Topic what ecosystem services do grasslands provide: Discover the vital role of grasslands in our ecosystem, from biodiversity preservation to climate regulation, and why their services are indispensable for sustaining life on Earth.
Table of Content
- What ecosystem services do grasslands provide?
- Importance of Grasslands in Biodiversity Conservation
- Carbon Sequestration and Climate Regulation
- Water Regulation and Purification Services
- Soil Erosion Control and Fertility Enhancement
- Supporting Livestock and Agricultural Production
- Recreational, Cultural, and Aesthetic Values
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Services of Grasslands
- Grasslands in Pollination and Habitat Provision
What ecosystem services do grasslands provide?
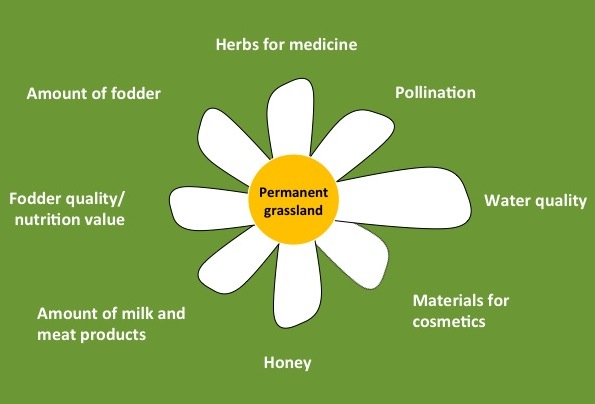
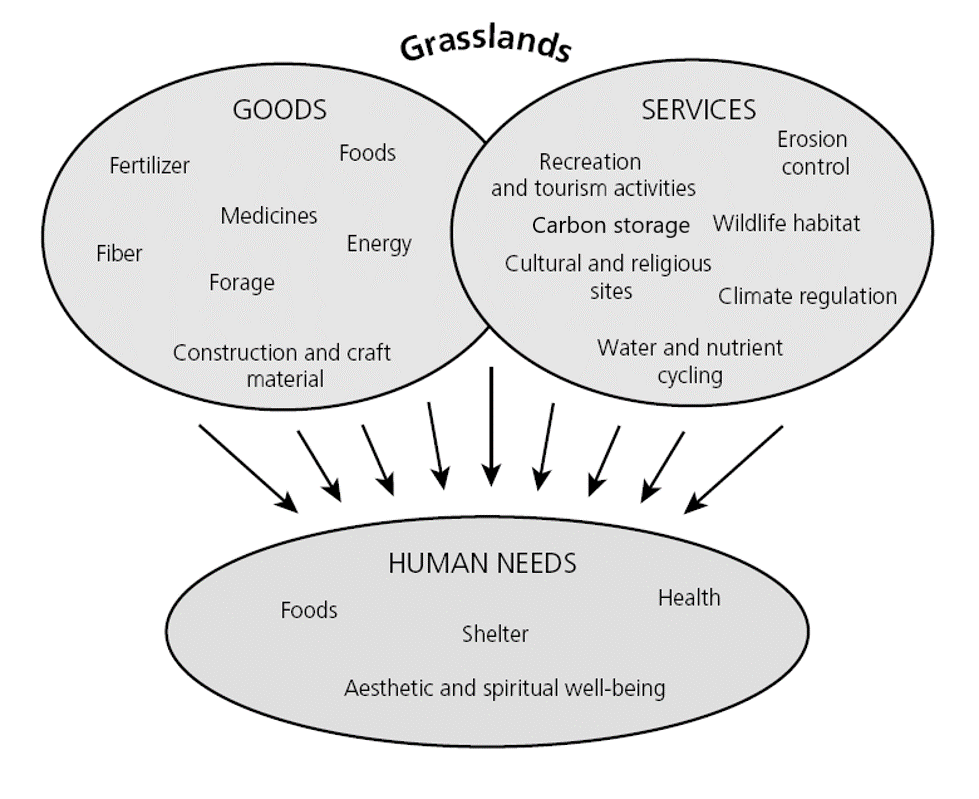
Grasslands provide a wide range of ecosystem services that are vital for the functioning of natural systems and the well-being of human populations. These services include:
- Nutrient Cycling: Grasslands play a crucial role in cycling nutrients through the soil and vegetation. They help to maintain nutrient-rich soils, which support the growth of diverse plant species and provide the foundation for a healthy ecosystem.
- Soil Formation and Protection: The deep roots of grasses help stabilize the soil, prevent erosion, and enhance soil fertility. Grasslands contribute to the formation of rich topsoil, which is essential for agricultural productivity and water filtration.
- Carbon Sequestration: Grasslands have a significant capacity to store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis. The extensive root systems of grasses can store carbon below ground, making grasslands important carbon sinks and helping to mitigate climate change.
- Water Regulation: Grasslands act as natural buffers against flooding by absorbing and storing large amounts of water during heavy rainfall. They also help regulate the flow of water in rivers and streams, reducing the risk of both droughts and floods.
- Habitat Provision: Grasslands provide essential habitat for a diverse range of plant and animal species, including grassland birds, mammals, insects, and pollinators. They support biodiversity and contribute to the overall health and functioning of ecosystems.
- Recreation and Cultural Value: Grasslands offer opportunities for recreational activities such as hiking, birdwatching, and photography. They also hold cultural value for indigenous communities and provide a connection to traditional practices and knowledge.
READ MORE:
Importance of Grasslands in Biodiversity Conservation
Grasslands, often undervalued, play a critical role in maintaining biodiversity. These ecosystems are not just vast expanses of open land but are teeming with life, supporting a wide range of plant and animal species.
- Home to Unique Species: Grasslands offer habitats for numerous species that are found nowhere else. This includes many types of grasses, herbs, and wildflowers, alongside a variety of insects, birds, and mammals.
- Genetic Diversity: The wide array of species in grasslands contributes to genetic diversity, which is crucial for resilience to diseases and changing environmental conditions.
- Migration Corridors: Many grasslands serve as vital migration corridors for wildlife, enabling seasonal and climatic migrations essential for the survival of certain species.
- Natural Selection and Evolution: The dynamic environment of grasslands, with its unique challenges and opportunities, fosters natural selection and promotes evolution, ensuring the continued vitality and adaptation of species.
By conserving grasslands, we protect an intricate web of life that forms the backbone of our ecological system, ensuring stability and resilience against environmental changes.

Carbon Sequestration and Climate Regulation
Grasslands play a pivotal role in the global carbon cycle and climate regulation, acting as significant carbon sinks. Through the process of photosynthesis, grasses and other vegetation absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, storing carbon in their roots and soil, effectively reducing greenhouse gas concentrations.
- Extensive Root Systems: Grasslands have deep and extensive root systems that contribute to soil organic matter, locking away carbon for centuries and improving soil health.
- Resilience to Climate Variability: The adaptability of grassland ecosystems to varying climate conditions enhances their capacity for long-term carbon storage, making them invaluable in climate mitigation efforts.
- Reduced Soil Erosion: By stabilizing the soil, grasslands prevent erosion, further protecting the soil"s carbon reservoirs and maintaining water quality.
- Enhancement of Soil Fertility: Through the decomposition of plant matter, grasslands contribute to the cycling of nutrients, enhancing soil fertility and promoting further carbon sequestration.
Conservation and restoration of grasslands are crucial strategies in combating climate change, offering a natural solution to carbon sequestration and enhancing the resilience of our planet.
Water Regulation and Purification Services
Grasslands are crucial for the regulation and purification of water within ecosystems. Their soil and vegetation play key roles in filtering pollutants, controlling floods, and ensuring the availability of clean water.
- Flood Mitigation: Grassland soils absorb rainfall, reducing runoff and mitigating the risk of floods. This absorption capacity is vital for protecting downstream communities and ecosystems.
- Groundwater Recharge: The porous nature of grassland soils allows water to percolate through the ground, replenishing aquifers and supporting groundwater supplies essential for both ecosystems and human use.
- Natural Filtration System: Grasslands act as natural filters, with plants and soil microorganisms breaking down pollutants from water as it moves through the soil, leading to improved water quality.
- Streamflow Regulation: By absorbing rainfall and slowly releasing water, grasslands help maintain consistent streamflows, supporting aquatic life and providing reliable water resources for agriculture and consumption.
The preservation and restoration of grassland ecosystems are critical for maintaining water quality, ensuring water availability, and protecting aquatic habitats, highlighting their invaluable role in water management.

Soil Erosion Control and Fertility Enhancement
Grasslands are essential for protecting soil integrity and enhancing its fertility. Their dense root systems and ground cover prevent erosion, while their natural lifecycle contributes to the enrichment of soil nutrients.
- Erosion Prevention: The extensive root network of grassland plants binds the soil, significantly reducing erosion caused by wind and water. This protection is vital for maintaining soil health and preventing land degradation.
- Organic Matter Addition: Dead plant material from grasslands decomposes into organic matter, enriching the soil with nutrients and improving its structure. This process enhances soil fertility and increases its water-holding capacity.
- Nitrogen Fixation: Certain grassland species, in association with soil bacteria, can fix atmospheric nitrogen, converting it into a form that plants can use, naturally fertilizing the soil.
- Biological Diversity: The biodiversity of grasslands contributes to the balance of soil nutrients through a variety of plant and animal interactions, promoting soil health and ecosystem productivity.
The conservation of grasslands is crucial for sustainable land management, preventing soil erosion, and enhancing soil fertility, thereby supporting agriculture and biodiversity.
Supporting Livestock and Agricultural Production
Grasslands serve as a foundation for livestock and agricultural production, offering a range of benefits that sustain and enhance these activities. Their natural resources provide essential fodder, support biodiversity, and maintain ecosystem health.
- Natural Fodder Resource: Grasslands provide high-quality forage for grazing animals, supporting the livelihoods of millions of people worldwide and contributing to the global meat and dairy industries.
- Sustainable Grazing: Well-managed grasslands support sustainable grazing practices, which can improve pasture quality, increase carbon sequestration, and reduce the need for artificial fertilizers and feed.
- Agrobiodiversity: The diversity of plant species in grasslands can be harnessed for crop improvement, offering genetic resources for developing more resilient and productive agricultural crops.
- Soil Health: The ecosystem services provided by grasslands, such as soil erosion control and nutrient cycling, are fundamental for maintaining fertile soils necessary for crop production.
By integrating grassland conservation with agricultural practices, we can ensure the sustainability of food production systems, support rural economies, and contribute to global food security.
Recreational, Cultural, and Aesthetic Values
Grasslands offer more than just ecological benefits; they are places of beauty, recreation, and cultural significance. These vast open spaces inspire, heal, and connect us to the natural world and our heritage.
- Outdoor Recreation: Grasslands provide a venue for a variety of recreational activities such as hiking, bird watching, and photography, contributing to physical and mental well-being.
- Cultural Heritage: Many grasslands are sites of cultural importance, preserving the history and traditions of indigenous peoples and local communities who have lived in harmony with these landscapes for centuries.
- Aesthetic Inspiration: The unique beauty of grasslands, with their sweeping vistas, diverse flora and fauna, and changing seasons, inspires artists, writers, and musicians, enriching our culture and sense of place.
- Educational Value: Grasslands serve as outdoor classrooms, offering invaluable opportunities for environmental education, conservation awareness, and research into sustainable land management practices.
Protecting grasslands ensures the preservation of their recreational, cultural, and aesthetic values, fostering a deeper appreciation for nature and our shared human heritage.
Ecosystem Services of Grasslands
\"Discover the beauty and diversity of grasslands in this captivating video! Immerse yourself in stunning landscapes and learn about the fascinating flora and fauna that thrive in these vibrant ecosystems. Join us on a journey through the grasslands and gain a deeper appreciation for the essential role they play in sustaining life on our planet.\"
Understanding Ecosystem Services
\"Learn how ecosystem services powerfully contribute to our well-being and the health of our planet in this must-watch video! Explore the countless ways in which our natural environment provides us with crucial services such as clean air, clean water, and climate regulation. Gain a new understanding of the importance of conserving and preserving these ecosystems for future generations.\"
READ MORE:
Grasslands in Pollination and Habitat Provision
Grasslands are critical for supporting pollination services and providing habitats for a myriad of species. These ecosystems foster a symbiotic relationship between plants and pollinators, ensuring the survival and proliferation of both.
- Support for Pollinators: Grasslands offer food and shelter for a wide range of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, birds, and bats, which are essential for the pollination of many plant species, contributing to biodiversity and food security.
- Diverse Habitats: The varied microenvironments within grasslands support diverse flora and fauna, offering niches for many species to thrive. This diversity ensures ecosystem resilience and stability.
- Source of Biodiversity: Grasslands act as a reservoir of genetic diversity, which is crucial for species adaptation to changing environmental conditions and for the continued evolution of flora and fauna.
- Connectivity Between Ecosystems: Grasslands often serve as ecological corridors that connect different habitats, facilitating the movement of species and contributing to landscape-level biodiversity conservation.
The preservation of grasslands is vital for maintaining pollination services and habitat provision, underpinning the health of global ecosystems and the services they provide to humanity.
Grasslands are vital ecosystems, offering unparalleled services that sustain biodiversity, regulate climate, and support human well-being. Their conservation is essential for a healthy planet and a hopeful future.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/164249141-56a006353df78cafda9fb0e5-be1ea8f1f1774e12bde868a948812d8d.jpg)