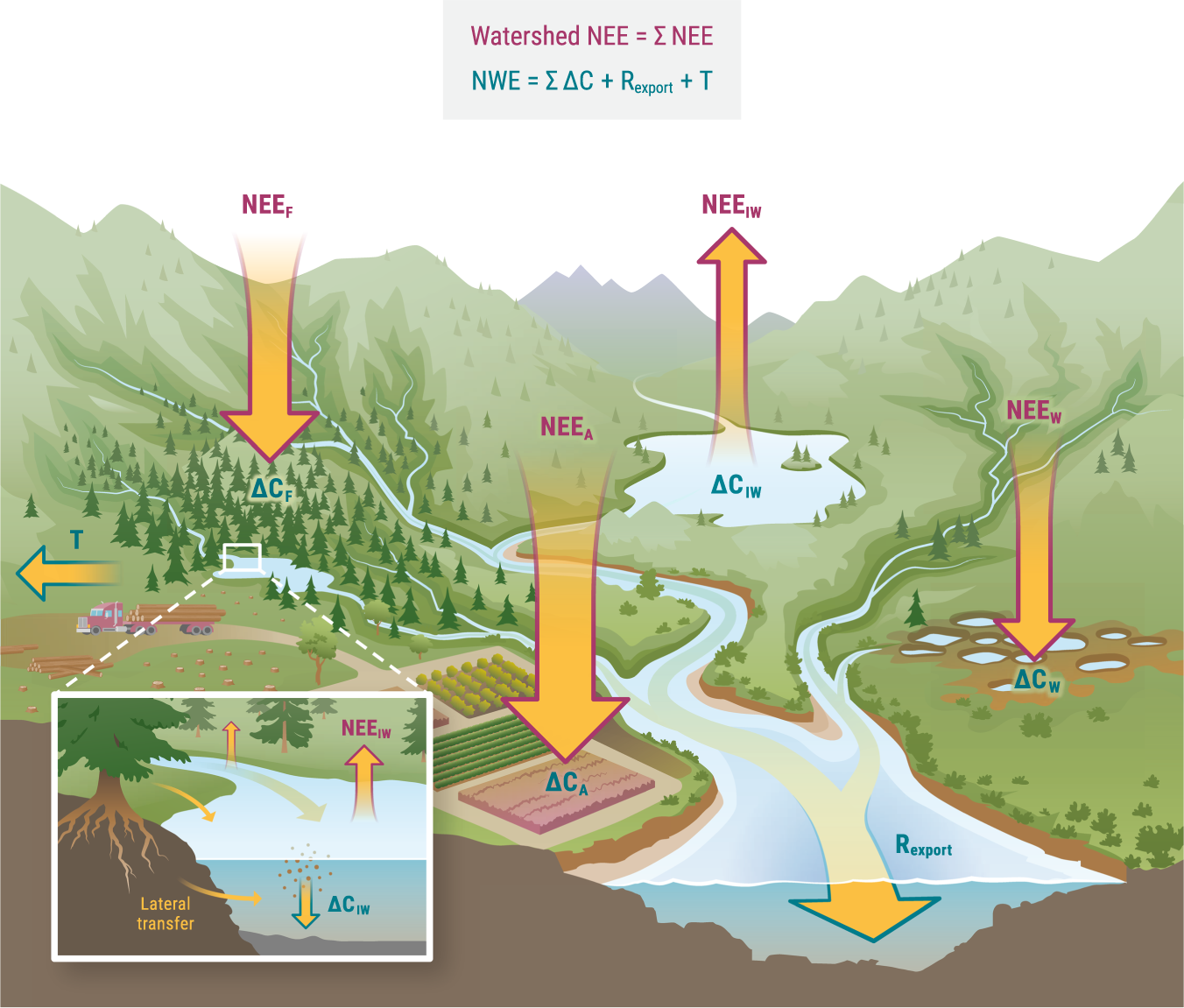
Topic easy ecosystem drawing: Discover the joy of creating your own ecosystems with our easy drawing guide, perfect for artists and nature enthusiasts of all skill levels. Unleash your creativity and bring the natural world to life on paper!
Table of Content
- How to create an easy ecosystem drawing?
- Understanding Ecosystems
- Steps to Draw Various Ecosystems
- Project Ideas for Visualizing Ecosystems
- Illustrating Ecosystem Interactions
- Creating Ecosystem Worksheets
- Assessing Understanding Through Drawing
- YOUTUBE: How to Draw Freshwater Ecosystem
- Exploring Ecosystem Components
How to create an easy ecosystem drawing?
Creating an easy ecosystem drawing can be a fun and educational activity. Here are the steps to help you create your drawing:
- Start by gathering your materials. You will need paper, a pencil or pen, and coloring tools like markers or colored pencils.
- Decide on the type of ecosystem you want to depict. It could be a forest, a desert, a pond, or any other ecosystem that interests you.
- Sketch the basic outline of the ecosystem on your paper. This could include the land, water bodies, and any prominent features like trees or rocks. Keep the shapes simple and easy to draw.
- Add the living organisms to your drawing. Think about the different plants and animals that exist in your chosen ecosystem. Start with the larger organisms and then gradually add smaller ones. You can use basic shapes and lines to represent the organisms.
- Add details to your drawing. This could include features like leaves on trees, scales on fish, or patterns on insects. Take your time and be creative with the details.
- Color your drawing to bring it to life. Use colors that are commonly found in the ecosystem you are depicting. For example, if it is a forest, you might use shades of green for the trees and brown for the soil.
- Once you are satisfied with your drawing, you can outline it with a pen or marker to make it stand out.
- You can also label the different organisms in your drawing to make it more informative.
Remember, the key to creating an easy ecosystem drawing is to keep it simple and have fun with it. Don\'t worry about making it perfect - the process itself is a great learning experience. Enjoy exploring and creating your own mini ecosystem on paper!
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystems
An ecosystem comprises all living things in a given area, interacting with each other and their non-living environments such as air, water, and mineral soil. These systems are the foundation of our planet"s biology, supporting life processes and biodiversity.
- Components of Ecosystems: Ecosystems consist of biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components. Biotic components include plants, animals, and microorganisms, while abiotic components encompass sunlight, water, air, and minerals.
- Energy Flow: Energy flows through an ecosystem via the food chain, starting with producers (usually plants) that create food through photosynthesis, then to consumers (animals and humans) that eat the plants, and finally to decomposers that break down dead matter.
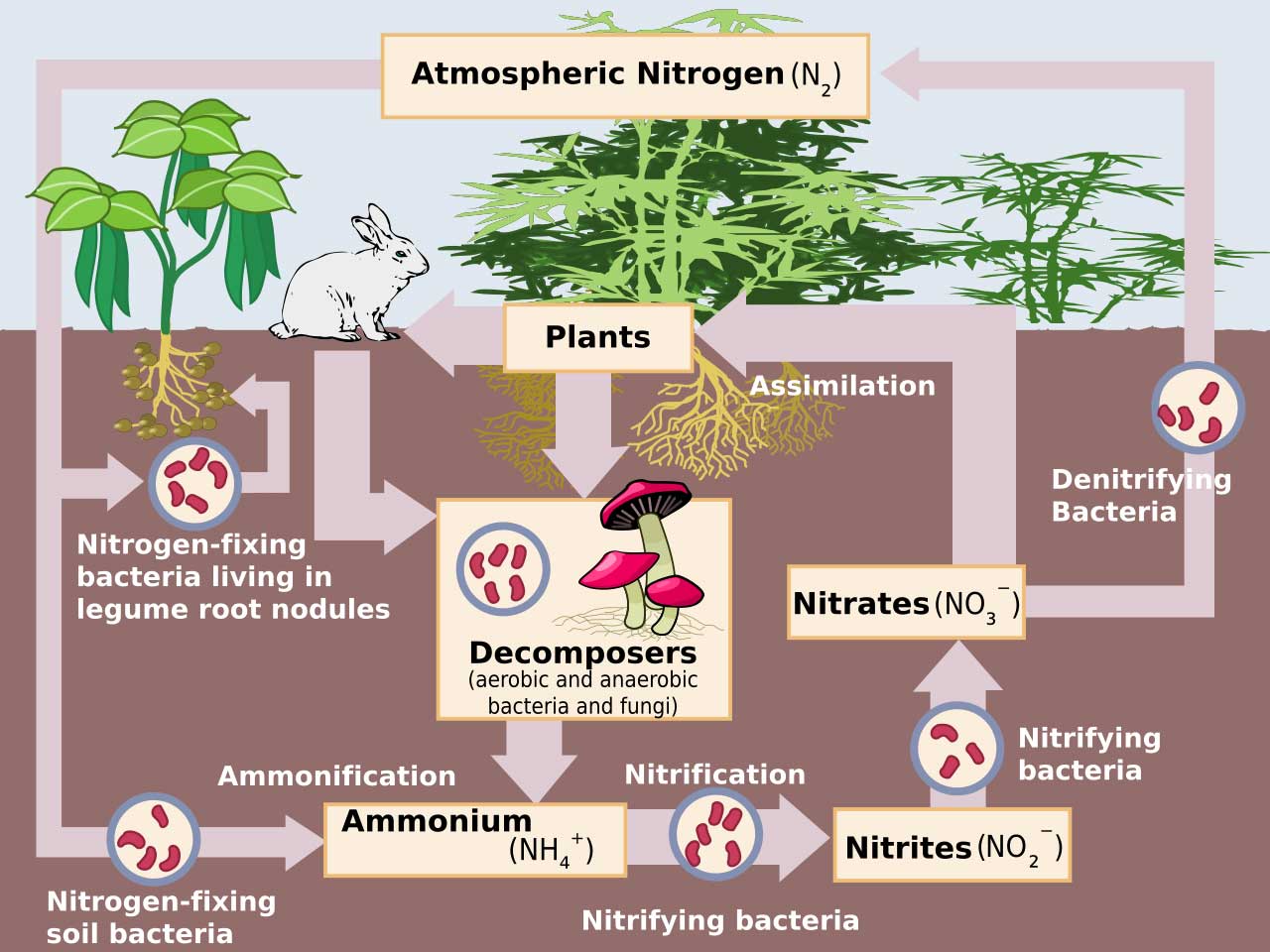
- Cycles of Matter: Matter cycles within ecosystems in various forms, such as the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle, ensuring that essential elements are recycled and available for all living organisms.
- Diversity and Stability: Biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem stability. Diverse ecosystems are more resilient and can better withstand environmental changes and disturbances.
Understanding the delicate balance of ecosystems is vital for conservation efforts and ensuring the longevity of our planet"s diverse habitats and the species that inhabit them.

Steps to Draw Various Ecosystems
Drawing ecosystems can be a fun and educational way to learn about the environment. Whether you"re interested in depicting a lush rainforest, a serene aquatic ecosystem, or a vibrant desert landscape, follow these steps to bring various ecosystems to life on paper.
- Choose Your Ecosystem: Decide on the type of ecosystem you want to draw, such as forest, desert, marine, or grassland.
- Gather References: Look up images and information about your chosen ecosystem to understand its key components and inhabitants.
- Sketch the Layout: Begin with a light pencil sketch to outline the main elements of your ecosystem, including landforms, water bodies, and vegetation.
- Add Biotic Elements: Draw the living components, such as animals, plants, and trees, placing them according to their natural habitat within the ecosystem.
- Illustrate Abiotic Factors: Include non-living elements like rocks, soil, and water. Show how these support the biotic components and create a complete ecosystem.
- Detail and Texture: Add details to your drawing to make it more realistic. Use textures to differentiate between various elements like fur, leaves, and water.
- Color Your Ecosystem: Carefully color your ecosystem, considering the natural colors found in your chosen environment. Use shading to add depth and dimension.
- Label Important Elements: Optionally, label key parts of your ecosystem to educate viewers about the different components and their roles.
Remember, the goal is to represent the interconnectedness of life and its environment. Take your time, enjoy the process, and express your creativity as you explore the beauty of natural ecosystems through art.
Project Ideas for Visualizing Ecosystems
Visualizing ecosystems through creative projects is a fantastic way to deepen understanding of environmental science and biodiversity. Here are some engaging project ideas that educators, students, and nature enthusiasts can explore to bring ecosystems to life.
- Create an Ecosystem Diorama: Use shoeboxes and craft materials to construct three-dimensional models of ecosystems. This project can be adapted to represent various habitats, such as rainforests, deserts, or coral reefs.
- Design an Ecosystem Poster: Combine drawing, painting, or digital art tools to create informative posters showcasing different ecosystems. Include key species, flora, and fauna, along with interesting facts about their interconnections.
- Ecosystem in a Bottle: Build a self-sustaining ecosystem in a sealed bottle or terrarium. This project illustrates the cycles of water, air, and life in a contained environment, demonstrating the balance of ecosystems.
- Interactive Ecosystem Maps: Create interactive maps using paper, fabric, or digital tools. These maps can feature movable pieces representing animals and plants, allowing for exploration of food chains and habitats.
- Ecosystem Animation Projects: Use stop motion animation or digital animation tools to bring ecosystem stories to life. Animations can show predator-prey interactions, seasonal changes, or the impact of human activities on natural habitats.
- Field Guide Creation: Research and compile a field guide for a local ecosystem. Include drawings, photographs, and descriptions of species found in the area, emphasizing the role each plays in the ecosystem.
These projects not only foster creativity but also encourage a deeper connection with the natural world, enhancing awareness and appreciation for the complexity and beauty of ecosystems.
Illustrating Ecosystem Interactions
Illustrating ecosystem interactions is key to understanding the dynamic balance between organisms and their environment. This section provides insights into depicting these complex relationships through art, enhancing both learning and appreciation for the natural world.
- Identify Key Species: Begin by identifying primary producers, consumers, and decomposers in your chosen ecosystem. Understanding these roles is crucial for illustrating realistic interactions.
- Draw Food Chains and Webs: Visualize the food chain by drawing arrows from prey to predator, highlighting the flow of energy. Expand this into a food web to show the interconnectedness of different species.
- Showcase Habitats: Accurately depict the physical environment where these interactions occur. Include elements like water bodies, terrain, and vegetation to provide context for the relationships being illustrated.
- Illustrate Symbiotic Relationships: Highlight symbiotic relationships such as mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Use visual cues to demonstrate how different species benefit from or harm each other.
- Depict Seasonal Changes: Show how ecosystem interactions vary with seasons. Illustrate changes in behaviors, migrations, and plant life through different seasonal scenes.
- Address Human Impact: Include elements that show human influences on ecosystems, such as pollution, deforestation, and urbanization, to raise awareness of environmental conservation.
By meticulously illustrating these interactions, artists and educators can convey the delicate balance of ecosystems, fostering a deeper understanding and respect for the complexity of life on Earth.
Creating Ecosystem Worksheets
Creating ecosystem worksheets is an effective way to engage students and enthusiasts in exploring the complexity of ecosystems. These worksheets can help reinforce concepts, assess understanding, and stimulate curiosity about the natural world.
- Choose an Ecosystem Theme: Decide on the focus of your worksheet, such as tropical rainforests, deserts, marine ecosystems, or polar habitats.
- Outline Key Concepts: Include sections on biotic and abiotic elements, food chains and webs, energy flow, and ecosystem dynamics.
- Design Interactive Activities: Incorporate matching exercises, labeling diagrams, crossword puzzles, and fill-in-the-blanks to make learning dynamic and engaging.
- Include Visual Elements: Use diagrams, pictures, and maps to visualize concepts. Encourage learners to color, label, and annotate these visuals.
- Provide Real-World Scenarios: Add case studies or hypothetical scenarios that challenge students to apply what they have learned to solve problems or predict outcomes in real ecosystems.
- Encourage Critical Thinking: Include questions that prompt analysis, evaluation, and synthesis of information, such as comparing different ecosystems or assessing human impacts.
- Add Resources for Further Exploration: Suggest websites, documentaries, and books for students eager to delve deeper into ecosystem studies.
With these steps, educators can create comprehensive and interactive worksheets that not only educate but also inspire students to appreciate the intricacies of ecosystems and their importance to our planet.

Assessing Understanding Through Drawing
Using drawing as a tool for assessment offers a unique and insightful way to evaluate comprehension of ecosystem concepts. This approach encourages learners to express their understanding creatively and visually, providing educators with a window into their cognitive processes.
- Set Clear Objectives: Before the drawing activity, outline what concepts or knowledge areas you aim to assess, such as food chains, biodiversity, or ecosystem services.
- Provide Guidelines: Give students a brief overview of what their drawings should include, such as specific biotic and abiotic elements, to ensure that the assessment criteria are clear.
- Encourage Creativity: Allow flexibility in how students represent their understanding. Encourage the use of symbols, annotations, and various colors to depict different elements of the ecosystem.
- Include Descriptive Labels: Ask students to label key components and interactions in their drawings. This not only aids in assessment but also reinforces vocabulary and concepts.
- Facilitate Reflection: After the drawing, have students explain their artwork. This reflection can provide deeper insights into their understanding and allow for immediate feedback.
- Use a Rubric: Develop a scoring guide based on accuracy, creativity, completeness, and understanding. This will help in providing objective feedback to students.
- Incorporate Peer Review: Encourage students to share their drawings with peers for review. This collaborative process can enhance learning through discussion and constructive criticism.
Assessing understanding through drawing not only makes learning more engaging but also allows for a comprehensive evaluation of students" grasp of complex ecosystem concepts in a visually intuitive manner.
How to Draw Freshwater Ecosystem
Dive into the captivating world of freshwater! Discover the awe-inspiring beauty of crystal-clear lakes, vibrant aquatic life, and the peaceful serenity that only freshwater can provide. This video will take you on an exploration of breathtaking landscapes and introduce you to the fascinating creatures that call these pristine waters home.
How to Draw Pond Ecosystem
Delve into the enchanting realm of ponds! Immerse yourself in the tranquility of still water, surrounded by lush greenery and delicate wildlife. Let this video transport you to a world where lily pads gently sway in the breeze and turtles gracefully glide through the calm, inviting waters of a pond.
READ MORE:
Exploring Ecosystem Components
Understanding the various components of an ecosystem is crucial for grasping how ecosystems function and support diverse life forms. Ecosystems are complex networks of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) elements that interact within a system. Here"s how to explore these components in detail:
- Biotic Elements: These are the living components of an ecosystem, which include:
- Producers or autotrophs, like plants and algae, that create their own food through photosynthesis.
- Consumers or heterotrophs, which can be further divided into primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores that eat herbivores), and tertiary consumers (carnivores that eat other carnivores).
- Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, that break down dead organisms, returning essential nutrients to the environment.
- Abiotic Elements: These are the non-living parts of an ecosystem that influence the living organisms, including:
- Water, air, minerals, and soil, which provide the essential elements and compounds organisms need to live.
- Sunlight, which is the primary source of energy for ecosystems, particularly for photosynthesis in plants.
- Temperature and climate, which determine the types of organisms that can survive in an ecosystem.
- Interactions and Relationships: Explore how biotic and abiotic elements interact, such as:
- Pollination of plants by animals, which is essential for the reproduction of many plants.
- The role of predators in controlling the population sizes of other species, thus maintaining balance within the ecosystem.
- Nutrient cycling through decomposition, which replenishes the soil and supports new life.
By examining these components and their interactions, we gain insights into the delicate balance of ecosystems and the importance of each element in sustaining life on Earth.
Embarking on the journey of ecosystem drawing not only nurtures your artistic skills but also deepens your appreciation for the intricate web of life. Let these insights inspire you to explore, create, and connect with the natural world around you.