Topic animals in rainforest ecosystems: Explore the vibrant heart of nature with "Animals in Rainforest Ecosystems," a journey into the lush, diverse habitats home to Earth"s most fascinating creatures.
Table of Content
- What types of animals inhabit rainforest ecosystems?
- Overview of Rainforest Ecosystems
- Diversity of Animals in Rainforests
- Key Species Highlight: Mammals
- Key Species Highlight: Birds
- Key Species Highlight: Reptiles and Amphibians
- Adaptations to the Rainforest Environment
- YOUTUBE: Rainforests 101 by National Geographic
- Role of Animals in Rainforest Ecosystems
- Threats to Animals in Rainforests
What types of animals inhabit rainforest ecosystems?
There are a diverse range of animals that inhabit rainforest ecosystems. Some examples include:
- Monkeys
- Sloths
- Tapirs
- Jaguars
- Ocelots
- Kinkajous
- Lemurs
- Agouti
- Scarlet Macaws (a type of parrot with bright red plumage)
- Gorillas (in African rainforest ecosystems)
These animals play important roles in maintaining the balance and diversity of the rainforest ecosystem.
READ MORE:
Overview of Rainforest Ecosystems
Rainforest ecosystems are among the most complex and biodiverse areas on Earth, covering less than 10% of the world"s surface but home to more than half of its wildlife and plant species. These ecosystems are characterized by high rainfall, dense canopies, and a warm climate year-round.
- Location: Rainforests are primarily found in the Amazon basin, Central Africa, and Southeast Asia.
- Climate: They enjoy a tropical climate with high humidity and temperatures ranging between 20-25°C (68-77°F).
- Canopy Layers: The rainforest is structured in layers, including the emergent, canopy, understory, and forest floor, each supporting unique flora and fauna.
- Biodiversity: Rainforests are rich in species diversity, hosting millions of species of insects, plants, birds, mammals, and reptiles.
- Role in the Earth"s Environment: They play a crucial role in regulating the global climate and are vital sources of oxygen and freshwater.
Rainforests are not just homes to an incredible variety of life but also vital to the health of our planet, acting as global air filters and playing a key role in water cycles.

Diversity of Animals in Rainforests
The rainforest teems with life, hosting an unparalleled diversity of animals that have adapted to its unique environment. From the forest floor to the canopy, every layer is a bustling world of biodiversity.
- Insects: The base of the food chain, insects like butterflies, beetles, and ants are incredibly varied and numerous.
- Birds: Rainforests are home to a dazzling array of birds, including toucans, parrots, and birds of paradise, known for their vivid colors and melodious songs.
- Mammals: Iconic rainforest mammals include jaguars, sloths, and various monkeys, each adapted to life in the dense foliage.
- Reptiles and Amphibians: The warm, moist conditions support a rich variety of frogs, snakes, and lizards, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth.
These animals are not only integral to the rainforest"s ecological balance but also to indigenous cultures and global biodiversity. Their varied diets, behaviors, and roles in the ecosystem highlight the interconnectedness of rainforest life.
Key Species Highlight: Mammals
Rainforests are a haven for some of the most fascinating and unique mammals on the planet. These creatures have evolved complex adaptations to navigate the dense and diverse habitats of the rainforest.
- Jaguars: The top predators of the rainforest, jaguars are powerful hunters that play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance by controlling other species" populations.
- Sloths: With their slow movements and tree-dwelling habits, sloths are perfectly adapted to life in the canopy, feeding on leaves and spending most of their time hanging upside down.
- Orangutans: These highly intelligent primates are native to the rainforests of Borneo and Sumatra. They are known for their incredible ability to use tools and have complex social structures.
- Tapirs: These large, herbivorous mammals are vital for seed dispersal, helping to maintain the diversity and health of rainforest flora.
These mammals are not only key to the rainforest"s biodiversity but also indicator species whose health reflects the overall well-being of their ecosystems.

Key Species Highlight: Birds
The rainforest"s avian population is a vibrant tapestry of color, sound, and diversity, with birds playing critical roles in pollination, seed dispersal, and controlling insect populations.
- Toucans: Known for their large, colorful bills, toucans are not just a symbol of the rainforest but also important seed dispersers.
- Harpy Eagles: As one of the largest and most powerful birds of prey, harpy eagles are apex predators in the rainforest, controlling populations of small mammals and birds.
- Hummingbirds: With their rapid wing beats and ability to hover, hummingbirds are vital pollinators for many rainforest plants.
- Scarlet Macaws: These brightly colored parrots are not only a stunning sight but also play a role in seed dispersal. Their strong beaks can crack nuts and seeds that other animals cannot.
These birds, with their unique adaptations and ecological roles, are essential for the health and continuity of rainforest ecosystems.
Key Species Highlight: Reptiles and Amphibians
The warm, humid climate of the rainforest is a perfect habitat for a wide variety of reptiles and amphibians, each playing a crucial role in the ecosystem"s balance through their roles as predators, prey, and pollinators.
- Anacondas: Among the largest snakes in the world, anacondas are formidable predators that thrive in the waterways of the rainforest.
- Poison Dart Frogs: Known for their vivid colors and potent toxins, these frogs are a key part of the rainforest"s biodiversity, warning predators with their bright colors.
- Chameleons: Masters of camouflage, chameleons are fascinating reptiles that blend into their surroundings, making them adept hunters.
- Turtles: Rainforest rivers and lakes are home to various turtle species that contribute to the ecosystem by dispersing seeds and supporting the aquatic food web.
These reptiles and amphibians are vital for maintaining the delicate balance of rainforest ecosystems, showcasing the incredible adaptability of life in these environments.

Adaptations to the Rainforest Environment
The warm, humid climate of the rainforest is a perfect habitat for a wide variety of reptiles and amphibians, each playing a crucial role in the ecosystem"s balance through their roles as predators, prey, and pollinators.
- Anacondas: Among the largest snakes in the world, anacondas are formidable predators that thrive in the waterways of the rainforest.
- Poison Dart Frogs: Known for their vivid colors and potent toxins, these frogs are a key part of the rainforest"s biodiversity, warning predators with their bright colors.
- Chameleons: Masters of camouflage, chameleons are fascinating reptiles that blend into their surroundings, making them adept hunters.
- Turtles: Rainforest rivers and lakes are home to various turtle species that contribute to the ecosystem by dispersing seeds and supporting the aquatic food web.
These reptiles and amphibians are vital for maintaining the delicate balance of rainforest ecosystems, showcasing the incredible adaptability of life in these environments.
Rainforests 101 by National Geographic
Immerse yourself in the vibrant and awe-inspiring world of rainforests! Explore the lush green canopies, encounter rare species of plants and animals, and witness the extraordinary diversity of life in this magnificent ecosystem. Get ready for a mesmerizing journey through nature\'s hidden gem!
World of the Wild: Episode 1 - The Amazon Rainforest by Free Documentary Nature
Embark on an unforgettable adventure deep into the heart of the Amazon Rainforest. Prepare to be amazed by the sheer magnificence of this unparalleled natural wonder. From the majestic flow of the Amazon River to the exotic wildlife that calls it home, this video will take you on a breathtaking tour you won\'t want to miss.
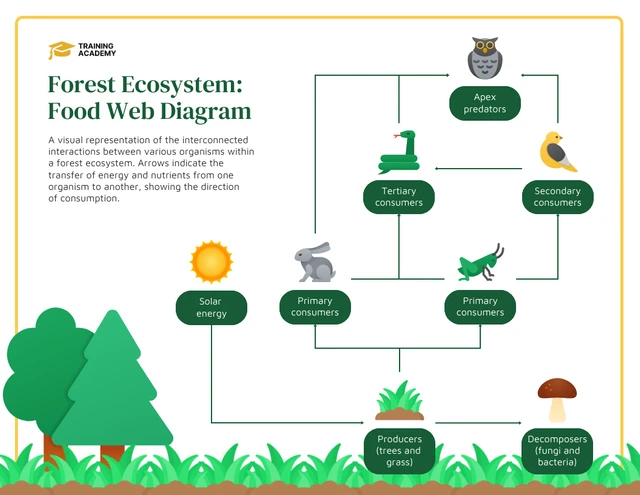
Role of Animals in Rainforest Ecosystems
The rainforest ecosystem is a complex and vibrant web of life, where animals play critical roles in maintaining the balance and health of this unique environment. From the forest floor to the canopy, animals contribute to the ecosystem"s diversity, productivity, and resilience. Here, we explore the multifaceted roles that animals serve in rainforest ecosystems.
- Pollinators: Many rainforest animals, including birds, bats, and insects, are vital pollinators. They help in the reproduction of plants by carrying pollen from one flower to another, facilitating the growth of fruit and seeds that are essential for the survival of countless plant species.
- Seed Dispersers: Animals such as monkeys, birds, and rodents eat fruits and nuts, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal. The seeds are often excreted some distance away from the parent plant, helping to spread plant species across the forest and promoting biodiversity.
- Decomposers: Decomposers, including termites and dung beetles, break down dead organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil. This process supports plant growth and maintains soil health, which is fundamental for a thriving rainforest.
- Predators and Prey: The predator-prey relationships in rainforests are vital for natural selection and maintaining population balances. Predators help control the population of other animals, ensuring no single species dominates the ecosystem, which could lead to its collapse.
- Nutrient Cycling: Larger animals, such as elephants and tapirs, contribute to nutrient cycling by trampling dense vegetation and breaking down the forest floor, making it more accessible for smaller decomposers. Their waste also enriches the soil with nutrients.
Furthermore, the presence and activities of animals in rainforests also support numerous ecological processes, such as water cycling and carbon storage, which have global impacts on climate regulation and air quality. By understanding the critical roles of animals in rainforest ecosystems, we can appreciate the importance of conserving these environments to protect the intricate web of life they support.

READ MORE:
Threats to Animals in Rainforests
Rainforests, the planet"s most vibrant and diverse ecosystems, are home to over half of the world"s wildlife species. However, the animals that inhabit these rainforests face numerous threats that endanger their survival and the balance of these ecosystems. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. Here are the primary dangers facing animals in rainforests:
- Deforestation: The clearing of rainforest land for agriculture, logging, and urban development is the most significant threat to rainforest animals. It results in the loss of habitat, leaving animals without shelter, food, or breeding grounds.
- Climate Change: Changes in temperature and weather patterns can alter the delicate balance of rainforest ecosystems. Animals may struggle to adapt to these changes, leading to shifts in population dynamics and species distribution.
- Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: Many rainforest animals are hunted for their fur, meat, or as pets. This illegal trade not only depletes populations but also disrupts the ecological balance, affecting other species and the forest as a whole.
- Pollution: Pollution from mining, oil extraction, and agricultural runoff can contaminate water sources and soil in rainforests. This not only harms the animals directly but also affects the quality of their habitat.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can have devastating effects on rainforest ecosystems. Invasive species often compete with native animals for resources or prey on them, leading to a decline in native populations.
- Disease: Diseases, both natural and those introduced through human activity, can spread rapidly among animals in dense rainforest environments. Outbreaks can decimate populations, especially those of already endangered species.
These threats are interconnected, often exacerbating each other and leading to a rapid decline in biodiversity. Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation and a commitment to sustainable practices that protect rainforest habitats and the animals that depend on them.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)