Topic does it rain in the sahara desert: Explore the intriguing phenomenon of rain in the Sahara Desert, a place often perceived as dry and barren, yet occasionally graced by nature"s unexpected showers.
Table of Content
- How often does it rain in the Sahara Desert?
- Overview of the Sahara Desert Climate
- Rainfall Patterns in the Sahara
- Factors Influencing Rainfall in the Sahara
- Historical and Seasonal Variations of Rain in the Sahara
- Impact of Rain on Sahara Desert Ecology
- Comparative Analysis with Other Deserts
- YOUTUBE: Rain in the Sahara Desert
- Climate Change and Future Predictions for Rain in the Sahara
- Human Activities and Their Influence on Sahara"s Rainfall
- Rare Weather Phenomena in the Sahara
- Myths and Misconceptions About Rain in the Sahara
How often does it rain in the Sahara Desert?
It is a common misconception that the Sahara Desert does not receive any rain. In reality, the Sahara Desert does experience rainfall, although it is very limited and infrequent.
According to the search results from Google, the Sahara Desert generally receives less than 100 millimeters (3.9 inches) of rain per year. The amount of precipitation can vary greatly from one year to another and within different regions of the desert.
The rainy season in the Sahara usually occurs during the winter months, from December through March. This is when most of the precipitation falls, although it is important to note that even during this time, the rainfall is minimal.
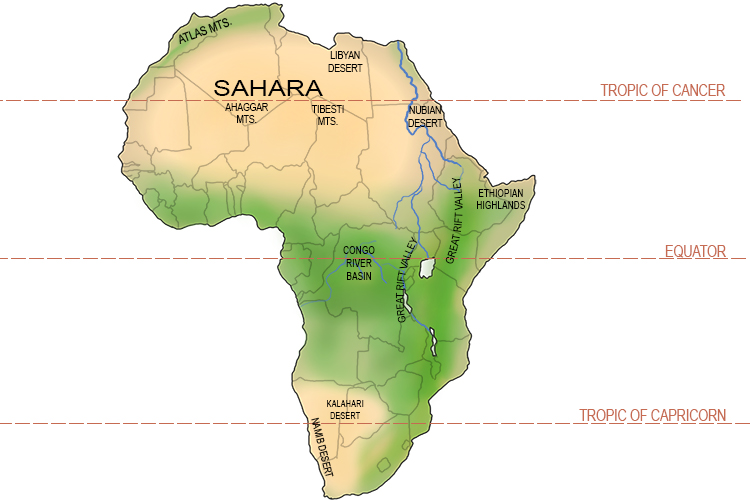
Keep in mind that the Sahara Desert is the largest hot desert in the world, covering a vast area of Northern Africa. As such, there can be variations in weather patterns and precipitation levels across different parts of the desert.
So, while rain does occur in the Sahara Desert, it is important to remember that it is a rare and scarce occurrence.
READ MORE:
Overview of the Sahara Desert Climate
The Sahara Desert, often synonymous with extreme dryness and scorching heat, presents a climate that is as fascinating as it is harsh. This vast region, stretching across North Africa, is characterized by its unique climatic conditions.
- Temperature Extremes: The Sahara is known for some of the most extreme temperatures on earth, soaring above 50°C (122°F) in summer, while nights can be surprisingly cold, especially in winter.
- Low Humidity Levels: The desert"s arid climate results in very low humidity, contributing to the dry conditions.
- Rare Rainfall: Rainfall in the Sahara is scarce and unpredictable, with many regions receiving less than 25 mm (1 inch) annually.
- Wind and Sandstorms: The Sahara is also known for its strong winds which can create massive sandstorms, reshaping the desert landscape.
- Variable Ecosystems: Despite the harsh conditions, the Sahara hosts diverse ecosystems, including oases and mountain ranges, supporting varied forms of life.
Understanding the Sahara"s climate is key to comprehending its unique environmental and cultural significance.
Rainfall Patterns in the Sahara
Despite its reputation as a dry and barren landscape, the Sahara Desert does experience rainfall, though it is rare and highly variable. The patterns of rainfall in this region are influenced by several climatic factors.
- Sporadic and Unpredictable: Rainfall in the Sahara is infrequent and irregular, with some areas seeing rain only a few times a decade.
- Geographical Variations: Certain areas, like the northern and southern edges of the Sahara, receive more rainfall compared to the central desert.
- Seasonal Differences: Most rain falls during the short "wet season", which can vary depending on the location within the desert.
- Impact of Climate Change: Recent studies suggest changes in rainfall patterns, possibly linked to global climate change, affecting the desert"s ecosystem.
- Flash Floods: When it does rain, the Sahara can experience sudden and intense downpours, leading to flash floods.
This unpredictable rainfall has profound effects on the life and landscape of the Sahara, making it a subject of ongoing study and fascination.
Factors Influencing Rainfall in the Sahara
Despite its reputation as a dry and barren landscape, the Sahara Desert does experience rainfall, though it is rare and highly variable. The patterns of rainfall in this region are influenced by several climatic factors.
- Sporadic and Unpredictable: Rainfall in the Sahara is infrequent and irregular, with some areas seeing rain only a few times a decade.
- Geographical Variations: Certain areas, like the northern and southern edges of the Sahara, receive more rainfall compared to the central desert.
- Seasonal Differences: Most rain falls during the short "wet season", which can vary depending on the location within the desert.
- Impact of Climate Change: Recent studies suggest changes in rainfall patterns, possibly linked to global climate change, affecting the desert"s ecosystem.
- Flash Floods: When it does rain, the Sahara can experience sudden and intense downpours, leading to flash floods.
This unpredictable rainfall has profound effects on the life and landscape of the Sahara, making it a subject of ongoing study and fascination.

Historical and Seasonal Variations of Rain in the Sahara
Despite its reputation as a dry and barren landscape, the Sahara Desert does experience rainfall, though it is rare and highly variable. The patterns of rainfall in this region are influenced by several climatic factors.
- Sporadic and Unpredictable: Rainfall in the Sahara is infrequent and irregular, with some areas seeing rain only a few times a decade.
- Geographical Variations: Certain areas, like the northern and southern edges of the Sahara, receive more rainfall compared to the central desert.
- Seasonal Differences: Most rain falls during the short "wet season", which can vary depending on the location within the desert.
- Impact of Climate Change: Recent studies suggest changes in rainfall patterns, possibly linked to global climate change, affecting the desert"s ecosystem.
- Flash Floods: When it does rain, the Sahara can experience sudden and intense downpours, leading to flash floods.
This unpredictable rainfall has profound effects on the life and landscape of the Sahara, making it a subject of ongoing study and fascination.
Impact of Rain on Sahara Desert Ecology
The infrequent rain in the Sahara Desert plays a crucial role in shaping its unique ecological landscape. Though sparse, these rain events have profound implications for the desert environment.
- Brief Floral Blooms: Rain sparks temporary but vibrant floral blooms, providing a critical food source for insects and animals.
- Wildlife Sustenance: Rainfall events are essential for the survival of desert wildlife, offering respite and hydration in an otherwise arid environment.
- Oasis Formation: These occasional rains contribute to the formation and maintenance of oases, which are vital for biodiversity and human settlements.
- Soil Erosion and Nutrient Distribution: Rain impacts soil composition, aiding in nutrient distribution but also causing erosion in some areas.
- Microclimate Creation: Rain creates microclimates that support varied life forms, adding to the desert"s ecological diversity.
- Impact on Human Agriculture: For local communities, rain is a blessing that supports agriculture and livestock, albeit unpredictably.
Despite its rarity, rain in the Sahara is a key driver of ecological change, demonstrating the resilience and adaptability of life in extreme environments.
Comparative Analysis with Other Deserts
When comparing the Sahara Desert"s climate with other deserts around the world, several interesting contrasts and similarities emerge, illustrating the diversity of desert environments.
- Rainfall Comparison: Unlike the Sahara, coastal deserts like the Atacama receive fog and dew. The Mojave and Sonoran deserts in North America experience higher annual rainfall.
- Temperature Extremes: While the Sahara is known for extreme heat, the Gobi Desert experiences more extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night.
- Desert Ecosystems: Each desert has unique ecosystems; for instance, the Sonoran is known for its rich plant life like the saguaro cactus, unlike the sparse vegetation of the Sahara.
- Sand Dunes: The Sahara is famous for its vast dune fields, which are larger and more prevalent than in deserts like the Great Basin in the USA.
- Human Adaptation: Human adaptation varies significantly, with the Sahara having a long history of nomadic tribes, unlike the largely uninhabited Atacama.
This comparative analysis highlights how each desert, including the Sahara, has unique characteristics shaped by its specific environmental conditions.
Rain in the Sahara Desert
Explore the awe-inspiring beauty of the Sahara Desert in this captivating video! Witness the mesmerizing sand dunes, golden sunsets, and the breathtaking vastness of this enchanting landscape. Immerse yourself in the rich culture and unique adventures this desert has to offer. Don\'t miss out on this unforgettable journey!
Rain in the Sahara Desert
Indulge in the soothing sounds and serene visuals of rain in this mesmerizing video. Allow yourself to be transported to a world of tranquility as you witness the raindrops gracefully dance and cleanse the earth. Experience the refreshing smell and calming ambiance rain brings, soothing your senses and revitalizing your spirit. Let this enchanting video wash away your stress and bring forth a sense of peace and rejuvenation.
Climate Change and Future Predictions for Rain in the Sahara
Climate change is expected to have significant impacts on the Sahara Desert"s rainfall patterns, making future predictions a vital area of study. Here"s how climate change might reshape rainfall in the Sahara:
- Increased Rainfall Predictions: Some climate models suggest that global warming could lead to more rainfall in the Sahara, potentially reversing desertification in some regions.
- Variability and Extremes: Increased variability in weather patterns is expected, leading to more extreme weather events, including unpredictable and intense rainfall.
- Impact on Desert Boundaries: Changes in rainfall patterns could alter the geographical boundaries of the Sahara, affecting neighboring ecosystems.
- Ecological Consequences: Any change in rainfall could have profound effects on the desert"s ecosystems, potentially leading to shifts in plant and animal populations.
- Human Impacts: Changes in rainfall patterns will affect local communities, influencing water availability, agriculture, and living conditions.
While the future is uncertain, understanding these potential changes is crucial for preparing and adapting to the impacts of climate change on the Sahara.

Human Activities and Their Influence on Sahara"s Rainfall
Human activities have exerted a considerable influence on the Sahara Desert"s climate, particularly its rainfall patterns. Here"s an insight into how human actions are impacting Sahara"s precipitation:
- Climate Change: Global emissions of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change, potentially altering the Sahara"s rainfall patterns and frequency.
- Deforestation: Deforestation in regions surrounding the Sahara can affect local climate conditions, influencing moisture and wind patterns that can alter desert precipitation.
- Agriculture and Irrigation Practices: Agricultural activities and large-scale irrigation projects in and around the Sahara affect regional humidity levels and could potentially impact rainfall.
- Urbanization: Urbanization near the desert changes land surfaces and can affect local weather patterns, including precipitation.
- Desertification: Activities leading to desertification, like overgrazing and poor land management, can exacerbate dry conditions and reduce likelihood of rainfall.
Understanding the impact of these human activities is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate adverse effects on the Sahara"s delicate climatic balance.
Rare Weather Phenomena in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, while predominantly known for its arid and hot climate, occasionally experiences rare and unusual weather phenomena that add to its mystique:
- Unexpected Rain and Flash Floods: Despite its aridity, the Sahara occasionally witnesses sudden, heavy rainfall leading to flash floods, transforming the dry landscape temporarily.
- Sand and Dust Storms: Intense sand and dust storms, known as "haboobs", are common, sometimes traveling vast distances and affecting air quality regionally.
- Snow in the Sahara: Rarely, snow has been reported in some of the higher altitudes of the Sahara, creating a surreal contrast with the typical desert scenery.
- Extreme Temperature Fluctuations: The desert experiences drastic temperature changes between day and night, which can be a surprising phenomenon to those unfamiliar with desert climates.
- Mirages: Optical phenomena like mirages are common in the Sahara, created by the refraction of light through layers of hot air.
These rare weather events not only challenge our typical understanding of deserts but also highlight the Sahara"s complex and dynamic climate system.
READ MORE:
Myths and Misconceptions About Rain in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, often associated with its extreme dryness, is also the subject of various myths and misconceptions regarding its rainfall. Let"s debunk some of these common myths:
- Myth: The Sahara Gets No Rain: Contrary to popular belief, the Sahara does receive rain, although it"s minimal and unpredictable.
- Misconception: Sahara is Always Hot: While generally hot, the Sahara can experience significant temperature drops, especially at night, and even more so after rare rainfall events.
- Myth: Rainfall is Uniform Across the Sahara: Rainfall in the Sahara varies greatly, with some regions receiving more due to geographical and climatic factors.
- Misconception: Rain in the Sahara Has No Impact: Even minimal rainfall can significantly affect the desert ecosystem, triggering a burst of life.
- Myth: Desertification is Solely Due to Lack of Rain: While low rainfall contributes to desertification, human activities like overgrazing and deforestation also play a crucial role.
Addressing these myths helps in understanding the true nature of the Sahara"s climate and its intricate relationship with rainfall.
In conclusion, the Sahara Desert"s relationship with rain is complex and fascinating, offering a unique glimpse into the resilience of nature in one of Earth"s most extreme environments.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ISS-42_Richat_Structure-5ae0e2bba18d9e00372f913e.jpg)

