Topic types of forest ecosystem: Explore the vibrant tapestry of the world"s forests, from lush tropics to serene boreals, understanding the diverse types of forest ecosystems enriches our appreciation for nature"s intricate beauty.
Table of Content
- What is the definition of a forest ecosystem?
- Overview of Forest Ecosystems
- Classification of Forest Ecosystems
- Tropical Forest Ecosystems
- Temperate Forest Ecosystems
- Boreal Forest Ecosystems
- YOUTUBE: Forest Ecosystem | Biology Animation
- Unique Characteristics of Different Forest Ecosystems
- Flora and Fauna in Forest Ecosystems
- Conservation and Threats to Forest Ecosystems
- Role of Forest Ecosystems in Global Ecology
What is the definition of a forest ecosystem?
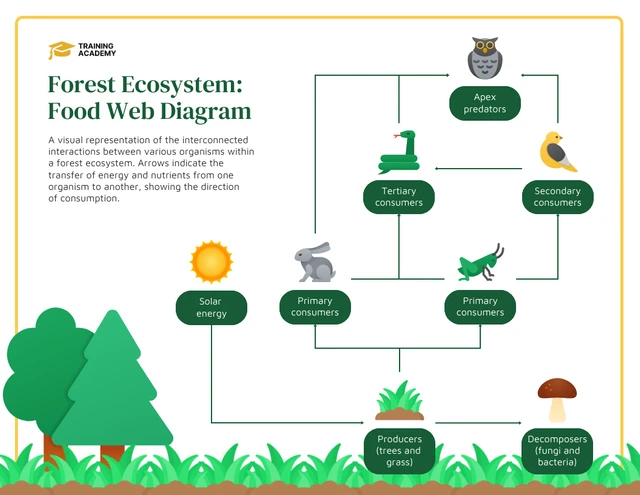
A forest ecosystem can be defined as a natural woodland area where various living organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, interact with each other and their surrounding environment. It is a complex ecological community that includes both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components.
Forests provide habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the Earth\'s ecosystems. They contribute to the production of oxygen, act as carbon sinks, provide food and shelter for wildlife, and offer numerous other ecosystem services.
The different types of forest ecosystems can be classified based on various factors such as climate, vegetation, and location. Some common types of forest ecosystems include:
- Temperate forests: These forests are found in regions with moderate climates, characterized by distinct seasons. They typically have a mix of deciduous and evergreen trees.
- Tropical forests: These forests are situated in tropical regions near the equator. They experience high temperatures and rainfall throughout the year, supporting a diverse range of plant and animal species.
- Boreal forests: Also known as taiga, these forests are found in high-latitude regions with cold climates. They are predominantly composed of coniferous trees and are often associated with subarctic and subalpine regions.
The composition and characteristics of forest ecosystems can vary greatly depending on factors such as geographical location, soil type, topography, and human activities. Each forest ecosystem possesses its own unique biodiversity and contributes to the overall health and functioning of the planet\'s ecosystems.
READ MORE:
Overview of Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are dynamic and complex environments where flora, fauna, and abiotic elements interact in a balanced system. These ecosystems are crucial for the health of our planet, providing essential services such as carbon sequestration, oxygen production, and biodiversity support.
- Definition: A forest ecosystem encompasses a community of plants and animals interacting with their physical environment, including soil, water, and air.
- Components: They consist of various biotic components (trees, shrubs, herbs, and fauna) and abiotic components (climate, soil, water).
- Functions: Forest ecosystems play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance, including regulating the climate, purifying water, and supporting a wide range of life forms.
- Types: Based on climatic conditions and geographical locations, forest ecosystems are categorized into tropical, temperate, and boreal forests, each with unique characteristics and species.
Understanding forest ecosystems is essential for their conservation and sustainable management, ensuring they continue to support life on Earth for future generations.

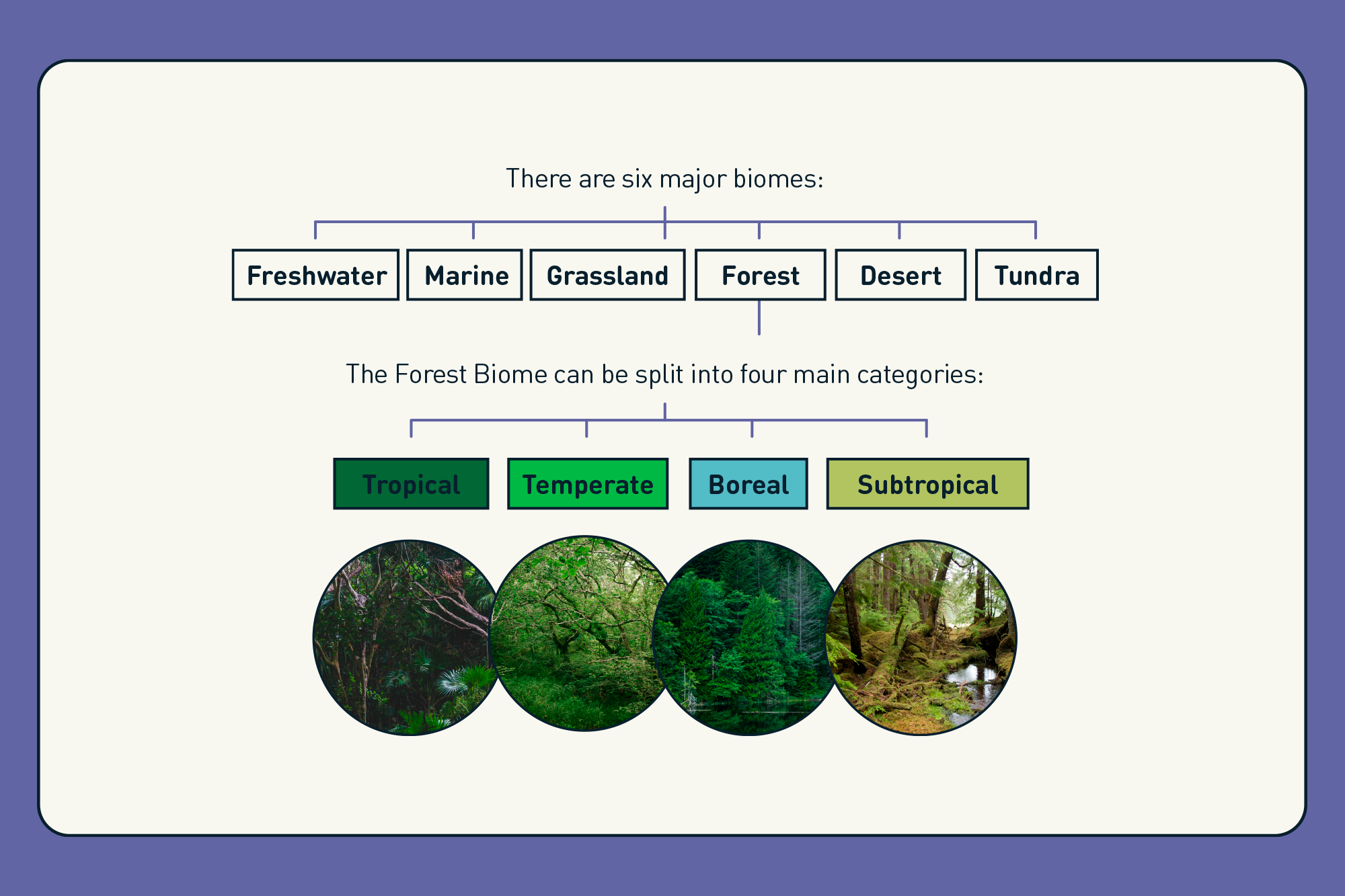
Classification of Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are classified into several types based on their geographical location, climate, and the types of flora and fauna they support. This classification helps in understanding the diversity and complexity of forests worldwide.
- Tropical Forests: Located near the equator, these forests experience a warm climate and high rainfall throughout the year. They are known for their immense biodiversity.
- Temperate Forests: Found in regions with distinct seasons, temperate forests have a mix of deciduous and evergreen trees and experience moderate rainfall.
- Boreal Forests (Taiga): Situated in the northern latitudes, boreal forests are characterized by cold climates and are dominated by coniferous trees.
- Mediterranean Forests: These forests are located in regions with a Mediterranean climate, featuring hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters.
- Cloud Forests: Typically found at high elevations, cloud forests are constantly enveloped in fog or mist, supporting a unique ecosystem.
Each forest type plays a crucial role in the Earth"s ecological balance, supporting a wide array of plant and animal life while offering various ecosystem services.
Tropical Forest Ecosystems
Tropical forests, teeming with life, stretch across the equator in regions like the Amazon, Africa, Southeast Asia, and Central America. These ecosystems are characterized by their dense canopy of broadleaf evergreen trees, which create a shaded forest floor and preserve moisture. The climate is warm with stable temperatures around 27°C, fostering an unparalleled biodiversity.
These forests are divided into various types based on rainfall patterns:
- Evergreen Forests: Experience heavy rainfall year-round without a dry season.
- Seasonal Forests: Have a short dry season but retain their lush greenery throughout the year.
- Dry Forests: Endure a prolonged dry season, causing trees to shed leaves.
- Montane Forests: Located at higher elevations, these "cloud forests" receive moisture primarily from mist or fog.
- Sub-tropical Forests: Situated in the north and south fringes of the tropics, adapted to resist summer drought.
- Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forests: Experience dry, hot climates with conifers adapted to fluctuating weather.
Tropical forests play a critical role in the Earth"s climate by sequestering carbon dioxide and are a source of wood, food, and medicines. Despite their importance, these ecosystems face threats from deforestation and climate change, highlighting the need for conservation efforts to protect these vital areas and their unique biodiversity.

Temperate Forest Ecosystems
Temperate forests are found in regions with four distinct seasons and moderate climates, including parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. These ecosystems are known for their rich biodiversity, characterized by deciduous trees that shed their leaves annually and, in some areas, evergreen species. Temperate forests play a crucial role in the Earth"s environment, acting as vital carbon sinks and providing habitats for diverse wildlife.
Key features of temperate forest ecosystems include:
- Distinct Seasons: Experience a clear division of four seasons - spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
- Deciduous Trees: Such as oak, maple, and birch, dominate these forests, shedding their leaves in autumn to conserve water during winter.
- Evergreen Trees: In some temperate forests, evergreen trees like pines and firs are also present, providing greenery year-round.
- Rich Biodiversity: Home to a wide variety of fauna including deer, bears, wolves, foxes, and numerous bird species.
- Soil Fertility: The annual leaf drop contributes to a thick layer of humus, making the soil fertile and ideal for undergrowth.
Conservation efforts in temperate forests focus on sustainable management practices to protect these ecosystems from deforestation, climate change, and habitat loss. Such forests are not only crucial for biodiversity but also for the livelihoods of local communities and global ecological health.
Boreal Forest Ecosystems
Boreal forests, also known as Taiga, represent the world"s largest terrestrial biome. They encircle the northern hemisphere, stretching across North America, Europe, and Asia. These ecosystems are characterized by their cold, harsh climates, long winters, and short, mild summers. Boreal forests are crucial for biodiversity, carbon storage, and climate regulation.
Key characteristics of boreal forest ecosystems include:
- Coniferous Trees: Dominated by evergreen conifers such as spruce, fir, and pine. These trees are adapted to the cold, with needle-like leaves that reduce water loss and snow accumulation.
- Adapted Fauna: Home to a variety of wildlife adapted to cold temperatures, including moose, bears, lynxes, wolves, and a range of bird species like owls and woodpeckers.
- Permafrost: Many areas of the boreal forest are underlain by permafrost, which affects water drainage and soil composition.
- Peatlands and Wetlands: Abundant, playing a significant role in carbon sequestration and serving as important habitats for migratory bird species.
The boreal forest plays a pivotal role in the global environment, but it faces threats from logging, mining, and climate change. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these ecosystems, their biodiversity, and their role in mitigating climate change.
Forest Ecosystem | Biology Animation
\"Experience the magical world of animation as characters come to life through vibrant colors and captivating storytelling. Dive into an enchanting journey that will ignite your imagination and leave you wanting more.\"
Temperate Forest Ecosystems
\"Take a visual voyage to temperate regions where picturesque landscapes and moderate climates create an oasis of tranquility. Discover the beauty of nature\'s perfect balance and embrace the allure of these captivating destinations.\"
Unique Characteristics of Different Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are diverse and vary greatly across the world, each possessing unique characteristics that define their flora, fauna, climate, and ecological role. Understanding these unique features is essential for the conservation and sustainable management of forests.
- Tropical Forests: Located near the equator, these forests are known for their high biodiversity, with a vast array of plant and animal species. They feature a dense canopy and a warm, humid climate year-round.
- Temperate Forests: These forests experience four distinct seasons with a mix of deciduous and evergreen trees. They are found in regions with moderate climates and provide habitats for a diverse range of wildlife.
- Boreal Forests (Taiga): Dominated by coniferous trees, boreal forests cover vast areas in the northern hemisphere. They are adapted to cold, harsh climates with long winters and short summers.
- Mediterranean Forests: Characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, these forests are adapted to fire and drought. They are rich in biodiversity, including many endemic plant species.
- Cloud Forests: These high-altitude forests are constantly shrouded in mist, leading to high humidity and a unique ecosystem with abundant mosses, ferns, and epiphytes.
Each forest type plays a crucial role in our planet"s ecology, supporting countless species and providing essential services such as carbon sequestration, oxygen production, and soil preservation. The conservation of these diverse ecosystems is vital for maintaining global biodiversity and ecological balance.
Flora and Fauna in Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are rich and complex habitats that support a diverse array of plant and animal life. Each type of forest ecosystem has its own unique flora and fauna, adapted to the climate, soil, and available resources of its environment.
- Tropical Forests: Boast the highest biodiversity among forest types, with countless species of trees, including mahogany, rubber, and teak, alongside a plethora of animal life such as jaguars, sloths, various monkeys, and numerous bird species like toucans and parrots.
- Temperate Forests: Home to broadleaf deciduous trees like oak, maple, and birch, as well as coniferous trees such as pine and fir. Wildlife includes deer, bears, wolves, and a variety of birds and small mammals.
- Boreal Forests: Dominated by coniferous trees such as spruce, pine, and fir. These forests shelter moose, black bears, lynx, and numerous bird species, including owls and woodpeckers.
- Mediterranean Forests: Characterized by hard-leaved evergreens, including cork oak and olive trees. The fauna includes a variety of mammals, reptiles, and birds, many of which are adapted to the dry summers, such as the Iberian lynx.
- Cloud Forests: Host to a unique assemblage of vegetation, including mosses, orchids, and ferns, due to the constant presence of cloud and mist. Unique bird species, such as the Resplendent Quetzal, and a variety of amphibians and insects thrive here.
The interdependence between the flora and fauna within each forest ecosystem plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and stability of our planet"s environment. Conservation efforts are vital to protect these ecosystems from threats such as deforestation, climate change, and biodiversity loss.

Conservation and Threats to Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems around the world are under threat from a variety of sources, which jeopardize their biodiversity, ecological functions, and the services they provide to humanity. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these invaluable natural resources for future generations.
- Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, and urban development leads to habitat loss, species extinction, and contributes to climate change.
- Climate Change: Alters precipitation patterns, increases the frequency of wildfires, and affects forest health and species distribution.
- Pollution: Air and water pollution from industrial and agricultural activities degrade forest ecosystems and affect both flora and fauna.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete native species for resources, leading to a loss of biodiversity.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable logging, hunting, and harvesting of forest resources diminish biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Conservation strategies include establishing protected areas, sustainable forest management practices, reforestation and afforestation projects, and efforts to combat climate change. Public awareness and community engagement are also vital components in conserving forest ecosystems. Protecting forests is not just about preserving the natural world, but also about ensuring a healthy planet for future generations.
READ MORE:
Role of Forest Ecosystems in Global Ecology
Forest ecosystems play a pivotal role in maintaining the health and balance of our planet. They are crucial for biodiversity, climate regulation, water cycle maintenance, and soil preservation. The services provided by forest ecosystems are invaluable to global ecological stability and human well-being.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and playing a critical role in mitigating climate change.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Serve as home to a majority of the world’s terrestrial biodiversity, hosting a wide variety of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms.
- Water Regulation: Forests influence hydrological cycles, ensuring the availability of fresh water through the regulation of river flows and rainfall.
- Soil Protection: Tree roots stabilize soil, preventing erosion, while the decomposition of leaf litter enriches soil fertility.
- Air Quality Improvement: Forests filter pollutants from the air, contributing to cleaner, healthier air.
- Climate Regulation: Forests influence local and global climates, helping to regulate temperatures and weather patterns.
Despite their importance, forests worldwide are under threat from deforestation, climate change, and pollution. It is essential to prioritize the conservation and sustainable management of forest ecosystems to protect these vital natural resources for future generations.
Explore the vital roles and diverse wonders of the world"s forest ecosystems, from the lush tropics to the serene boreal realms. Join us in uncovering the beauty, challenges, and crucial importance of these ecological treasures for our planet"s future.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)