Topic facts about the desert ecosystem: Discover the breathtaking resilience of the desert ecosystem, where life thrives against all odds, revealing nature"s most fascinating survival strategies and untold stories.
Table of Content
- What are some interesting facts about the desert ecosystem?
- Unique Characteristics of Desert Ecosystems
- Types of Deserts: Hot and Dry, Semiarid, Coastal, and Cold
- Flora Adaptations: Water Conservation and Sunlight Absorption
- Fauna Adaptations: Nocturnal Lifestyles and Water Conservation
- Desert Climate: Temperature Extremes and Precipitation Patterns
- Desertification: Causes, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies
- YOUTUBE: Desert Animals and Plants | Desert Ecosystem | Desert Video for Kids
- Biodiversity in Deserts: Endemic Species and Ecological Importance
- Human Life in Deserts: Cultures, Economies, and Challenges
- Conservation Efforts: Protecting Fragile Desert Ecosystems
- Role of Deserts in the Global Ecosystem
What are some interesting facts about the desert ecosystem?
Deserts, as unique ecosystems, have several interesting facts worth knowing. Here are some of them:
- Deserts are incredibly dry environments with very little rainfall, making them the driest places on Earth.
- There are different types of deserts, including hot and dry deserts, cold deserts, coastal deserts, and semiarid deserts.
- Despite their extreme conditions, deserts are home to a variety of specially adapted plants and animals.
- Camels are well-known desert animals, perfectly adapted to the harsh desert environment with features like humps for water storage and long eyelashes to protect their eyes from blowing sand.
- Desert plants have unique survival strategies, such as succulents that store water in their leaves or stems, and cacti with spines that reduce water loss.
- The Sahara Desert in Africa is the largest hot desert in the world, covering an area of around 3.6 million square miles.
- Deserts can be quite cold at night due to the absence of cloud cover, which allows heat to quickly radiate into space.
- Some deserts, known as coastal deserts, are located near the sea and experience cool summers and mild winters.
- Sand dunes are prominent features of many deserts, formed by wind-blown sand and constantly changing due to their movement.
- Despite their arid nature, deserts can still support life, including insects, reptiles, small mammals, and birds that have adapted to the harsh conditions.
These are just a few fascinating facts about the desert ecosystem, highlighting the incredible adaptability of life in such extreme environments.
READ MORE:
Unique Characteristics of Desert Ecosystems
Deserts are remarkable biomes defined by their dry conditions, yet they are brimming with life uniquely adapted to thrive in such harsh environments. Below are the key features that distinguish desert ecosystems:
- Low Precipitation: Deserts typically receive less than 250 mm of rain per year, creating arid conditions where only the hardiest of life forms can flourish.
- Extreme Temperatures: Desert temperatures can swing dramatically, from scorching daytime heat to chilly nights, challenging the survival of its inhabitants.
- Specialized Flora: Plants like cacti have evolved to store water and reduce water loss, showcasing incredible adaptations to minimal rainfall.
- Adapted Fauna: Animals have developed unique survival strategies, such as nocturnal lifestyles to avoid daytime heat and conserve water.
- Soil Composition: Desert soils are often sandy, rocky, and low in organic matter, limiting plant life but also supporting a diverse microbial community.
- Wind Erosion: With little vegetation to anchor the soil, winds can reshape the landscape, creating dunes and other landforms unique to deserts.
These characteristics not only define the desert ecosystem but also highlight the resilience and adaptability of life in one of Earth"s most extreme environments.

Types of Deserts: Hot and Dry, Semiarid, Coastal, and Cold
Deserts are not a monolith; they vary widely in climate, location, and characteristics. Here"s a closer look at the four main types of deserts found around the world:
- Hot and Dry Deserts: These are the quintessential deserts, like the Sahara, characterized by extreme heat during the day and cold at night, with very sparse rainfall.
- Semiarid Deserts: Also known as steppe deserts, these areas, such as the sagebrush of North America, experience slightly more rainfall than their hot and dry counterparts, supporting a more diverse range of life.
- Coastal Deserts: Found along coastal areas, these deserts, like the Namib, receive fog and mist but little rain, creating unique ecosystems with plants and animals adapted to harvest moisture from the air.
- Cold Deserts: Located in regions like the Gobi, these deserts experience cold winters with snow, and their summers are cool compared to hot deserts, offering a different set of survival challenges.
Each desert type supports a unique ecosystem, showcasing the adaptability of life in diverse conditions and the importance of these habitats in the global ecological balance.
Flora Adaptations: Water Conservation and Sunlight Absorption
Desert plants exhibit remarkable adaptations that allow them to survive in an environment with intense sunlight and minimal water. These adaptations are crucial for their survival and reproduction:
- Thick, Waxy Cuticles: Many desert plants have thick, waxy skins on their leaves or stems to minimize water loss through evaporation.
- Deep Root Systems: To access water from deep underground, some desert plants develop extensive root systems that can reach far below the surface.
- Reduced Leaf Surface Area: Plants like cacti reduce their leaf surface area to spines, decreasing water loss and providing defense against herbivores.
- Water Storage: Succulents, such as agaves and aloes, store water in their leaves, stems, or roots to use during dry periods.
- Photosynthesis Adaptations: Many desert plants use a special form of photosynthesis called CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) that allows them to take in CO2 at night and reduce water loss during the hot day.
- Reflective Surfaces: Some plants have shiny leaves or stems that reflect sunlight, helping to keep the plant cool and reduce water loss.
These adaptations not only allow desert flora to thrive under extreme conditions but also contribute to the biodiversity and stability of the desert ecosystem.

Fauna Adaptations: Nocturnal Lifestyles and Water Conservation
Animals in the desert have evolved fascinating adaptations to cope with the extreme temperatures and scarcity of water. These adaptations help them conserve water, avoid heat, and thrive in their arid environments:
- Nocturnal Behavior: Many desert animals are nocturnal, becoming active at night to avoid the extreme heat of the day. This includes mammals, reptiles, and insects.
- Water Conservation: Desert fauna have developed ways to minimize water loss, such as producing highly concentrated urine and dry feces. Some species can go for long periods without drinking, obtaining moisture from their food.
- Burrowing: Animals like rodents and reptiles burrow underground to escape the heat during the day and conserve moisture.
- Heat Tolerance: Some desert animals have high tolerance to body temperature fluctuations, allowing them to endure the heat without overheating.
- Camouflage: Many desert animals have coloration that blends with their surroundings, providing camouflage from predators and helping them ambush prey.
- Efficient Hunting and Foraging: Desert predators are often highly efficient hunters, conserving energy until the perfect moment to strike, while herbivores are adapted to forage for nutrient-rich plants that can sustain them.
These adaptations are essential for survival, showcasing the resilience and ingenuity of life in one of the planet"s most challenging habitats.
Desert Climate: Temperature Extremes and Precipitation Patterns
The climate of desert regions is characterized by challenging conditions, including significant temperature extremes and limited precipitation, which shape the ecosystem and its inhabitants:
- Temperature Extremes: Deserts often experience a wide range of temperatures in a single day, with scorching heat during the day and significantly cooler temperatures at night.
- Low Precipitation: Deserts are defined by their dry conditions, receiving less than 250 mm (10 inches) of rainfall annually, making water a scarce resource.
- High Evaporation Rates: The intense heat leads to high evaporation rates, quickly drying out soils and water sources.
- Seasonal Rainfall: When rain does fall, it is often in brief, heavy showers that can cause flash floods, dramatically altering the landscape in a short period.
- Sunlight Intensity: Clear skies and minimal cloud cover result in high levels of sunlight, contributing to the desert"s high temperatures.
This unique climate requires both flora and fauna to develop extraordinary adaptations for survival, making desert ecosystems among the most fascinating on Earth.

Desertification: Causes, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies
Desertification is a significant environmental challenge that transforms fertile land into desert as a result of natural and human activities. Understanding its causes, impacts, and mitigation strategies is crucial for sustainable development:
- Causes of Desertification:
- Overgrazing by livestock, which removes vegetation cover.
- Deforestation, leading to soil erosion and loss of fertility.
- Unsustainable farming practices that deplete soil nutrients.
- Climate change, increasing the frequency of droughts and altering precipitation patterns.
- Impacts of Desertification:
- Loss of biodiversity, as species that once thrived in fertile areas disappear.
- Decreased agricultural productivity, leading to food insecurity.
- Water scarcity, as the water cycle is disrupted and groundwater levels drop.
- Increased carbon emissions, as vegetation that stores CO2 is lost.
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Reforestation and afforestation projects to restore vegetation.
- Sustainable land management practices to prevent soil degradation.
- Water conservation techniques to manage scarce water resources effectively.
- Community involvement in conservation efforts to ensure sustainable practices are adopted and maintained.
Addressing desertification requires a concerted effort from global to local levels, integrating environmental conservation with socio-economic development to protect our planet for future generations.
Desert Animals and Plants | Desert Ecosystem | Desert Video for Kids
Experience the breathtaking beauty of the desert as you embark on a journey filled with towering sand dunes, golden sunsets, and a sense of tranquility that can only be found in this vast, untouched wilderness. Watch the video and let yourself be mesmerized by the wonders of the desert.
Desert Ecosystem Facts You Didn\'t Know!
Dive into the fascinating world of ecosystems and discover the delicate balance between living organisms and their environment. Join us on an immersive journey through lush forests, vibrant coral reefs, and vast grasslands in this captivating video that celebrates the wonders of nature\'s interconnectivity.
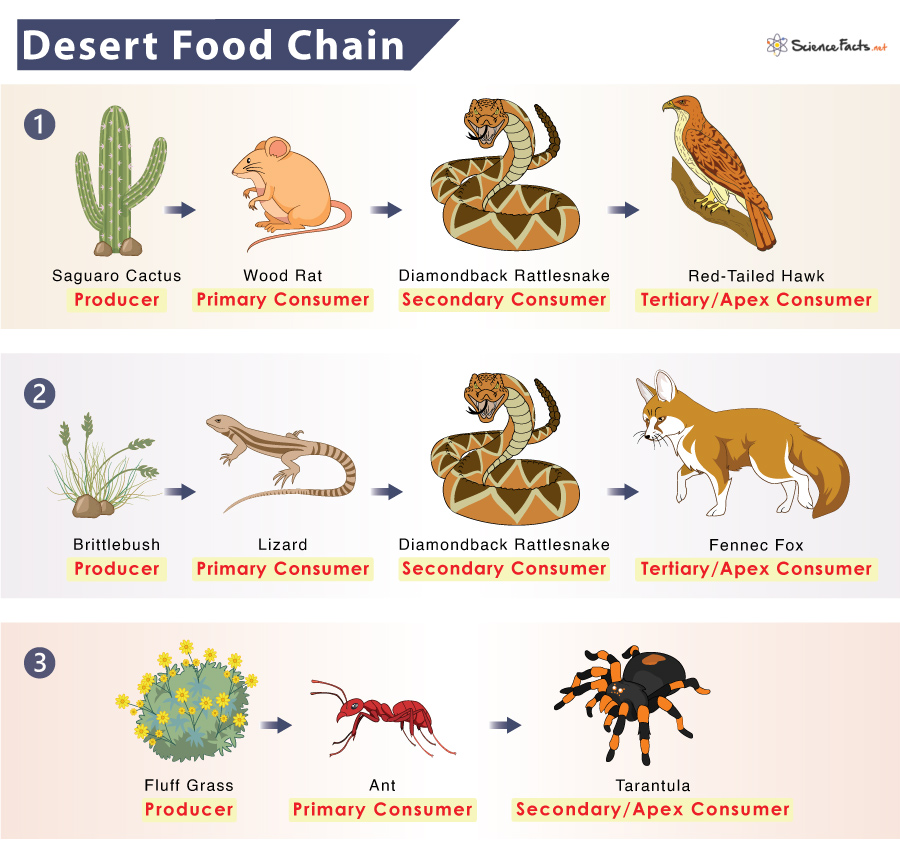
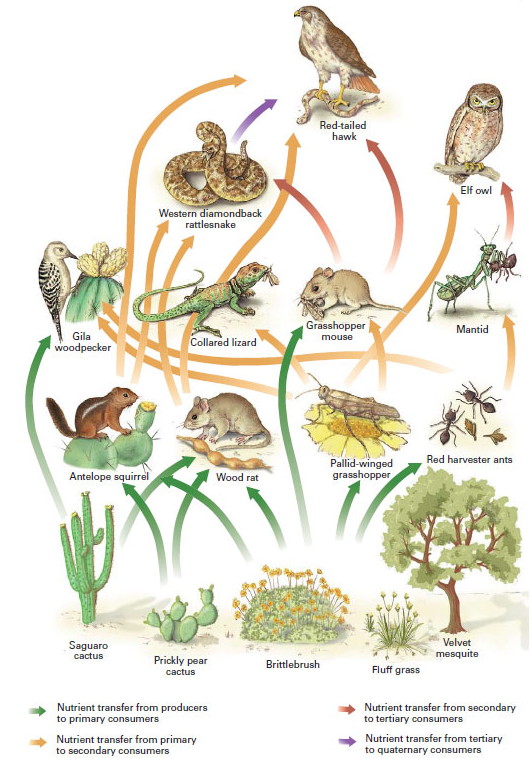
Biodiversity in Deserts: Endemic Species and Ecological Importance
Despite harsh conditions, deserts are home to a surprising array of biodiversity, including many endemic species that play crucial roles in their ecosystems:
- Endemic Species: Deserts are habitat to unique species that are found nowhere else on Earth. These include various plants, reptiles, mammals, and birds that have adapted to the extreme desert environment.
- Ecological Roles: Desert species often have specific roles, such as pollinators, seed dispersers, and predators, contributing to the ecological balance and supporting the food web.
- Adaptation Examples:
- Plants like the Saguaro cactus store water in their thick stems and open their flowers at night to be pollinated by bats.
- Animals such as the Fennec fox, with its large ears for dissipating heat and nocturnal habits to avoid daytime temperatures.
- Conservation Importance: Preserving desert biodiversity is vital for maintaining ecosystem health, supporting local livelihoods, and contributing to global biodiversity.
Understanding and protecting the unique biodiversity of deserts is essential for ecological research, conservation efforts, and appreciating the resilience of life in extreme conditions.

Human Life in Deserts: Cultures, Economies, and Challenges
Deserts, often seen as inhospitable landscapes, are home to vibrant communities with rich cultures, diverse economies, and unique challenges:
- Indigenous Cultures: Many desert regions are inhabited by indigenous peoples who have adapted their lifestyles to the harsh environment, preserving rich traditions, languages, and knowledge of the natural world.
- Economic Activities: Economies in desert areas are often based on agriculture (through irrigation), mining, tourism, and the exploitation of other natural resources, adapting to the limitations and opportunities of the desert.
- Technological Innovations: Residents have developed innovative solutions for water collection, sustainable agriculture, and habitat conservation to thrive in arid conditions.
- Challenges: Life in desert regions comes with challenges such as water scarcity, extreme temperatures, and the threat of desertification, impacting livelihoods and community well-being.
- Adaptation Strategies: Communities employ various strategies to cope with environmental challenges, including the construction of sustainable dwellings, water conservation techniques, and the development of resilient agricultural practices.
Understanding the complexities of human life in deserts highlights the resilience of communities that have found ways to flourish in some of the planet"s most challenging environments.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Fragile Desert Ecosystems
Desert ecosystems, while resilient, are vulnerable to a variety of threats, making conservation efforts vital for their protection and sustainability:
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks and protected areas to conserve habitat for native species and prevent land degradation.
- Combating Desertification: Implementing strategies to combat desertification, such as reforestation, sustainable land management practices, and water conservation techniques.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting research to understand desert ecosystems better and monitoring changes to assess the effectiveness of conservation strategies.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts, providing education on sustainable practices, and promoting eco-tourism as a sustainable income source.
- Policy and Legislation: Developing and enforcing laws and policies that protect desert environments from overexploitation and pollution.
Through these and other efforts, conservationists aim to preserve the unique beauty and biodiversity of desert ecosystems for future generations.

READ MORE:
Role of Deserts in the Global Ecosystem
Deserts play a crucial role in the Earth"s ecological balance, contributing to biodiversity, climate regulation, and even human culture and innovation:
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Deserts are home to a unique range of biodiversity, with many species adapted to the extreme conditions found only in these habitats.
- Climate Influence: Deserts affect global climate patterns by reflecting sunlight back into the atmosphere and acting as major heat sinks, influencing weather and climate far beyond their borders.
- Carbon Sequestration: Certain desert plants and soils are effective at storing carbon dioxide, playing a role in mitigating climate change.
- Cultural Significance: Deserts have been the backdrop for human history and evolution, influencing cultures, religions, and lifestyles with their unique challenges and opportunities.
- Scientific Research: The extreme conditions of deserts provide unique opportunities for scientific research, from studying life"s adaptability to extreme environments to testing space exploration technologies.
The protection and study of desert ecosystems are essential for understanding the complexities of life on Earth and ensuring the health of our global environment.
Exploring the desert ecosystem reveals a world of extraordinary adaptations and resilience, showcasing the beauty and critical importance of these habitats within our global ecological tapestry.