Topic sahara desert map egypt: Explore the majestic Sahara Desert through the lens of Egypt"s rich history and geography, where ancient mysteries and modern wonders blend seamlessly on the map of this timeless landscape.
Table of Content
- What is the geographical location of the Sahara Desert in Egypt?
- Geography and Location of the Sahara Desert
- Climatic Conditions in the Sahara Desert
- Ecological Regions and Biodiversity
- Historical Significance and Cultural Aspects
- Sahara Desert in Egypt: Key Features and Landmarks
- Map of the Sahara Desert: Boundaries and Countries
- YOUTUBE: Circles in the Sahara: Who Made Them?
- Travel and Tourism in the Sahara Desert
- Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts
- Frequently Asked Questions about the Sahara Desert
What is the geographical location of the Sahara Desert in Egypt?
The Sahara Desert is located in the northeastern part of Africa, including a portion of Egypt. Its geographical location in Egypt can be described as follows:
- The Sahara Desert stretches across the eastern and southeastern regions of Egypt.
- It covers parts of Egypt\'s Western Desert, which is located to the west of the Nile River.
- The vast majority of the Sahara Desert lies outside of Egypt\'s borders and extends into several other African countries such as Libya, Sudan, and Algeria.
- In Egypt, the Sahara Desert occupies a significant portion of the country, particularly in the areas south of the Western Mediterranean coastline.
- It is characterized by its arid and barren landscape, with vast expanses of sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and occasional oasis.
- The Sahara Desert in Egypt is sparsely populated, with only a few scattered settlements and nomadic tribes.
- The desert plays a crucial role in Egypt\'s history and culture, as it influenced the development of ancient civilizations and served as a trade route.
Overall, the Sahara Desert occupies a substantial portion of Egypt\'s eastern and southeastern regions, contributing to the diverse geography of the country.
READ MORE:
Geography and Location of the Sahara Desert
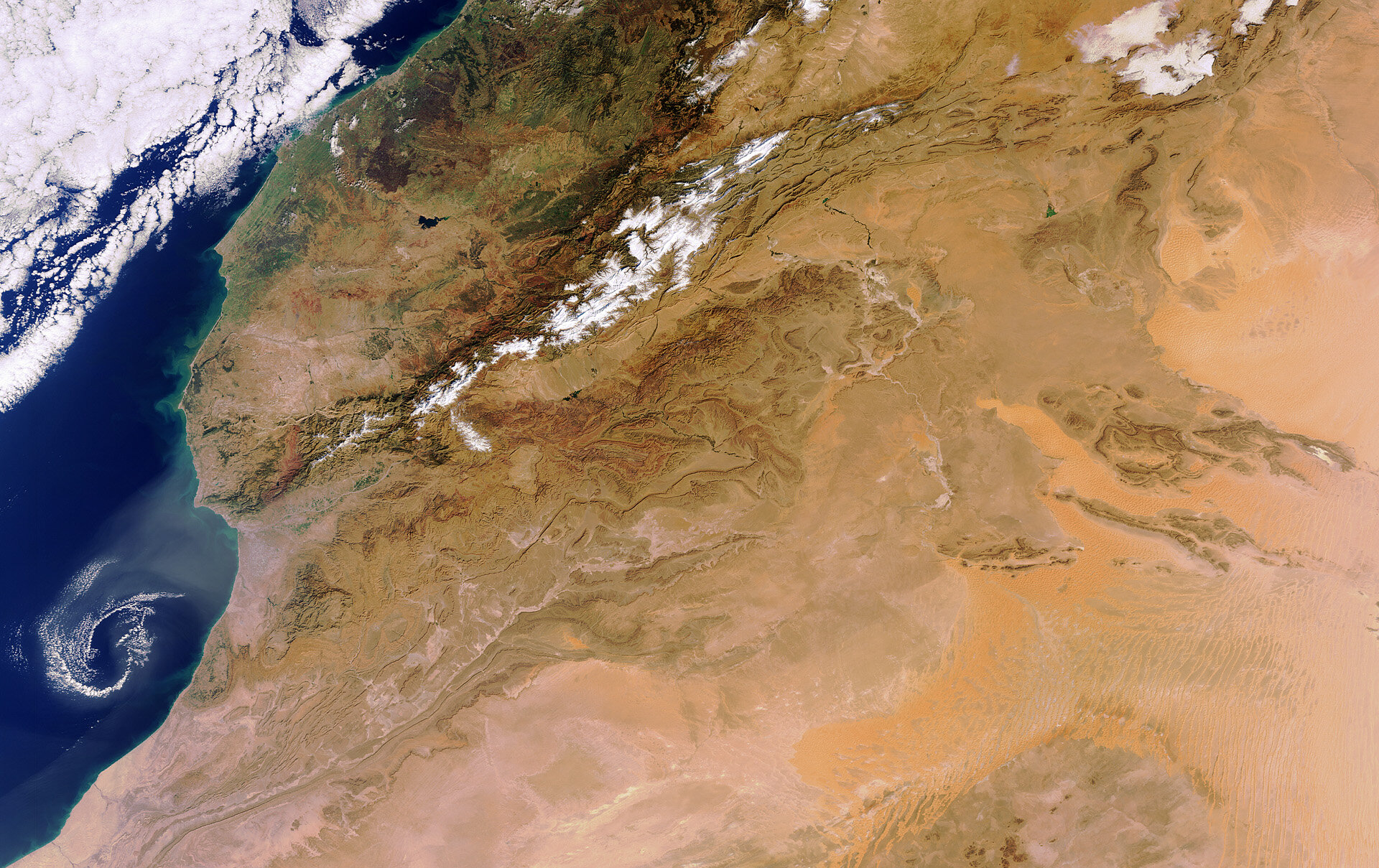
The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, spans across North Africa, covering significant portions of several countries including Egypt. With an area of approximately 9.2 million square kilometers, it extends over 31% of the African continent. The Sahara is known for its harsh climatic conditions, supporting unique ecosystems and diverse wildlife adapted to the extreme environment.
- Geographical Spread: The desert encompasses parts of Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, and Tunisia.
- Ecological Diversity: Despite its arid conditions, the Sahara contains various ecological regions like the Atlantic Coastal Desert, the North Saharan steppe and woodlands, and the central Sahara ecoregion. Each of these regions hosts a variety of flora and fauna specially adapted to survive in such extreme environments.
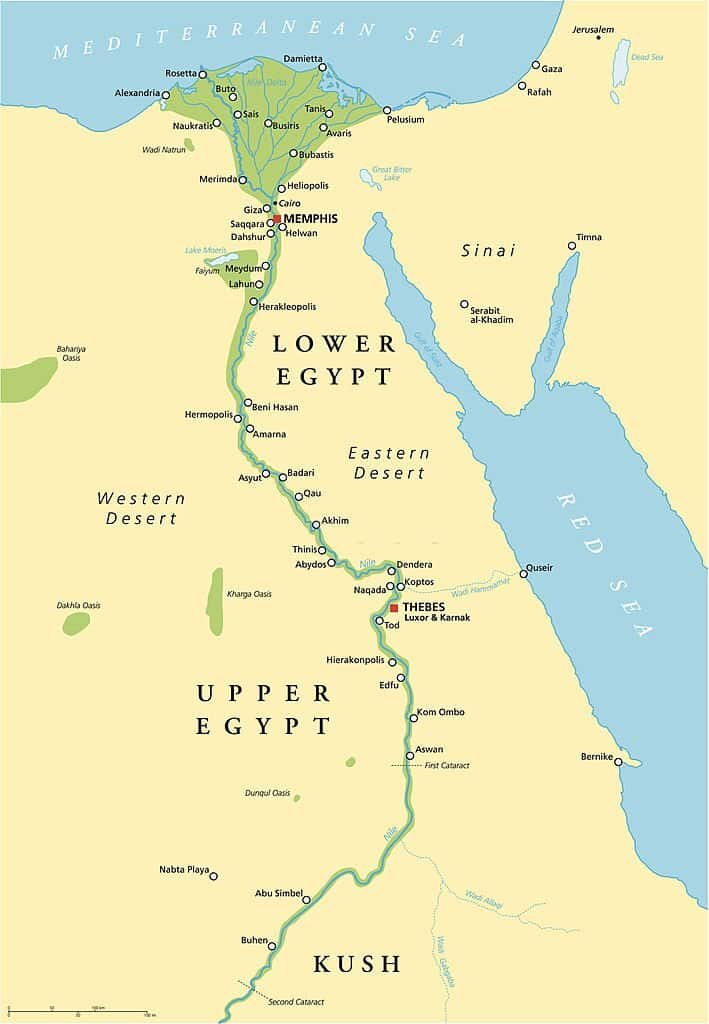
- Egypt"s Western Desert: In Egypt, the Sahara is predominantly known as the Western Desert, extending west of the Nile up to the Libyan border. This region includes unique geological formations such as the Great Sand Sea, a vast area covered by sand dunes.
- Historical and Cultural Significance: The Sahara has been a cradle of ancient civilizations and trade routes, profoundly influencing the culture and history of the region. Landmarks like the Great Sphinx of Giza in Egypt stand as testament to the intricate relationship between the desert and early human civilizations.
The Sahara"s diverse landscape, ranging from rocky plateaus to vast sand dunes, and its position stretching from the Red Sea in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west, make it a significant geographical feature on the map of Egypt and North Africa.

Climatic Conditions in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, encompassing Egypt"s Western Desert, experiences extreme climatic conditions, characterized by its arid environment and minimal rainfall. This vast desert undergoes significant climatic variations, influenced by its geographical expanse and topographical features.
- Climate Variability: The Sahara"s climate is divided into two primary regimes. The northern region experiences arid subtropical climate with two rainy seasons, while the southern region has a more tropical climate with one rainy season.
- Rainfall Patterns: The northern edges of the Sahara, affected by Mediterranean systems, receive minimal annual rainfall between 4 and 10 inches. The southern fringes, bordering the Sahel, also receive similar levels of rainfall due to the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
- Central Sahara Dryness: The central part of the Sahara is exceptionally arid, receiving almost no rainfall, often less than 0.04 inches annually, due to prevailing anticyclonic weather patterns.
- Historical Climate Fluctuations: Studies indicate that the Sahara undergoes cycles between being a dry desert and a lush, green oasis approximately every 20,000 years, driven by changes in the Earth"s axial tilt and consequent variations in monsoon activity.
- Winds and Dust Storms: The Sahara is known for its powerful and unpredictable northeastern winds, which can cause severe dust storms, reducing visibility to zero and transporting dust across continents.
The climatic stability of the Sahara over the last 2,000 years has contributed to its current desert landscape, making it both a challenging and fascinating subject for climatologists and historians alike.
Ecological Regions and Biodiversity
The Sahara Desert, including its extension in Egypt, is not just a barren expanse but a region of diverse ecological zones and a surprising array of wildlife that has adapted to its extreme conditions.
- Ecological Regions: The Sahara encompasses several ecological regions such as the Atlantic Coastal Desert, North Saharan steppe and woodlands, the central Sahara Desert ecoregion, South Saharan steppe and woodlands, and the West Saharan Montane Xeric Woodlands.
- Biodiversity: Despite its arid nature, the Sahara is home to a range of flora and fauna. Notable plant species include acacia trees, succulents, and Saharan cypress. Wildlife includes species such as the cheetah, gazelles, ostrich, Fennec fox, and monitor lizards, alongside venomous creatures like the deathstalker scorpion and the sand viper.
- Adaptations to Arid Conditions: The plants and animals in the Sahara have evolved remarkable adaptations to survive the harsh climate. Plants often have features to conserve water, while animals have developed behaviors and physical characteristics to cope with the extreme temperatures and scarce water resources.
- Human Life: Approximately 2.5 million people inhabit the Sahara, many of whom are of Berber or Arabic descent. They have historically adapted to the desert environment, with some leading nomadic lifestyles, moving with herds of livestock.
The ecological complexity of the Sahara, often underestimated, plays a crucial role in the environmental dynamics of North Africa, including Egypt"s Western Desert region.
Historical Significance and Cultural Aspects
The Sahara Desert, stretching into Egypt"s Western Desert, holds profound historical and cultural significance. This vast expanse has been a cradle of civilizations and a nexus of cultural interactions for millennia.
- Ancient Civilizations: The Sahara, particularly along the Nile River, was the birthplace of one of the world"s oldest civilizations – the Ancient Egyptians. The Kingdom of Kush also thrived along these fertile banks, showcasing the desert"s role in nurturing early human societies.
- Trade and Commerce: The Sahara"s trade routes, used for the transport of goods like gold, salt, and ivory, were crucial to the economies of ancient African civilizations. Camel caravans, often traveling in cooler hours, were a common sight, underlining the desert"s role in regional trade.
- Nomadic Cultures: The Berbers, known for their nomadic lifestyle, have long traversed the Sahara, moving in search of grazing grounds for their livestock, showcasing the adaptability of human life in harsh conditions.
- Architectural Marvels: The Great Sphinx of Giza, near the edge of the Sahara in Egypt, stands as a testament to the desert"s historical significance. This monumental sculpture, representing Pharaoh Khafre, illustrates the intricate relationship between the desert and the development of monumental architecture in ancient Egypt.
- Environmental Transformations: Historically, the Sahara has undergone significant environmental changes, alternating between desert and savanna grassland. These transformations have had a profound impact on the cultures and civilizations that have inhabited the region.
The Sahara Desert"s rich history is interwoven with the development of human civilizations, trade networks, and unique cultures, making it a fascinating subject for historians and archaeologists alike.
Sahara Desert in Egypt: Key Features and Landmarks
The Sahara Desert in Egypt, also known as the Western Desert, is a vast and historically rich landscape, boasting unique features and landmarks of great significance.
- Great Sand Sea: A vast area of sand dunes, the Great Sand Sea is a prominent feature of the Sahara in Egypt. It covers a large part of the Western Desert and is known for its majestic and ever-changing dune formations.
- White Desert: Famous for its surreal, chalk-white landscapes and unique limestone formations, the White Desert is a popular tourist destination and a natural wonder within the Egyptian Sahara.
- Siwa Oasis: Situated near the Libyan border, Siwa Oasis is an ecological and cultural haven amidst the desert. Known for its rich history, unique culture, and natural springs, Siwa offers a glimpse into traditional desert life.
- Valley of the Whales (Wadi Al-Hitan): This UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Western Desert is renowned for its fossil remains of ancient whales, providing crucial insights into the evolution of these marine mammals.
- Black Desert: Known for its dark hills and mountains covered with black quartz, the Black Desert offers a stark contrast to the more typical sandy landscapes of the Sahara.
- The Great Sphinx of Giza: Although on the edge of the Sahara, the Sphinx is an iconic symbol of Egypt"s ancient heritage. This monumental limestone statue epitomizes the civilization"s architectural and artistic achievements.
These key features and landmarks highlight the diversity and cultural richness of the Sahara Desert in Egypt, making it a region of immense historical and natural value.

Map of the Sahara Desert: Boundaries and Countries
The Sahara Desert is an immense geographical feature with significant boundaries and spans several countries in North Africa, including a notable part in Egypt.
- Geographical Extent: The Sahara is the world"s largest hot desert, covering around 9 million square kilometers, which equates to about 31% of Africa.
- Country Coverage: This vast desert spans across multiple countries such as Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Western Sahara, Sudan, and Tunisia.
- Northern and Southern Boundaries: The northern boundary of the Sahara is marked by the Mediterranean Sea, while the southern boundary transitions into the Sahel region, a semi-arid zone situated south of the desert.
- Eastern and Western Extent: To the east, the Sahara reaches to the Red Sea, covering a large part of Egypt, including the Western Desert, up to the Libyan border. The western boundary of the Sahara extends to the Atlantic coast of Western Sahara and Mauritania.
- Physical Features: The Sahara is known for its diverse terrain, including rocky hamada (stone plateaus), ergs (sand seas with dunes), dry valleys (wadis), and salt flats. Some of the sand dunes can reach over 180 meters in height.
The map of the Sahara Desert highlights its vastness and the varied landscapes it encompasses, contributing to its unique geological and cultural significance in Egypt and across North Africa.
Circles in the Sahara: Who Made Them?
\"Unlock the mysteries of the past and embark on a journey through time with our captivating archaeology video. Explore ancient ruins, decipher ancient scripts, and uncover the hidden treasures of our ancestors. Join us as we delve into the vibrant world of archaeology!\"
The Sahara Desert Ecosystems
\"Dive into the breathtaking realm of biodiversity with our mesmerizing video. Immerse yourself in the wonders of the natural world, from lush rainforests teeming with life to vast oceans inhabited by a plethora of fascinating creatures. Witness the beauty of biodiversity and its crucial role in sustaining our planet. Don\'t miss out on this awe-inspiring adventure!\"
Travel and Tourism in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, including its vast expanse within Egypt, offers unique and captivating experiences for travelers and tourists. With its diverse landscape and historical significance, the Sahara is a destination for adventure, exploration, and cultural discovery.
- Desert Safaris: One of the most popular activities in the Sahara is a desert safari, where visitors can explore the vast dunes, either on camelback or in a 4x4 vehicle. These safaris often include camping under the stars, giving travelers a taste of Bedouin life.
- Historical Landmarks: The Sahara is home to several historical sites, such as the Great Sphinx of Giza and the ruins of ancient civilizations. These landmarks offer a glimpse into the rich history and culture that has thrived in this harsh environment.
- Natural Wonders: The Sahara"s varied landscape includes features like the Great Sand Sea, with its impressive dunes, and unique geological formations in the White and Black Deserts. The Valley of the Whales, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is another must-visit location.
- Oases and Local Culture: Visiting the oases scattered across the Sahara, such as Siwa Oasis, allows travelers to experience the local culture, traditional crafts, and cuisine. These oases are hubs of life and culture in the midst of the desert.
- Adventure Activities: For those seeking adventure, the Sahara offers activities like sandboarding, hot air ballooning, and trekking. The desert"s vastness and beauty provide a perfect backdrop for these exhilarating experiences.
Travel and tourism in the Sahara Desert, particularly in Egypt, combine the thrill of adventure with cultural and historical exploration, making it a unique destination for travelers from around the world.

Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts
The Sahara Desert, including its extension in Egypt, faces several environmental challenges, which have prompted various conservation efforts.
- Desertification: The expansion of desert lands due to climate change and human activities is a major concern. Efforts to combat desertification include reforestation projects and sustainable land management practices.
- Water Scarcity: The Sahara"s arid climate and the overuse of water resources pose challenges for both the ecosystem and the human populations. Conservation efforts focus on efficient water use and exploring sustainable sources.
- Biodiversity Loss: Habitat destruction and climate change threaten the unique flora and fauna of the Sahara. Conservation programs aim to protect endangered species and their habitats.
- Pollution: Air and groundwater pollution have adverse effects on both natural habitats and archaeological sites in the Sahara region of Egypt. Measures to reduce pollution include stricter regulations and awareness campaigns.
- Climate Change Impacts: The Sahara is affected by global climate change, which alters its ecosystems and weather patterns. Research and monitoring are key to understanding these impacts and developing adaptation strategies.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation: Historical sites in the Sahara, like the Great Sphinx of Giza, face threats from environmental factors. Conservation efforts include restoration projects and protective measures against erosion and water damage.
Addressing these environmental concerns in the Sahara Desert is crucial for preserving its unique ecosystem, cultural heritage, and sustaining the livelihoods of people who depend on this vast landscape.
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions about the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, extending into Egypt, is a region of immense interest and curiosity. Here are some commonly asked questions about this vast and enigmatic desert.
- What is the Sahara Desert"s Climate?: The Sahara has two major climatic regimes. The northern part experiences an arid subtropical climate with two rainy seasons, while the southern part is more tropical with one rainy season. The Sahara"s climate is known for its high temperature ranges and minimal rainfall.
- How Did the Sahara Get Its Name?: The name "Sahara" comes from the Arabic word ṣaḥrāʾ, meaning "desert". This word is a testament to the vast expanse of arid land that characterizes the region.
- Can Flora and Fauna Survive in the Sahara?: Despite its harsh conditions, the Sahara supports life. Plants and animals have adapted to the arid environment. Over 2,800 vascular plant species, including many that are endemic, and various animal species like reptiles and birds, have adapted to thrive in the desert"s extreme conditions.
- What Are Some Key Destinations in Egypt Near the Sahara?: Egypt is rich in cultural and historical sites. Key destinations include the pyramids of Giza, the Sphinx, the Egyptian Museum, Luxor"s Valley of the Kings, Karnak, and Hatshepsut temple, as well as wonders in Aswan like the Abu Simbel temples.
These questions highlight the Sahara Desert"s unique characteristics, from its challenging climate to its rich biodiversity and cultural heritage, making it a fascinating topic for study and exploration.
Exploring the Sahara Desert in Egypt unveils a tapestry of history, culture, and natural splendor, offering a journey through time and an adventure in the vastness of the world"s largest hot desert.