Topic what are provisioning ecosystem services: Discover the wonders of provisioning ecosystem services, nature"s invaluable gifts that nourish, clothe, and sustain our lives, laying the foundation for a sustainable future.
Table of Content
- What are provisioning ecosystem services?
- Overview of Ecosystem Services
- Types of Ecosystem Services
- Provisioning Services Explained
- Benefits and Examples of Provisioning Services
- Impact of Human Activities on Provisioning Services
- Strategies for Sustainable Management
- YOUTUBE: Provisioning Ecosystem Services
- Case Studies on Provisioning Services
- Future Trends in Ecosystem Service Management
What are provisioning ecosystem services?
Provisioning ecosystem services refer to the products or resources that are obtained from ecosystems and play a crucial role in meeting human needs. These services provide various essentials for human survival and well-being.
- Food: Ecosystems are a source of diverse food items such as crops, fish, meat, and wild edible plants.
- Water: Ecosystems contribute to the availability and quality of water resources that we rely on for drinking, agriculture, and industrial purposes.
- Minerals: Many ecosystems contain mineral deposits that are extracted for various purposes, including construction and manufacturing.
- Shelter: Ecosystems provide materials such as wood, thatch, and fibers used for constructing shelters and buildings.
- Fuel: Biomass and fossil fuels derived from ecosystems serve as a source of energy for cooking, heating, and transportation.
Overall, provisioning services ensure the availability of essential resources from nature that support our daily lives and economic activities.
READ MORE:
Overview of Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans freely gain from the natural environment and properly functioning ecosystems. These services are vital for human well-being, economic stability, and environmental health. They encompass a wide range of functions that the earth"s ecosystems provide, including but not limited to, the production of food and water, regulation of climate, flood and disease control, and cultural, spiritual, and recreational benefits.
- Provisioning Services: These are the products obtained from ecosystems, such as food, fresh water, timber, fiber, and genetic resources.
- Regulating Services: These services include the regulation of climate, floods, disease, wastes, and water quality.
- Cultural Services: This includes non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, reflection, recreation, and aesthetic experiences.
- Supporting Services: Such services are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, including soil formation, photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, and water cycling.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem services is crucial for sustainability and ensuring that future generations can also benefit from the natural environment. This involves managing natural resources wisely, protecting natural habitats, and implementing practices that support ecosystem functions.
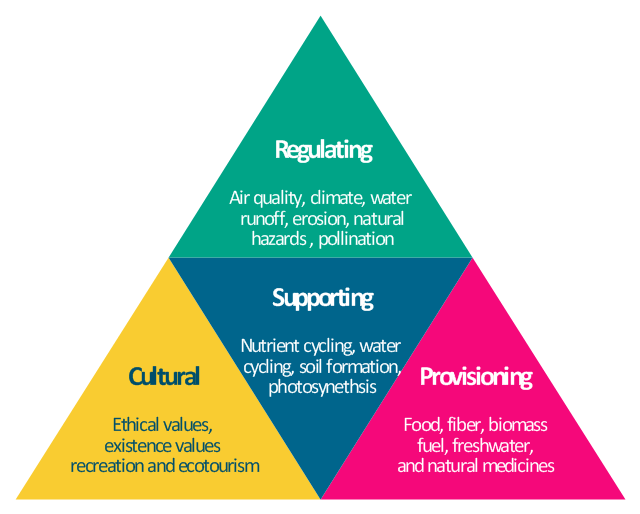
Types of Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the benefits that nature provides to humanity, which support our survival and quality of life. These services are categorized into four main types, each essential for the health of the planet and the well-being of all living beings.
- Provisioning Services: These include the products provided by ecosystems, such as food, water, timber, fiber, and genetic resources. Provisioning services are the tangible goods that we can extract from nature to support human life and economic activities.
- Regulating Services: These are the benefits obtained from the regulation of ecosystem processes, including air quality maintenance, climate regulation, water purification, pollination, and disease control. Regulating services help to maintain the balance of the environment, making the planet habitable.
- Cultural Services: Cultural services represent the non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, recreation, and aesthetic experiences. This category includes cultural diversity, spiritual and historical sites, and recreational experiences (such as hiking, camping, and bird watching).
- Supporting Services: These services are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services. They include soil formation, photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, and water cycling. Supporting services underpin the functioning of provisioning, regulating, and cultural services, thereby making life on Earth possible.
Recognizing the importance of these ecosystem services is crucial for sustainable management and conservation efforts. It highlights the need to protect and restore natural habitats and ecosystems to ensure that they continue to provide these invaluable services to humanity.
Provisioning Services Explained
Provisioning services are one of the four main categories of ecosystem services that nature offers to human society. These services are essentially the products obtained from ecosystems that are vital for survival and contribute significantly to our economy and culture. Provisioning services play a crucial role in sustaining human life by providing essential resources.
- Food: This includes the vast array of edible products we obtain from plants (vegetables, fruits, grains) and animals (meat, fish, dairy products), which are fundamental for human nutrition and culinary traditions.
- Water: Freshwater extracted from surface and underground sources is critical for drinking, sanitation, agriculture, and industrial processes.
- Raw Materials: Ecosystems provide raw materials such as wood for construction and furniture, fibers for clothing, and oils for cooking and cosmetics.
- Medicinal Resources: Many plants and animals provide compounds used in traditional and modern medicines to treat and prevent illness.
- Energy: Biofuels, including wood, ethanol, and biodiesel, are derived from biomass, offering alternatives to fossil fuels.
The sustainable management of provisioning services is essential to ensure that ecosystems continue to provide these resources for future generations. It involves balancing extraction and consumption with conservation and restoration efforts, to maintain the health of ecosystems and the services they provide.

Benefits and Examples of Provisioning Services
Provisioning services are essential for sustaining human life and economies, offering a wide range of benefits and examples that illustrate their importance.
- Food Production: Ecosystems provide a diverse array of foods, such as grains, fruits, vegetables, and livestock, supporting global food security and dietary needs. For example, rice paddies, orchards, and fisheries are critical sources of global nutrition.
- Water Supply: Freshwater ecosystems like rivers, lakes, and aquifers supply water for drinking, agriculture, and industry. The Nile River and Great Lakes are vital water sources for millions of people.
- Raw Materials: Forests, grasslands, and aquatic ecosystems supply materials for clothing, shelter, and daily needs. Bamboo and cotton are renewable resources used for building materials and textiles.
- Medicinal Resources: Many modern medicines are derived from plants and animals found in ecosystems. The rosy periwinkle provides compounds used in cancer treatments, showcasing the medicinal value of biodiversity.
- Energy Resources: Biofuels, such as ethanol made from corn or sugarcane, are renewable energy sources that ecosystems provide, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
The benefits of provisioning services extend beyond mere resource extraction, contributing to cultural practices, traditional knowledge, and the global economy. Sustainable management and conservation of these services are crucial to ensure their availability for future generations.
Impact of Human Activities on Provisioning Services
Human activities have profound impacts on the provisioning services ecosystems provide, often leading to significant changes in their capacity to support life and economies. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate negative impacts and promote sustainability.
- Agricultural Expansion: While agriculture supports food production, excessive expansion and intensive farming practices degrade soil, reduce biodiversity, and can lead to the loss of ecosystem services such as water purification and pollination.
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for timber, agriculture, and development reduces the availability of raw materials, impacts climate regulation, and diminishes biodiversity, all of which are critical components of provisioning services.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices threaten fish populations and marine biodiversity, undermining the long-term availability of seafood and the health of marine ecosystems.
- Pollution: Contamination of water, air, and soil from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources affects the quality and safety of food and water supplies, and can lead to the loss of usable land and water bodies.
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns, rising temperatures, and increased frequency of extreme weather events can disrupt the natural processes that underpin provisioning services, affecting food security, water availability, and the viability of certain raw materials.
Addressing the impact of human activities on provisioning services requires a concerted effort towards sustainable management practices, conservation, and restoration of ecosystems. This includes adopting sustainable agriculture, fishing, and forestry practices, reducing pollution, and taking action on climate change to ensure the resilience of ecosystem services.

Strategies for Sustainable Management
Sustainable management of provisioning ecosystem services is essential for ensuring that natural resources are available for future generations while maintaining ecosystem health. Implementing effective strategies can mitigate the impact of human activities and promote resilience in ecosystems.
- Adopting Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Techniques such as crop rotation, organic farming, integrated pest management, and conservation tillage help in preserving soil health, reducing chemical use, and increasing biodiversity.
- Implementing Sustainable Fishing Practices: Practices such as setting catch limits, using selective fishing gear, and establishing marine protected areas can help in conserving fish populations and marine ecosystems.
- Responsible Forestry Management: Sustainable forestry practices, including selective logging, reforestation, and afforestation, ensure the long-term availability of timber resources while conserving forest ecosystems.
- Water Conservation Measures: Efficient water use, pollution prevention, and the protection of water sources are critical for sustaining freshwater provisioning services.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing ecosystem resilience to climate impacts are crucial for preserving ecosystem services.
- Protecting and Restoring Ecosystems: Conservation efforts, such as establishing protected areas and restoring degraded ecosystems, are vital for maintaining the natural processes that provisioning services rely on.
- Encouraging Community Involvement and Education: Engaging local communities in conservation and sustainable management efforts and raising awareness about the importance of ecosystem services can foster stewardship and sustainable use of natural resources.
- Policy and Regulation: Implementing laws, regulations, and incentives that promote sustainable resource use and protect ecosystems can guide industries and individuals towards more sustainable practices.
By integrating these strategies into planning and development processes, societies can ensure the sustainable use of provisioning ecosystem services, securing the well-being of both current and future generations.
Provisioning Ecosystem Services
Looking for top-notch services that cater to all your needs? Look no further! Our video showcases the best-in-class services that guarantee customer satisfaction and leave you wanting more. Watch now to discover the perfect solution for all your service requirements!
Explaining \'Provisioning Services\' Provided by Nature
Immerse yourself in the breathtaking beauty of nature with our mesmerizing video. From stunning landscapes to awe-inspiring wildlife, our footage captures the essence of the natural world in all its glory. Don\'t miss your chance to experience the wonder of nature firsthand - click now and let your senses come alive!
Case Studies on Provisioning Services
Exploring case studies on provisioning services reveals the diverse ways in which ecosystems contribute to human well-being and economic development. These studies highlight the importance of sustainable management practices and the potential consequences of neglecting ecosystem health.
- The Amazon Rainforest - A Source of Medicinal Resources: The Amazon rainforest is home to an abundance of plant species that are sources of new drugs and medicinal compounds. Sustainable harvesting practices are essential for ensuring that these resources remain available for future pharmaceutical developments.
- Sustainable Fishing in the Coral Triangle: The Coral Triangle, located in the waters of Indonesia, the Philippines, and surrounding countries, is a biodiversity hotspot for marine life. Implementing sustainable fishing practices here has helped to preserve fish stocks, supporting local economies and food security.
- Water Management in the Aral Sea Basin: Once one of the world"s largest lakes, the Aral Sea has significantly shrunk due to the diversion of rivers for agricultural irrigation. Efforts to improve water management practices in the region aim to restore this vital provisioning service of freshwater supply.
- Agroforestry in Costa Rica: Costa Rica has become a leading example of how agroforestry can enhance provisioning services such as food and timber while maintaining ecological integrity. This approach integrates tree planting with crop and livestock farming to create more diverse, productive, and sustainable land-use systems.
- Rooftop Gardens in Urban Areas: Rooftop gardens in cities around the world demonstrate how urban areas can contribute to food provisioning services. These gardens not only provide fresh produce but also help to reduce urban heat islands, manage stormwater, and increase biodiversity in cities.
These case studies underscore the importance of integrating ecological considerations into planning and management decisions to ensure the continued provision of essential ecosystem services.

READ MORE:
Future Trends in Ecosystem Service Management
As awareness of the importance of ecosystem services to human well-being and economic stability grows, future trends in ecosystem service management are likely to emphasize sustainability, restoration, and innovative approaches to conservation. Here are some key trends expected to shape the future of ecosystem service management:
- Increased Use of Technology: Advances in technology, including remote sensing, GIS, and big data analytics, will enable more precise monitoring and management of ecosystem services, allowing for targeted conservation efforts and better decision-making.
- Focus on Restoration and Rehabilitation: There will be a growing emphasis on restoring degraded ecosystems and rehabilitating lands to enhance provisioning services, with initiatives such as reforestation and wetland restoration becoming increasingly common.
- Integration of Ecosystem Services into Planning: Urban and regional planning will increasingly incorporate ecosystem service assessments to ensure that development projects sustain or enhance these services rather than degrade them.
- Expansion of Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES) Schemes: PES schemes, which provide financial incentives to landowners for managing their land in ways that provide ecological benefits, are expected to become more widespread, supporting sustainable land use practices.
- Greater Emphasis on Climate Change Adaptation: Managing ecosystem services will increasingly involve adaptation strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change, ensuring the resilience of ecosystems and the services they provide.
- Community Engagement and Indigenous Knowledge: Recognizing the value of local and indigenous knowledge in ecosystem management, there will be a greater emphasis on inclusive approaches that involve communities in conservation efforts.
- Policy and Regulatory Innovations: New policies and regulations that support ecosystem service management and promote sustainability are likely to be developed, reflecting an integrated approach to environmental, social, and economic objectives.
These trends highlight the evolving nature of ecosystem service management, moving towards approaches that are sustainable, inclusive, and adaptive to changing environmental conditions.
Embracing the bounty of provisioning ecosystem services illuminates a path towards sustainability, urging us to protect the natural gifts that sustain life and prosperity. Let"s steward these resources for the future, safeguarding our planet"s wealth for generations to come.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)



