Topic ecosystems in tropical rainforests: Explore the vibrant ecosystems of tropical rainforests, where unparalleled biodiversity and intricate interactions weave the fabric of Earth"s most vital habitats.
Table of Content
- What are the main characteristics of ecosystems in tropical rainforests?
- Importance of Tropical Rainforests
- Biodiversity in Tropical Rainforests
- Climate and Weather Patterns
- Flora and Fauna
- Ecosystem Services and Benefits
- Layers of the Rainforest
- YOUTUBE: Exploring Ecosystems: Tropical Rainforest Diversity
- Human Impact and Conservation Efforts
- Role in Global Climate Regulation
- Unique Ecosystem Interactions
- Research and Studies in Tropical Rainforests
What are the main characteristics of ecosystems in tropical rainforests?
The main characteristics of ecosystems in tropical rainforests can be described as follows:
- High annual rainfall: Tropical rainforests receive a significant amount of rainfall throughout the year. This consistent rainfall contributes to the lush and dense vegetation found in these ecosystems.
- High average temperatures: Tropical rainforests are located in regions near the Equator, where the temperatures remain warm all year round. The average temperatures in these ecosystems are typically between 75°F (24°C) and 86°F (30°C).
- Nutrient-poor soil: Despite the abundant vegetation, tropical rainforest soils are relatively poor in essential nutrients. The rapid decomposition of organic matter leads to a quick recycling of nutrients, leaving the soil nutrient-poor.
- High levels of biodiversity: Tropical rainforests are known for their incredible biodiversity. These ecosystems are home to a vast array of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic and found nowhere else on Earth.
- Tall and dense canopy: The vegetation in tropical rainforests is characterized by a multi-layered structure. The canopy layer, consisting of tall trees that form a dense roof, shades the lower layers of the forest, creating a unique microclimate.
- Abundance of epiphytes: Epiphytes, such as orchids, ferns, and bromeliads, thrive in the tropical rainforest environment. These plants grow on other plants, utilizing them for support while obtaining nutrients from the air and rainwater.
- Presence of diverse animal life: From insects to mammals, tropical rainforests support an incredible diversity of animal species. This includes iconic creatures like monkeys, jaguars, toucans, and countless insect species.
Overall, the ecosystems in tropical rainforests are characterized by their high rainfall, warm temperatures, nutrient-poor soil, incredible biodiversity, dense canopy, abundance of epiphytes, and diverse animal life.
READ MORE:
Importance of Tropical Rainforests
Tropical rainforests play a crucial role in sustaining the global ecosystem through their vast biodiversity, climate regulation, and contribution to the water cycle. They are home to more than half of the world"s plant and animal species, acting as a massive living reservoir of genetic diversity. Rainforests also serve as the lungs of our planet, absorbing large quantities of CO2 and producing oxygen, which is vital for life on Earth. Additionally, they influence weather patterns and the global climate, help regulate river levels, and support the livelihoods of many indigenous communities.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Hosts an unparalleled variety of life forms.
- Climate Regulation: Crucial in balancing global temperatures and weather patterns.
- Carbon Sequestration: Absorbs significant amounts of CO2, mitigating climate change.
- Water Cycle: Plays a key role in the global water cycle, influencing rainfall patterns.
- Medicinal Resources: Source of numerous medicines and potential for undiscovered cures.
- Economic Benefits: Provides resources like timber, fruits, and nuts, supporting economies.
- Cultural Significance: Vital to the heritage and traditions of indigenous peoples.
Protecting tropical rainforests is not just about conserving a vast array of species; it"s about preserving the health of our planet and ensuring a stable climate for future generations.

Biodiversity in Tropical Rainforests
Tropical rainforests are the most biologically diverse terrestrial ecosystems on the planet. This incredible biodiversity encompasses a vast array of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Rainforests are home to many species that are not found anywhere else in the world, making them critical for preserving global biodiversity. The complex interdependence among these species helps to maintain the ecological balance and ensures the stability and resilience of these ecosystems.
- High Species Richness: Contains millions of different species, many yet to be discovered or studied.
- Unique Flora and Fauna: Home to a wide variety of plants, including thousands of tree species, as well as countless insect, bird, amphibian, and mammal species.
- Endemism: A significant portion of the species found in rainforests are endemic, meaning they exist nowhere else on Earth.
- Genetic Diversity: Offers a genetic reservoir which is vital for species adaptation and survival.
- Ecological Interactions: Complex food webs and symbiotic relationships are fundamental to the functioning of these ecosystems.
This extraordinary biodiversity is not just crucial for the ecosystem"s health but also has profound implications for human well-being, providing essential services such as disease regulation, and a source of food, medicine, and materials.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Tropical rainforests play a critical role in influencing global and regional climate and weather patterns. Their location around the equator allows them to receive a consistent amount of sunlight throughout the year, leading to warm temperatures and high levels of humidity. This environment is ideal for the growth of a wide range of plant species, which in turn support a diverse array of wildlife. The dense vegetation and continuous transpiration (the process by which plants release water vapor into the air) contribute significantly to the formation of rain clouds, which is why rainforests receive such high amounts of rainfall annually.
- High Humidity: Rainforests maintain a high level of humidity, typically between 77% and 88%, creating a greenhouse-like effect that supports diverse life forms.
- Consistent Rainfall: These ecosystems experience heavy rainfall, with annual precipitation often exceeding 2000 mm, crucial for sustaining the dense vegetation.
- Temperature Regulation: The dense canopy helps regulate surface temperatures, preventing extreme temperature variations and creating a stable environment.
- Carbon Storage: By absorbing carbon dioxide, tropical rainforests play a vital role in the global carbon cycle and in mitigating climate change.
- Weather Influence: The evapotranspiration from rainforest plants contributes to cloud formation and precipitation, affecting weather patterns both locally and globally.
The climate and weather patterns of tropical rainforests not only support an incredible diversity of life within these ecosystems but also have far-reaching effects on global climate regulation, highlighting the importance of their conservation.

Flora and Fauna
The flora and fauna of tropical rainforests are unparalleled in their diversity and complexity. These ecosystems are home to more than two-thirds of the world"s plant species and provide habitats for countless animal species, many of which are endemic to these environments. The rich biodiversity is not only a testament to the evolutionary prowess of these ecosystems but also a critical resource for research, medicine, and conservation efforts.
- Diverse Plant Life: Rainforests are characterized by their dense canopy, emergent layer, understory, and forest floor, each hosting distinct plant species, including numerous types of trees, shrubs, ferns, and epiphytes.
- Unique Animal Species: These forests teem with life, including a variety of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and insects. Iconic species include jaguars, sloths, toucans, and countless insects.
- Adaptations: Both flora and fauna have developed unique adaptations to thrive in the rainforest environment. For example, many trees have buttress roots for stability, and animals have adaptations for arboreal living.
- Endemism: A high level of endemism means that many species found in these rainforests cannot be found anywhere else in the world, highlighting the importance of their protection.
- Interdependence: The complex interrelationships among species, such as pollination and seed dispersal, underscore the ecological balance of these ecosystems.
This incredible diversity and the intricate connections between organisms highlight the ecological significance of tropical rainforests and the urgent need for their conservation to protect these unique species.
Ecosystem Services and Benefits
Tropical rainforests offer a myriad of ecosystem services and benefits that are essential for the survival of humans and the planet. These services are not only crucial for the environment but also provide significant economic, health, and cultural benefits to societies around the world.
- Climate Regulation: By absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, rainforests play a vital role in mitigating climate change and maintaining the global climate balance.
- Water Regulation: Rainforests contribute to the stability of the world"s water cycle by influencing rainfall patterns and providing freshwater resources.
- Biodiversity: Serving as a home for millions of species, rainforests are key to preserving biodiversity, offering genetic resources for food, medicine, and agriculture.
- Soil Protection: The dense vegetation prevents soil erosion, promotes nutrient recycling, and maintains fertile soils for agriculture.
- Air Quality: The vast expanses of flora purify the air by filtering pollutants and providing clean air.
- Medicinal Resources: Many pharmaceuticals are derived from rainforest plants, offering treatments for diseases and contributing to health and well-being.
- Cultural Value: Indigenous communities depend on rainforests for their livelihoods, culture, and traditions, underscoring the importance of these ecosystems for cultural heritage.
- Economic Benefits: Rainforests contribute to economies through tourism, agriculture, and the harvesting of sustainable resources like rubber and nuts.
The preservation of tropical rainforests is therefore not just an environmental imperative but a necessity for health, well-being, and economic stability across the globe.

Layers of the Rainforest
Tropical rainforests are structured in distinct layers, each supporting unique ecosystems and hosting a diverse array of flora and fauna. These layers work together to form a complex habitat that supports the vast biodiversity characteristic of these environments.
- Emergent Layer: The highest rainforest layer, featuring tall trees that reach heights of up to 200 feet. It is home to many birds and insects, adapted to life at high elevations.
- Canopy Layer: Often referred to as the primary layer of the rainforest, the canopy houses the majority of plant, insect, bird, and some mammal species. Its dense leaf coverage forms a continuous layer of foliage.
- Understory Layer: A dimly lit, cool environment under the canopy, the understory is characterized by shorter plants and trees. It"s home to a variety of birds, reptiles, and insects, with many plants adapted to low light.
- Forest Floor: The ground layer, receiving minimal sunlight, is covered with decomposing plant and animal matter, which nourishes the soil. It"s inhabited by insects, ground-dwelling mammals, and decomposers.
Understanding the layers of the rainforest is crucial for comprehending the complexity of these ecosystems and the importance of each layer in maintaining the ecological balance.
Exploring Ecosystems: Tropical Rainforest Diversity
\"Embark on a captivating visual journey through lush forests, breathtaking coral reefs and majestic mountains, as you explore the wonders of biodiversity in this mesmerizing video. Discover the incredible array of life on our planet and gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate interconnectedness of all living beings.\"
Rainforests for Kids: Learn all about the two types of rainforests
\"Are you passionate about education and its transformative power? Join us in this enlightening video that delves into innovative teaching methods, inspiring success stories, and the limitless potential of lifelong learning. Let\'s ignite a passion for education and empower future generations to shape a brighter tomorrow.\"
Human Impact and Conservation Efforts
The tropical rainforests, while resilient, are increasingly threatened by human activities. Deforestation, illegal logging, mining, and agriculture are depleting these precious ecosystems at an alarming rate. However, global and local conservation efforts are underway to protect and restore these vital habitats.
- Deforestation Reduction: Efforts to reduce deforestation include enforcing laws against illegal logging, promoting sustainable land use practices, and establishing protected areas.
- Reforestation Projects: Many organizations are engaged in reforestation, planting trees to restore degraded areas of the rainforest and improve biodiversity.
- Community Engagement: Empowering local communities through education and sustainable livelihood programs helps to reduce the pressure on rainforest resources and promotes conservation.
- International Agreements: Countries around the world are participating in international agreements aimed at conserving tropical rainforests and combating climate change.
- Research and Monitoring: Scientific research and monitoring are crucial for understanding the impacts of human activities on rainforests and for developing effective conservation strategies.
- Wildlife Protection: Initiatives to protect endangered species through anti-poaching laws and wildlife sanctuaries are vital for preserving rainforest biodiversity.
These conservation efforts are essential for safeguarding the future of tropical rainforests, ensuring that they continue to provide their invaluable ecosystem services for generations to come.

Role in Global Climate Regulation
Tropical rainforests play a pivotal role in regulating the Earth"s climate. Their vast expanses of foliage act as a global thermostat, stabilizing temperatures, and weather patterns. Through the processes of photosynthesis and transpiration, these ecosystems manage a significant portion of the Earth"s carbon and water cycles, making them critical in the fight against climate change.
- Carbon Sequestration: Rainforests absorb vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, reducing greenhouse gases and mitigating global warming.
- Oxygen Production: Through photosynthesis, they contribute to the oxygen balance, providing the air we breathe.
- Water Cycle Regulation: Rainforests influence global and regional precipitation patterns through the release of water vapor into the atmosphere.
- Climate Stabilization: By storing carbon and regulating water vapor, rainforests help to maintain the Earth"s climate, preventing extreme weather events.
- Biodiversity Protection: The maintenance of rainforests is also essential for the survival of countless species, which in turn supports healthy ecosystems vital for climate balance.
The protection and restoration of tropical rainforests are therefore crucial not only for the health of the planet but also for the well-being of humanity, highlighting the need for global cooperation in conservation efforts.
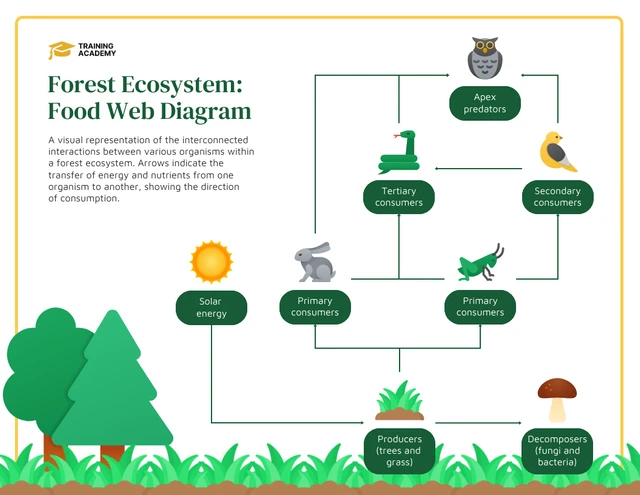
Unique Ecosystem Interactions
Tropical rainforests are renowned for their complex ecosystem interactions that contribute to the high levels of biodiversity and ecological stability observed. These interactions, ranging from pollination and seed dispersal to predator-prey relationships, form a web of life that is intricate and finely balanced.
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal: A myriad of animals, including birds, bats, and insects, play critical roles in the pollination of plants and the dispersal of seeds, ensuring plant species" survival and propagation.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Mutualistic interactions, such as those between certain tree species and fungi (mycorrhizae), or insects and plants, facilitate nutrient exchange and defense mechanisms, enhancing ecosystem resilience.
- Predator-Prey Dynamics: These dynamics regulate species populations, maintaining ecological balance. Predators help control the population of herbivores, ensuring that vegetation is not overexploited.
- Decomposition: Decomposers break down dead plant and animal matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil, which is crucial for plant growth and maintaining soil health.
- Niche Differentiation: The diverse habitats within rainforests allow species to specialize and occupy different niches, reducing competition and promoting biodiversity.
These unique interactions are fundamental to the functioning of tropical rainforest ecosystems, illustrating the complexity and interdependence of life forms within these habitats.

READ MORE:
Research and Studies in Tropical Rainforests
Research and studies conducted in tropical rainforests are vital for understanding these complex ecosystems, their biodiversity, and the impact of human activities on their conservation. Scientists from around the world are involved in ongoing research efforts to uncover the secrets of these forests and to find sustainable ways to protect them.
- Ecological and Biological Research: Studies focus on understanding the intricate relationships between different species and their environment, including the effects of climate change on biodiversity.
- Conservation Strategies: Research is aimed at developing effective conservation strategies that balance human needs with the preservation of biodiversity.
- Climate Change Impact: Scientists study how tropical rainforests respond to climate change, including their role in carbon sequestration and their vulnerability to warming temperatures.
- Pharmacological Studies: Many projects explore the medicinal properties of rainforest plants, searching for new drugs and treatments for diseases.
- Sustainable Use: Research into sustainable use practices helps ensure that rainforest resources can be utilized without causing long-term harm to these ecosystems.
- Indigenous Knowledge: Studies often incorporate indigenous knowledge, recognizing the value of traditional practices in managing and conserving rainforests.
The insights gained from these studies are critical for the global effort to preserve tropical rainforests and to mitigate the impacts of climate change, highlighting the importance of continued research and collaboration.
Embracing the wonders of tropical rainforests reveals the interconnectedness of life and the critical role these ecosystems play in sustaining our planet, urging us to act now to preserve these irreplaceable treasures for future generations.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)