Topic sahara desert location on map: Discover the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, its intriguing location on the map, and the mysteries it holds as the world"s largest hot desert in our detailed guide.
Table of Content
- Where is the Sahara Desert located on a map?
- Geographical Coordinates of the Sahara Desert
- Overview of Sahara Desert"s Size and Extent
- Mapping the Sahara: Countries and Regions Covered
- Key Physical Features Within the Sahara
- Historical Maps and the Evolution of Sahara"s Boundaries
- Climate Zones and Ecological Diversity in the Sahara
- YOUTUBE: Sahara Desert on Africa Map
- Major Cities and Settlements Near the Sahara
- Navigation and Exploration Routes Through the Sahara
- Impact of Climate Change on Sahara"s Geography
- Interactive Maps and Tools to Visualize Sahara"s Geography
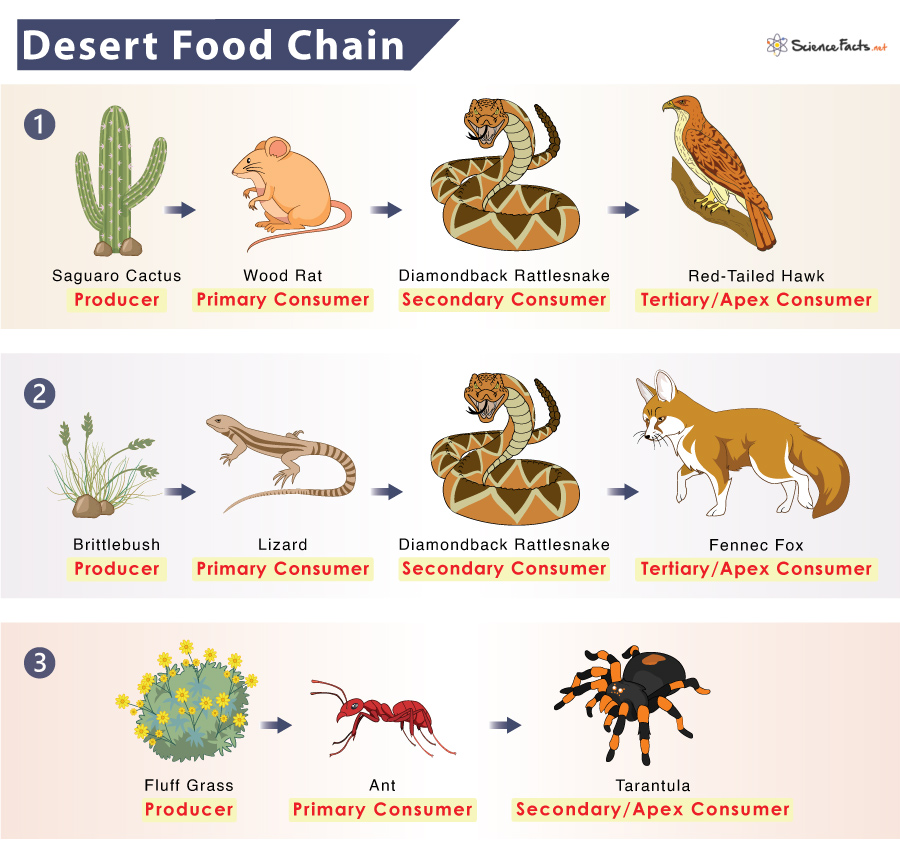
Where is the Sahara Desert located on a map?
The Sahara Desert is located in northern Africa. Here are the steps to find its location on a map:
- Open a map of Africa.
- Find the continent of Africa on the map.
- Locate the northern part of Africa on the map.
- Within the northern part of Africa, you will see a vast desert area covering most of the region.
- This desert is the Sahara Desert.
So, to find the Sahara Desert on a map, you need to locate the northern region of Africa where you will see the extensive Sahara Desert.
READ MORE:
Geographical Coordinates of the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, renowned as the world"s largest hot desert, spans several nations in North Africa. Its vastness and geographical spread are defined by specific coordinates that mark its extent on the global map.
- Northernmost Point: Near the Mediterranean coast, approximately at 37° N latitude.
- Southernmost Point: Close to the border of the Sahel region, around 16° N latitude.
- Easternmost Point: Bordering the Red Sea, near 25° E longitude.
- Westernmost Point: Reaching towards the Atlantic Ocean, close to 17° W longitude.
These coordinates encompass a region that stretches over approximately 9,200,000 square kilometers (3,600,000 sq mi), making the Sahara an immense part of the African continent.

Overview of Sahara Desert"s Size and Extent
The Sahara Desert is an expansive and awe-inspiring natural wonder, known for being the world"s largest hot desert. Covering a vast area, it is a significant geographical landmark on the African continent.
- Total Area: Approximately 9,200,000 square kilometers (3,600,000 sq mi), making it the third-largest desert in the world after Antarctica and the Arctic.
- Stretching Across Continents: Extends across North Africa, from the Red Sea in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west.
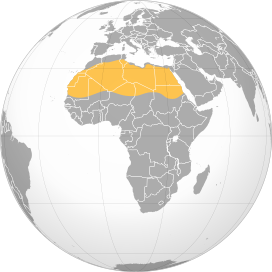
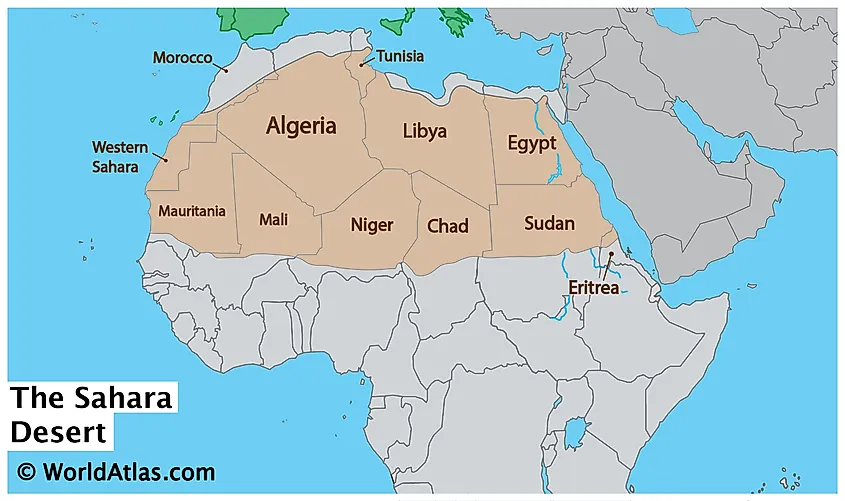
- Spanning Countries: Encompasses parts of many countries, including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Western Sahara, Sudan, and Tunisia.
- Landscape Diversity: Features a varied landscape comprising vast sand dunes (ergs), rocky plateaus (hamadas), and gravel plains (reg).
This remarkable desert not only dominates the landscape of North Africa but also plays a crucial role in the region"s climate, culture, and history.
Mapping the Sahara: Countries and Regions Covered
The Sahara Desert is not just a vast expanse of sand; it"s a significant geographic feature that spans across multiple countries in North Africa. Each region within the Sahara has its unique characteristics and cultural significance.
- Algeria: Home to a large portion of the Sahara, including varied landscapes from sand dunes to mountain ranges.
- Chad: The Sahara covers much of the northern region, featuring the striking Tibesti Mountains.
- Egypt: The Sahara here is known for its beautiful oases and the famous Western Desert.
- Libya: The Libyan Desert, a part of the Sahara, is noted for its remote and extreme environment.
- Mali: Features some of the Sahara"s most famous cultural sites, like the ancient city of Timbuktu.
- Mauritania: Known for the Richat Structure, a prominent geological feature in the Sahara.
- Morocco: The Sahara extends into Morocco, offering stunning landscapes like the Erg Chebbi dunes.
- Niger: Encompasses the eastern portion of the Sahara, including the Aïr Mountains.
- Sudan: The Sahara"s eastern frontier, characterized by its rocky terrain and mountain ranges.
- Tunisia: The northernmost reach of the Sahara, featuring unique ecosystems and salt lakes.
- Western Sahara: A disputed territory with a coastline along the Atlantic Ocean, part of the Sahara.
This mapping of the Sahara Desert through its encompassing countries reveals the diversity and vastness of this iconic desert landscape.
Key Physical Features Within the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, a marvel of nature, is not only vast in size but also rich in diverse physical features. These features are not just breathtakingly beautiful but also key to understanding the desert"s ecological and geographical diversity.
- Sand Dunes (Ergs): Iconic sand dunes, some towering up to 150 meters, are a hallmark of the Sahara, providing the classic desert landscape.
- Rocky Plateaus (Hamadas): Vast, barren rocky plateaus that offer a stark contrast to the sandy dunes.
- Mountain Ranges: Including the Tibesti Mountains in Chad, the highest in the desert, and the Ahaggar Mountains in Algeria.
- Dry Valleys and Wadis: Seasonal rivers forming valleys and basins, crucial for the desert"s ecosystem.
- Salt Flats (Chotts): Extensive salt flats, especially in Algeria and Tunisia, creating unique landscapes.
- Oases: Fertile areas where water is available, supporting wildlife and human settlements.
- Craters and Volcanic Fields: Such as the Trou au Natron in Chad, adding geological diversity.
These features not only shape the Sahara"s landscape but also its climate and habitability, making it a region of both extreme conditions and surprising biodiversity.
Historical Maps and the Evolution of Sahara"s Boundaries
The boundaries of the Sahara Desert have evolved over centuries, shaped by both natural forces and human activities. Historical maps provide a fascinating insight into how perceptions and realities of the Sahara"s extent have changed over time.
- Ancient Civilizations: Early maps from civilizations like the Egyptians and Romans depicted the Sahara as a mysterious, uncharted territory.
- Medieval Period: Islamic scholars and European explorers began to more accurately chart the Sahara, although much remained unknown.
- Colonial Era: European colonization led to more detailed mapping, emphasizing the desert"s natural resources and geopolitical significance.
- 20th Century Advances: Technological advancements in cartography and aerial surveys provided a more precise understanding of the Sahara"s geography.
- Modern Satellite Imagery: Today, satellites offer detailed and dynamic mapping of the Sahara, revealing its changing landscapes and environmental challenges.
These historical perspectives highlight the dynamic nature of the Sahara, constantly reshaped by climatic shifts and human exploration.

Climate Zones and Ecological Diversity in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert is characterized by its extreme climate and diverse ecology, which vary across different zones of the desert. Understanding these climatic conditions and ecological varieties is key to comprehending the Sahara"s environmental uniqueness.
- Hyper-Arid Core: Central Sahara experiences extreme heat with minimal rainfall, defining the quintessential desert climate.
- Subtropical Margins: The northern and southern edges of the Sahara have a subtropical climate with slightly more rainfall and vegetation.
- Mountain Climate Zones: Higher elevations like the Tibesti Mountains have cooler temperatures and more rainfall, supporting diverse flora and fauna.
- Seasonal Variability: Climate can vary seasonally, with some regions experiencing short wet seasons.
- Ecological Diversity: From barren sand dunes to areas rich in flora and fauna around oases and mountains, the Sahara hosts diverse ecosystems.
- Adaptations to Aridity: Plant and animal life in the Sahara have evolved unique adaptations to survive in harsh desert conditions.
These climate zones and ecological regions showcase the Sahara"s complexity, far beyond a simple expanse of sand, encompassing a range of environments and life forms.
Sahara Desert on Africa Map
Embark on a breathtaking journey across the mesmerizing Sahara Desert, as you witness the majestic sand dunes and vibrant landscapes that stretch as far as the eye can see. Uncover the secrets of this wondrous place in our captivating video that will leave you in awe of the immense beauty and fascinating ecosystem that thrives within this arid expanse.
Physical Geography of Africa Continent / Physical Map of Africa Continent / Africa Geographic Map
Dive deep into the captivating world of physical geography, where the wonders of our natural environment come to life. Join us as we explore the intricate web of processes that shape our planet, from the formation of mountains to the carving out of mighty rivers. This enlightening video is a visual feast that will ignite your curiosity and deepen your understanding of the awe-inspiring forces at play in our physical world.
Major Cities and Settlements Near the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, while predominantly uninhabitable, is bordered by several major cities and settlements that have adapted to its harsh conditions. These cities are not just centers of human habitation but also hubs of cultural and economic activities influenced by the desert.
- Cairo, Egypt: A major city to the east of the Sahara, known for its rich history and proximity to the Nile River.
- Tripoli, Libya: Located on the Mediterranean coast, Tripoli lies to the north of the Sahara and is a key economic center.
- Niamey, Niger: Situated to the south of the Sahara, it serves as an important crossroads for Saharan trade.
- Nouakchott, Mauritania: On the western edge of the Sahara, this city links the desert with the Atlantic Ocean.
- Tamanrasset, Algeria: Deep in the Sahara, it"s an oasis city and a gateway to the desert"s interior.
- Timbuktu, Mali: An historic city located on the southern edge of the Sahara, known for its ancient manuscripts and rich history.
- Agadez, Niger: A key Saharan city, known for its stunning architecture and role as a trading hub.
- Faya-Largeau, Chad: A northern Chadian city that acts as an important stopover in Sahara crossings.
- Merzouga, Morocco: Known for its proximity to the impressive Erg Chebbi dunes.
- El Aaiún, Western Sahara: The largest city of the disputed territory of Western Sahara, located near the Atlantic coast.
These cities and settlements showcase the human aspect of living near the Sahara, highlighting how societies have adapted to and thrived alongside this vast desert landscape.
Navigation and Exploration Routes Through the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, with its vast and challenging landscape, has a rich history of exploration and trade routes that have been used for centuries. These routes not only facilitated commerce but also cultural exchange between various regions.
- Trans-Saharan Trade Routes: Historic trade routes connecting North Africa with Sub-Saharan Africa, crucial for the trade of gold, salt, and other commodities.
- The Nile River: Serving as a natural navigation route along its western edge, the Nile has been vital for transportation and sustenance.
- Caravan Routes: Used by nomadic tribes, these routes connected oasis towns, facilitating trade and travel across the desert.
- European Exploration Trails: Since the 19th century, European explorers charted new routes for scientific, geographic, and colonial purposes.
- Modern Highways and Railroads: Contemporary infrastructure, such as the Trans-Sahara Highway, has modernized access across the desert.
- Off-Road Safaris and Adventure Tours: In recent times, guided tours for adventure and exploration have become popular, using off-road vehicles.
These routes, from ancient caravan paths to modern highways, illustrate the Sahara"s role as a crossroads of cultures, commerce, and exploration throughout history.
Impact of Climate Change on Sahara"s Geography
Climate change has a profound impact on the Sahara Desert, affecting its geography and ecosystem. These changes are not just environmental concerns but also have significant implications for the human populations living in and around the Sahara.
- Desert Expansion: Climate change is contributing to the desertification of areas around the Sahara, expanding its boundaries.
- Temperature Increase: The Sahara is experiencing rising temperatures, leading to more extreme heat conditions.
- Altered Rainfall Patterns: Changes in rainfall patterns are affecting the Sahara, leading to both droughts and unpredictable heavy rains.
- Impact on Flora and Fauna: The changing climate is affecting the delicate balance of flora and fauna in the Sahara, with some species struggling to adapt.
- Human Settlements: These environmental changes are impacting human settlements, with communities facing challenges like water scarcity and agricultural disruption.
- Increased Sandstorms: Climate change is leading to more frequent and intense sandstorms, affecting air quality and visibility.
The impact of climate change on the Sahara"s geography underscores the need for environmental awareness and sustainable practices to protect this unique ecosystem.
READ MORE:
Interactive Maps and Tools to Visualize Sahara"s Geography
In the digital age, various interactive maps and tools have been developed to provide detailed and dynamic visualizations of the Sahara Desert"s geography. These resources are invaluable for education, research, and even navigation.
- Google Earth and Satellite Imagery: Offers high-resolution images and 3D terrain models of the Sahara, allowing users to explore its vastness virtually.
- NASA World Wind: Provides detailed satellite imagery and allows users to experience the Sahara"s topography and climatic conditions.
- National Geographic Maps: These maps offer detailed and educational views of the Sahara, highlighting physical and cultural features.
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems): GIS tools enable in-depth analysis of Sahara"s geographical data, useful for scientific and environmental studies.
- Travel and Adventure Apps: Apps like iOverlander and Maps.me provide practical information for travelers exploring the Sahara.
- Climate Change Visualization Tools: Tools like Global Forest Watch show the impact of climate change on the Sahara"s landscapes.
These interactive tools not only help visualize the Sahara Desert in great detail but also play a crucial role in understanding and conserving its unique environment.
In exploring the Sahara Desert"s location on the map, we uncover a world of wonder, rich in history and natural beauty, inviting us to appreciate and preserve this extraordinary and ever-changing landscape.