Topic ecosystem forest animals: Discover the vibrant world of "Ecosystem Forest Animals," where the untold stories of nature"s intricate relationships unfold, inviting readers into the heart of biodiversity and conservation efforts that shape our planet.
Table of Content
- Which animals are found in the rainforest ecosystem?
- Understanding Forest Ecosystems
- Key Forest Ecosystems Around the World
- Diversity of Animals in Forest Ecosystems
- Role of Predators in Forest Ecosystems
- Impact of Climate Change on Forest Ecosystems
- Conservation Efforts for Forest Animals
- YOUTUBE: Rainforests 101
- Human Activities and Their Impact on Forest Ecosystems
- Restoration Projects in Forest Ecosystems
- Education and Awareness About Forest Conservation
- Innovations in Protecting Forest Ecosystems and Wildlife
Which animals are found in the rainforest ecosystem?
In the rainforest ecosystem, you can find a diverse range of animals. Some of the animals found in the rainforest include:
- Sloths
- Tapirs
- Jaguars
- Ocelots
- Kinkajous
- Lemurs
- Agouti
- Long-eared owls
- Otters
- Porcupines
- Bobcats
- Coyotes
- Black bears
- Beavers
READ MORE:
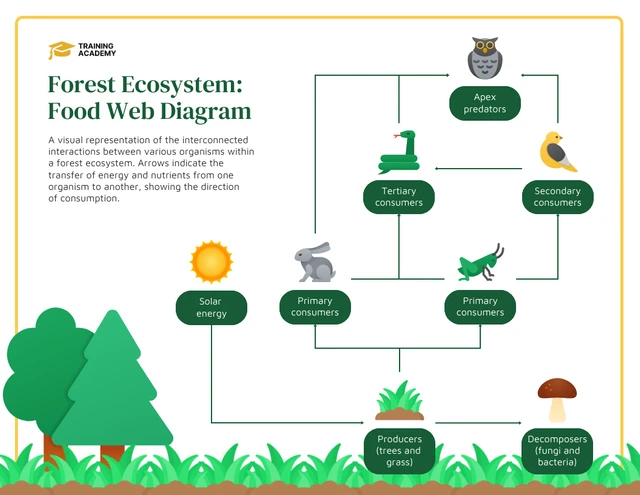
Understanding Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are dynamic environments that provide vital habitats for a diverse range of animal species. These ecosystems are characterized by their complex interrelationships among various organisms, including trees, shrubs, mammals, birds, insects, and microorganisms. The health and stability of forest ecosystems depend on biodiversity, which ensures the resilience of the forest to environmental changes and disturbances.
- The role of trees in producing oxygen, storing carbon, and providing shelter.
- Importance of predatory animals in maintaining the balance of populations within the ecosystem.
- The significance of decomposers in recycling nutrients back into the soil.
- How various species rely on one another for food, shelter, and pollination.
Understanding forest ecosystems is crucial for developing conservation strategies to protect these habitats and their animal inhabitants. It involves recognizing the importance of each species, no matter how small, in maintaining the ecological balance.

Key Forest Ecosystems Around the World
Our planet is home to an array of forest ecosystems, each harboring unique flora and fauna. These ecosystems are crucial for biodiversity, climate regulation, and the livelihoods of many communities worldwide.
- Amazon Rainforest: Known as the "lungs of the Earth," it"s the largest tropical rainforest, rich in biodiversity.
- Congo Basin: The world"s second-largest rainforest, vital for its carbon storage capabilities.
- Southeast Asian Rainforests: Home to diverse species, these forests are under threat from deforestation.
- Boreal Forests of the North: Circumpolar forests crucial for carbon sequestration, known for their coniferous trees.
- Madagascar"s Spiny Forests: Unique ecosystems with high levels of endemism.
Protecting these key ecosystems is essential for preserving the planet"s biodiversity, combating climate change, and ensuring ecosystems" services for future generations.
Diversity of Animals in Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are teeming with a rich diversity of animal life, each playing a unique role in the ecosystem"s balance. From the dense undergrowth to the towering canopies, animals of all sizes contribute to the complexity of these habitats.
- Insects and arthropods act as pollinators and decomposers, essential for nutrient cycling.
- Amphibians and reptiles, sensitive to environmental changes, serve as indicators of ecosystem health.
- Birds, with their varied diets, are crucial for seed dispersal and pest control.
- Mammals, ranging from small rodents to large predators, maintain the structure of the forest through their feeding habits.
This biodiversity ensures the resilience of forest ecosystems, enabling them to withstand and recover from disturbances. Protecting this diversity is key to maintaining the health and functionality of our planet"s forests.

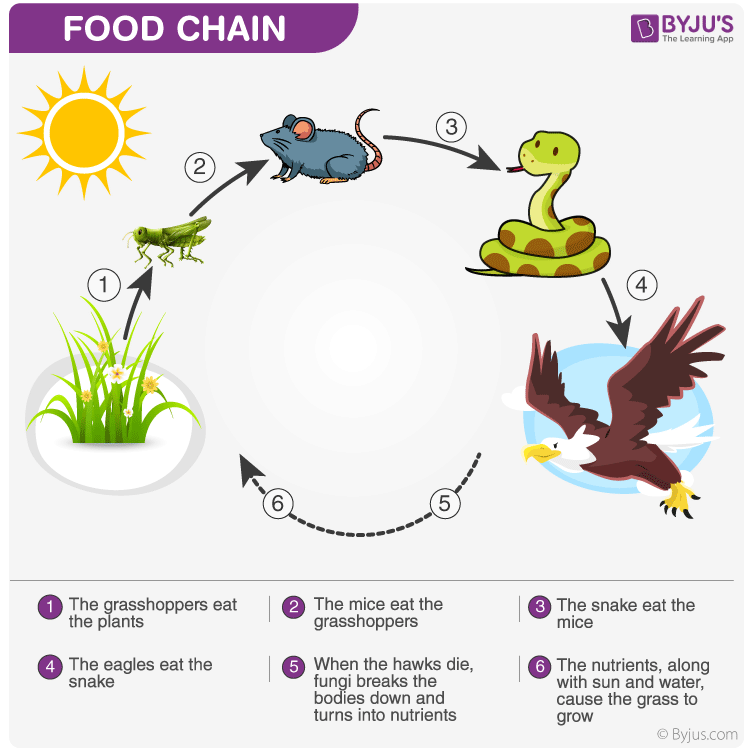
Role of Predators in Forest Ecosystems
Predators play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of forest ecosystems. They help regulate the populations of other species, preventing overgrazing and the depletion of vegetation. This balance ensures the sustainability of the forest and supports a diverse range of life forms.
- Top predators, like wolves and big cats, control the numbers of herbivores, protecting plant populations.
- Smaller predators, including birds of prey and snakes, manage populations of insects and rodents, contributing to ecological equilibrium.
- Predators also aid in disease control by targeting weak and sick individuals, reducing the spread of illnesses.
The presence of predators is a sign of a healthy ecosystem, indicating the integrity and complexity of the forest"s food web.
Impact of Climate Change on Forest Ecosystems
Climate change poses significant threats to forest ecosystems worldwide, affecting their structure, function, and the vast diversity of life they support. However, understanding these impacts also guides us towards effective adaptation and mitigation strategies that can help preserve these vital habitats. Here"s how climate change is affecting forest ecosystems and the positive steps being taken to address these challenges:
- Altered Weather Patterns: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can lead to droughts, increased fire frequency, and pest outbreaks, all of which can significantly alter forest landscapes. Adaptive management strategies, such as controlled burns and pest management plans, are being implemented to reduce these risks.
- Shifts in Species Distribution: As temperatures rise, many plant and animal species are moving to higher elevations or latitudes in search of suitable habitats. Conservation efforts are focused on creating wildlife corridors and protected areas that facilitate species migration and preserve biodiversity.
- Phenological Changes: Climate change affects the timing of natural events, such as flowering, migrations, and hibernation. Research and monitoring programs are crucial in understanding these changes, allowing for better management of wildlife and forest resources.
- Carbon Storage: Forests play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. Efforts to protect existing forests, reforest degraded areas, and practice sustainable forestry are key to enhancing this natural carbon sink capability.
- Increased Vulnerability to Invasive Species: Warmer temperatures can make forests more susceptible to invasive species, which can outcompete native flora and fauna. Integrated pest management and community engagement in invasive species removal projects are essential components of conservation strategies.
Despite these challenges, there is hope. Innovative conservation strategies, such as the use of technology for monitoring forest health, community-based forest management, and international cooperation on climate action, are making a difference. Education and awareness programs are also vital, empowering people to take action for forest conservation. Together, we can mitigate the impact of climate change on forest ecosystems and ensure their resilience for future generations.
Conservation Efforts for Forest Animals
The conservation of forest animals is critical for maintaining biodiversity, ecosystem stability, and the overall health of our planet. A variety of innovative and traditional conservation efforts are being undertaken globally to protect these vital inhabitants of forest ecosystems. Here are some key strategies and initiatives that are making a positive impact:
- Protected Areas: The establishment of national parks, wildlife reserves, and conservation areas is one of the most effective ways to ensure the survival of forest animals. These areas provide safe havens where animals can live and breed without the threat of habitat destruction, poaching, or competition for resources.
- Wildlife Corridors: To facilitate the natural migration of animals and maintain genetic diversity, wildlife corridors connect separate protected areas. These corridors are crucial for the survival of species that require large territories, such as elephants and big cats, and help prevent genetic bottlenecks.
- Reforestation and Habitat Restoration: Programs aimed at planting trees and restoring degraded lands help replenish lost habitats and connect fragmented forests. These efforts are vital for species that are highly sensitive to habitat changes, providing them with the space and resources needed to thrive.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is key to sustainable protection. Community-based conservation projects educate and empower locals, providing them with the tools and knowledge to protect their native wildlife. These projects often include sustainable livelihood programs that reduce reliance on the forest for resources.
- Research and Monitoring: Scientific research and continuous monitoring are essential to understand the needs of forest animals and the threats they face. Data collected from these activities inform conservation strategies and policies, ensuring they are effective and adaptable to changing conditions.
- Anti-Poaching Measures: Poaching remains a significant threat to many forest species. Anti-poaching patrols, legal enforcement, and technologies like satellite tracking and camera traps are being deployed to deter poachers and monitor wildlife populations.
- International Cooperation: Many forest animals migrate across national borders, making international cooperation essential for their conservation. Agreements and partnerships between countries help protect migratory routes and ensure the conservation of shared species and habitats.
These efforts, combined with global awareness and support for conservation, are crucial for the protection of forest animals. By working together, we can ensure the survival of these species and the health of forest ecosystems for future generations.
Rainforests 101
Discover the wonders and beauty of our planet\'s incredible biodiversity in this captivating video. Immerse yourself in the vibrant colors of diverse ecosystems and witness the delicate balance of life that exists in every corner of the world.
Forest Ecosystem
Join us on a journey towards sustainability as we explore innovative solutions to protect our planet for future generations. From renewable energy sources to eco-friendly practices, this video will inspire you to make a positive impact and create a more sustainable world.
Human Activities and Their Impact on Forest Ecosystems
Human activities have profound impacts on forest ecosystems, some of which pose significant challenges to their health and biodiversity. However, recognizing these impacts is the first step toward mitigating negative effects and promoting sustainable coexistence. Here"s an overview of the main human activities affecting forests and the positive actions being taken to address these challenges:
- Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, and urban expansion drastically reduces forest cover, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation. Efforts to combat deforestation include promoting sustainable land management practices, reforestation projects, and the use of certified wood products.
- Pollution: Air and water pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources can degrade forest ecosystems. Initiatives such as stricter pollution controls, the use of environmentally friendly technologies, and the restoration of polluted areas help reduce the impact on forests.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change affects forests through altered precipitation patterns, increased temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events. Adaptive management strategies, such as selecting resilient tree species for reforestation and implementing conservation practices, are vital to help forests adapt.
- Overexploitation: The unsustainable harvesting of timber, non-timber forest products, and wildlife puts pressure on forest ecosystems. Sustainable harvesting practices, community-based forest management, and wildlife conservation laws are key measures to ensure the long-term viability of these resources.
- Invasive Species: Human activities facilitate the spread of invasive species that can outcompete native flora and fauna. Efforts to control invasive species include biosecurity measures, public education, and the restoration of native habitats.
- Infrastructure Development: The construction of roads, dams, and other infrastructure can fragment forests and disrupt wildlife. Planning and implementing green infrastructure projects that minimize environmental impacts are crucial for balancing development needs with forest conservation.
While the challenges are significant, there is a growing global commitment to sustainable forest management and conservation. By integrating conservation goals with economic development, fostering international cooperation, and encouraging community participation, it is possible to mitigate the impact of human activities on forest ecosystems. This collective action can secure the health of forests and their inhabitants for future generations.

Restoration Projects in Forest Ecosystems
Restoration projects play a crucial role in the recovery and maintenance of healthy forest ecosystems, contributing to biodiversity, climate mitigation, and the well-being of local communities. These projects range from local initiatives to global efforts, all aiming to restore the natural balance and function of forested areas. Below are key components and examples of successful restoration strategies:
- Reforestation: Planting trees in areas where forests have been cut down or degraded is a fundamental restoration activity. Projects often focus on native species to ensure the recovery of natural forest conditions and support local biodiversity.
- Eradication of Invasive Species: Removing non-native species that threaten local ecosystems is crucial for the restoration of native biodiversity. Efforts include physical removal, biological control methods, and public education campaigns to prevent future invasions.
- Soil Restoration: Healthy soils are essential for successful forest restoration. Activities such as composting, mulching, and controlled burns are used to improve soil health, structure, and fertility, facilitating the growth of new vegetation.
- Water Management: Restoring natural water flows through the removal of barriers, such as dams, and the rehabilitation of wetlands and riparian zones helps to reestablish healthy aquatic ecosystems, which are integral to forest environments.
- Wildlife Reintroduction: In some cases, the reintroduction of species that have been extirpated or are locally extinct can be necessary to restore ecological balance. This requires careful planning to ensure the sustainability of both the reintroduced species and the ecosystem.
- Community Engagement and Education: Involving local communities in restoration projects is key to their success. Educational programs and participatory restoration activities help build local stewardship and ensure long-term conservation efforts.
- Monitoring and Research: Continuous monitoring and research are essential to assess the progress of restoration projects and adapt strategies as needed. This involves tracking biodiversity, ecosystem functions, and the socio-economic impacts of restoration activities.
Restoration projects in forest ecosystems are a beacon of hope and a testament to the resilience of nature. Through collaborative efforts, innovative approaches, and a commitment to sustainability, these projects pave the way for a future where forests thrive and continue to provide essential services for the planet and its inhabitants.
Education and Awareness About Forest Conservation
Educating the public and raising awareness about forest conservation are essential steps towards ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of forest ecosystems worldwide. Through various platforms and initiatives, individuals and communities are empowered with knowledge and tools to contribute effectively to conservation efforts. Here are key aspects and strategies for enhancing education and awareness:
- Curriculum Integration: Incorporating forest conservation topics into school curriculums at various levels educates young minds about the importance of forests, the threats they face, and ways to protect them. Interactive lessons, field trips, and project-based learning can foster a deeper understanding and commitment to conservation.
- Community Workshops and Training: Providing practical training and workshops for communities, especially those living in or near forested areas, on sustainable practices and conservation techniques helps in building local capacity for forest stewardship.
- Public Campaigns: Awareness campaigns through media, social platforms, and public events play a crucial role in highlighting the importance of forests and the need for conservation. These campaigns can focus on specific issues like deforestation, biodiversity loss, or climate change impacts on forests.
- Partnerships with NGOs and Government Agencies: Collaborating with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and government agencies that specialize in environmental conservation can amplify education and awareness efforts. These partnerships can facilitate access to resources, expertise, and networks for broader outreach.
- Use of Technology and Social Media: Leveraging technology and social media platforms to share information, stories, and conservation successes can engage a wider audience. Interactive apps, virtual reality experiences, and online courses offer accessible ways for people to learn about forest conservation.
- Volunteer Programs: Encouraging participation in volunteer programs related to tree planting, wildlife monitoring, and forest cleanup activities provides hands-on experience and fosters a personal connection to forest conservation efforts.
- Citizen Science Projects: Engaging the public in citizen science projects related to forest ecosystems allows individuals to contribute to scientific research while gaining a deeper understanding of the natural world and the importance of conservation.
Through education and awareness, we can cultivate a global community that values, protects, and actively contributes to the conservation of forest ecosystems. This collective effort is vital for preserving the biodiversity and ecological services forests provide for future generations.

READ MORE:
Innovations in Protecting Forest Ecosystems and Wildlife
In the face of increasing threats to forest ecosystems and wildlife, innovative solutions are being developed and deployed to enhance conservation efforts. These advancements leverage technology, community engagement, and interdisciplinary approaches to create effective and sustainable strategies. Here are some of the most promising innovations in forest conservation:
- Remote Sensing and Satellite Monitoring: The use of satellite imagery and remote sensing technology allows for the real-time monitoring of forest cover, deforestation rates, and habitat changes. This technology provides invaluable data for making informed conservation decisions and tracking the effectiveness of restoration efforts.
- Drones for Reforestation and Monitoring: Drones are being used to plant seeds in hard-to-reach areas, making reforestation efforts more efficient and less labor-intensive. They also monitor wildlife populations and track illegal activities such as poaching and logging.
- AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of environmental data to predict threats such as forest fires, disease outbreaks, and invasive species spread. These tools help in preemptive action to mitigate risks.
- Conservation Genetics: Advances in genetics are helping conservationists understand the genetic diversity within wildlife populations, guiding breeding programs and reintroduction efforts to ensure healthy, resilient populations.
- Community-based Conservation Apps: Mobile applications that engage local communities in conservation efforts, such as reporting wildlife sightings or illegal logging, are strengthening the connection between people and their natural environment, fostering a culture of conservation.
- Eco-friendly Infrastructure: The development of green infrastructure, such as wildlife crossings over or under roads and eco-friendly barriers, reduces the impact of human development on forest ecosystems and improves animal safety.
- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES): PES schemes incentivize conservation by compensating landowners for maintaining forest ecosystems that provide essential services, such as carbon sequestration and water purification. These financial mechanisms support sustainable land management practices and conservation goals.
These innovations, coupled with traditional conservation methods, are enhancing our ability to protect forest ecosystems and wildlife. By continuing to develop and implement such technologies and approaches, we can ensure the preservation of these vital natural resources for future generations.
Explore the fascinating world of forest ecosystems and their wildlife through our comprehensive guide. Discover innovative conservation strategies, the importance of education, and the latest in technological advancements to protect these vital habitats for future generations.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-170074807-fc568317496947adb9a5dec71be44380.jpg)