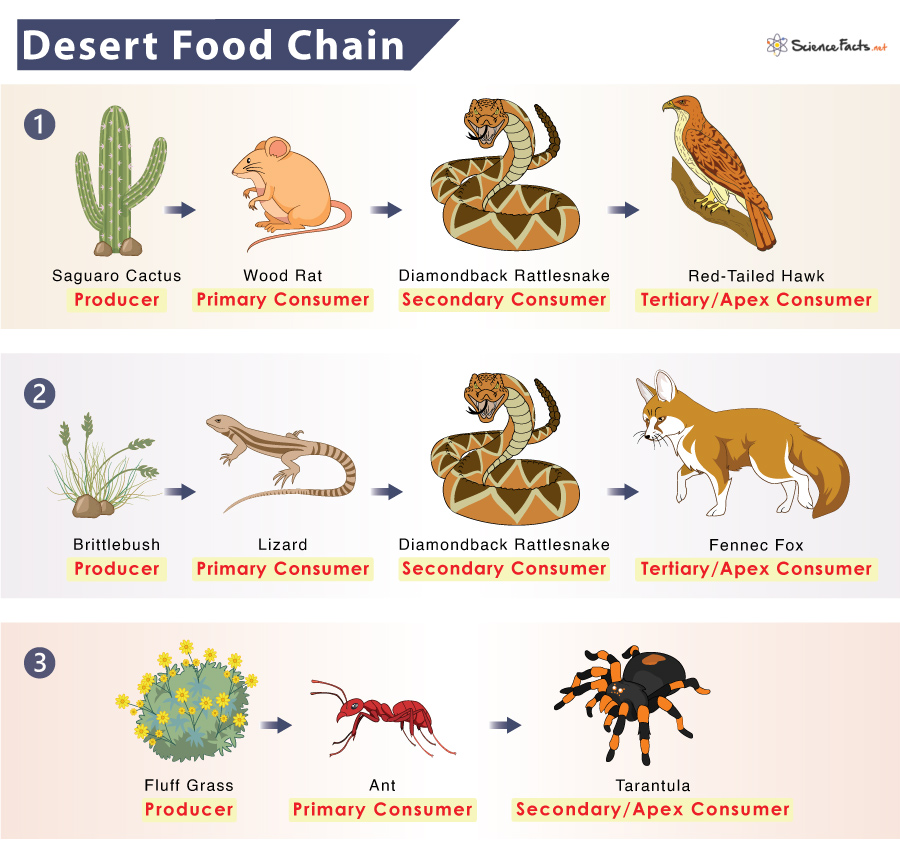
Topic sahara desert snakes: Discover the enthralling world of Sahara Desert snakes, where survival and beauty intertwine in one of Earth"s most extreme environments.
Table of Content
- What are the most venomous snakes found in the Sahara Desert?
- Overview of Snakes in the Sahara Desert
- Common Species of Sahara Desert Snakes
- Adaptations of Snakes to the Sahara Desert Environment
- Interaction of Sahara Snakes with the Ecosystem
- Human and Snake Interactions in the Sahara
- Conservation Status of Sahara Desert Snakes
- YOUTUBE: The Venomous Snakes of Africa - Deserts, Cape Cobra, Red Spitting Cobra, Puff Adder, Carpet Viper
- Research and Studies on Sahara Desert Snakes
- Myths and Misconceptions about Sahara Desert Snakes
- Guidelines for Safe Encounters with Desert Snakes
- Interesting Facts about Sahara Desert Snakes
What are the most venomous snakes found in the Sahara Desert?
The most venomous snakes found in the Sahara Desert include:
- Algerian Whip Snake
- Nubian Spitting Cobra
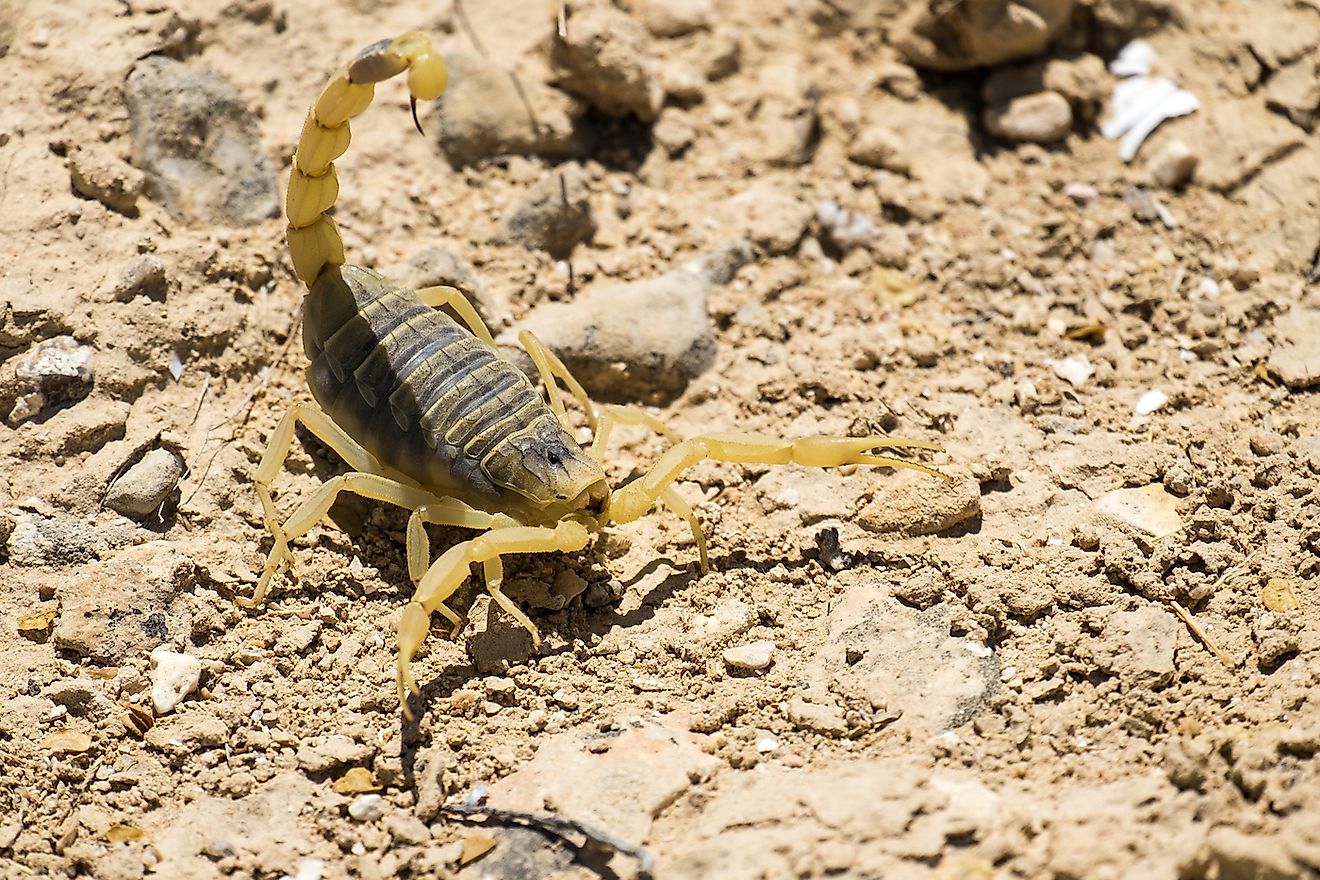
- Sahara Sand Viper
- Saw Scaled Viper
These snakes are known for their venomous bites and should be avoided if encountered in the desert.
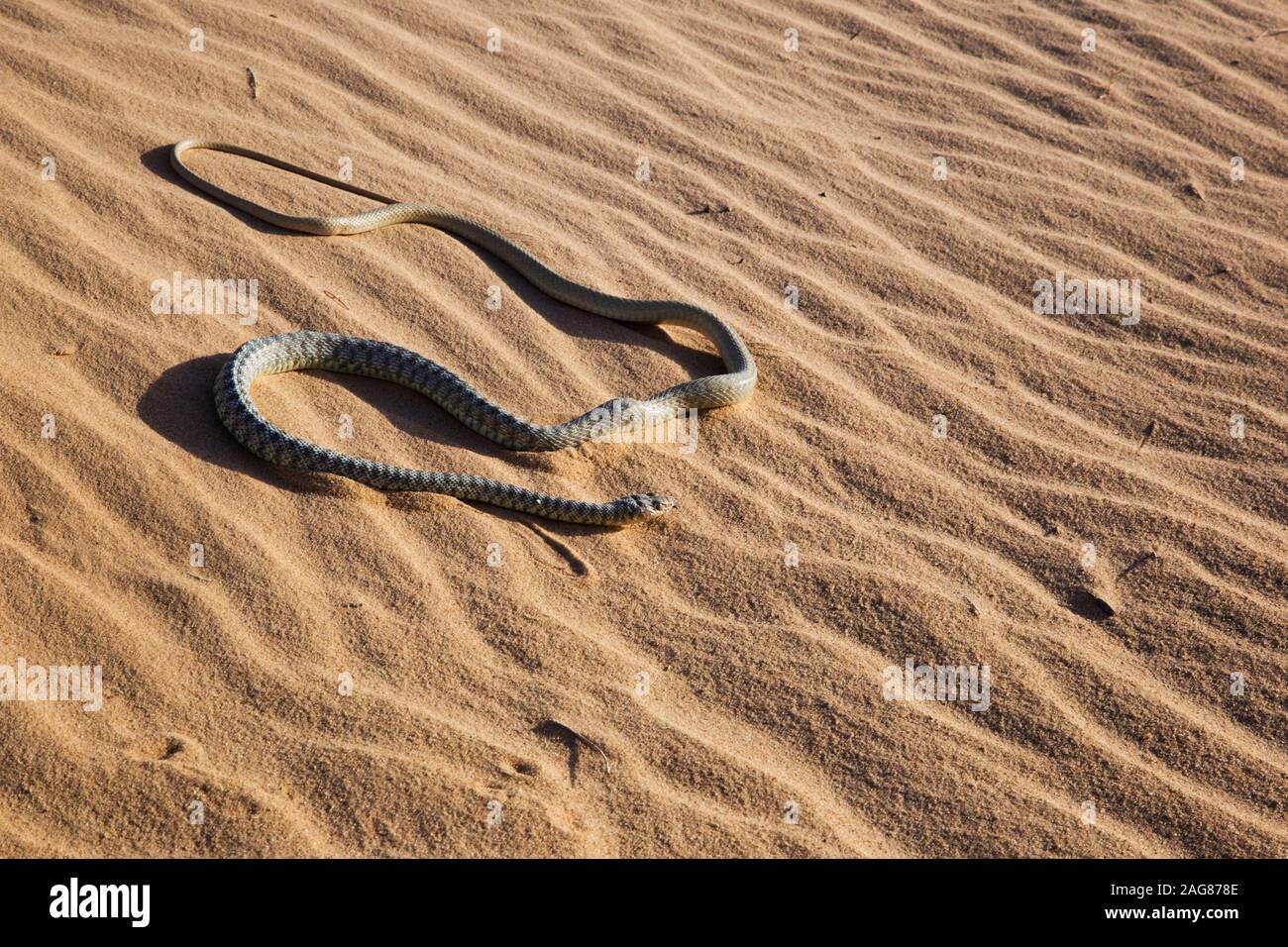
Additionally, the desert horned viper (Cerastes cerastes) is also a common venomous snake found in the Sahara Desert. It is known for its ability to blend into the sandy terrain and can even bury itself in the sand to disguise itself.
READ MORE:
Overview of Snakes in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, a vast and diverse ecosystem, is home to an array of snake species uniquely adapted to its harsh conditions. This section provides a detailed exploration of these fascinating reptiles, their habitats, and their survival strategies in one of the world"s most extreme environments.
- Diversity of Species: The Sahara hosts a variety of snake species, ranging from the venomous sand viper to the elusive desert cobra.
- Adaptations for Survival: These snakes have developed remarkable adaptations, such as burrowing abilities and heat resistance, to thrive in the desert climate.
- Habitats within the Desert: They inhabit diverse areas, from sandy dunes to rocky outcrops, each species favoring different environments for shelter and hunting.
- Dietary Habits: Sahara snakes predominantly feed on small mammals, birds, and other reptiles, playing a crucial role in the desert"s ecological balance.
- Behavioral Characteristics: Many of these snakes are nocturnal, avoiding the extreme daytime heat and emerging in cooler temperatures to hunt and mate.
Understanding these snakes is key to appreciating the biodiversity and ecological complexity of the Sahara Desert.

Common Species of Sahara Desert Snakes
The Sahara Desert is home to a fascinating variety of snakes, each adapted to thrive in the harsh desert environment. This section highlights some of the most common and intriguing snake species found in the Sahara.
- Horned Viper (Cerastes cerastes): Known for its distinct horns above the eyes, this viper is well-adapted to sandy environments.
- Saharan Sand Viper (Cerastes vipera): A smaller viper species, adept at burying itself in the sand to ambush prey.
- Egyptian Cobra (Naja haje): One of the larger species in the Sahara, the Egyptian Cobra is known for its potent venom and distinctive hood.
- Sahara Sand Boa (Eryx colubrinus): A non-venomous boa that burrows in the sand and primarily feeds on rodents.
- West African Carpet Viper (Echis ocellatus): A highly venomous species, characterized by its patterned appearance and fast-acting venom.
These species represent the incredible adaptability and diversity of snakes in the Sahara Desert, each contributing uniquely to the desert"s ecosystem.
Adaptations of Snakes to the Sahara Desert Environment
Snakes in the Sahara Desert have evolved a range of unique adaptations to survive in one of the harshest environments on Earth. This section delves into the remarkable physiological and behavioral traits that enable these reptiles to thrive in extreme conditions.
- Thermoregulation: Many Sahara snakes are adept at regulating their body temperature, utilizing the warm sun and cool sands to maintain optimal body temperatures.
- Camouflage: Desert snakes exhibit coloration and patterns that blend seamlessly with the desert sands, aiding in both predation and protection from predators.
- Burrowing Ability: Species like the sand viper have developed the ability to burrow into the sand, which provides shelter from heat and a strategic hunting position.
- Water Conservation: These snakes have adapted to survive with minimal water, extracting moisture from their prey and minimizing water loss through specialized scales.
- Venom Adaptation: Venomous snakes in the Sahara, such as the horned viper, possess potent venom to quickly immobilize prey, conserving energy in the harsh desert environment.
- Nocturnal Behavior: Many species are nocturnal, active during cooler nights to avoid the extreme daytime temperatures.
These adaptations highlight the incredible resilience and evolutionary ingenuity of Sahara Desert snakes, enabling them to master the art of desert survival.

Interaction of Sahara Snakes with the Ecosystem
Sahara Desert snakes play a pivotal role in their ecosystem, contributing to environmental balance and biodiversity. This section explores how these reptiles interact with their surroundings and other species in the Sahara Desert.
- Predators and Prey Dynamics: Sahara snakes, both as predators and prey, are integral to the desert food web. They control rodent populations and are prey for larger animals like birds of prey and certain mammals.
- Seed Dispersal: Some snake species inadvertently contribute to seed dispersal through their fecal matter, aiding in plant diversity.
- Soil Aeration: The burrowing activities of snakes like the sand boa help aerate the soil, promoting a healthier desert ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Indicators: The presence and health of snake populations can indicate the overall health of the desert ecosystem, serving as bioindicators.
- Ecosystem Engineers: By altering their environment through activities like burrowing, snakes create microhabitats that benefit other species.
- Biological Control: Snakes help control pest populations, maintaining a balance in the ecosystem and preventing overpopulation of certain species.
The complex interactions of Sahara snakes with their environment underscore their importance in maintaining the ecological equilibrium of the desert.
Human and Snake Interactions in the Sahara
In the Sahara Desert, the interactions between humans and snakes are multifaceted, ranging from cultural significance to environmental impact. This section discusses the various aspects of human-snake interactions in this unique ecosystem.
- Cultural Significance: In many Saharan cultures, snakes are seen as symbols of wisdom or omens, and feature prominently in folklore and mythology.
- Encounters and Safety: With increasing human activity in the Sahara, encounters with snakes have become more common, highlighting the need for awareness and safety measures.
- Conservation Efforts: Conservationists work to protect endangered snake species in the Sahara, balancing ecological needs with human development.
- Impact of Climate Change: Human-induced climate change affects snake habitats in the Sahara, altering their behavior and survival strategies.
- Educational Outreach: Educational programs aim to teach locals and tourists about the importance of snakes in the ecosystem and how to coexist safely.
- Research and Study: Scientists study Sahara snakes to understand their adaptations and roles in the desert, contributing to broader ecological knowledge.
The relationship between humans and Sahara snakes is complex, shaped by cultural, environmental, and scientific factors, each playing a crucial role in the coexistence of humans and these remarkable reptiles.

Conservation Status of Sahara Desert Snakes
The conservation status of snakes in the Sahara Desert is a topic of increasing importance, as these species face various environmental and human-induced challenges. This section examines the current status and efforts to protect these unique reptiles.
- Threats to Sahara Snakes: Habitat loss, climate change, and human encroachment are major threats to the survival of Sahara Desert snakes.
- Endangered Species: Some species, like the horned viper, face significant risks and are classified as endangered or vulnerable.
- Conservation Initiatives: Efforts are underway to conserve these species, including habitat protection and legal measures against illegal trade and poaching.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring are crucial to understand the population dynamics and threats faced by these snakes.
- Community Involvement: Local community engagement and education are key to successful conservation efforts, promoting coexistence and awareness.
- Global Awareness: International awareness and collaboration are essential to address cross-border environmental issues affecting these species.
Conservation of Sahara Desert snakes is vital not only for the survival of these species but also for maintaining the ecological balance of this unique desert ecosystem.
The Venomous Snakes of Africa - Deserts, Cape Cobra, Red Spitting Cobra, Puff Adder, Carpet Viper
Discover the breathtaking beauty of Africa through this captivating video. Immerse yourself in the vibrant cultures, stunning landscapes, and majestic wildlife that make Africa truly unforgettable.
Sahara Sand Viper Burrowing in Sand
Prepare to be mesmerized by the enchanting world of sand in this awe-inspiring video. From expansive desert vistas to intricate sand sculptures, you\'ll be spellbound by the fascinating stories this humble substance has to tell.
Research and Studies on Sahara Desert Snakes
Scientific research and studies on Sahara Desert snakes are crucial for understanding these species and their roles in the ecosystem. This section highlights significant research efforts and discoveries about these fascinating reptiles.
- Behavioral Studies: Research on the behavioral patterns of Sahara snakes, including hunting strategies, mating rituals, and habitat preferences.
- Ecological Impact: Studies examining the ecological role of snakes in the Sahara, their impact on prey populations, and their interactions with other species.
- Adaptation and Survival Mechanisms: Investigations into the unique adaptations of Sahara Desert snakes, allowing them to thrive in extreme conditions.
- Venom Research: Analysis of venom composition and its potential medical applications, as well as understanding venom"s role in prey immobilization and defense.
- Conservation Biology: Research focused on the conservation status of these snakes, threats to their survival, and strategies for protection and preservation.
- Climate Change Effects: Studies on how changing climate conditions affect the habitat, behavior, and survival of Sahara Desert snakes.
The ongoing research and studies are vital for protecting these snakes and maintaining the ecological balance of the Sahara Desert.

Myths and Misconceptions about Sahara Desert Snakes
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding Sahara Desert snakes, often leading to misunderstandings about these creatures. This section aims to dispel some common myths and provide factual information about these snakes.
- Myth: All Desert Snakes are Highly Venomous: While there are venomous species, not all Sahara Desert snakes are venomous, and many pose no threat to humans.
- Myth: Snakes Pursue Humans to Attack: Snakes generally avoid human contact and only attack in self-defense when threatened or provoked.
- Myth: Snakes Can Hypnotize Prey: The notion that snakes can hypnotize their prey is a misconception; their hunting success relies on stealth and speed.
- Myth: Snakes are Always Aggressive: Sahara Desert snakes exhibit a range of behaviors, and aggression is typically a defensive response rather than a natural disposition.
- Myth: Larger Snakes are More Dangerous: The danger a snake poses is not necessarily related to its size but to its species, behavior, and venom potency if it is venomous.
Understanding the truth about Sahara Desert snakes is important for appreciating their role in the ecosystem and reducing unnecessary fear or hostility towards them.
Guidelines for Safe Encounters with Desert Snakes
Encountering snakes in the Sahara Desert can be a daunting experience. This section provides guidelines to ensure safe and respectful interactions with these desert inhabitants.
- Stay Aware of Your Surroundings: Always be vigilant when walking in snake habitats, especially in sandy or rocky areas where they may be hidden.
- Avoid Disturbing Snakes: If you see a snake, maintain a safe distance and do not attempt to touch, capture, or disturb it.
- Wear Protective Clothing: When walking in areas where snakes might be present, wear long pants and sturdy boots to reduce the risk of bites.
- Use a Flashlight at Night: Many desert snakes are nocturnal. Use a flashlight to check your path when walking at night.
- Learn Snake Identification: Familiarize yourself with the common snake species in the area to better understand potential risks.
- Carry a First-Aid Kit: Always have a basic first-aid kit on hand in case of snake bites or other emergencies.
- Know Emergency Procedures: Be aware of the correct first-aid measures for snake bites and the location of the nearest medical facility.
Respecting these guidelines can help ensure safe experiences in the Sahara Desert and reduce negative encounters with its snake population.

READ MORE:
Interesting Facts about Sahara Desert Snakes
The Sahara Desert, with its extreme environment, is home to some of the most fascinating snake species. Here are some interesting facts that highlight the uniqueness of these reptiles.
- Exceptional Survivors: Sahara Desert snakes have adapted to survive in one of the most arid and extreme climates on Earth.
- Variety of Species: The Sahara hosts a diverse range of snake species, from the small, elusive sand snakes to the iconic, venomous horned vipers.
- Camouflage Experts: Many Sahara snakes, like the horned viper, have remarkable camouflage that blends perfectly with the sandy environment.
- Unique Hunting Techniques: Some species use unique hunting strategies, like sidewinding movement, to navigate and hunt in the desert sands.
- Thermal Regulation: These snakes are adept at regulating their body temperature, often burrowing underground to escape the desert"s intense heat.
- Nighttime Predators: Many Sahara snakes are nocturnal, hunting at night when the temperatures are more bearable.
- Venom Potency: Some species, like the Saharan sand viper, have highly potent venom, adapted to quickly immobilize their prey in the harsh desert environment.
These intriguing facts offer a glimpse into the captivating world of Sahara Desert snakes, showcasing their adaptability and survival skills in one of the toughest habitats on the planet.
In conclusion, Sahara Desert snakes are a testament to nature"s resilience, embodying adaptability and mystery in one of Earth"s most challenging environments, inviting us to explore and respect this remarkable aspect of the natural world.