Topic sonoran desert ecosystem: Explore the vibrant Sonoran Desert ecosystem, a unique blend of diverse wildlife, stunning landscapes, and rich cultural heritage, promising an enlightening journey into nature"s marvels.
Table of Content
- What is the biodiversity of the Sonoran Desert ecosystem in North America?
- Overview of the Sonoran Desert Ecosystem
- Unique Flora and Fauna of the Sonoran Desert
- Geographical Features and Climate
- YOUTUBE: Sonoran Desert Wildlife
- Conservation Efforts and Challenges
- Human Impact and Cultural Significance
- Research and Education in the Sonoran Desert
- Ecotourism and Sustainable Practices
- Future Prospects and Climate Change Impact
What is the biodiversity of the Sonoran Desert ecosystem in North America?
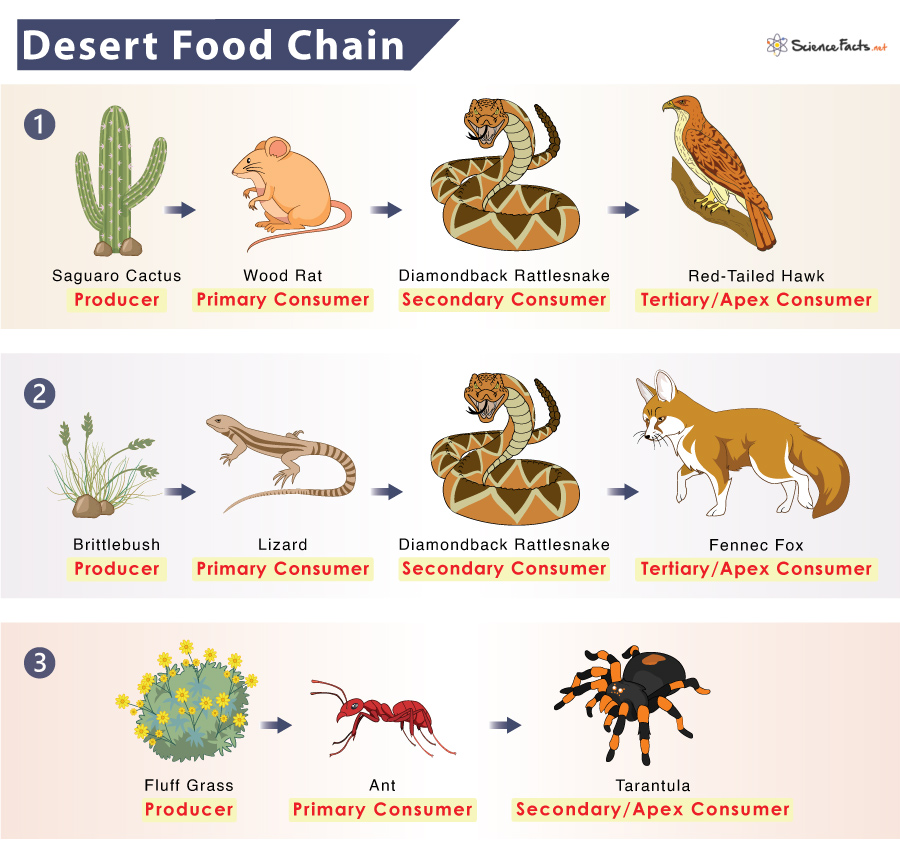
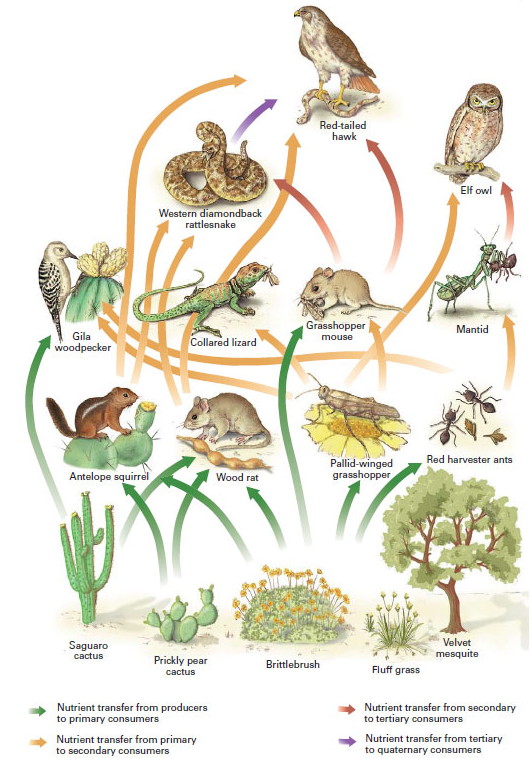
The Sonoran Desert ecosystem in North America is known for its remarkable biodiversity. It is considered to have the greatest species diversity among all deserts in North America.
To further understand the biodiversity of the Sonoran Desert ecosystem, let\'s examine some key points:
- The ecosystem is home to a wide variety of mammals, reptiles, birds, and other wildlife species.
- It offers a unique habitat for numerous plant species, including cacti, shrubs, and succulents.
- The desert serves as a crucial corridor for migration and habitat connectivity, supporting the movement of various species.
- Due to its favorable climate, many animals and plants have developed specialized adaptations to survive in this arid environment.
- The Sonoran Desert ecosystem has numerous distinct microhabitats, such as desert washes, rocky slopes, and sand dunes, which further contribute to its biodiversity.
- The presence of diverse ecosystems within the Sonoran Desert, such as desert grasslands, riparian areas, and mountain ranges, further enhances its overall biodiversity.
- The ecosystem\'s biodiversity also extends to its insect population, with a multitude of species found within the desert.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to preserve and protect the Sonoran Desert\'s unique biodiversity, as human development and climate change pose threats to this fragile ecosystem.
Overall, the Sonoran Desert ecosystem in North America stands out for its exceptional biodiversity, supporting a wide range of plant and animal species uniquely adapted to the arid conditions of the desert.
READ MORE:
Overview of the Sonoran Desert Ecosystem
The Sonoran Desert, sprawling across the Southwestern United States and Northwestern Mexico, stands as a testament to the resilience and diversity of life in arid environments. This vast expanse, characterized by its hot desert climate, is home to a remarkable array of plants and animals adapted to thrive in its extreme conditions.
Geographically, the Sonoran Desert encompasses parts of Arizona and California in the U.S., as well as significant portions of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur in Mexico. It is uniquely positioned around the northern end of the Gulf of California, making it distinct from its neighboring deserts with its subtropical warmth and bi-seasonal rainfall patterns, contributing to its high biodiversity.
The desert is renowned for its iconic saguaro and organ pipe cacti, which stand as symbols of its rich flora. The landscape is a mosaic of various sub-regions and elevations, each hosting unique ecosystems. From the Colorado Desert in California to the diverse Sky Island regions, the Sonoran Desert is a complex tapestry of life. These Sky Islands, in particular, are biodiversity hotspots, providing habitat to a wide range of species from birds to mammals and hosting over 2,100 plant species.
Climate-wise, the Sonoran Desert experiences warm temperatures year-round with rainfall that is both infrequent and irregular, making it the most tropical desert in North America. This climate supports a variety of ecosystems, from arid lowlands to lush high-elevation forests, contributing to the desert"s status as a biological treasure trove.
Conservation efforts are crucial in this region due to its ecological significance and the pressures of human activity and climate change. The Sonoran Desert not only offers a window into the adaptability of life in extreme environments but also serves as a vital area for scientific research, conservation, and appreciation of natural beauty.
Unique Flora and Fauna of the Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert, a vast and vibrant ecosystem, is celebrated for its exceptional biodiversity, housing an array of unique flora and fauna. This desert is not only the most biologically diverse of the North American deserts but also one of the most species-rich dry regions in the world.
Flora
The plant life in the Sonoran Desert is both diverse and fascinating, with over 2,000 native plant species thriving in its varied climates. The desert is famously home to the iconic saguaro cactus, recognized as the signature plant of the region. Other common plant species include:
- Barrel Cactus
- Organ-Pipe Cactus
- Prickly Pear
- Cholla
- Ocotillo
- Yucca
- Century Plant
- Ironwood
- Palo Verde
- Elephant Tree
- Mesquite
- Creosote Bush
Endemic to Baja California are the cardon, akin to the saguaro but capable of reaching up to 60 feet in height, and the distinctive boojum tree.
Fauna
The Sonoran Desert is a sanctuary for a wide range of animal species, each uniquely adapted to the desert"s harsh conditions. The desert is home to more than 100 reptile species, 60 mammal species, and 350 bird species. Notable wildlife includes:
- Desert Bighorn Sheep
- Mule Deer
- Collared Peccaries (Javelinas)
- Mountain Lions
- Cactus Ferruginous Pygmy Owl
- American Jaguar
These species not only survive but thrive in the Sonoran Desert, as long as their habitats remain intact. However, increasing human activities and climate change pose significant threats to this delicate ecosystem, making conservation efforts more critical than ever.
Geographical Features and Climate
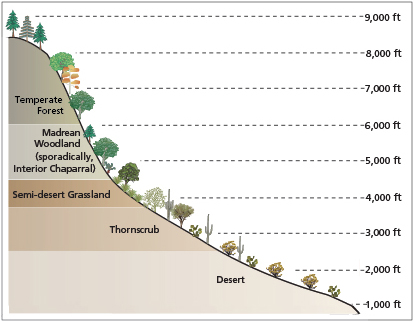
The Sonoran Desert, spanning over 120,000 square miles across the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico, is distinguished by its unique geographical features and diverse climate. This desert encompasses parts of Arizona, California, and extends into the Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur. Its landscape is marked by a mix of alluvial basins and rugged mountain ranges, creating a variety of habitats.
The climate of the Sonoran Desert is characterized by its subtropical nature, making it the most tropical desert in North America. It experiences two distinct seasons of rainfall: the summer monsoon brings sudden, intense storms, while lighter precipitation occurs in winter. Average annual rainfall ranges from 3 to 15 inches, depending on the region. Temperature extremes can surpass 120°F in summer, especially near the lower Colorado River, while frosts are rare.
Notable sub-regions within the Sonoran Desert include the Colorado Desert of southeastern California and the Yuma Desert in southwest Arizona. The desert also features the Gran Desierto de Altar, home to North America"s only active erg dune region, and the Sky Island Region, which boasts a high diversity of bird and mammal species due to its elevation gradient.
Environmental conservation is vital in this region to protect its unique ecosystems and the diverse flora and fauna they support. The Sonoran Desert is not only a place of natural beauty but also a crucial area for biodiversity, research, and education.
Sonoran Desert Wildlife
Get ready for an incredible adventure in the wild world of wildlife! From majestic lions to playful dolphins, this captivating video is guaranteed to leave you in awe of nature\'s most extraordinary creatures. Don\'t miss the chance to witness the beauty and diversity of wildlife in all its glory!
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Conservation in the Sonoran Desert is marked by multifaceted efforts aimed at addressing the diverse challenges this unique ecosystem faces. The Nature Conservancy, along with the Conservation Biology Institute, developed a comprehensive management framework to tackle threats like development, habitat fragmentation, and invasive species. This framework emphasizes regional cooperation among land managers to enhance conservation efficiency despite financial and logistical constraints.
In Saguaro National Park, the invasive buffelgrass poses a significant threat by fueling wildfires and outcompeting native species, transforming the desert"s landscape. Efforts to control this invasive species have been bolstered by funding from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, enabling more extensive and effective eradication measures. Techniques include spot spraying from helicopters and the formation of specialized teams to tackle difficult terrains.
The Sonoran Desert Conservation Plan (SDCP), initiated by Pima County, aims to guide growth without compromising the desert"s natural beauty and biodiversity. Key components of the SDCP include habitat conservation for numerous species, adoption of land use guidelines to protect ecological and cultural resources, and the development of a comprehensive open space preserve system funded by public bonds.
Despite these efforts, challenges persist due to rapid urbanization, climate change, and the need for continuous funding and public support. The success of conservation initiatives in the Sonoran Desert hinges on ongoing collaboration between government agencies, non-profit organizations, and the community to adapt and respond to emerging threats.
Saguaro Cactus and the Sonoran Desert Ecosystem
Embark on a journey to the enchanting desert landscapes filled with vibrant and resilient cacti. Discover the hidden beauty of these fascinating plants as you delve into the captivating world of cacti. Prepare to be amazed by intricate formations and stunning blooms in this mesmerizing video!
Human Impact and Cultural Significance
The Sonoran Desert has been shaped by human activity for over 10,000 years, starting with Paleoindian hunters and progressing through various cultural periods including the Archaic, Hohokam, and historic eras. Each group left its mark on the desert, from the extensive canal systems and agricultural terraces of the Hohokam to the trade networks and cultural exchanges of later periods. The introduction of domesticated crops from Mesoamerica and the innovative irrigation techniques developed by these desert farmers facilitated the transition from nomadic lifestyles to more settled communities, which had a profound impact on the landscape.
European arrival brought further transformation with new crops, animals, and technologies, altering the ecosystem and indigenous ways of life. Diseases introduced by Europeans had devastating effects on the native population, leading to significant cultural and demographic shifts. The legacy of these ancestral peoples, particularly the Hohokam, is still evident in modern-day irrigation practices, agricultural products, and the continued cultural traditions of their descendants, such as the O"Odham, Hopi, and Zuni peoples.
Today, the Sonoran Desert faces challenges from urbanization, mining, ranching, and agriculture, which have led to habitat destruction and water scarcity. The desert"s history of human habitation offers valuable lessons on sustainability and conservation, underscoring the need for responsible stewardship to preserve its unique cultural and natural heritage for future generations.
- The Hohokam"s sophisticated agriculture and water management systems highlight early human innovation and adaptation to harsh desert conditions.
- The Columbian Exchange introduced by Europeans significantly altered the Sonoran Desert"s ecology and human societies.
- Current challenges such as urban sprawl and environmental degradation underscore the importance of learning from the past to protect the desert"s future.
Cultural events, archaeological sites, and museums in the region offer opportunities to explore the rich history and ongoing relationship between humans and the Sonoran Desert, emphasizing the importance of preserving its cultural and ecological integrity.
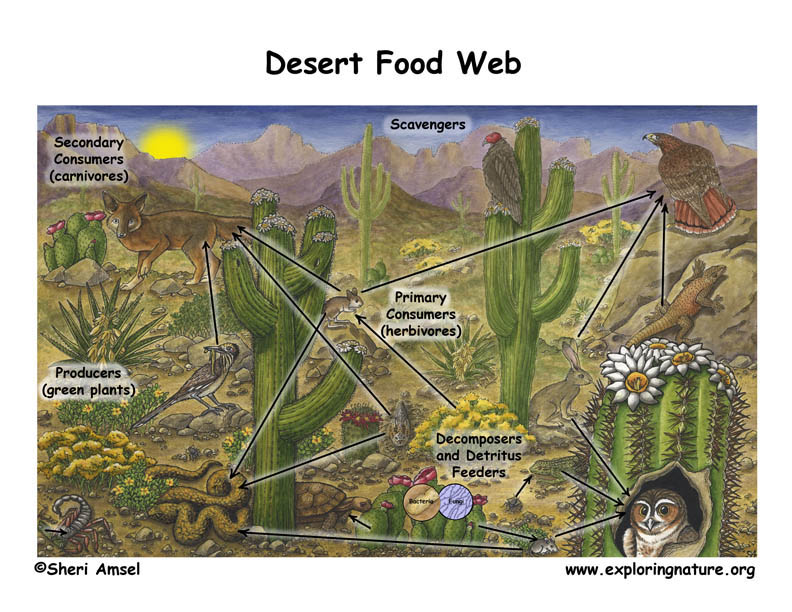
Research and Education in the Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert serves as a vibrant hub for research and education, fostering a deeper understanding of its unique ecosystems and promoting conservation efforts. The Desert Research Learning Center (DRLC), positioned adjacent to Saguaro National Park, epitomizes this mission by supporting a wide range of research projects and internships focused on natural resources. The center is equipped with laboratories, on-site housing for researchers, and outdoor spaces conducive to field trainings and educational activities. Through collaborations with public land agencies and educational institutions, the DRLC delivers programs that emphasize hands-on nature education, research dissemination, and conservation awareness.
Similarly, the McDowell Sonoran Conservancy champions environmental education through diverse programs aimed at all age groups. With initiatives like Expedition Days, the Conservancy engages elementary students in interactive learning, encouraging them to become desert advocates. The program, aligned with state curriculum standards, combines classroom-based learning with outdoor experiences to enrich students" understanding of the desert"s flora, fauna, and geological features. For adults, the Conservancy offers lectures, educational hikes, and virtual learning opportunities, all designed to deepen knowledge of the Sonoran Desert"s rich natural and cultural heritage.
The Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum"s Conservation Education & Science Department further amplifies the educational landscape by integrating scientific research with public education. This department conducts ecological research while providing a plethora of educational programs for both children and adults. Their interdisciplinary approach covers various scientific domains, ensuring that all educational content is grounded in the latest research. The museum emphasizes collaborative projects, especially with Mexican partners, acknowledging the significant portion of the Sonoran Desert and its biodiversity located in Mexico.
- Interdisciplinary research and education initiatives focus on botany, ecology, zoology, and more.
- Programs are designed for diverse audiences, including school groups, families, and individual learners.
- Outdoor education and field training opportunities facilitate hands-on learning and conservation practices.
- Collaborative efforts with Mexican organizations underscore the transboundary nature of the Sonoran Desert ecosystem.
Together, these institutions underscore the importance of integrating research and education to foster a sustainable relationship with the Sonoran Desert, promoting conservation and inspiring future generations to appreciate and protect this unique ecosystem.
Ecotourism and Sustainable Practices
The Sonoran Desert, a region celebrated for its extreme conditions and diverse ecosystem, offers unique opportunities for ecotourism and sustainable practices. Despite its arid environment, the desert supports a surprising variety of life, thanks to the remarkable adaptations of its flora and fauna. Conservation efforts play a critical role in preserving this fragile ecosystem, with a focus on implementing sustainable practices to mitigate human impact and maintain biodiversity.
As interest in desert travel grows, it"s vital to prioritize sustainable practices to protect these ecosystems. Ecotourism, which emphasizes conserving nature and supporting local communities, is key to ensuring the Sonoran Desert"s longevity. Sustainable practices for desert travel include adhering to principles like Leave No Trace, conserving resources, and choosing eco-friendly accommodations and ecotours. These practices help minimize the environmental footprint of tourism and promote the preservation of the desert"s unique landscape and biodiversity.
- Adopting minimal impact practices such as packing out all waste and minimizing disturbance to wildlife.
- Engaging with and respecting local communities, traditions, and customs.
- Choosing accommodations and tours that prioritize sustainability and conservation.
Examples of eco-tourism initiatives in deserts worldwide highlight the global importance of sustainable travel. From the Namib Desert"s walking tours that minimize environmental impact to Wadi Rum"s cultural exchange tours guided by indigenous Bedouin people, and eco-friendly experiences in the Mojave Desert, such as camping and stargazing in Joshua Tree National Park, these initiatives showcase the potential for responsible adventure in desert environments.
By embracing ecotourism and sustainable practices, visitors can enjoy the mesmerizing beauty of the Sonoran Desert and other arid landscapes while contributing to their preservation for future generations. As we plan our adventures in these captivating environments, it"s crucial to make eco-conscious choices that support conservation and sustainable tourism.

READ MORE:
Future Prospects and Climate Change Impact
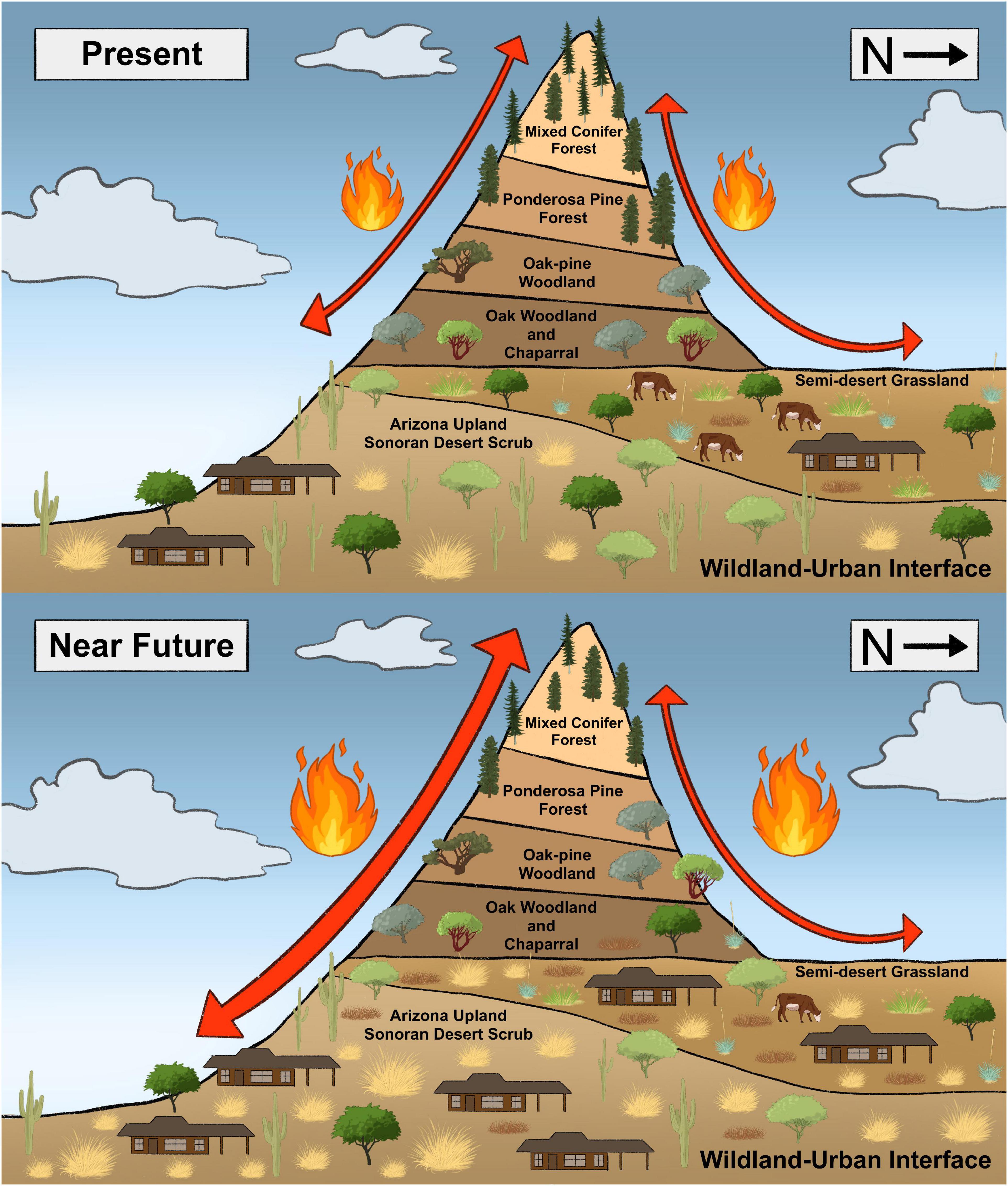
The Sonoran Desert, known for its resilience and unique biodiversity, faces significant challenges and changes due to climate change. The desert"s flora and fauna, once thought to be nearly indestructible, are showing signs of stress and transformation. Climate change is causing an increase in temperatures and erratic precipitation patterns, leading to a decline in species that were once abundant and introducing new dynamics in the ecosystem.
- Amphibians like the Chiricahua leopard frog and the Mexican spadefoot toad have been significantly affected, with some species no longer found in their traditional habitats.
- Increased air temperatures and changes in precipitation are influencing the dynamics of small mammals and lizard populations, impacting the entire food web.
- Changes in water availability are expected to affect critical water sources like seeps, springs, and tinajas, which are essential for the desert"s biodiversity.
- Uplands and forest communities may experience biome shifts, with lower elevation species moving upslope, potentially leading to the loss of mixed-conifer ecosystems and the species that depend on them.
- Landbirds and other fauna that rely on high-elevation habitats may find their living conditions altered, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem balance.
- Invasive plant species, facilitated by climate change, could further disrupt the desert"s ecological integrity by altering fire regimes and competing with native species.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for conservation and adaptation. By understanding these changes, conservationists can devise strategies to mitigate impacts and preserve the Sonoran Desert"s unique ecosystem. Cutting fossil fuel emissions and adopting sustainable practices can help alleviate some of the pressures on this delicate ecosystem.
Discover the resilience and beauty of the Sonoran Desert ecosystem, a marvel of adaptation and diversity, shaping a future of conservation and coexistence in a changing world.