Topic desert ecosystem facts: Explore the captivating world of desert ecosystems, where life thrives against all odds, revealing nature"s remarkable adaptability and beauty.
Table of Content
- What are some interesting facts about desert ecosystems?
- Understanding Desert Ecosystems
- Types of Deserts: Hot, Cold, Coastal, and Semi-Arid
- Climate and Weather Patterns in Deserts
- Flora and Fauna Adaptations to Arid Conditions
- Geographical Distribution of Deserts Worldwide
- Role of Deserts in Earth"s Ecology
- YOUTUBE: Desert Biome Facts
- Conservation Efforts and Protecting Desert Habitats
- Human Life and Cultures in Desert Regions
- Desertification: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
- Exploring Desert Landscapes: Tourism and Adventure
What are some interesting facts about desert ecosystems?
Desert ecosystems are fascinating and unique environments that are home to a variety of interesting features and adaptations. Here are some interesting facts about desert ecosystems:
- Deserts cover approximately one-fifth of the Earth\'s surface.
- Desert biomes are characterized by their extremely dry conditions, receiving very little rainfall.
- Some deserts receive less than 10 inches (25 centimeters) of rain per year.
- In certain desert regions, rainfall may occur in heavy bursts rather than being evenly distributed throughout the year.
- Desert soil can be sandy, gravelly, or stony, depending on the specific desert.
- Despite the scarcity of water, desert ecosystems support a surprising variety of plant and animal life that have adapted to survive under harsh conditions.
- Plants in desert ecosystems have developed specialized mechanisms to conserve water, such as deep root systems and waxy coatings on leaves.
- Animals in deserts have evolved various physical and behavioral adaptations, such as storing water, staying active during cooler hours, and burrowing to escape extreme temperatures.
- Desert ecosystems often exhibit high temperature fluctuations, with scorching hot days and chilly nights.
- Sand dunes are common features in desert landscapes, formed by wind-blown sand.
These are just a few of the many interesting facts about desert ecosystems. Exploring the intricacies of these unique habitats reveals the remarkable adaptations and resilience of life in challenging environments.
READ MORE:
Understanding Desert Ecosystems
Desert ecosystems are unique landscapes that thrive under extreme conditions. They are defined not just by their lack of precipitation, but by their biodiversity, climate, and adaptation strategies of both flora and fauna. Understanding these ecosystems is essential to appreciating their role in the global environment.
- Climate and Conditions: Deserts are characterized by low rainfall, high evaporation rates, and significant temperature variations between day and night.
- Adaptations: Life in desert ecosystems has evolved with remarkable adaptations. Plants have adapted to conserve water, while animals have developed strategies to survive the harsh climate.
- Biodiversity: Despite harsh conditions, deserts are home to a wide range of life forms. Each organism plays a crucial role in the ecosystem"s balance.
- Geographical Diversity: Deserts span both hot and cold climates, from the Sahara"s vast dunes to the cold deserts of Antarctica, each with its unique ecosystem.
- Human Impact: Human activities, such as land use changes and climate change, pose threats to desert ecosystems. Conservation efforts are vital to protect these unique landscapes.
By understanding desert ecosystems, we can better appreciate the resilience of life and the importance of conserving these extraordinary environments for future generations.

Types of Deserts: Hot, Cold, Coastal, and Semi-Arid
Deserts are not a monolith; they vary greatly based on climate, location, and environmental conditions. Understanding the different types of deserts is crucial to appreciating their ecological diversity and the unique challenges and opportunities each presents.
- Hot Deserts: Characterized by high temperatures and low rainfall. The Sahara and the Arabian Desert are prime examples, where temperatures can soar above 50°C (122°F).
- Cold Deserts: Found in higher latitudes and altitudes, these deserts experience cold winters with snow. The Gobi and the Great Basin Desert are cold deserts with more precipitation than their hot counterparts.
- Coastal Deserts: These deserts are located along coastlines where cold ocean currents reduce precipitation. The Namib and the Atacama deserts are among the driest places on earth due to their coastal influences.
- Semi-Arid Deserts: Also known as steppe climates, these areas receive slightly more rainfall than true deserts, allowing for more diverse plant and animal life. The sagebrush of North America is an example of a semi-arid desert ecosystem.
Each type of desert supports a unique ecosystem with specially adapted plants and animals that have evolved to thrive in these extreme conditions. Understanding these classifications helps highlight the importance of targeted conservation efforts to protect these fragile environments.
Climate and Weather Patterns in Deserts
Deserts are renowned for their extreme climate and distinct weather patterns, which play a crucial role in shaping the ecosystem. Understanding these patterns is essential for comprehending how life adapts and thrives in such challenging environments.
- Low Precipitation: A defining characteristic of deserts is their low rainfall, often less than 250mm per year, which significantly impacts the availability of water for flora and fauna.
- High Temperature Variability: Deserts typically experience a wide range of temperatures in a single day, with scorching daytime heat quickly giving way to cold nights due to the lack of humidity to retain heat.
- Seasonal Winds: Many deserts experience seasonal winds that can result in sandstorms and dust storms, reshaping the landscape and affecting local and global climates.
- Evaporation Rates: High temperatures lead to high evaporation rates, further reducing available moisture and creating the arid conditions characteristic of deserts.
- Sunlight and Cloud Cover: Deserts typically enjoy high levels of sunlight with minimal cloud cover, contributing to the extreme temperature variations and influencing the types of vegetation that can survive.
The climate and weather patterns of deserts are integral to the unique ecosystems they support. These conditions demand remarkable adaptations from the living organisms that inhabit these landscapes, underscoring the resilience of life in the face of adversity.

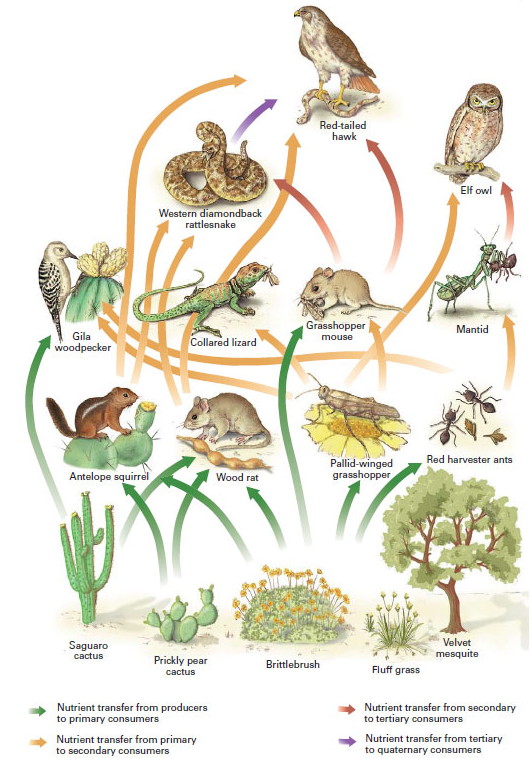
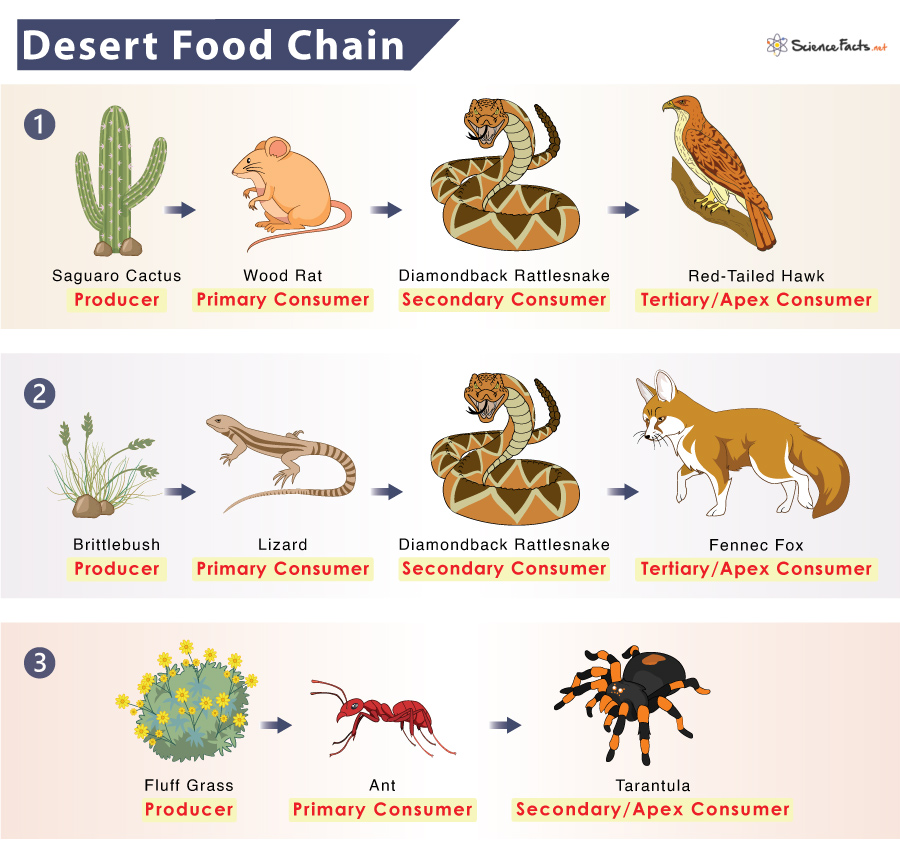
Flora and Fauna Adaptations to Arid Conditions
The harsh conditions of deserts demand extraordinary adaptations from both plant and animal life. These adaptations are essential for survival in an environment with limited water and extreme temperatures.
- Flora Adaptations:
- Deep Root Systems: Many desert plants have deep or extensive root systems to access water from far below the surface.
- Water Storage: Succulents, such as cacti, store water in their leaves or stems to use during droughts.
- Reduced Leaf Surface Area: To minimize water loss, many desert plants have small leaves or spines, reducing evaporation.
- Fauna Adaptations:
- Nocturnal Lifestyles: Many desert animals are nocturnal, active at night to avoid the extreme daytime heat.
- Water Conservation: Animals like the kangaroo rat can survive with very little water, producing concentrated urine and dry feces to minimize water loss.
- Heat Tolerance: Some species have developed high tolerance to heat and can regulate their body temperature to adapt to the hot desert climate.
These adaptations illustrate the incredible resilience and ingenuity of life in desert ecosystems, enabling a diverse range of species to flourish in conditions that would otherwise be inhospitable.
Geographical Distribution of Deserts Worldwide
Deserts cover about one-fifth of the Earth"s surface and are found on every continent. Their geographical distribution is influenced by global climate patterns, landforms, and proximity to bodies of water. Here"s a closer look at where deserts are located around the world.
- Africa: Home to the Sahara, the largest hot desert in the world, stretching across several countries in North Africa.
- Asia: Features the Arabian Desert in the Middle East and the Gobi Desert in China and Mongolia, among others.
- North America: Hosts the Mojave, Sonoran, and Great Basin deserts in the United States, along with the Chihuahuan Desert in Mexico and the U.S.
- South America: The Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on earth, is located in Chile and Peru.
- Australia: Contains the Great Victoria, Great Sandy, and Simpson deserts, showcasing diverse desert landscapes.
- Antarctica: While not a hot desert, it is the largest cold desert in the world, characterized by its dry, icy conditions.
This wide geographical spread of deserts showcases the diversity of desert ecosystems, each with unique characteristics and adaptations influenced by their location and climate.

Role of Deserts in Earth"s Ecology
Deserts play a critical and multifaceted role in Earth"s ecological balance, contributing to biodiversity, climate regulation, and even human culture. Their unique characteristics and adaptations offer insight into resilience and sustainability.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Despite their harsh conditions, deserts are home to a wide range of species that have adapted to survive in extreme environments, contributing to Earth"s biodiversity.
- Climate Influence: Deserts impact global climate patterns by reflecting sunlight back into the atmosphere and influencing precipitation patterns in adjacent regions.
- Carbon Sequestration: Certain desert plants and soils act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change.
- Soil Formation and Preservation: Desert processes contribute to soil formation and preservation, including the creation of important mineral deposits that can be beneficial for agriculture and industry.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: Human cultures have thrived in desert regions for thousands of years, developing unique ways of life adapted to these environments, and contributing richly to human heritage and knowledge.
- Scientific Research: Deserts serve as natural laboratories for scientific research, offering insights into life"s adaptability, climate change, and even the study of other planets with similar arid conditions.
The role of deserts in Earth"s ecology is profound, reminding us of the importance of these ecosystems not just for their inherent value but also for their significant contributions to the global environment and human society.
Desert Biome Facts
Explore the fascinating world of biomes and discover the rich variety of plant and animal life that thrives in these diverse environments. Journey through lush rainforests, vast deserts, and frozen tundras in this captivating video that will leave you in awe of the incredible wonders of our planet.
Desert Animals and Plants | Desert Ecosystem | Desert Video for Kids
Get ready to embark on an extraordinary adventure into the animal kingdom! From the fastest land animals to the most elusive sea creatures, this captivating video showcases the incredible diversity and wonder of the animal world. Dive into captivating stories and breathtaking footage that will leave you amazed and inspired by the extraordinary creatures that inhabit our planet.
Conservation Efforts and Protecting Desert Habitats
Protecting desert habitats is crucial for preserving biodiversity, combating desertification, and ensuring the sustainability of these unique ecosystems. Conservation efforts are diverse, targeting various challenges that deserts face globally.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks and protected areas to conserve critical habitats and prevent land degradation.
- Combating Desertification: Implementing sustainable land management practices to prevent overgrazing, deforestation, and soil erosion that contribute to desertification.
- Water Conservation: Developing technologies and practices for efficient water use in desert regions to preserve scarce water resources and support ecosystems.
- Restoration Projects: Engaging in habitat restoration efforts to rehabilitate areas that have been degraded by human activity or natural processes.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting ongoing research to understand desert ecosystems better and monitoring changes to respond effectively to conservation challenges.
- Community Involvement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their knowledge and stake in the sustainable management of desert resources.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing the impacts of climate change on deserts through global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to changing conditions.
These efforts are essential for ensuring the long-term health and resilience of desert ecosystems, supporting the myriad forms of life that depend on them, and maintaining their role in Earth"s ecological balance.

Human Life and Cultures in Desert Regions
Desert regions, with their extreme climates and challenging landscapes, have been home to human cultures for millennia. These communities have developed unique ways of life, deeply intertwined with and adapted to their environments.
- Nomadic Traditions: Many desert societies have historically been nomadic, moving across vast landscapes in search of water and grazing land for their livestock.
- Architectural Innovations: Desert dwellers have developed architectural styles that reflect the need for cooling and protection from the harsh sun, including thick-walled mud houses and underground dwellings.
- Water Management: Ingenious methods of water conservation and irrigation, such as fog nets and qanats (underground canals), showcase human ingenuity in adapting to arid conditions.
- Cultural Richness: Deserts are cradles of cultural and spiritual traditions, from the Bedouins of the Middle East to the Indigenous peoples of the American Southwest, each with their own rich traditions, art, and music.
- Sustainable Practices: Traditional desert communities often exemplify sustainable living, utilizing local resources without depleting them, and offering lessons in conservation and resilience.
- Adaptation to Modern Challenges: Contemporary desert communities face modern challenges such as climate change and globalization, navigating the balance between tradition and adaptation.
The resilience, creativity, and rich cultural heritage of human life in desert regions highlight the complex interplay between humans and their environments, offering valuable insights into sustainable living and adaptation.
Desertification: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
Desertification is a critical environmental issue, transforming once fertile land into non-productive desert as a result of natural and human activities. Understanding its causes, effects, and potential solutions is essential for mitigating its impact.
- Causes:
- Overgrazing by livestock, which removes vegetation and leads to soil erosion.
- Deforestation, which reduces the land"s ability to retain moisture.
- Unsustainable farming practices that deplete soil nutrients.
- Climate change, increasing the frequency and intensity of droughts.
- Effects:
- Loss of biodiversity as species that depend on the land disappear.
- Reduced agricultural productivity, leading to food insecurity.
- Increased vulnerability to natural disasters like floods and sand storms.
- Socio-economic impacts, including migration and conflicts over dwindling resources.
- Solutions:
- Implementing sustainable land management practices to restore soil health.
- Reforestation and afforestation efforts to increase ground cover and reduce erosion.
- Adopting agroforestry and permaculture to enhance biodiversity and productivity.
- International cooperation and policy-making to address the global scale of desertification.
Combating desertification requires a concerted global effort, integrating local knowledge with innovative management strategies to restore and protect vulnerable landscapes for future generations.

READ MORE:
Exploring Desert Landscapes: Tourism and Adventure
Desert landscapes offer unique opportunities for tourism and adventure, attracting visitors with their stark beauty and the challenge of exploring some of the most inhospitable terrains on Earth. Here are some ways to experience these captivating environments.
- Safari Tours: Wildlife safaris in deserts allow visitors to observe the unique flora and fauna adapted to arid conditions. The Namib and Sahara deserts are popular for such tours.
- Adventure Sports: Deserts are perfect for adventure sports, including sandboarding, off-road 4x4 driving, and camel trekking, offering thrilling experiences in vast open spaces.
- Cultural Experiences: Many desert regions are home to indigenous communities with rich cultural heritages. Visitors can learn about traditional ways of life, crafts, and survival techniques.
- Astronomy: With clear skies and minimal light pollution, deserts provide excellent conditions for stargazing and astronomy-related activities.
- Photography: The dramatic landscapes, from towering sand dunes to rocky outcrops, make deserts a photographer"s paradise, capturing the natural beauty and contrast of these environments.
- Eco-Tourism: Sustainable tourism initiatives focus on minimizing impact while maximizing visitor experiences, promoting conservation and awareness of desert ecosystems.
Exploring desert landscapes offers a blend of adventure, cultural immersion, and the chance to witness the resilience of life in extreme conditions, making it a unique and enriching experience for travelers.
Discovering the secrets of desert ecosystems reveals a world of extraordinary adaptations and breathtaking landscapes, inviting us to appreciate and protect these vital parts of our planet"s ecological diversity.