Topic forest ecosystem gizmo: Discover the wonders of the forest ecosystem gizmo, an innovative tool designed to explore and understand the complex interrelationships within forest ecosystems, enhancing both education and environmental awareness.
Table of Content
- How does the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo demonstrate the effects of adding or removing organisms from a forest?
- Key Features of the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo
- Exploring Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers in a Forest Ecosystem
- Interactive Learning: Manipulating Populations and Observing Effects
- The Role of the Carbon Cycle in Forest Ecosystems
- Feeding Relationships and Food Webs in Forest Ecosystems
- Utilizing Gizmo for Educational Purposes: Benefits for Students
- YOUTUBE: Forest Ecosystem Gizmo Instructions
- Scientific Concepts and Vocabulary Enhancement through Gizmo
- Case Studies: Real-world Application of Forest Ecosystem Concepts
- Assessment and Evaluation Features in the Gizmo Platform
How does the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo demonstrate the effects of adding or removing organisms from a forest?
The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo is a simulation tool that allows users to observe and manipulate the populations of organisms in a forest ecosystem. It demonstrates the effects of adding or removing organisms from the ecosystem. Below are the steps to understand how the Gizmo works:
- Start the Gizmo by following the instructions provided.
- Observe the initial populations of the four creatures in the forest: trees, deer, bears, and mushrooms.
- Investigate the feeding relationships, also known as the food web, between the organisms present in the forest.
- Experiment with adding or removing organisms from the forest ecosystem.
- Observe and analyze the effects of these changes on the populations of the organisms.
The Gizmo allows you to understand the interdependence and balance within the forest ecosystem. By manipulating the populations, you can see how the addition or removal of organisms can disrupt or restore equilibrium in the ecosystem.
READ MORE:
Key Features of the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo
The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo is a dynamic, interactive tool that offers users an immersive experience into understanding and analyzing forest ecosystems. It incorporates several key features that make learning both engaging and educational.
- Interactive Simulations: Experience real-time ecosystem changes as you adjust variables like climate, animal populations, and plant growth.
- Detailed Analytics: Track and analyze the impact of various factors on the ecosystem"s health through comprehensive graphs and data reports.
- Customizable Scenarios: Create and manipulate different forest scenarios to understand the complexity of ecological relationships.
- Educational Resources: Access a wealth of information, including guided lessons, vocabulary lists, and quizzes to reinforce learning.
- User-Friendly Interface: Navigate easily through the gizmo"s features with an intuitive design suitable for all ages.
- Real-World Application: Apply concepts learned in virtual simulations to real-world ecological challenges and conservation efforts.
This tool is designed not only for students but also for educators and environmental enthusiasts, offering a comprehensive platform to explore the delicate balance of forest ecosystems.

Exploring Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers in a Forest Ecosystem
Understanding the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers is fundamental in studying forest ecosystems. The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo provides an interactive platform to explore these relationships in depth.
- Producers: These are primarily green plants and trees that produce their own food through photosynthesis. The Gizmo allows users to simulate the growth of various plant species and observe how they form the basis of the ecosystem"s food web.
- Consumers: Animals that depend on producers and other consumers for their food are shown in detailed simulations. Users can explore different categories, including herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores, and their effects on the ecosystem balance.
- Decomposers: These organisms, including fungi and bacteria, break down dead organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil. The Gizmo demonstrates the crucial role decomposers play in nutrient cycling and ecosystem sustainability.
This section of the Gizmo offers interactive features to manipulate populations of these groups and observe the resulting impacts on the ecosystem, highlighting the interconnectedness and importance of each group in maintaining the health and stability of forest ecosystems.
Interactive Learning: Manipulating Populations and Observing Effects
The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo excels in providing an interactive learning environment where users can experiment with manipulating populations of various species and observe the effects on the ecosystem. This hands-on approach facilitates a deeper understanding of ecological balance and interdependence.
- Adjusting Populations: Users can increase or decrease the populations of producers, consumers, and decomposers to see how each change affects the overall ecosystem. This demonstrates the importance of each group in maintaining ecological balance.
- Simulating Environmental Changes: Experiment with different environmental conditions, such as changes in temperature, precipitation, and human impacts, to observe how these factors influence the ecosystem.
- Observing Food Web Dynamics: Visualize how changes in one species population affect others through the food web. This includes the ripple effects on predators, prey, and plant life.
- Evaluating Conservation Strategies: Use the Gizmo to test various conservation strategies and their potential impacts on forest ecosystems, helping users understand the complexity of ecosystem management.
- Real-Time Feedback: The Gizmo provides immediate feedback on the ecosystem"s health through indicators and data charts, making learning outcomes clear and measurable.
This interactive feature of the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo is a powerful educational tool, allowing for an immersive exploration of the cause and effect relationships within ecosystems, and highlighting the delicate balance needed for their sustainability.

The Role of the Carbon Cycle in Forest Ecosystems
The carbon cycle plays a pivotal role in regulating the Earth"s climate and is a key component of forest ecosystems. The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo offers an insightful exploration into how carbon moves through these ecosystems, impacting everything from individual organisms to global climate patterns.
- Photosynthesis: Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and use sunlight to convert it into glucose and oxygen, illustrating the beginning of the carbon cycle"s terrestrial journey.
- Respiration: Animals and plants release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere through respiration, highlighting the cycle"s continuous nature.
- Decomposition: Decomposers break down dead matter, returning carbon to the soil and atmosphere, demonstrating the cycle"s contribution to soil fertility and atmospheric composition.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests play a critical role in sequestering carbon dioxide, effectively reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and mitigating climate change.
- Human Impact: The Gizmo also sheds light on how human activities, such as deforestation and fossil fuel combustion, disrupt the carbon cycle, leading to increased atmospheric carbon dioxide and global warming.
Through interactive simulations, the Gizmo helps users understand the intricate role of the carbon cycle within forest ecosystems and the importance of forests in maintaining the Earth"s carbon balance.
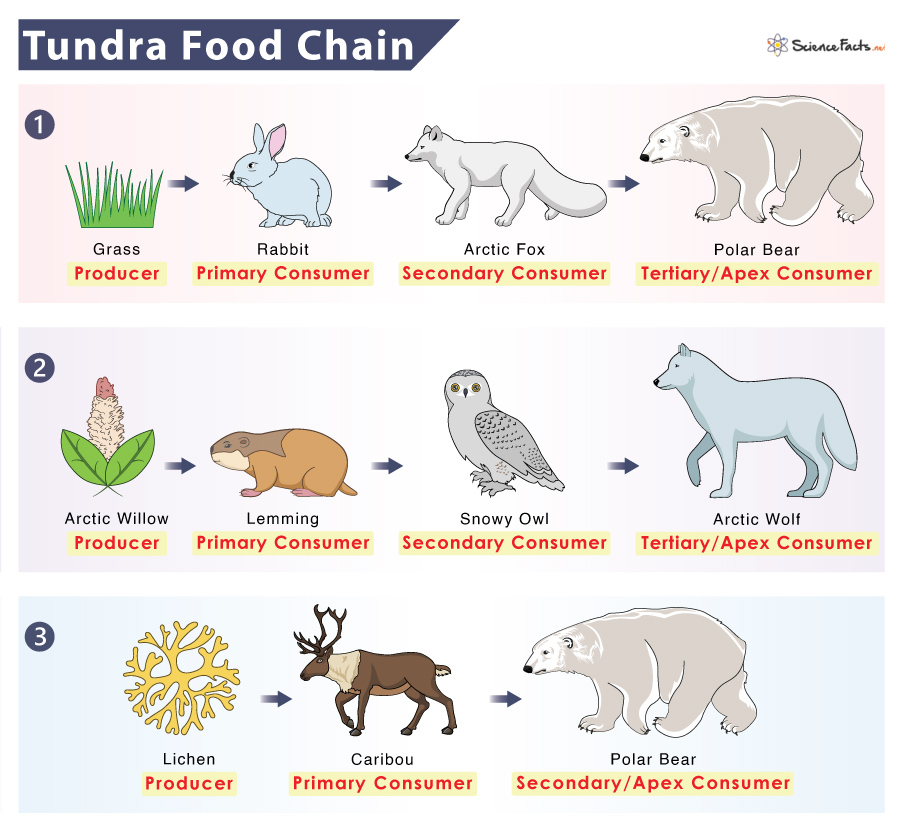
Feeding Relationships and Food Webs in Forest Ecosystems
The complexity and diversity of feeding relationships and food webs are crucial for the stability and resilience of forest ecosystems. The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo allows users to delve into these intricate networks, illustrating how energy flows from one organism to another and highlighting the interdependence of species.
- Primary Producers: At the base are the primary producers, usually plants and algae, which generate energy through photosynthesis, serving as the foundation for all food webs.
- Primary Consumers: These are herbivores that eat the producers, transferring energy up the food chain. The Gizmo shows various herbivore species and their feeding patterns.
- Secondary and Tertiary Consumers: Carnivores and omnivores that feed on primary consumers or other carnivores demonstrate higher trophic levels. Users can explore how these relationships affect ecosystem dynamics.
- Decomposers: Decomposers break down dead organisms, returning nutrients to the soil, which supports new plant growth, thus completing the cycle.
- Impact of Changes: The Gizmo enables manipulation of species populations to observe effects on the food web, such as what happens when a key species is introduced or removed.
This section of the Gizmo provides a hands-on approach to understanding the balance of ecosystems, the importance of each species within the food web, and the potential impact of environmental changes on these delicate systems.

Utilizing Gizmo for Educational Purposes: Benefits for Students
The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo serves as a powerful educational tool, offering a myriad of benefits to students. By simulating real-world ecological processes, it enhances learning in engaging and impactful ways.
- Interactive Learning: Students gain hands-on experience by manipulating variables within the ecosystem, fostering a deeper understanding of ecological principles through active participation.
- Visual Representation: Complex ecological concepts are presented in a visual format, making it easier for students to grasp and retain information.
- Critical Thinking: The Gizmo encourages students to hypothesize, experiment, and observe outcomes, thereby enhancing their analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Real-World Application: By exploring real-world scenarios, students can understand the importance of ecosystems and the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Engagement and Motivation: The interactive and gamified aspects of the Gizmo increase student engagement and motivation to learn science.
- Accessibility: The Gizmo"s online platform makes ecological education accessible to a wider audience, breaking down geographical and physical barriers to learning.
By integrating the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo into educational curricula, educators can provide students with a dynamic and comprehensive learning experience that prepares them for future challenges in environmental science and conservation.
Forest Ecosystem Gizmo Instructions
Instructions: Get ready to unlock the secret to success with these game-changing instructions! Let our expert guide lead you step by step towards achieving your goals and watch as your life transforms before your eyes.
Forest Ecosystem Gizmo
Gizmo: Dive into the fascinating world of gizmos and discover the incredible inventions that will leave you in awe! Join us as we explore the latest cutting-edge technology that will revolutionize your everyday life. Don\'t miss out on witnessing the future firsthand!
Scientific Concepts and Vocabulary Enhancement through Gizmo
The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo is not only an interactive tool for exploring ecological relationships but also a valuable resource for enhancing scientific concepts and vocabulary. It introduces students to a wide range of terminologies and concepts, making the learning process more comprehensive and enriching.
- Ecological Principles: Through simulation, students learn about key principles such as energy flow, trophic levels, and carrying capacity in an ecosystem context.
- Biodiversity and Conservation: The Gizmo provides insights into the importance of biodiversity, conservation efforts, and the impact of human activities on ecosystems.
- Carbon Cycle and Climate Change: Students explore the carbon cycle"s role in forest ecosystems and its broader implications for climate change and global warming.
- Species Interaction: It covers various types of species interactions like predation, competition, and symbiosis, enhancing understanding of complex ecological dynamics.
- Vocabulary Building: The Gizmo introduces students to scientific vocabulary related to forest ecosystems, aiding in language development and conceptual understanding.
- Assessment Tools: Quizzes and assessments within the Gizmo help reinforce learning and ensure comprehension of key concepts and terminology.
By engaging with the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo, students not only broaden their scientific knowledge but also enhance their ecological vocabulary, better preparing them for academic success and informed environmental stewardship.

Case Studies: Real-world Application of Forest Ecosystem Concepts
The integration of real-world case studies in the Forest Ecosystem Gizmo provides invaluable insights into the practical application of forest ecosystem concepts. These case studies illustrate the complexity of ecosystems and the importance of sustainable practices.
- Conservation Efforts: Explore successful conservation projects, such as reforestation initiatives and the protection of endangered species, demonstrating the positive impact of human intervention on forest ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Analyze how forest management practices contribute to carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation, offering solutions to global environmental challenges.
- Biodiversity Maintenance: Examine the role of biodiversity in maintaining ecological balance and resilience, through studies on species reintroduction and habitat restoration.
- Impact of Pollution: Understand the effects of pollution on forest ecosystems, including soil degradation and water contamination, through detailed case analyses.
- Ecotourism and Sustainable Development: Review how ecotourism and sustainable development projects can support forest conservation while benefiting local communities.
These case studies not only enhance students" understanding of theoretical concepts but also foster an appreciation for the interconnectedness of human activities and natural ecosystems, emphasizing the critical need for sustainable management of forest resources.
READ MORE:
Assessment and Evaluation Features in the Gizmo Platform
The Gizmo platform incorporates comprehensive assessment and evaluation features to track learning progress and understanding of forest ecosystem concepts. These tools are designed to provide both students and educators with feedback, ensuring educational objectives are met effectively.
- Quizzes and Tests: Integrated quizzes and tests with immediate feedback allow students to assess their understanding of concepts covered in the Gizmo, reinforcing learning and identifying areas for improvement.
- Customizable Assessments: Educators have the ability to create customized assessments tailored to their curriculum, enabling them to focus on specific learning goals and concepts.
- Progress Tracking: The platform offers tools for tracking student progress over time, providing insights into learning trends, concept mastery, and areas needing further attention.
- Interactive Feedback: Feedback is not just limited to correct or incorrect answers; detailed explanations and hints are provided, fostering a deeper understanding of the material.
- Performance Reports: Comprehensive reports are available for both students and educators, highlighting achievements and providing a detailed overview of performance on various aspects of the curriculum.
These assessment and evaluation features are essential for a holistic educational experience, allowing for a personalized approach to learning and ensuring that students gain a robust understanding of forest ecosystems through the Gizmo platform.
The Forest Ecosystem Gizmo offers an unparalleled journey into understanding ecosystems, empowering learners with interactive tools, real-world applications, and comprehensive assessments to explore and conserve our natural world.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tundra-58bf1be55f9b58af5cc29755.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-901482062-6470b1099c6a47a881f9a22d7bca0d0a.jpg)