Topic gizmo forest ecosystem answers key: Dive into the intricate world of forest ecosystems with our Gizmo Forest Ecosystem Answers Key, your ultimate guide to understanding nature"s complex interactions and biodiversity.
Table of Content
- What is the answer key for the Gizmo Forest Ecosystem?
- Understanding the Basics of Forest Ecosystems
- Key Components and Organisms in Forest Ecosystems
- Exploring the Gizmo Forest Ecosystem Simulation
- Interactions Between Species in Forest Ecosystems
- Human Impact on Forest Ecosystems
- Conservation Efforts and the Importance of Forest Ecosystems
- YOUTUBE: Forest Ecosystem Gizmo
- Quizlet Flashcards as a Study Tool
- Teacher Guides and Answer Keys for Educators
- Assessment Questions to Test Understanding
- Advanced Topics: Deforestation, Pollution, and Climate Change
What is the answer key for the Gizmo Forest Ecosystem?
Unfortunately, the specific answer key for the Gizmo Forest Ecosystem is not provided in the search results. However, there are screenshots and exploration sheets available for subscribers and teachers. To obtain the answer key for the Gizmo Forest Ecosystem, you may need to access the Gizmo Warm-up and complete the activities on the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo.
You can start by following these steps:
- Access the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo from the Gizmo Warm-up.
- Explore the effects of adding or removing organisms from the forest.
- Observe the changes in the ecosystem as you interact with the Gizmo.
- Record your observations and responses in the provided Exploration Sheet.
- Once you have completed the activities on the Gizmo, compare your answers and observations with the provided Exploration Sheet Answer Key.
Keep in mind that the exact answer key may vary depending on the specific tasks and questions within the Gizmo Forest Ecosystem. It is recommended to refer to the Exploration Sheet Answer Key or seek guidance from your teacher or instructor to ensure accuracy and completeness in your answers.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Basics of Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are dynamic environments where plants, animals, and microorganisms interact within a physical and chemical framework. These interactions create a complex and interdependent system that supports a wide range of life forms.
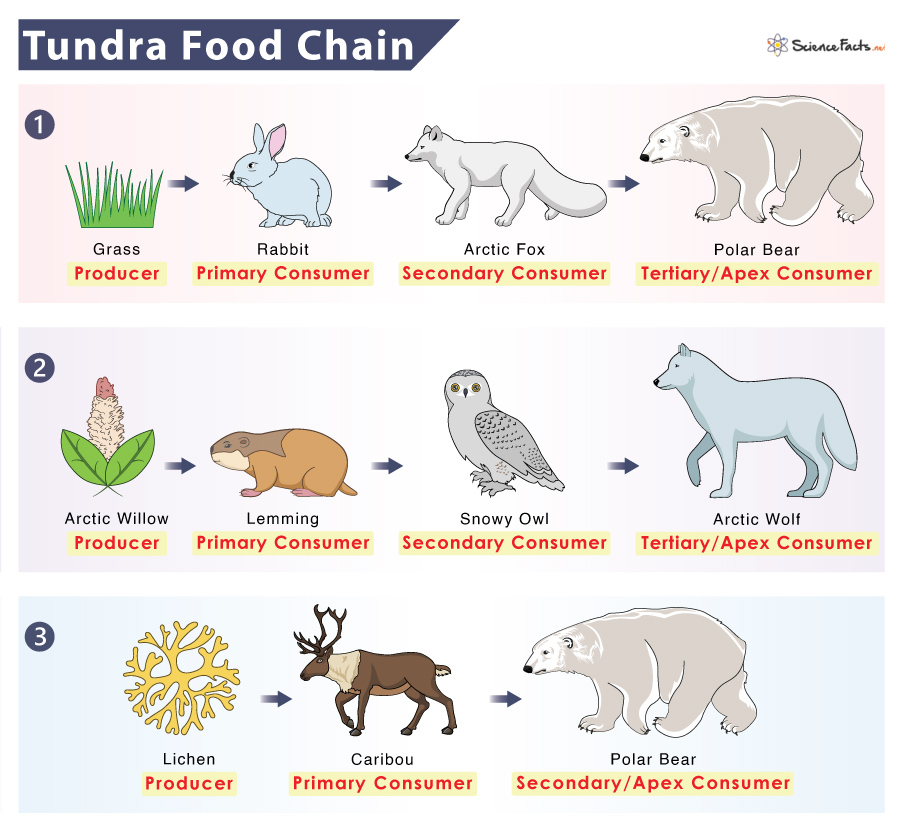
- Components of Forest Ecosystems: Includes trees, shrubs, herbs, decomposers, herbivores, and carnivores.
- Energy Flow: Sunlight is the primary energy source, which is harnessed by plants through photosynthesis. This energy then flows through the ecosystem via the food chain.
- Nutrient Cycling: Decomposers play a critical role in breaking down dead organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the soil for plants to use.
- Habitats and Niches: Forests provide diverse habitats for species, each occupying a unique niche within the ecosystem.
Understanding these basics helps us appreciate the importance of forest ecosystems in maintaining biodiversity, regulating climate, and supporting human needs.

Key Components and Organisms in Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are composed of living and non-living components that interact to sustain a diverse and vibrant environment. Understanding these components and organisms is essential for grasping how forests function and the roles they play in the broader ecological context.
- Producers: These are primarily trees and undergrowth plants that produce oxygen and food through photosynthesis, using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
- Consumers: Animals in the forest, ranging from insects to large mammals, depend on producers and other consumers for food. They are categorized into herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores.
- Decomposers: Fungi, bacteria, and some insects break down dead organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil and ensuring nutrient cycling within the ecosystem.
- Soil and Water: Non-living components that are crucial for the survival of forest ecosystems. Soil provides nutrients and a medium for plant growth, while water is essential for life.
Together, these components form a complex web of life that supports the diverse species living in forest ecosystems and ensures their resilience and productivity.
Exploring the Gizmo Forest Ecosystem Simulation
The Gizmo Forest Ecosystem Simulation is an interactive tool designed to help students and enthusiasts understand the complexities of forest ecosystems through virtual experimentation. By manipulating variables, users can observe how changes impact the ecosystem, offering insights into the balance of natural habitats.
- Interactive Learning: Users can simulate different environmental conditions to see how they affect the forest"s flora and fauna.
- Variable Control: Elements such as precipitation, temperature, and human activities can be adjusted to observe their effects on biodiversity, growth rates, and the survival of organisms.
- Species Interaction: The simulation demonstrates interactions between various species, including competition, predation, and symbiosis, highlighting the importance of each species in the ecosystem.
- Data Analysis: Provides tools for data collection and analysis, allowing users to graph and track changes over time, fostering a deeper understanding of ecological principles.
This simulation is a powerful tool for education, offering a hands-on approach to learning about forest ecosystems, their components, and the importance of conservation efforts.

Interactions Between Species in Forest Ecosystems
In forest ecosystems, species interactions are fundamental processes that drive the dynamics and stability of the environment. These interactions can be complex, with each playing a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance.
- Predation and Herbivory: Predators consuming prey and herbivores feeding on plants are interactions that regulate population sizes and stimulate new growth.
- Competition: Species compete for limited resources like light, water, and nutrients. This competition can lead to diverse adaptations and niche differentiation.
- Mutualism: Symbiotic relationships where both species benefit, such as pollinators feeding on nectar while helping plants reproduce.
- Parasitism: One species benefits at the expense of another, like parasites that live on or inside other organisms, often causing harm.
- Decomposition: Decomposers break down dead organisms, returning essential nutrients to the soil, which supports new plant growth.
Understanding these interactions is key to conserving forest ecosystems and ensuring their resilience against environmental changes.
Human Impact on Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are vital components of the world"s environment, providing a range of ecosystem services that benefit humanity, including air and water purification, carbon storage, and habitats for biodiversity. However, human activities have significantly impacted these ecosystems. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate negative effects and promote sustainable interaction with our planet"s forests.
- Deforestation: One of the most significant human impacts is deforestation, driven by logging for timber, agricultural expansion, and urban development. This leads to habitat loss, decreases in biodiversity, and contributes to global climate change through the release of stored carbon.
- Pollution: Forests are also affected by pollution. Air pollution from industrial activities and vehicle emissions can lead to acid rain, which damages trees and soils. Water pollution from agricultural runoff can harm aquatic ecosystems connected to forests.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change poses a significant threat to forest ecosystems. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events can disrupt the balance of forest ecosystems, affecting species distribution and forest health.
- Land Use Changes: The conversion of forest land to other uses, such as agriculture or urban areas, not only reduces forest area but also fragments habitats, making it difficult for wildlife to migrate and find resources.
- Introduction of Invasive Species: Human activities have led to the introduction of invasive species into forest ecosystems. These species can outcompete native species for resources, leading to a loss of biodiversity.
Despite these challenges, there are numerous efforts underway to reduce human impact on forest ecosystems. Conservation initiatives, sustainable management practices, reforestation projects, and policies aimed at protecting forests are all part of a global effort to preserve these vital ecosystems for future generations.

Conservation Efforts and the Importance of Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems play a critical role in maintaining the health of our planet. They act as global carbon sinks, help regulate the climate, support a vast diversity of species, and provide essential services to humanity, including clean air, water, and resources for medicines. Recognizing their value, various conservation efforts are underway to protect and restore these vital natural resources.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, reserves, and wildlife sanctuaries to protect forest lands from deforestation, poaching, and other threats. These areas serve as refuges for biodiversity and help preserve ecosystems in their natural state.
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees in deforested areas and creating new forests on previously non-forested lands. These efforts not only increase forest cover but also restore habitat for wildlife, enhance carbon sequestration, and improve soil and water quality.
- Sustainable Forestry Practices: Implementing sustainable management practices that allow for the use of forest resources while ensuring the long-term health and regeneration of the forest. This includes selective logging, controlled burns, and the protection of old-growth forests.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their dependence on forest resources for livelihoods. Community-based forestry initiatives can help promote sustainable use and stewardship of forest lands.
- Legislation and International Agreements: Developing laws and policies at both the national and international levels to protect forests. This includes regulations on logging, land use, and trade in forest products, as well as international agreements like the Convention on Biological Diversity and the Paris Agreement on climate change.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research to better understand forest ecosystems and the impacts of human activities. Monitoring programs help track changes in forest health and biodiversity, informing conservation strategies and policy decisions.
The importance of forest ecosystems cannot be overstated. Their conservation is essential for sustaining the planet"s biodiversity, combating climate change, and supporting the well-being of all species, including humans. Through concerted global efforts, we can ensure that these magnificent ecosystems continue to thrive for generations to come.
Forest Ecosystem Gizmo
Discover the magic of the latest gizmo that will revolutionize your daily life! This innovative device is designed to make tasks easier and more enjoyable. Watch the video to see how this gizmo can enhance your everyday activities.
Quizlet Flashcards as a Study Tool
Quizlet flashcards offer an innovative and interactive way to learn and review the complex concepts associated with forest ecosystems. This digital tool enables students and educators to create, share, and study educational flashcards, making learning more engaging and effective. Here"s how Quizlet can be utilized to enhance understanding of forest ecosystems:
- Customizable Learning Sets: Users can create tailored sets of flashcards that focus on specific aspects of forest ecosystems, such as types of forests, key species, ecological processes, and conservation strategies.
- Interactive Study Modes: Quizlet provides various modes such as Learn, Flashcards, Write, Spell, and Test to accommodate different learning styles and help reinforce the material through repetition and active recall.
- Collaborative Learning: Students can collaborate with classmates by sharing flashcard sets, enabling them to learn from each other and tackle complex topics together.
- Accessibility: With Quizlet"s mobile app and website, learning can take place anytime and anywhere, making it easier to fit study sessions into busy schedules.
- Visual Aids: Users can enhance flashcards with images and diagrams to better understand and remember the structural and functional aspects of forest ecosystems.
- Teacher Resources: Educators can use Quizlet to provide students with supplemental study materials, track progress, and even create games and quizzes to make learning more fun and engaging.
By leveraging Quizlet flashcards as a study tool, learners can deepen their comprehension of forest ecosystems, improve retention of key concepts, and prepare more effectively for assessments. This interactive approach to studying not only aids in academic success but also fosters a greater appreciation for the importance of conserving our planet"s forests.

Teacher Guides and Answer Keys for Educators
Teacher guides and answer keys are essential resources for educators aiming to provide comprehensive and effective education about forest ecosystems. These materials support teaching by offering detailed lesson plans, background information, student activities, and answers to assessment questions. Utilizing these tools allows educators to enhance their curriculum and foster a deeper understanding of forest ecosystems among students.
- Comprehensive Lesson Plans: Guides often include lesson plans that outline objectives, key concepts, teaching strategies, and timelines. This helps educators structure their lessons to cover all necessary topics effectively.
- Background Information: To ensure educators are well-prepared, these guides provide extensive background information on forest ecosystems, including key components, ecological processes, and conservation issues.
- Engaging Student Activities: Activities designed to engage students in active learning are included, such as hands-on experiments, research projects, field trips, and interactive simulations like the Gizmo Forest Ecosystem.
- Assessment Tools: Various assessment tools, including quizzes, project rubrics, and reflection questions, help educators evaluate students" understanding of the material. Answer keys offer guidance on expected responses to facilitate grading.
- Adaptation Suggestions: Guides provide suggestions for adapting lessons to different grade levels or learning abilities, ensuring all students can access and engage with the content.
- Resources for Further Exploration: Additional resources, such as recommended readings, websites, and videos, are often included to encourage further exploration of forest ecosystems.
By integrating these teacher guides and answer keys into their teaching strategies, educators can provide students with a well-rounded education on forest ecosystems. This not only aids in meeting educational standards but also instills in students a sense of responsibility towards environmental conservation and sustainability.
Assessment Questions to Test Understanding
To evaluate students" comprehension of forest ecosystems, educators can use a variety of assessment questions. These questions are designed to test knowledge of key concepts, critical thinking, and the ability to apply what has been learned in practical contexts. Below is a set of sample questions that cover different aspects of forest ecosystems:
- Describe the main components of a forest ecosystem and explain how they interact with each other.
- What role do decomposers play in the forest ecosystem? Provide examples.
- Explain the concept of ecological succession in forests. How does a forest change over time?
- Discuss the impact of deforestation on biodiversity and the global climate. What are the long-term consequences?
- How do invasive species affect forest ecosystems? Give examples of invasive species and their impact.
- Describe the significance of conservation efforts in protecting forest ecosystems. Can you name any successful conservation strategies?
- Explain how climate change is affecting forest ecosystems. What are the observable changes and potential future impacts?
- Identify human activities that harm forest ecosystems and propose sustainable alternatives.
- How can reforestation help in mitigating the effects of climate change and restoring biodiversity?
- Discuss the role of education and awareness in promoting forest conservation. How can individuals contribute to this effort?
These questions can be used in quizzes, written assignments, or discussions to encourage students to think deeply about forest ecosystems and their importance. By assessing students" answers, educators can gauge their understanding, clarify misconceptions, and provide further learning opportunities.

READ MORE:
Advanced Topics: Deforestation, Pollution, and Climate Change
Understanding the intricate relationships between deforestation, pollution, and climate change is crucial for addressing the challenges facing forest ecosystems today. These advanced topics delve into the complex interactions that impact global environmental health and biodiversity. By exploring these subjects, learners can grasp the urgency of action and the importance of sustainable practices.
- Deforestation: This refers to the clearing or thinning of forests by humans, often for agriculture, logging, or urban development. Deforestation has significant implications for carbon sequestration, soil erosion, water cycles, and biodiversity. Exploring the causes and effects of deforestation helps highlight the need for balanced land use planning and sustainable forest management.
- Pollution: Pollution affects forests directly and indirectly through air, water, and soil contamination. Airborne pollutants from industrial and agricultural activities can lead to acid rain, harming trees and ecosystems. Water pollution from runoff carries nutrients and chemicals into rivers and forests, affecting aquatic and terrestrial life. Investigating pollution sources and impacts underscores the importance of reducing emissions and adopting cleaner technologies.
- Climate Change: Forest ecosystems are both affected by and play a critical role in climate change. Trees absorb CO2, a major greenhouse gas, but when forests are degraded or removed, this carbon is released back into the atmosphere, exacerbating global warming. Understanding the feedback loops between forests and climate change is essential for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Addressing these advanced topics requires an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating science, policy, and community engagement. Education on these issues encourages informed decision-making and proactive measures to protect and restore forest ecosystems. Through comprehensive study and action, we can mitigate the impacts of deforestation, pollution, and climate change, ensuring the health and resilience of forests for future generations.
Explore the intricate world of forest ecosystems with our comprehensive guide. From basics to advanced topics, unlock the secrets of nature"s balance and learn how we can contribute to its preservation for future generations.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tundra-58bf1be55f9b58af5cc29755.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-901482062-6470b1099c6a47a881f9a22d7bca0d0a.jpg)