Topic ecosystems journal: Welcome to the Ecosystems Journal, where we explore the latest trends, innovations, and challenges in ecosystem research, aiming to foster understanding and conservation through interdisciplinary collaboration.
Table of Content
- What is the ISSN number for the journal Ecosystems?
- Understanding Ecosystems: Scope and Aims
- Recent Trends and Innovations in Ecosystem Research
- Integrating Social and Natural Sciences in Ecosystem Studies
- Technological Advancements and Methodologies in Ecosystem Analysis
- YOUTUBE: Food Webs and Energy Pyramids: Foundations of Biodiversity
What is the ISSN number for the journal Ecosystems?
The ISSN number for the journal Ecosystems is 1432-9840.
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystems: Scope and Aims
The study of ecosystems encompasses the examination of living organisms, their physical environment, and the complex processes that link them together. This section aims to lay a foundational understanding of ecosystems, exploring their diversity, dynamics, and the critical role they play in sustaining life on Earth. Our journey through ecosystem science will illuminate the intricate balance of natural systems and the importance of conserving these vital resources for future generations.
- Definition and Components: An overview of what constitutes an ecosystem, highlighting the interactions between biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components.
- Types of Ecosystems: A exploration of the variety of ecosystems, from terrestrial to aquatic, and the unique characteristics of each.
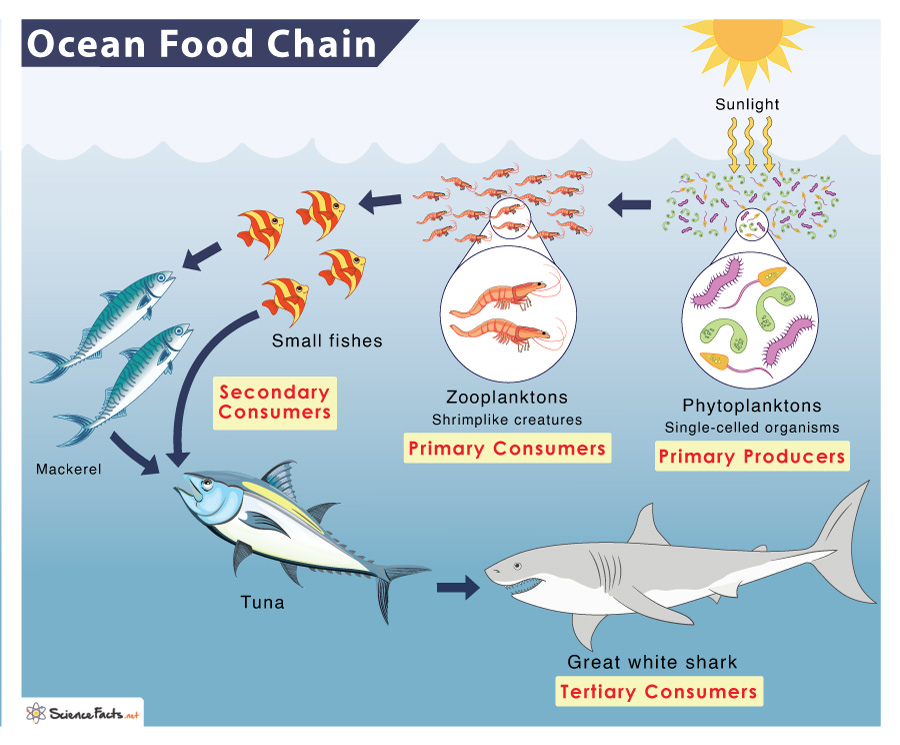
- Ecological Processes: Insight into the fundamental processes such as energy flow and nutrient cycling that govern ecosystem functioning.
- Biodiversity: Discussion on the importance of biodiversity within ecosystems, including species richness, genetic diversity, and ecosystem resilience.
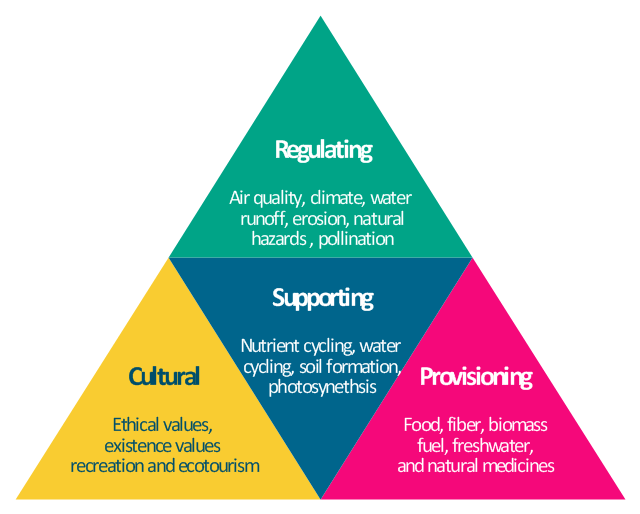
- Ecosystem Services: Examination of the essential services ecosystems provide, such as air and water purification, climate regulation, and pollination, which support human life and economic activities.
- Human Impact: Analysis of human activities on ecosystems, including habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, and the need for sustainable management practices.
- Conservation and Restoration: Strategies for the preservation and restoration of ecosystems to ensure their health and longevity for future generations.
This section serves as a primer for understanding the vast scope and critical aims of ecosystem studies, emphasizing the interconnectedness of life and the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in addressing the challenges facing natural systems today.

Recent Trends and Innovations in Ecosystem Research
The field of ecosystem research is continually evolving, with recent trends and innovations driving forward our understanding and management of ecosystems. This dynamic area of study harnesses the latest technologies and interdisciplinary approaches to address the pressing environmental challenges of our time. Below, we explore some of the most significant recent developments in ecosystem research.
- Remote Sensing and Big Data: The use of satellite imagery, drones, and remote sensing technology has revolutionized the way we monitor and analyze ecosystems. Coupled with big data analytics, researchers can now track changes in ecosystems over time with unprecedented detail and scale.
- Genomics and Biodiversity: Advances in genetic sequencing and bioinformatics are providing new insights into the biodiversity of ecosystems, allowing for the identification and conservation of genetic diversity critical to ecosystem resilience.
- Climate Change Studies: Research focusing on the impacts of climate change on ecosystems has become increasingly important. Studies are exploring how rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are affecting biodiversity, ecosystem services, and their capacity to support human life.
- Ecosystem Services Valuation: There is a growing trend towards quantifying the economic value of ecosystem services. This approach helps in making informed decisions regarding land use, conservation priorities, and the development of policies to protect natural resources.
- Nature-based Solutions: Innovative approaches to conservation and sustainability that harness the power of nature to address environmental challenges, such as green infrastructure, reforestation, and wetland restoration, are gaining traction.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: The complex nature of ecosystems requires a holistic approach, leading to increased collaboration between ecologists, economists, social scientists, and policymakers to develop integrated solutions for ecosystem management and conservation.
- Citizen Science and Community Engagement: Engaging the public in ecosystem research through citizen science projects has emerged as a powerful tool for data collection and raising awareness about environmental issues.
These trends and innovations underscore the vibrant and transformative nature of ecosystem research today, highlighting its critical role in guiding our responses to environmental challenges and shaping a sustainable future for all.
Integrating Social and Natural Sciences in Ecosystem Studies
The intersection of social and natural sciences in ecosystem studies has become increasingly important to address the multifaceted challenges facing ecosystems worldwide. This integrated approach recognizes that human actions and natural processes are deeply intertwined, necessitating a comprehensive understanding that crosses traditional disciplinary boundaries. Here, we delve into how combining these disciplines enhances our ability to conserve and sustainably manage ecosystems.
- Understanding Human-Environment Interactions: Studies now frequently incorporate social science methodologies to better understand how human behaviors, economies, and cultures influence, and are influenced by, the natural environment. This holistic view is crucial for effective ecosystem management and conservation efforts.
- Participatory Research Methods: Engaging local communities and stakeholders in the research process ensures that diverse perspectives and knowledge systems are considered. This collaborative approach can lead to more sustainable and socially acceptable environmental solutions.
- Policy and Governance: Integrating social sciences helps to unravel the complex governance and policy dimensions of ecosystem management. By understanding the social, economic, and political contexts, researchers can propose actionable and equitable policies that support both ecological sustainability and human well-being.
- Valuation of Ecosystem Services: Social sciences contribute to the valuation of ecosystem services, including cultural and recreational benefits, which are often overlooked in traditional economic analyses. This comprehensive valuation is essential for making informed decisions that balance conservation with human development needs.
- Adaptation and Resilience to Climate Change: The combined insights from social and natural sciences are critical in developing strategies for adaptation and resilience to climate change, considering both ecological processes and human vulnerability, capacities, and actions.
- Sustainability Science: This emerging field explicitly aims to bridge social and natural sciences to address complex sustainability challenges. It focuses on creating a transdisciplinary framework that promotes a sustainable coexistence between humans and nature.
By integrating social and natural sciences, ecosystem studies can more effectively address the complex and interconnected challenges of our time, paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient future.

Technological Advancements and Methodologies in Ecosystem Analysis
Technological advancements and innovative methodologies are revolutionizing the field of ecosystem analysis, offering new insights and tools for researchers to study and understand ecosystems with unprecedented precision and scale. These developments enable a deeper understanding of complex ecological processes and facilitate more effective conservation and management practices. Below, we explore some key technological and methodological advancements that are shaping the future of ecosystem research.
- Remote Sensing Technology: The use of satellites and drones equipped with sensors provides detailed data on land cover, vegetation health, water resources, and changes in ecosystems over time. Remote sensing allows for the monitoring of large and inaccessible areas, making it invaluable for global ecosystem analysis.
- GIS and Spatial Analysis: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are crucial for mapping and analyzing spatial data on ecosystems. GIS tools enable the integration of various data types, facilitating the study of spatial patterns, habitat fragmentation, and the impact of human activities on natural landscapes.
- Ecological Modelling: Advanced computer models simulate ecological processes, predict the impacts of environmental changes, and assess conservation strategies. These models are essential for understanding potential future scenarios and making informed decisions.
- Big Data Analytics: The field of ecosystem research is increasingly leveraging big data analytics to process large datasets from remote sensing, citizen science, and long-term ecological research. Big data techniques support the identification of trends, patterns, and anomalies in complex ecological systems.
- Molecular Ecology: Techniques such as DNA barcoding and environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis allow for the identification of species and the assessment of biodiversity without the need for physical specimens. These molecular tools are transforming biodiversity assessments and monitoring.
- Citizen Science: The involvement of the public in data collection and observation projects has expanded the scale and scope of ecological research. Citizen science engages communities, increases scientific literacy, and provides vast amounts of data for ecosystem analysis.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms are being applied to ecological data to automate the classification of species, predict ecological outcomes, and identify environmental changes. These technologies enhance the efficiency and accuracy of ecosystem analysis.
These technological advancements and methodologies are not only expanding the frontiers of ecosystem research but also empowering scientists, policymakers, and the public with the tools needed to safeguard our planet"s ecosystems for future generations.
Food Webs and Energy Pyramids: Foundations of Biodiversity
Interconnectedness: Explore the beauty of interconnectedness in nature as this captivating video showcases the intricate relationships between different species and ecosystems. Witness the harmony and balance that comes from all living beings working together in perfect synchrony. Watch now and be amazed by the wonders of interconnectedness. Variety: Delve into a world full of variety and diversity in this eye-opening video that celebrates the different cultures, landscapes, and traditions of our planet. From colorful festivals to breathtaking natural wonders, experience the richness of human creativity and nature\'s splendor. Embrace the beauty of variety and expand your horizons by watching this mesmerizing video.
READ MORE:
Ecosystem Diversity
009 - Ecosystem Diversity In this video Paul Andersen explains how biodiversity can be measured through genetic, species, ...


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/3-3612f0362edd4dbcb192589a466f2cb4.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)