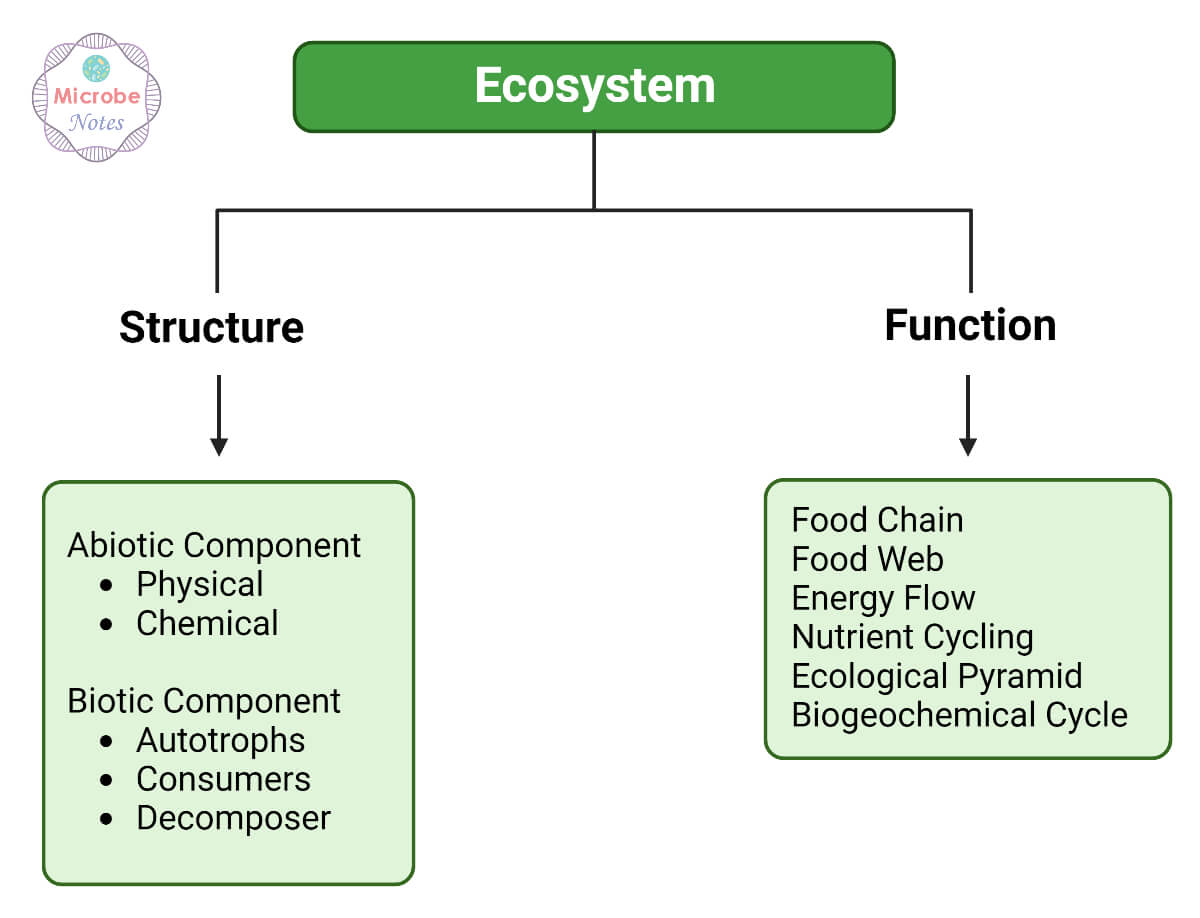
Topic the role of kelp in the ecosystem answer key: Discover how kelp forests, the underwater rainforests, play a pivotal role in marine ecosystems, supporting biodiversity and combating climate change.
Table of Content
- What are the key roles of kelp in the ecosystem as provided in the answer key related to its ecological community?
- The Importance of Kelp in Marine Ecosystems
- Introduction to Kelp Forests and Their Ecosystem Role
- Key Functions of Kelp in Marine Ecosystems
- Ecological and Economic Importance of Kelp
- YOUTUBE: Kelp from A-Z: Pre-launch of the UNEP and NBFN global kelp assessment
- The Impact of Kelp on Biodiversity and Marine Life
- Challenges Facing Kelp Forests: Threats and Conservation Efforts
- Kelp"s Role in Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation
- Benefits of Kelp to Coastal Communities and Industries
- Sustainable Management and Conservation Strategies for Kelp
- Future Perspectives: The Importance of Research and Monitoring
- Conclusion: The Integral Role of Kelp in Maintaining Healthy Marine Ecosystems
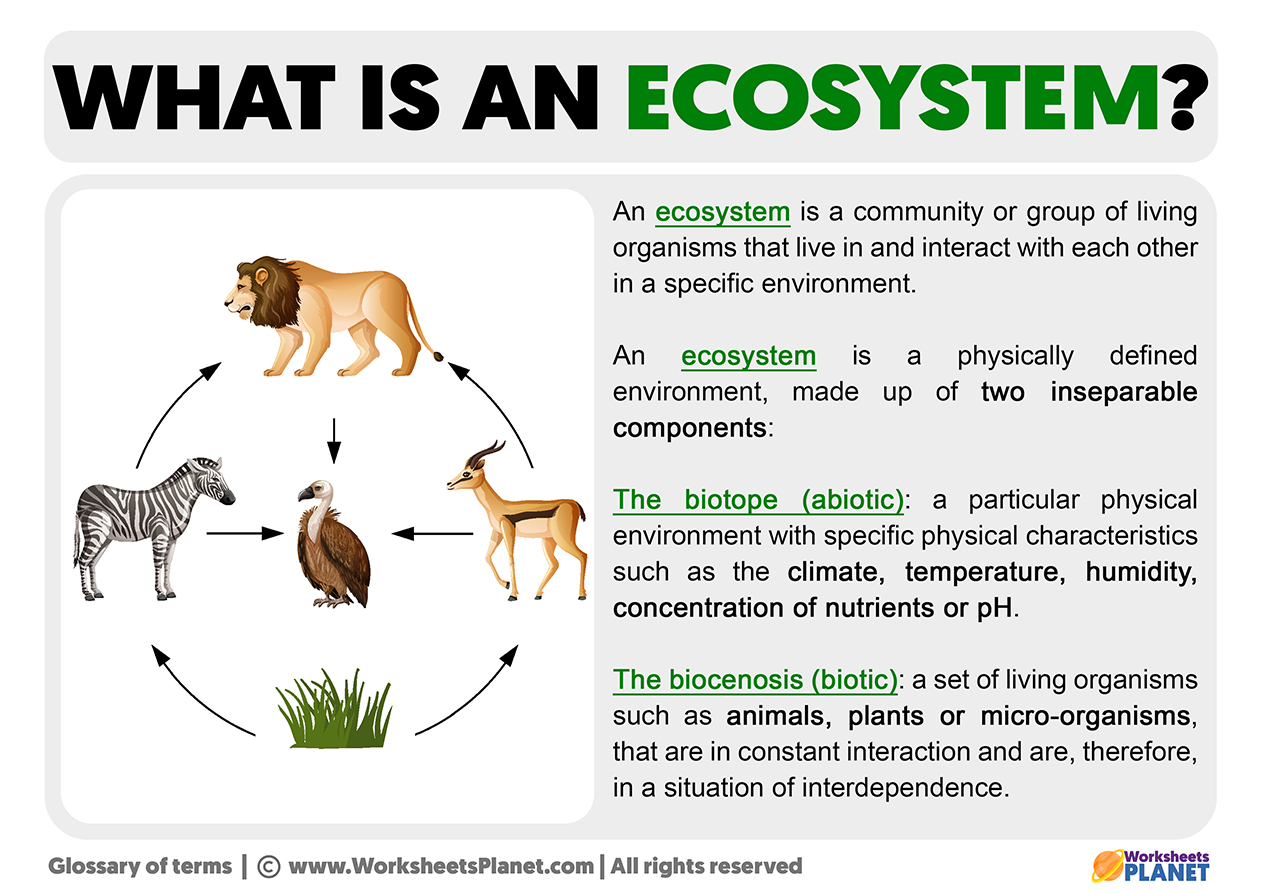
What are the key roles of kelp in the ecosystem as provided in the answer key related to its ecological community?
Based on the answer key related to the role of kelp in the ecosystem, some key roles of kelp in its ecological community include:
- Kelp serves as a habitat and food source for various marine organisms such as fish, invertebrates, and sea otters.
- It contributes to the overall biodiversity of the marine ecosystem by creating complex underwater habitats.
- Kelp helps in nutrient cycling by absorbing nutrients from the water and releasing them back into the environment.
- It plays a crucial role in carbon sequestration by absorbing carbon dioxide from the water and converting it into biomass.
- Kelp provides protection for coastal areas by attenuating wave energy and reducing coastal erosion.
READ MORE:
The Importance of Kelp in Marine Ecosystems
Kelp forests are one of the ocean"s most productive and dynamic ecosystems, playing a critical role in the marine environment. These underwater forests, composed of large brown algae, provide essential habitat, food, and shelter for a diverse array of marine life.
Key Functions of Kelp
- Biodiversity Support: Kelp forests harbor a wide variety of fish, invertebrates, and marine mammals, significantly contributing to ocean biodiversity.
- Coastal Protection: By dampening wave energy, kelp forests protect coastlines from erosion and storm damage.
- Carbon Sequestration: Kelp absorbs carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, helping mitigate climate change by storing carbon.
- Nutrient Cycling: Kelp plays a critical role in nutrient cycling, providing essential nutrients to marine organisms through the decomposition of its biomass.
- Economic Value: Kelp forests support commercial fisheries and aquaculture, contributing to the economy and food security.
Ecosystem Services
Kelp ecosystems provide invaluable services, including habitat provision, water quality improvement, and support for recreational activities such as diving and surfing. The economic and ecological benefits of kelp highlight the need for conservation and sustainable management practices.
Challenges and Conservation
Despite their importance, kelp forests face threats from climate change, pollution, and overharvesting. Protecting these vital ecosystems requires efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, implement sustainable harvesting practices, and restore damaged kelp forests.
Conclusion
Kelp forests are essential to the health and productivity of marine ecosystems. Their conservation is crucial for maintaining biodiversity, protecting coastal communities, and supporting economies. By understanding and preserving kelp forests, we can ensure the sustainability of these important ecosystems for future generations.

Introduction to Kelp Forests and Their Ecosystem Role
Kelp forests, the marine equivalent of terrestrial rainforests, are underwater ecosystems formed by kelp, a type of large brown algae. These forests thrive in cool, nutrient-rich waters and are known for their incredible biodiversity and productivity. Serving as the foundation for one of the most dynamic and biologically diverse habitats on Earth, kelp forests offer critical habitat, food, and shelter for a myriad of marine species.
- Kelp forests support a diverse array of marine life, including fish, invertebrates, and marine mammals.
- They play a crucial role in coastal protection, mitigating wave energy and preventing erosion.
- Kelp acts as a significant carbon sink, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and mitigating climate change effects.
- These ecosystems are vital for nutrient cycling, providing essential elements for marine food webs.
- Kelp forests contribute to the economy by supporting fisheries and tourism industries.
Kelp forests are not only remarkable for their ecological value but also for their ability to influence local climate conditions and support commercial activities. They are ecosystems of paramount importance, offering services from biodiversity support to acting as natural coastal defenses. However, they face threats from climate change, pollution, and overharvesting, highlighting the need for conservation efforts to protect these underwater forests for future generations.
Key Functions of Kelp in Marine Ecosystems
Kelp forests are not only majestic underwater landscapes but also vital components of marine ecosystems, providing essential services and functions. These large brown algae play a significant role in maintaining marine biodiversity, protecting coastlines, and supporting local economies.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Kelp forests create complex habitats that support a vast array of marine species, from invertebrates to large fish and marine mammals, enhancing marine biodiversity.
- Natural Coastal Defense: By dampening wave energy, kelp forests protect shorelines from erosion, safeguarding habitats and human communities.
- Carbon Sequestration: Kelp absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere, contributing to climate change mitigation by acting as a carbon sink.
- Nutrient Cycling: They are involved in nutrient cycling, transforming nutrients into forms accessible to other marine organisms.
- Economic Benefits: Kelp supports commercial fisheries and aquaculture, providing livelihoods and contributing to food security. Recreational activities such as diving and surfing also benefit from the presence of kelp forests.
Kelp forests also play a crucial role in water quality by filtering and absorbing pollutants, thereby maintaining the health of marine ecosystems. Their decline due to environmental stressors highlights the need for conservation efforts to preserve these vital ecosystems for future generations.

Ecological and Economic Importance of Kelp
Kelp forests stand as pillars of marine ecosystems, offering unmatched ecological and economic benefits. These underwater ecosystems are critical for the health of the planet and the prosperity of human communities along coastlines.
- Support for Marine Biodiversity: Kelp forests provide habitat, food, and shelter for thousands of marine species, enhancing marine biodiversity and supporting fisheries.
- Climate Change Mitigation: As efficient carbon sinks, kelp forests absorb significant amounts of CO2, helping to combat climate change.
- Protection of Shorelines: The physical structure of kelp forests reduces wave energy, protecting coastlines from erosion and storm damage.
- Nutrient Cycling: Kelp plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling, enriching marine environments with essential nutrients.
- Economic Value: Beyond their ecological roles, kelp forests contribute to local economies through fisheries, aquaculture, and tourism. They are also a source of valuable products, including food and alginate.
The ecological functions of kelp extend beyond the immediate marine environment, influencing global carbon cycles and coastal resilience. Economically, kelp forests underpin sectors critical to coastal communities, highlighting their importance in sustainable ocean management and conservation efforts.
Kelp from A-Z: Pre-launch of the UNEP and NBFN global kelp assessment
Kelp: Dive into the mesmerizing world of kelp forests, filled with vibrant marine life and swaying seaweed. Discover the beauty and importance of these underwater ecosystems in our captivating video. UNEP: Learn how the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is working towards a sustainable future for our planet. Explore the innovative initiatives and global collaborations that are making a positive impact in our world. Assessment: Delve into the world of environmental assessments and their crucial role in understanding the health of our planet. See how data and research are used to drive positive change and protect our ecosystems. Ecosystem: Embark on a journey through diverse ecosystems around the world, from lush rainforests to vast oceans. Witness the interconnectedness of flora and fauna and the importance of preserving these delicate balances.
The Impact of Kelp on Biodiversity and Marine Life
Kelp forests are crucial for marine biodiversity, providing a habitat that supports a wide range of marine life. These underwater ecosystems play a significant role in the ocean"s biological productivity, making them essential for the health and sustainability of marine environments.
- Habitat Provision: Kelp forests offer shelter and breeding grounds for numerous species, including fish, invertebrates, and marine mammals, contributing to a rich biodiversity.
- Food Source: They serve as a primary food source for many marine organisms, forming the base of a complex food web that sustains the marine food chain.
- Nursery Areas: Young fish and invertebrates find refuge among the kelp, where they can grow safely away from predators, ensuring the survival of various species.
- Species Diversity: The structural complexity of kelp forests supports a diverse range of species by providing varied habitats, from the canopy to the forest floor.
- Ecosystem Connectivity: Kelp forests connect different marine ecosystems, facilitating the movement and dispersal of species across ocean environments.
The role of kelp in supporting marine life is vast, affecting not only the species that directly inhabit these forests but also those in adjacent ecosystems. The loss of kelp forests can lead to a significant reduction in marine biodiversity and the collapse of local fisheries, underscoring the need for conservation efforts to protect these vital ecosystems.

Challenges Facing Kelp Forests: Threats and Conservation Efforts
Kelp forests, crucial for marine biodiversity and coastal protection, are facing significant threats that impact their health and survival. Understanding these challenges is key to developing effective conservation strategies.
- Climate Change: Rising ocean temperatures and changes in sea conditions disrupt kelp growth and survival, leading to forest decline.
- Pollution: Runoff containing pollutants and excessive nutrients from agriculture can lead to harmful algal blooms that overshadow kelp, inhibiting its growth.
- Overharvesting: Kelp is harvested for commercial uses, and unsustainable practices can deplete local populations.
- Predation by Sea Urchins: With the decline of natural predators like sea otters, sea urchin populations can explode, overgrazing and decimating kelp forests.
- Habitat Destruction: Coastal development and human activities can physically damage or destroy kelp habitats.
To combat these threats, conservation efforts are focusing on several fronts:
- Implementing marine protected areas to safeguard kelp forests from overharvesting and other harmful activities.
- Restoring sea otter populations to control sea urchin numbers and promote healthy kelp growth.
- Reducing pollution through better agricultural and urban water management practices.
- Monitoring and research to understand the impacts of climate change on kelp ecosystems and identify resilience strategies.
- Community engagement and education to raise awareness about the importance of kelp forests and the need for their protection.
Through these concerted efforts, there is hope for the preservation and recovery of kelp forests, ensuring their role in marine biodiversity and coastal protection for future generations.
Kelp"s Role in Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation
Kelp forests are vital players in the global carbon cycle, offering natural solutions for carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation. These underwater ecosystems act as significant carbon sinks, capturing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass and the surrounding sediment.
- Carbon Absorption: Kelp photosynthesizes, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, much like terrestrial plants, but at a potentially higher rate due to kelp"s rapid growth.
- Long-term Storage: When kelp dies, it can sink to the ocean floor, where the carbon in its biomass is sequestered away from the atmosphere for long periods.
- Reducing Acidification: By absorbing CO2, kelp helps mitigate ocean acidification, a direct threat to marine life, particularly shell-forming organisms.
- Supporting Biodiversity: The carbon sequestration process supports marine biodiversity, creating habitats and food sources for various marine species.
Moreover, kelp forests" ability to sequester carbon highlights their importance in climate change mitigation strategies. Protecting and restoring kelp forests can enhance their capacity to absorb CO2, offering a natural, effective way to combat climate change and protect marine biodiversity.
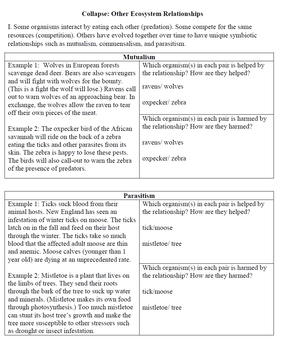
Benefits of Kelp to Coastal Communities and Industries
Kelp forests are invaluable to coastal communities and various industries, offering a wide range of benefits from ecological health to economic prosperity. These ecosystems provide critical resources and services that sustain local economies and environmental well-being.
- Support for Fisheries: Kelp forests serve as vital nursery grounds for many species of fish and shellfish, supporting commercial and recreational fisheries.
- Coastal Protection: The physical structure of kelp forests helps to dissipate wave energy, reducing coastal erosion and protecting shorelines.
- Source of Livelihood: Communities rely on kelp for livelihoods through harvesting for food, alginate, and other products used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Recreational Opportunities: Kelp forests attract tourists for diving, snorkeling, and other recreational activities, contributing to the local tourism industry.
- Marine Biodiversity: By supporting a rich diversity of marine life, kelp forests contribute to the ecological health and resilience of marine ecosystems.
Moreover, the role of kelp in mitigating climate change through carbon sequestration further enhances its value to communities and industries by contributing to a healthier planet. Efforts to conserve and restore kelp forests not only support biodiversity but also bolster economic activities, making them a cornerstone for sustainable coastal development.
Sustainable Management and Conservation Strategies for Kelp
Kelp forests are vital ecosystems that support a diverse range of marine life and provide essential services to humans and the planet. To ensure their sustainability and conservation, several strategies can be adopted:
- Monitoring and Research: Continuous monitoring and research are crucial to understand the dynamics of kelp ecosystems, the impacts of environmental changes, and the effectiveness of conservation measures.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing the root causes of climate change is essential to protect kelp forests from warming waters and ocean acidification, which can lead to kelp decline.
- Protection from Overharvesting: Implementing regulations to prevent overharvesting of kelp is necessary to maintain healthy populations and ensure the sustainability of kelp-based industries.
- Management of Coastal Development: Sustainable coastal development practices can help minimize the negative impacts on kelp habitats from pollution, sedimentation, and physical disturbances.
- Restoration Projects: In areas where kelp forests have been degraded, restoration projects can help to re-establish these important ecosystems. This may include reseeding efforts or the removal of invasive species that compete with kelp.
- Ecosystem-Based Management: Adopting an ecosystem-based approach to marine management that considers the interconnectivity of kelp forests with other marine habitats and species can enhance the resilience of these ecosystems.
- Community Involvement and Education: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts and raising awareness about the importance of kelp forests can foster stewardship and support for protective measures.
By implementing these strategies, we can ensure the sustainable management and conservation of kelp forests, preserving their ecological and economic value for future generations.

Future Perspectives: The Importance of Research and Monitoring
As we look towards the future, the importance of research and monitoring in understanding and protecting kelp forests cannot be overstated. These vibrant ecosystems, crucial for marine biodiversity, are facing unprecedented challenges due to changing ocean conditions and human activities. The insights gathered from ongoing and future studies will be pivotal in shaping conservation strategies that are both effective and sustainable.
- Understanding Kelp Dynamics: Research efforts need to focus on the life cycles of kelp, their growth patterns, and their responses to environmental stressors. This knowledge is essential for predicting how kelp forests will adapt to changing ocean temperatures, acidification, and other climate-related impacts.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Monitoring the effects of climate change on kelp ecosystems will help in developing adaptive management practices. As kelp forests play a critical role in carbon sequestration and coastal protection, understanding their capacity to mitigate climate change effects is crucial.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Kelp forests are biodiversity hotspots, providing habitat and food for numerous marine species. Continuous monitoring can help assess the health of these ecosystems and the effectiveness of conservation measures in preserving marine life diversity.
- Technological Advancements: Leveraging new technologies in remote sensing, underwater robotics, and data analysis will enhance the precision and scope of kelp forest research and monitoring, providing more comprehensive insights into these complex ecosystems.
- Community and Stakeholder Engagement: Involving local communities, industries, and policymakers in research and monitoring efforts will foster a collaborative approach to kelp conservation, ensuring that the strategies developed are both practical and inclusive.
- Policy and Management: The findings from research and monitoring activities should inform policy-making and management decisions, ensuring that they are based on the best available science. This will help in implementing effective conservation measures and in the sustainable management of kelp forest resources.
In conclusion, the future health and resilience of kelp forests hinge on our commitment to research and monitoring. By deepening our understanding of these ecosystems and their role in the marine environment, we can better protect them for future generations.
READ MORE:
Conclusion: The Integral Role of Kelp in Maintaining Healthy Marine Ecosystems
Kelp forests, with their remarkable growth and extensive coverage, play a pivotal role in marine ecosystems. These underwater habitats, primarily composed of large brown algae, provide crucial support for a wide array of marine life. From offering shelter and food to diverse species, including invertebrates, fishes, and other algae, to acting as key biodiversity hubs, kelp ecosystems are indispensable for the health of our oceans.
- Ecosystem Support: Kelp forests serve as the backbone for complex marine ecosystems, supporting thousands of species. They offer a three-dimensional habitat that is essential for the survival and proliferation of marine biodiversity.
- Environmental Benefits: Beyond biodiversity, kelp forests contribute to coastal protection, mitigating the strength of waves and preventing erosion. They also play a significant role in carbon sequestration, helping to combat climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Economic and Cultural Value: Kelp forests are not only ecological treasures but also provide significant economic benefits. They support fisheries and aquaculture, contribute to food security, and are a source of bioplastics and other materials. Moreover, kelp holds cultural significance for many coastal communities around the world.
- Conservation Challenges: Despite their importance, kelp forests face numerous threats, including climate change, ocean acidification, and human activities such as pollution and overharvesting. The balance of kelp ecosystems is also affected by the populations of their grazers, like the purple sea urchin, which can grow unchecked in the absence of natural predators like sea otters.
In conclusion, the conservation and sustainable management of kelp forests are crucial for maintaining the health and productivity of marine ecosystems. Ongoing research, monitoring, and community engagement are essential to understanding these complex habitats and mitigating the threats they face. By protecting kelp forests, we safeguard a vital component of our planet"s biodiversity and ensure the resilience of marine ecosystems against the challenges of the future.
Discover the vital role of kelp in marine ecosystems, a key to biodiversity, climate resilience, and economic prosperity, underscoring the urgency of its conservation.