Topic abiotic factors in the sahara desert: Discover the intriguing abiotic factors of the Sahara Desert, where extreme temperatures, diverse soil compositions, and unique physicochemical conditions shape one of Earth"s most fascinating ecosystems.
Table of Content
- What are the abiotic factors present in the Sahara Desert?
- Temperature and Climate
- Physicochemical Conditions
- Solar Radiation and Light Availability
- Soil Composition and Characteristics
- Water Availability and Precipitation Patterns
- Atmospheric Gases and Greenhouse Effect
- YOUTUBE: Responses to Abiotic Factors in Organisms and Populations in Biology
- Wind Patterns and Aeolian Processes
- Geographical Features and Terrain
- Ecological Impacts of Abiotic Factors
- Human Influence on Abiotic Factors
What are the abiotic factors present in the Sahara Desert?
- Low precipitation: The Sahara Desert is known for its extremely low levels of rainfall. The average annual precipitation is less than 100 mm, making it one of the driest places on Earth.
- Extreme temperatures: The desert experiences scorching hot temperatures during the day, with the average daytime temperature exceeding 38°C (100°F). At night, temperatures can drop drastically, sometimes below freezing point. The temperature fluctuations are due to the lack of moisture and vegetation in the area.
- Lack of humidity: The air in the Sahara Desert is extremely dry, with humidity levels often dropping below 25%. This lack of moisture can cause dehydration and make the environment challenging for both flora and fauna.
- Sandy and rocky soils: The Sahara Desert is primarily composed of dunes and sand, along with vast rocky plateaus. The sandy soil is often poor in nutrients, making it difficult for plants to grow, while the rocky areas offer little to no substrate for vegetation.
- Exposed bedrock: The desert is characterized by large stretches of exposed bedrock, which contributes to its aridity. Bedrock does not retain water well, leading to rapid water runoff and preventing the growth of plants.
READ MORE:
Temperature and Climate
The Sahara Desert is renowned for its extreme climate, characterized by some of the highest temperatures recorded on earth. This section explores the various aspects of the desert"s temperature and climate.
- Daytime Temperatures: During daytime, temperatures can soar above 40°C (104°F), particularly in the hottest months, creating an intensely hot environment.
- Nighttime Temperatures: Contrasting the day, nights in the Sahara can be extremely cold, with temperatures dropping significantly, showcasing the desert"s dramatic diurnal temperature variation.
- Annual Temperature Range: The Sahara experiences a wide range of temperatures throughout the year, with annual averages nearing 30°C in many areas, influenced by its geographic location.
- Climate Extremes: The Sahara is known for its arid climate, with very little rainfall, creating one of the driest regions on Earth. This lack of moisture significantly impacts the ecosystem.
- Heat"s Impact on Ecosystem: The intense heat affects various aspects of the desert ecosystem, including water availability, plant and animal physiology, and soil moisture levels.
- Role of Sunlight: The Sahara receives abundant sunlight throughout the year, contributing to its high temperatures and driving factors like wind erosion and sand dune formation.

Physicochemical Conditions
The Sahara Desert presents a range of physicochemical conditions that significantly influence its ecosystem. These conditions include various factors related to the physical and chemical environment of the desert.
- Soil Composition: The Sahara"s soil varies greatly, characterized by low organic matter, high sand content, and significant salinity. These features affect soil fertility and water retention.
- Salinity: High salinity levels are common due to limited rainfall and intense evaporation, impacting plant growth and soil health.
- pH Levels: The soil in the Sahara tends to be more alkaline, influencing nutrient availability and soil chemistry.
- Mineral Content: The desert soil contains various minerals like silicates, carbonates, and oxides, playing a crucial role in soil structure and fertility.
- Temperature Fluctuations: The Sahara experiences extreme temperature variations, which affect soil moisture levels and biological activities within the soil.
- Humidity and Aridity: Low humidity and high aridity define the Sahara, impacting the rate of evaporation and the availability of water for organisms.
Understanding these physicochemical conditions is essential for comprehending how life adapts and thrives in such an extreme environment as the Sahara Desert.
Solar Radiation and Light Availability
The Sahara Desert, one of the sunniest places on Earth, experiences intense solar radiation. This section delves into how solar radiation and light availability influence the desert"s environment and its inhabitants.
- High Solar Exposure: The Sahara"s geographical location ensures high levels of sunlight throughout the year, with minimal cloud cover.
- Impact on Temperature: This abundant sunlight contributes significantly to the desert"s high daytime temperatures, affecting both the climate and the living organisms.
- Solar Radiation"s Role in Ecosystem: Solar radiation drives many of the desert"s ecological processes, including photosynthesis in plants and the formation of wind patterns.
- Influence on Evaporation and Precipitation: The intense sunlight increases evaporation rates, contributing to the desert"s dry conditions, and influences irregular precipitation patterns.
- Effect on Soil and Terrain: Continuous exposure to sunlight affects the soil"s moisture and temperature, impacting its composition and the formation of desert features like sand dunes.
This high level of solar radiation is a defining characteristic of the Sahara Desert, playing a crucial role in shaping its unique abiotic environment.

Soil Composition and Characteristics
The Sahara Desert"s soil is a unique feature that significantly impacts its ecosystem. This section explores the diverse aspects of soil composition and characteristics in this extreme environment.
- General Soil Features: Sahara"s soil is predominantly sandy with varying degrees of organic matter and mineral content. It plays a pivotal role in supporting desert life.
- Arid Soil Conditions: The arid climate of the Sahara leads to soils with low moisture content, impacting the growth of vegetation and soil organisms.
- High Salinity: Due to low rainfall and high evaporation rates, Sahara"s soils often have high salinity levels, affecting plant growth and soil health.
- Soil pH Levels: The soils in the Sahara tend to be more alkaline, which influences nutrient availability and overall soil chemistry.
- Mineral Composition: The soil contains various minerals such as silicates, carbonates, and oxides, which contribute to soil structure and fertility.
- Impact of High Temperatures: The extreme temperatures in the Sahara affect soil moisture levels and biological activity within the soil.
This section provides an insight into the unique soil characteristics of the Sahara Desert, highlighting how these factors contribute to the harsh but fascinating desert ecosystem.
Water Availability and Precipitation Patterns
The Sahara Desert is characterized by its extremely arid climate, significantly impacting water availability and precipitation patterns. This section explores the crucial aspects of these factors in the Sahara"s environment.
- Low and Sporadic Rainfall: The Sahara is one of the driest regions on Earth, with rainfall patterns being low and sporadic, which limits vegetation growth and restricts water resources for plants and animals.
- Impact on Soil and Vegetation: The lack of precipitation results in arid soil conditions, characterized by reduced organic matter, high sand content, and high salinity levels. This affects nutrient availability and plant growth.
- Evaporation and Salinization: High temperatures lead to increased evaporation rates, contributing to the arid conditions and salinization of the soil.
- Occasional Rainfall Events: Though rare, occasional rainfall can trigger short-term blooms of vegetation, offering a brief respite in the otherwise harsh environment.
- Role in Ecosystem Dynamics: The scarcity of water plays a significant role in shaping the Sahara"s ecosystem, influencing the types of plant and animal species that can survive in these conditions.
This section provides an insight into the challenging water conditions of the Sahara Desert, highlighting the adaptation strategies of its flora and fauna to survive in an environment with limited water availability.
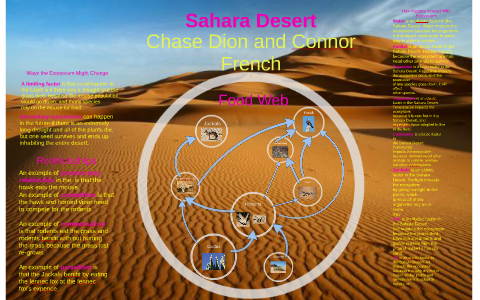
Atmospheric Gases and Greenhouse Effect
The Sahara Desert"s unique atmospheric conditions play a crucial role in its ecosystem. This section explores the interaction between atmospheric gases and the greenhouse effect in this extreme environment.
- Presence of Key Gases: The Sahara"s atmosphere contains essential gases like carbon dioxide and nitrogen, which are critical for plant photosynthesis and soil enrichment through nitrogen fixation by microorganisms.
- Greenhouse Effect: Atmospheric gases like water vapor and carbon dioxide contribute to the greenhouse effect, trapping heat in the Earth"s atmosphere, which is essential for maintaining a habitable climate.
- Impact on Local Climate: The greenhouse effect influences the desert"s temperature and weather patterns, playing a role in the development and regulation of the desert climate.
- Human Activities and Climate Change: Excessive production of greenhouse gases from human activities leads to global warming and climate change, affecting ecosystems worldwide, including the Sahara Desert.
- Desert Dust and Global Climate: The Sahara is a significant source of atmospheric dust, which has a cooling effect and interacts with the warming potential of greenhouse gases.
This section sheds light on the vital role of atmospheric gases and the greenhouse effect in shaping the climatic and ecological dynamics of the Sahara Desert.
Responses to Abiotic Factors in Organisms and Populations in Biology
Adaptation: Dive into the fascinating world of adaptation, where nature\'s incredible resilience and creativity are on full display. Discover how organisms evolve and thrive in changing environments in this captivating video. Extreme: Brace yourself for an adrenaline-pumping journey to the extreme. Witness jaw-dropping feats, breathtaking landscapes, and pulse-pounding challenges in this thrilling video that will leave you on the edge of your seat.
The Temperature of Sahara Desert Facts Temperature
This fact is all about Sahara desert temperature which is to high. Subscribe me here. @LetsEatKnowledge #factshorts #sahara ...
Wind Patterns and Aeolian Processes
The Sahara Desert is greatly influenced by distinct wind patterns and aeolian processes. This section delves into how these abiotic factors shape the desert landscape and affect its ecosystem.
- Desert Wind Characteristics: The Sahara experiences strong and persistent winds, which play a significant role in shaping the desert"s topography and influencing its climate.
- Formation of Sand Dunes: These winds contribute to the formation and movement of the Sahara"s iconic sand dunes, continuously reshaping the desert landscape.
- Impact on Erosion and Deposition: Aeolian processes, driven by wind, lead to significant soil erosion and deposition, affecting soil composition and fertility.
- Desert Dust Transport: Sahara"s winds transport desert dust over long distances, impacting regional and global climate patterns.
- Biological Implications: Wind patterns influence vegetation distribution and animal behavior, affecting the overall biodiversity of the desert.
This section highlights the crucial role of wind patterns and aeolian processes in the Sahara Desert, emphasizing their impact on the physical environment and biological life.

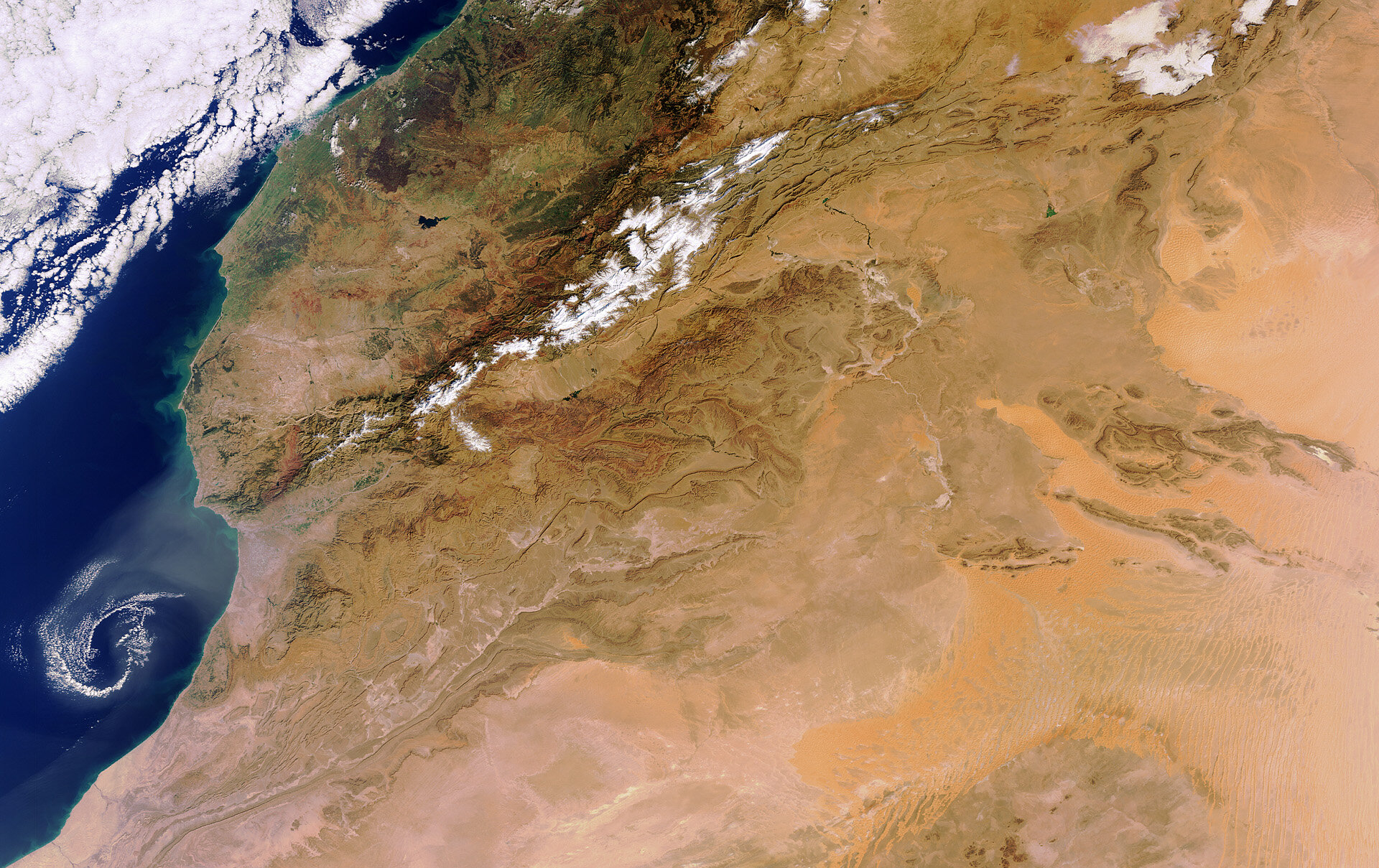
Geographical Features and Terrain
The Sahara Desert"s landscape is defined by unique geographical features and diverse terrains. This section explores these characteristics and their significance in the desert"s ecosystem.
- Vast Sand Dunes: A significant portion of the Sahara is covered by large sand dunes, known as ergs, which are constantly reshaped by wind patterns.
- Rocky Plateaus: The desert features extensive rocky plateaus, or hamadas, that are the result of wind erosion and provide a different habitat than the sandy areas.
- Mountain Ranges: Several mountain ranges, including volcanic mountains, are found within the Sahara, influencing local climate and providing habitats for various species.
- Gravel Plains and Dry Valleys: The desert also includes gravel plains and dry valleys, which are important for the desert"s hydrology and ecology.
- Salt Flats: Salt flats, or sabkhas, are another distinctive feature, formed in areas where evaporation rates are extremely high.
- Impact on Biodiversity: These geographical features and terrains contribute to the Sahara"s unique biodiversity, influencing the distribution and adaptation of flora and fauna.
This section provides an insight into the Sahara Desert"s varied geographical features and terrains, highlighting their impact on the desert"s ecology and biodiversity.
Ecological Impacts of Abiotic Factors
The Sahara Desert, shaped by various abiotic factors, exhibits a unique ecological landscape. This section explores how these factors impact the desert"s ecosystem and its inhabitants.
- Temperature Extremes: The Sahara experiences extreme temperatures, both high and low, influencing the distribution and behavior of plant and animal life, as well as their physiological adaptations to survive in such conditions.
- Soil Composition: Arid soil conditions, characterized by low moisture, high sand content, and salinity, play a significant role in determining soil fertility, nutrient cycling, and the types of vegetation that can thrive in the desert.
- Water Scarcity: Limited rainfall and high evaporation rates result in scarce water resources, shaping the types of species that can survive and the strategies they employ to conserve water.
- Light and Solar Radiation: The abundant sunlight and intense solar radiation in the Sahara drive key ecological processes, such as photosynthesis, and influence the formation of various landforms.
- Wind and Aeolian Processes: Strong winds contribute to soil erosion and the formation of distinct desert features like sand dunes, affecting the habitat and mobility of desert species.
- Human Impact: Historical and present human activities, including land management practices, have influenced the Sahara"s environment, contributing to changes in vegetation and the broader ecosystem.
This section provides insights into how abiotic factors such as temperature, soil composition, water availability, and others critically shape the ecological dynamics of the Sahara Desert.

READ MORE:
Human Influence on Abiotic Factors
Human activities have significantly influenced the abiotic factors of the Sahara Desert. This section examines the various ways in which human intervention has impacted the desert"s environment.
- Overgrazing: Pastoralism, including livestock grazing, has led to soil erosion and changed vegetation patterns, affecting the desert ecosystem.
- Land Use and Soil Erosion: Human-induced land use changes have contributed to soil erosion, altering the desert"s physical landscape and its ability to support life.
- Climate Change: Anthropogenic activities contributing to global warming and climate change have implications for the Sahara"s climate, affecting rainfall patterns and temperatures.
- Deforestation: Removal of vegetation for fuel and other purposes has led to habitat loss and changed the microclimate, further exacerbating desertification.
- Agricultural Practices: Certain agricultural practices, not ideally suited for desert conditions, have led to soil degradation and reduced biodiversity.
- Water Resource Management: Mismanagement of water resources, including the use of non-sustainable irrigation methods, has impacted the desert"s hydrological cycle.
This section highlights the profound effects human activities have had on the Sahara Desert, altering its abiotic factors and, consequently, its overall ecological health.
The Sahara Desert"s abiotic factors create a landscape of stark beauty and ecological wonder, showcasing the resilience of nature in extreme conditions and reminding us of the intricate balance between our planet"s diverse environments.











