Topic ecosystem and biodiversity services: Discover the vital role of ecosystem and biodiversity services in sustaining life on Earth, offering invaluable benefits for environmental health, economic prosperity, and societal well-being.
Table of Content
- What is the relationship between ecosystem services and biodiversity?
- The Importance of Ecosystem and Biodiversity Services
- Types of Ecosystem Services: Provisioning, Regulating, Supporting, and Cultural
- The Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
- Challenges Facing Ecosystems and Biodiversity
- Conservation Strategies for Protecting Ecosystem Services
- The Economic Value of Ecosystem and Biodiversity Services
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity - Science for Environment Policy
- Case Studies: Success Stories in Ecosystem and Biodiversity Conservation
- Future Directions in Ecosystem Service and Biodiversity Research
- How Individuals and Communities Can Support Ecosystem and Biodiversity Services
What is the relationship between ecosystem services and biodiversity?
The relationship between ecosystem services and biodiversity is one of interdependence and mutual support. Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in an ecosystem, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. Ecosystem services, on the other hand, are the benefits that humans derive from healthy ecosystems.
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in providing ecosystem services. It contributes to the stability and resilience of ecosystems, making them better able to withstand disturbances such as climate change or human activities. Ecosystem services, in turn, support and sustain biodiversity by providing the necessary conditions and resources for various organisms to thrive.
There are several ways in which ecosystem services and biodiversity are interconnected:
- Food production: Biodiversity is essential for the production of food crops and livestock. Different plant and animal species contribute to agricultural diversity, making agriculture more resilient to pests, diseases, and environmental changes. Ecosystem services such as pollination and natural pest control provided by diverse insect populations are crucial for crop yields.
- Climate regulation: Biodiverse ecosystems, such as forests and wetlands, play a vital role in climate regulation. They absorb carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas responsible for climate change, and help mitigate its effects. Additionally, diverse vegetation helps regulate local and regional climates, influencing temperature, humidity, and precipitation patterns.
- Water purification: Biodiversity facilitates the natural filtration and purification of water resources. Wetlands, for example, act as natural filters, trapping sediments and pollutants and improving water quality. Diverse plant species also help prevent soil erosion, reducing sedimentation in rivers and lakes.
- Ecotourism and recreation: Diverse and well-preserved ecosystems attract ecotourism and recreational activities, promoting economic and cultural benefits for local communities. The presence of diverse plant and animal species makes nature-based tourism more appealing and provides opportunities for educational and recreational experiences.
In summary, the relationship between ecosystem services and biodiversity is integral and mutually beneficial. Biodiversity is essential for the provision of ecosystem services, while ecosystem services help maintain and support biodiversity. Recognizing and preserving the importance of biodiversity is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems and ensuring the continued provision of ecosystem services.
READ MORE:
The Importance of Ecosystem and Biodiversity Services
Ecosystem and biodiversity services are indispensable to our planet"s health and human well-being, providing a multitude of benefits that sustain and enrich our lives.
- Provisioning Services: These include the supply of food, fresh water, wood, fiber, and genetic resources, all crucial for human survival and economic activities.
- Regulating Services: Ecosystems regulate climate, floods, diseases, wastes, and water quality among other things, helping to mitigate environmental hazards.
- Supporting Services: These are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, including soil formation, photosynthesis, and nutrient cycling, which underpin our food supply and health.
- Cultural Services: Ecosystems provide recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits that contribute to human culture, mental health, and well-being.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem and biodiversity services is essential for sustainable development, economic stability, and ensuring a resilient environment that can withstand and adapt to climate change and other environmental stresses.

Types of Ecosystem Services: Provisioning, Regulating, Supporting, and Cultural
Ecosystem services, the many benefits provided by nature, are vital for human survival and well-being. These services are broadly categorized into four types:
- Provisioning Services: These are the products obtained from ecosystems, including food, water, timber, fiber, and genetic resources. They play a critical role in meeting our basic needs and supporting economic activities.
- Regulating Services: These include the benefits obtained from the regulation of ecosystem processes, such as climate regulation, flood control, disease regulation, and water purification. They help maintain the environment"s balance and ensure its sustainability for future generations.
- Supporting Services: Essential for the production of all other ecosystem services, supporting services include soil formation, nutrient cycling, and primary production. These processes are fundamental to the Earth"s functioning and to our agricultural productivity and health.
- Cultural Services: These are the non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, recreation, and aesthetic experiences. Cultural services significantly contribute to the development of human culture, mental health, and leisure activities.
Each type of service is interlinked, demonstrating the complex interdependencies within ecosystems and the importance of biodiversity in maintaining ecological balance and resilience. By understanding and valuing these services, we can better advocate for conservation and sustainable management practices that protect our natural heritage.
The Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
Biodiversity, the variety of life in all its forms, levels, and combinations, plays an essential role in ecosystem functioning and the provision of ecosystem services. Its significance cannot be overstated, as it contributes to:
- Resilience: A diverse ecosystem is more resilient to changes and stresses, such as climate change and natural disasters. This resilience ensures ecosystems can continue to provide essential services even in the face of adversity.
- Productivity: High biodiversity increases the efficiency with which ecological communities capture energy, produce biomass, and decompose organic matter, leading to more robust and sustainable ecosystems.
- Nutrient Cycling: Diverse ecosystems are better at recycling nutrients, ensuring the sustainability of the biosphere"s nutrient pools and supporting all forms of life.
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal: Biodiversity supports processes like pollination and seed dispersal, which are critical for the reproduction of many plant species and, consequently, for agriculture and food security.
- Disease Regulation: Ecosystems with higher biodiversity can regulate diseases more effectively, as they are less likely to have a single species become overwhelmingly dominant, potentially hosting and spreading pathogens.
The interdependence between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning underscores the importance of conserving diverse biological communities. Protecting biodiversity is not only an ethical imperative but also a practical strategy for ensuring ecosystems continue to sustain life on Earth.

Challenges Facing Ecosystems and Biodiversity
The preservation of ecosystems and biodiversity is facing numerous challenges, which threaten their ability to continue providing essential services. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the health of our planet and the well-being of future generations.
- Habitat Destruction: Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, which is the primary cause of biodiversity loss.
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns affect the distribution and abundance of species, disrupt ecosystems, and can lead to the loss of biodiversity.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources can degrade ecosystems and harm wildlife, reducing biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can become invasive, outcompeting, predating, or bringing diseases to native species, which can lead to significant shifts in ecosystem composition.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and harvesting at rates beyond an ecosystem"s ability to replenish can lead to the decline or extinction of species.
- Policy and Economic Pressures: Lack of effective conservation policies and economic incentives for exploitation over preservation further exacerbate the threats to ecosystems and biodiversity.
Combating these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable management practices, and the development of policies that balance human needs with the preservation of the natural world.
Conservation Strategies for Protecting Ecosystem Services
Effective conservation strategies are essential to safeguard ecosystem services and the biodiversity that underpins them. These strategies can help maintain ecological balance, ensure sustainable resource use, and preserve our natural heritage for future generations.
- Establishment of Protected Areas: Designating national parks, nature reserves, and marine protected areas to conserve critical habitats and species, providing them with a refuge from human activities.
- Sustainable Land and Water Management: Implementing practices that minimize environmental impact, such as sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fisheries management, to protect natural resources and biodiversity.
- Restoration of Degraded Ecosystems: Rehabilitating forests, wetlands, grasslands, and other ecosystems that have been degraded by human activity to restore their ecological functionality and services.
- Combating Climate Change: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting adaptation strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Community Engagement and Education: Involving local communities in conservation efforts and raising awareness about the importance of ecosystem services and biodiversity through education and outreach.
- Policy and Legislation: Developing and enforcing laws and policies that promote biodiversity conservation and the sustainable use of ecosystem services, including international treaties and agreements.
- Integrating Biodiversity into Business Practices: Encouraging businesses to adopt practices that reduce their environmental footprint and promote biodiversity conservation, including responsible sourcing and green infrastructure.
By employing a comprehensive and multifaceted approach, we can protect ecosystem services and the biodiversity upon which we all depend.

The Economic Value of Ecosystem and Biodiversity Services
The economic value of ecosystem and biodiversity services is immense and multifaceted, underpinning economies worldwide by providing essential resources, regulating services, and support for human well-being. Recognizing this value is crucial for sustainable development and conservation efforts.
- Natural Resource Provision: Ecosystems supply raw materials for industries such as agriculture, forestry, and fisheries, contributing significantly to global economic activity and employment.
- Climate Regulation: Natural habitats like forests and wetlands sequester carbon, helping to mitigate climate change and its economic impacts, saving billions in potential climate adaptation costs.
- Water Purification and Supply: Ecosystems play a key role in water filtration and the cycle, ensuring clean water supply which is vital for health, agriculture, and industry.
- Pollination Services: The natural pollination by bees and other species supports agriculture, which is essential for food production and security, with an estimated value of hundreds of billions annually.
- Tourism and Recreation: Natural areas attract tourism, a major source of revenue and employment for many communities and countries, highlighting the cultural and aesthetic value of biodiversity.
- Flood Protection: Wetlands and forests reduce the risk of floods, saving economies from huge losses in property damage and livelihood disruption.
Quantifying the economic value of these services encourages investment in conservation and sustainable management, ensuring the long-term health of ecosystems and the services they provide.
Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity - Science for Environment Policy
Dive into the fascinating world of biodiversity and discover the incredible variety of life on our planet. From exotic creatures to unique ecosystems, this video will inspire awe and wonder as you explore the beauty and importance of biodiversity in sustaining our delicate balance of life.
Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity and Nature\'s Benefits for Humans
Immerse yourself in the awe-inspiring wonders of nature and discover the countless benefits it provides us. From clean air and water to mental and physical health, this captivating video will show you how nature\'s gifts are essential for our well-being and inspire you to take action in preserving our precious natural resources.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Ecosystem and Biodiversity Conservation
Highlighting success stories in ecosystem and biodiversity conservation provides inspiration and valuable lessons on effective strategies and approaches. Here are several notable examples from around the world:
- The Great Green Wall, Africa: An ambitious initiative to combat desertification, improve food security, and strengthen resilience to climate change by planting a vast belt of trees across Africa.
- Coral Triangle Initiative, Southeast Asia: A comprehensive partnership to safeguard the marine and coastal biological resources of the Coral Triangle, known for its unparalleled coral diversity.
- Amazon Rainforest Conservation, South America: Efforts to protect and sustainably manage the Amazon rainforest, which is vital for global biodiversity, climate regulation, and indigenous cultures.
- New Zealand Predator-Free 2050: A groundbreaking conservation project aiming to eradicate invasive predator species to protect New Zealand"s unique native wildlife and restore natural ecosystems.
- Community Forest Management in Nepal: Empowering local communities to manage forests sustainably has led to improved forest conditions, biodiversity conservation, and economic benefits.
These case studies exemplify how innovative, collaborative, and community-based approaches can effectively conserve ecosystems and biodiversity, offering hope and direction for future conservation efforts worldwide.
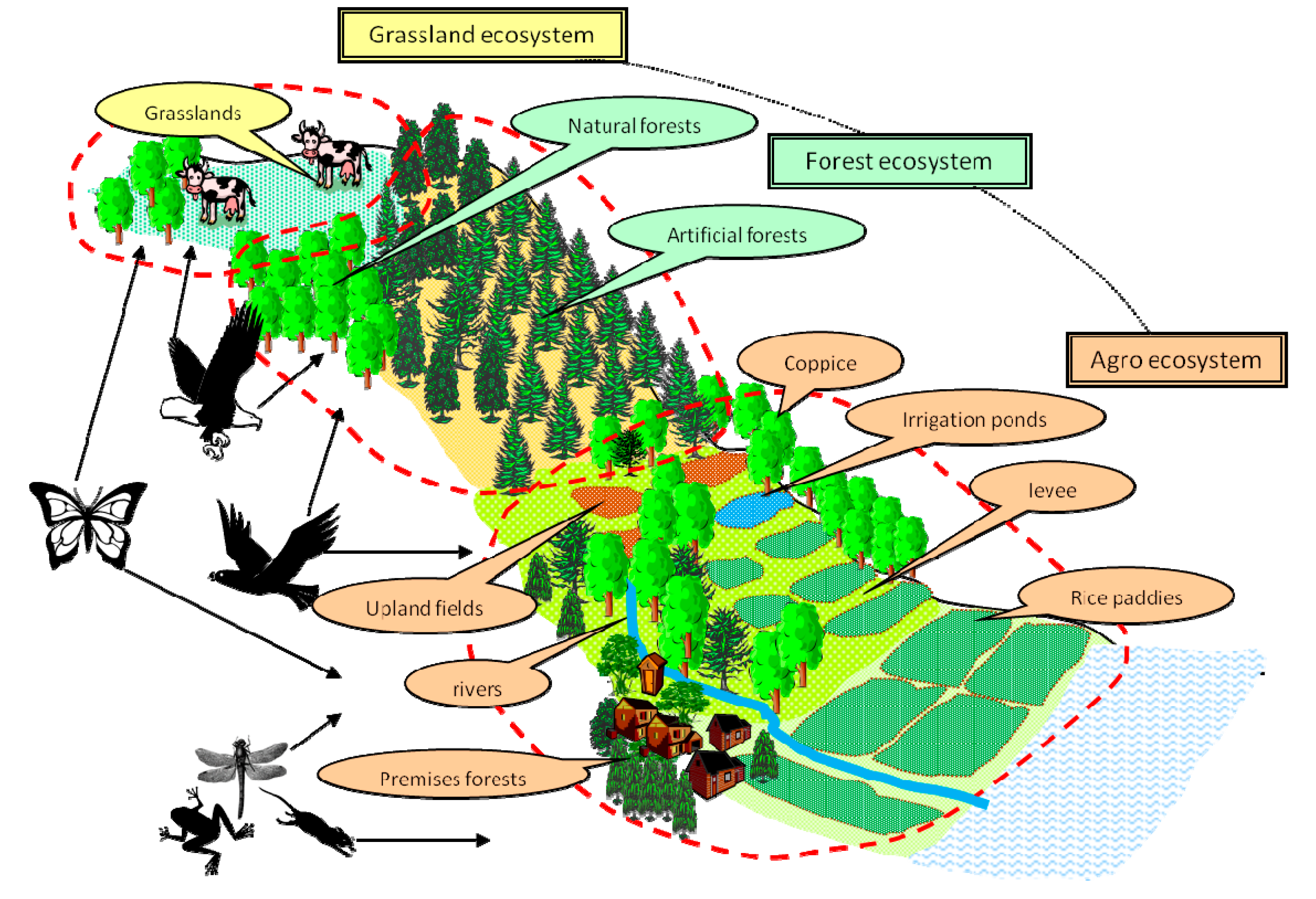
Future Directions in Ecosystem Service and Biodiversity Research
As we advance into the future, research on ecosystem services and biodiversity will play a pivotal role in guiding conservation efforts, shaping policy, and fostering sustainable development. Key areas of focus include:
- Integrating Technology: Leveraging satellite imagery, drones, and AI for monitoring biodiversity and ecosystem changes, enhancing our ability to predict and manage ecological shifts.
- Understanding Human-Wildlife Interactions: Deepening research on the impacts of human activity on wildlife and ecosystems to develop more effective conservation strategies that also consider human needs.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Focusing on how ecosystems can be managed to enhance resilience to climate change, including the role of biodiversity in carbon sequestration and climate regulation.
- Economic Valuation of Ecosystem Services: Advancing methods for the economic valuation of ecosystem services to better inform policy-making and investment in conservation.
- Policy Integration: Encouraging the incorporation of ecosystem service and biodiversity research into national and international policy and planning, ensuring a sustainable foundation for development.
- Participatory Conservation: Expanding community-based conservation research to understand how local and indigenous knowledge can contribute to ecosystem management and biodiversity conservation.
By prioritizing these research directions, we can ensure a deeper understanding of ecosystem services and biodiversity, leading to more effective conservation and sustainable use of our natural resources.
READ MORE:
How Individuals and Communities Can Support Ecosystem and Biodiversity Services
Individuals and communities play a crucial role in supporting ecosystem and biodiversity services. Through simple, actionable steps, we can all contribute to the conservation and enhancement of our natural environment.
- Adopt Sustainable Practices: Reducing waste, recycling, and using sustainable products can lessen our environmental footprint and support ecosystem health.
- Support Conservation Efforts: Participating in or donating to conservation projects and organizations helps protect and restore natural habitats and species.
- Plant Native Vegetation: Cultivating native plants in gardens and community spaces supports local wildlife, including pollinators, and enhances biodiversity.
- Participate in Citizen Science Projects: Engaging in biodiversity monitoring and research projects contributes valuable data to conservation efforts and increases awareness.
- Educate and Advocate: Raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity and ecosystem services and advocating for sustainable policies can drive collective action and policy change.
- Support Sustainable Businesses: Choosing products and services from companies that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices promotes a green economy.
- Community Conservation Initiatives: Joining or initiating community-based conservation projects can lead to significant local environmental improvements and strengthen community bonds.
By taking these steps, individuals and communities can significantly impact the preservation and enhancement of ecosystem and biodiversity services, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
Embracing the stewardship of ecosystem and biodiversity services is vital for our sustainable future. Together, we can forge a path that honors the intricate balance of nature and secures a thriving planet for generations to come.


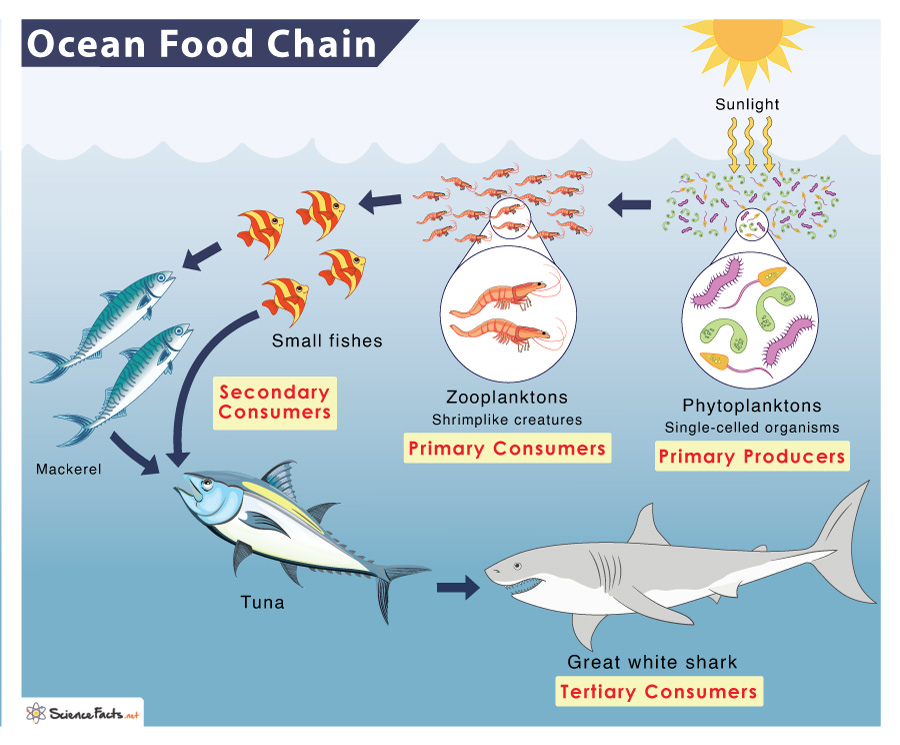

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)




