the search bar, and the map will show you the location.
READ MORE:
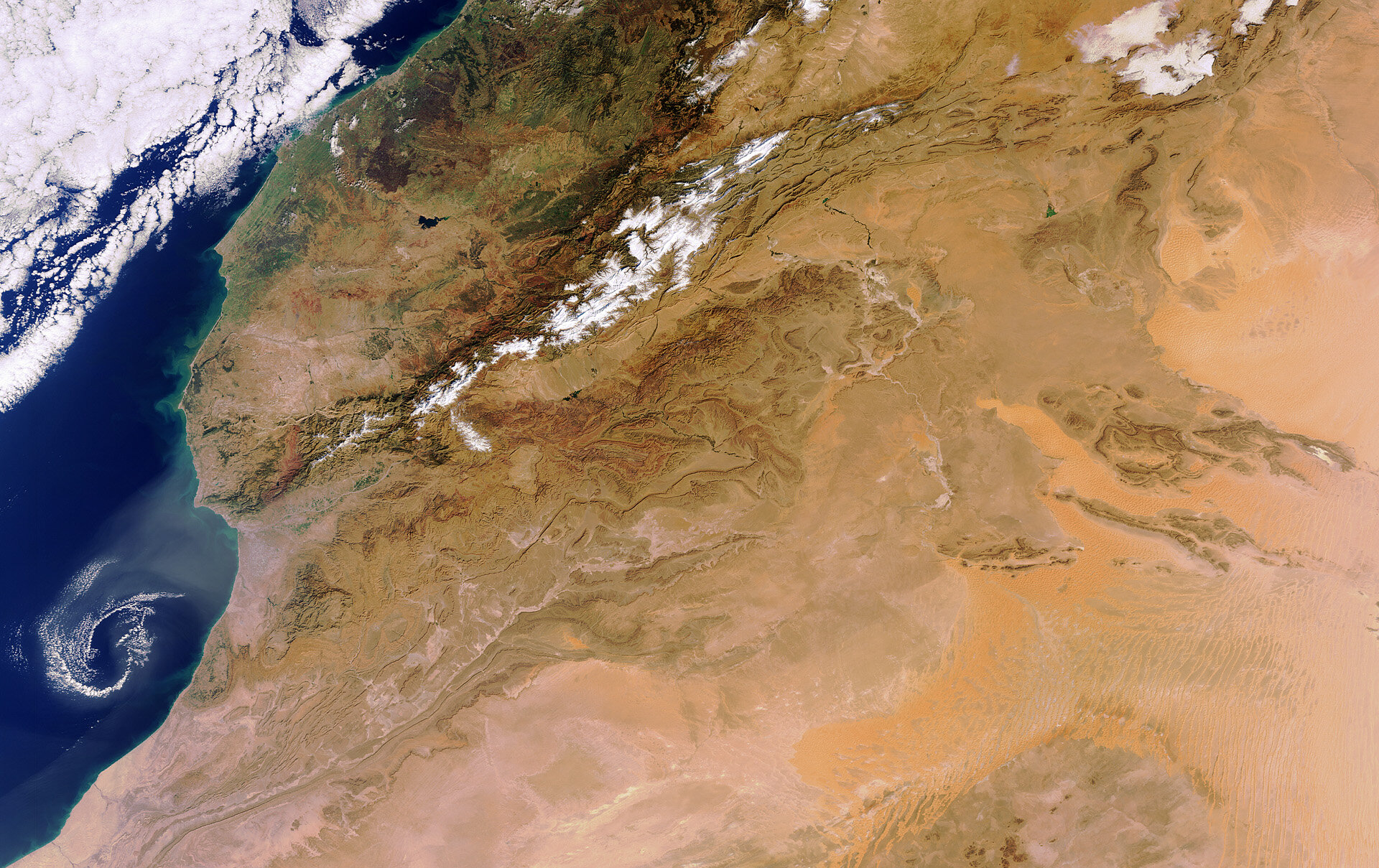
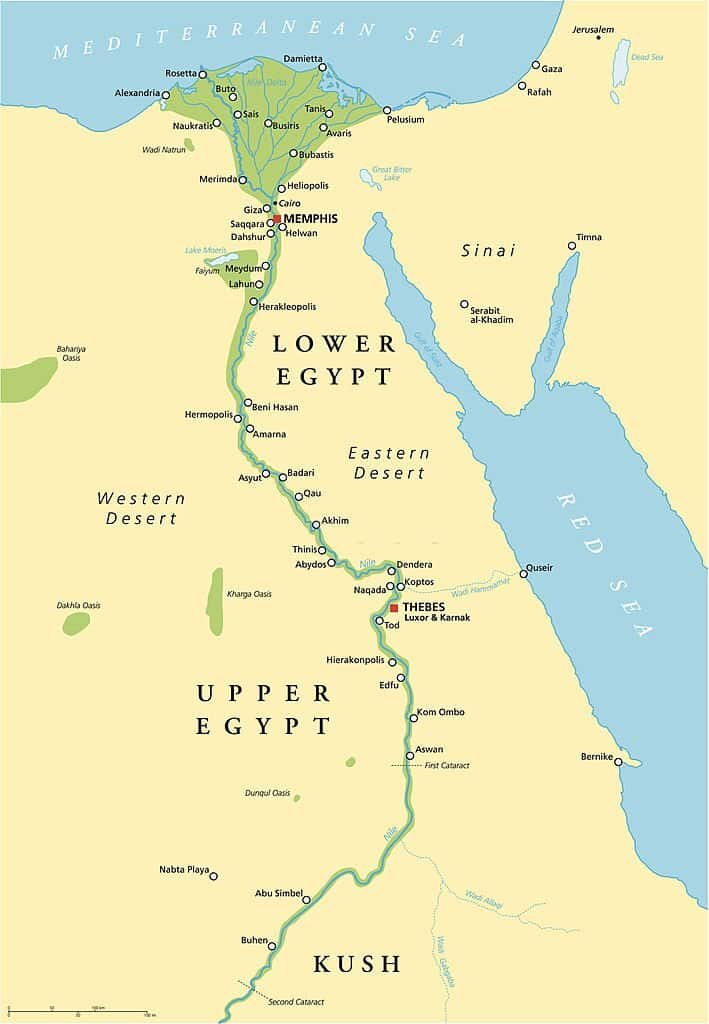
Geographical Location of the Sahara in Egypt
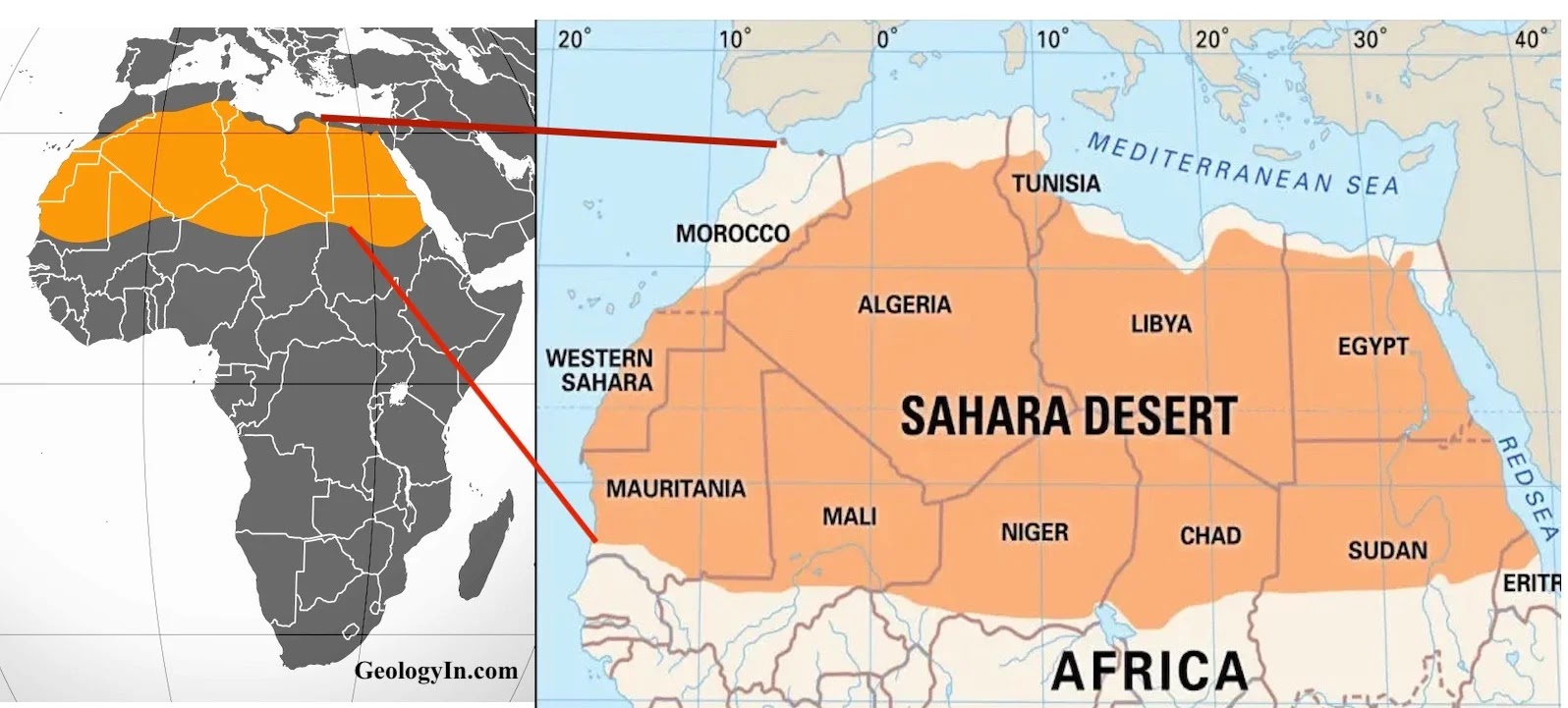
The Sahara Desert, encompassing a significant portion of North Africa, stretches across multiple countries, including Egypt. It is known for its varied landscapes, ranging from vast sand dunes to rocky hamada and ergs, the latter being large areas covered in sand dunes. The Sahara"s terrain is shaped by elements like wind and occasional rainfall, creating unique features such as sand seas, stone plateaus, dry valleys, and salt flats.
In Egypt, the Sahara Desert forms a major part of the country"s land area, particularly the Western Desert, which lies west of the Nile River and extends to the Libyan border. This region is a part of the greater Sahara and is characterized by its arid conditions, sand dunes, and distinct oases.
The Great Sand Sea, a prominent feature of the Egyptian Sahara, is a vast sand desert located between western Egypt and eastern Libya. This desert region is characterized by large sand dunes and covers about 72,000 square kilometers. The Great Sand Sea stretches approximately 650 kilometers from north to south and 300 kilometers from east to west, displaying a pattern of long sand ridges.
Furthermore, the Sahara"s geographical reach in Egypt is highlighted by its boundaries, extending from the Red Sea in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west. The Sahara"s southern boundary is marked by the Sahel, a semi-arid region that transitions between the desert and more fertile areas.
The Sahara has undergone significant changes over thousands of years, shifting between desert and savanna grassland. This is largely due to the Earth"s axial precession, which affects the location of the North African monsoon, thus influencing the desert"s climate and geography over millennia.

Size and Extent of the Sahara Desert in Egypt
The Sahara Desert, one of the largest deserts globally, stretches across a significant portion of North Africa, including Egypt. In Egypt, the Sahara primarily covers the Western Desert, which lies west of the Nile River and extends to the Libyan border. This desert region is a significant part of Egypt"s land area, characterized by its diverse landscapes, including vast sand dunes, rugged plateaus, and distinctive oases.
The Great Sand Sea is a notable part of the Egyptian Sahara, spanning approximately 72,000 square kilometers (28,000 square miles). It is located between western Egypt and eastern Libya, showcasing a vast expanse of sand dunes. The Great Sand Sea features a mix of different types of megadunes and stretches about 650 kilometers from north to south and 300 kilometers from east to west.
Overall, the Sahara Desert in Egypt presents a diverse and extensive landscape, encompassing a significant portion of the country"s land area. The desert"s terrain includes features shaped by wind and occasional rainfall, such as sand dunes, dry valleys, and salt flats, contributing to its unique and vast expanse.
Major Landmarks and Features in the Egyptian Sahara
The Egyptian Sahara is home to several significant landmarks and features that make it a unique and intriguing landscape. Key among these is the Western Desert, which encompasses a vast area west of the Nile River, extending up to the Libyan border. This desert region is characterized by its arid conditions, sand dunes, oases, and rugged plateaus.
- The Great Sand Sea: This is an expansive sand desert, or erg, located between western Egypt and eastern Libya. Covering approximately 72,000 square kilometers, it is known for its extensive dunes, which form a significant portion of the Western Desert.
- Giza Necropolis: Though not directly in the desert, the Giza pyramid complex, including the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure, along with the Great Sphinx, are located near the edge of the Sahara in Egypt.
- Black Desert: Characterized by its volcano-shaped and widely spaced mounds, the Black Desert is a region in the Western Desert between the White Desert in the south and the Bahariya Oasis in the north. Its unique black color comes from basalt sills capping its mounds.
Each of these landmarks contributes to the diverse and historic landscape of the Egyptian Sahara, making it a region rich in both natural wonders and ancient cultural heritage.
Climate and Weather Patterns in the Sahara of Egypt
The Sahara Desert in Egypt, part of the vast Sahara that stretches across North Africa, exhibits distinct climatic characteristics. The climate of the Sahara is primarily hyperarid and tropical, with minimal annual precipitation, high daytime temperatures, and cooler nights.
- Temperature Variations: Daytime temperatures can be extremely high, often exceeding 40°C (104°F). However, at night, the desert can experience significant drops in temperature, occasionally nearing freezing points in some regions.
- Annual Precipitation: The Sahara receives very little rainfall annually, often less than 250 mm (9.8 inches). Rainfall is scarce and unpredictable, with some regions remaining dry for several years.
- Wind Patterns: The Sahara is known for its wind patterns, which can result in severe sandstorms. These winds, such as the Khamsin in Egypt, are hot, dry, and can carry large amounts of sand and dust.
- Geographical Influence: The topography and geography of the Sahara in Egypt, including features like the Great Sand Sea and the Black Desert, play a significant role in the local climate. These areas are characterized by vast sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and unique landforms shaped by the prevailing climatic conditions.
- Seasonal Variations: Although the Sahara is predominantly arid, there are seasonal variations. The summer months are generally the hottest, while winter can bring milder temperatures, especially during the night.
Overall, the Sahara Desert in Egypt presents a harsh and challenging environment, dominated by extreme temperatures, scarce rainfall, and shifting sand dunes, making it one of the most iconic deserts in the world.
Flora and Fauna Unique to the Egyptian Sahara
The Egyptian Sahara, while harsh and arid, supports a variety of flora and fauna adapted to the extreme desert conditions. The vegetation is generally sparse, with plants that can survive the extreme heat and dryness. Animals in this region have also adapted to the challenging environment.
- Flora: The vegetation mainly consists of grasses, shrubs, and trees found in the highlands, oases, and along wadis (dry riverbeds). These include various halophytes (salt-tolerant plants) in saline depressions and heat- and drought-tolerant grasses, herbs, and small shrubs.
- Fauna: The wildlife of the Egyptian Sahara includes a range of species adapted to desert life. These include various reptiles like lizards and snakes, as well as mammals such as the fennec fox, which is known for its distinctive large ears that help dissipate heat. Birds, insects, and small mammals also populate the region, each with adaptations to survive the desert conditions.
Despite the extreme conditions, these plants and animals have evolved unique ways to thrive in the Egyptian Sahara, making it a unique ecosystem within the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert.

Explaining Egypt\'s Geography in Under 3 Minutes
Explore the mesmerizing world of geography like never before! Immerse yourself in breathtaking landscapes, diverse cultures, and fascinating natural wonders as you embark on an unforgettable journey through this incredible video.
The Sahara Desert Ecosystems
Dive into the enchanting world of ecosystems and witness the delicate balance of nature come to life. From lush rainforests teeming with exotic wildlife to the vast depths of the ocean, this captivating video will leave you in awe of our planet\'s incredible biodiversity.
Historical Significance of the Sahara in Egyptian History
The Sahara Desert has played a significant role in Egyptian history, shaping the culture, economy, and development of ancient Egyptian civilization. From serving as a barrier to influencing trade routes, the Sahara"s impact is profound.
- Barrier and Protector: The Sahara served as a natural barrier, protecting ancient Egypt from external invasions, thanks to its harsh climate and difficult terrain.
- Trade Routes: Despite its arid conditions, the Sahara was home to important trade routes. Caravans traversed the desert, connecting Egypt with Sub-Saharan Africa, which facilitated the trade of gold, salt, and other commodities.
- Cultural Exchanges: These trade routes also enabled cultural exchanges, allowing for the transfer of knowledge, religion, and cultural practices between Egypt and other African civilizations.
- Archaeological Significance: The Sahara has been a rich source of archaeological discoveries, revealing insights into ancient Egyptian civilization and its interaction with neighboring regions.
- Environmental Changes: Historical evidence suggests that the Sahara was once a much greener area, with a climate that supported more abundant life, which had a significant impact on early human settlements in the region.
Overall, the Sahara Desert"s vast and challenging landscape has been both a shield and a crossroads for ancient Egypt, deeply influencing the course of its history and development.
Impact of the Sahara on Egyptian Culture and Society
The Sahara Desert has profoundly influenced Egyptian culture and society throughout history. Its vast, arid expanse has shaped the way of life, traditions, and even the historical development of Egypt.
- Geographical Barrier: The Sahara acted as a natural barrier, shaping Egypt"s early development by isolating and protecting it from external influences and invasions, thereby allowing a unique culture to flourish.
- Trade and Connectivity: Despite its harshness, the Sahara was a conduit for trade. Ancient caravan routes crossed this desert, connecting Egypt to the rest of Africa, facilitating trade in goods like gold and ivory, and influencing cultural and social exchanges.
- Religious and Mythological Significance: The vastness and mystery of the Sahara have been reflected in Egyptian mythology and religious beliefs, often symbolizing death and the afterlife, as seen in their burial practices and the reverence for deserts in their mythology.
- Agricultural Development: The contrast between the fertile Nile Valley and the barren Sahara highlighted the importance of the Nile for survival and prosperity, leading to significant agricultural advancements.
- Archaeological Importance: The Sahara has been a source of invaluable archaeological discoveries, offering insights into ancient Egyptian civilization, their way of life, and their interaction with the environment.
In summary, the Sahara Desert has been more than just a backdrop in Egyptian history; it has been a key player in shaping the society, culture, and even the physical development of ancient Egypt.

Navigation and Travel Routes Through the Egyptian Sahara
The Egyptian Sahara, with its vast and challenging terrain, has a network of traditional and modern navigation and travel routes. These routes have been crucial for trade, exploration, and connecting different regions of Egypt and beyond.
- Ancient Caravan Routes: Historically, caravan routes were the lifelines of travel across the Sahara. They connected various oases, which served as rest stops and trading hubs. These routes facilitated the movement of goods, people, and cultural exchanges across the desert.
- Modern Roadways: In recent times, modern roadways have been developed, enhancing connectivity within the desert regions. These roads link major towns and cities to the remote areas of the Sahara, making travel more accessible and faster.
- The Great Sand Sea: The Great Sand Sea, an expansive area of the Egyptian Sahara, is known for its large dunes and unique landscapes. It has been a point of interest for both historical exploration and modern tourism. Navigation through this area requires skill and knowledge of the terrain.
- Oases as Navigational Landmarks: Oases like Siwa, located near the Libyan border, have historically been important navigational landmarks. They not only provide respite in the harsh desert environment but also act as cultural and trade centers.
- Role of Technology: Modern technology, including GPS and satellite imagery, has revolutionized navigation in the Sahara, making it safer and more reliable. However, traditional knowledge and techniques of desert navigation are still valued and used.
Navigation through the Egyptian Sahara, with its unique combination of historical routes and modern technology, continues to be an integral part of the region"s character and cultural heritage.
Conservation Efforts in the Sahara Desert of Egypt
The Sahara Desert, encompassing a large part of Egypt, is an environment of extreme conditions and unique ecosystems. Conservation efforts in this region are focused on preserving its natural heritage and biodiversity. These efforts include a combination of government initiatives, international cooperation, and local community engagement.
- Protected Areas: Several areas within the Egyptian Sahara have been designated as protected areas. These regions aim to conserve the unique flora, fauna, and geological features of the desert, while also promoting sustainable tourism.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Efforts are being made to preserve the unique species of plants and animals that have adapted to the harsh desert conditions. This includes studies and measures to protect endangered species and their habitats.
- Combating Desertification: Actions to combat desertification include reforestation projects and the sustainable management of water resources. These initiatives help in maintaining the ecological balance and preventing further degradation of the desert environment.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research and environmental monitoring are crucial for understanding the Sahara’s ecosystem. This includes tracking climate change impacts and developing strategies to mitigate them.
- Community Involvement: Local communities play a vital role in conservation efforts. Programs that involve community participation aim to promote sustainable living practices and the use of traditional knowledge in conservation strategies.
- International Cooperation: Egypt collaborates with international organizations and neighboring countries to share knowledge and resources for the effective conservation of the Sahara Desert.
Overall, the conservation efforts in the Egyptian Sahara are a blend of protecting natural heritage, supporting sustainable development, and fostering global and local cooperation.
READ MORE:
Future Challenges and Opportunities in the Egyptian Sahara
The Egyptian Sahara, a vast and historic desert, faces numerous challenges and opportunities in the coming years. This section explores these aspects in detail, offering insights into what the future may hold for this iconic region.
Challenges
- Climate Change: The impact of climate change poses significant challenges, including more extreme weather patterns and potential alterations in the Sahara"s size and ecosystem.
- Water Scarcity: Water scarcity remains a critical issue, demanding innovative solutions for sustainable water management in desert communities and oases.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Preserving the unique flora and fauna of the Sahara, which have adapted to its arid conditions, is crucial in the face of expanding human activities and climate change.
- Sustainable Tourism: Balancing the growth of tourism with the protection of natural and historical sites is essential to ensure the sustainability of this sector.
Opportunities
- Renewable Energy Development: The vast, sunny expanses of the Sahara offer enormous potential for solar energy production, contributing to Egypt"s energy security and economic growth.
- Eco-Tourism: Developing eco-friendly tourism initiatives can help preserve the desert"s natural beauty while promoting sustainable economic development.
- Archaeological Discoveries: Ongoing archaeological research in the Sahara continues to uncover insights into ancient civilizations, enhancing our understanding of human history.
- Technological Innovations: Advanced technologies, such as satellite monitoring and water conservation techniques, can improve life in desert regions and mitigate environmental impacts.
In conclusion, the Egyptian Sahara stands at a crossroads of challenges and opportunities. With thoughtful management and innovative approaches, this timeless desert can continue to be a source of wonder, history, and development for future generations.
Discover the enigmatic beauty of the Sahara in Egypt, a land where ancient secrets and modern challenges intertwine, beautifully illustrated on our map. Embark on a journey through time and sand, and be captivated by its enduring allure.