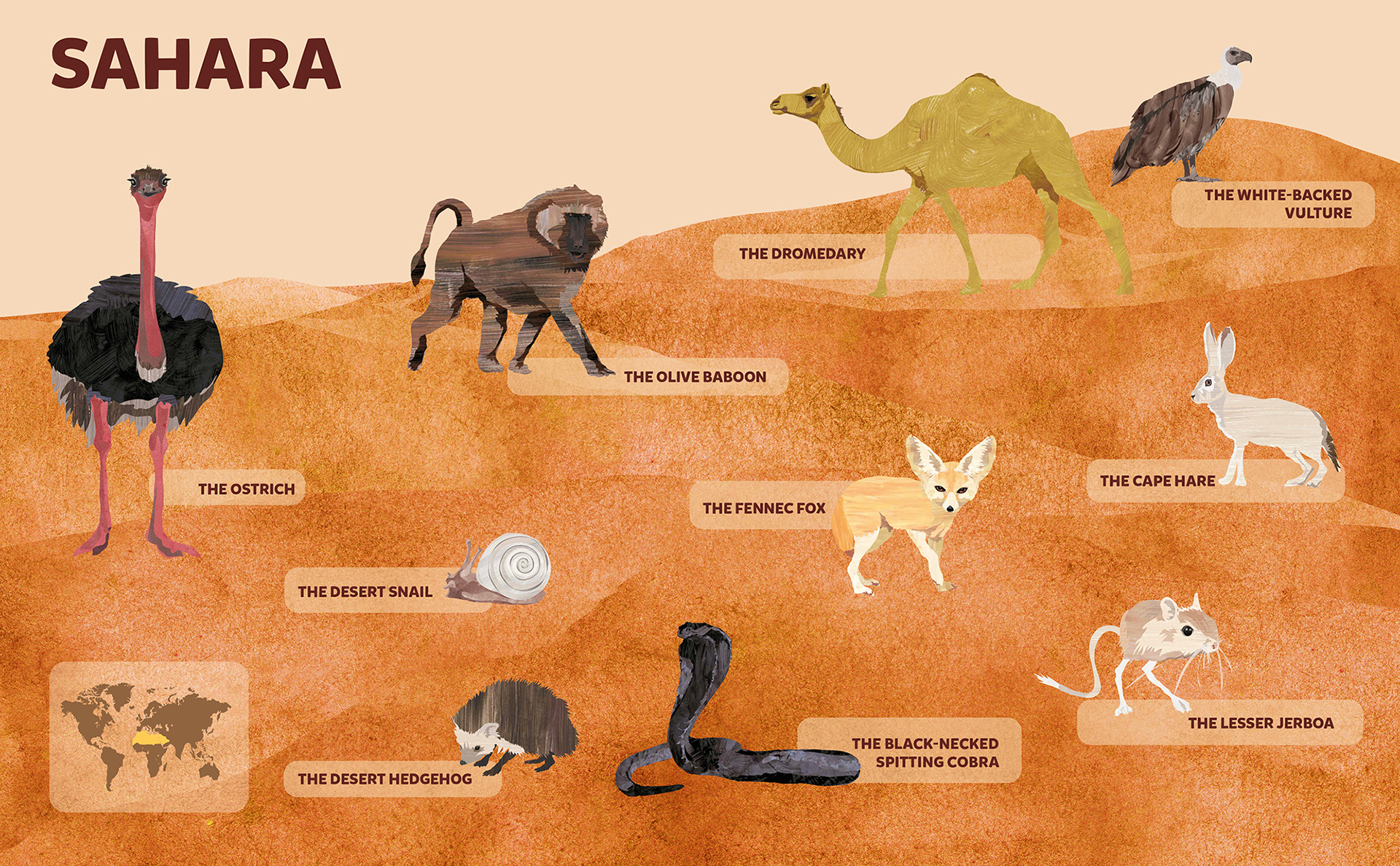
Topic animals that live in the sahara desert: Embark on a fascinating journey through the Sahara Desert, exploring the unique and resilient animals that thrive in this extreme environment.
Table of Content
- What are some animals that live in the Sahara Desert?
- Overview of Sahara Desert Ecosystem
- Adaptations of Sahara Desert Animals
- Mammals of the Sahara Desert
- Birds in the Sahara Desert
- Reptiles and Amphibians of the Sahara
- Insects and Arthropods in the Sahara
- YOUTUBE: Sahara Desert Animals
- Endangered Species in the Sahara Desert
- Human Impact on Sahara Wildlife
- Conservation Efforts in the Sahara
- Interesting Facts about Sahara Desert Animals
What are some animals that live in the Sahara Desert?
Some animals that live in the Sahara Desert include:
- Sand Viper
- Saharan Silver Ant
- Deathstalker Scorpion
- Desert Crocodile
- Monitor Lizards
- Black Desert Cobra
- Dromedary Camel
- Barbary Sheep
- Scimitar-Horned Oryx
- Gerbil
- Jerboa
- Cape Hare
- Desert Hedgehog
These are just a few examples of the diverse array of animals that have adapted to survive in the harsh conditions of the Sahara Desert.
READ MORE:
Overview of Sahara Desert Ecosystem
The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, spans across North Africa. It"s a diverse ecosystem, home to a range of unique flora and fauna adapted to extreme conditions.
- Geography: Encompassing over 9 million square kilometers, the Sahara"s landscapes include dunes, mountains, plateaus, and oases.
- Climate: Characterized by extreme heat, scarce rainfall, and drastic temperature fluctuations between day and night.
- Flora: Consists primarily of xerophytic plants like cacti, date palms, and acacia trees, adapted to arid conditions.
- Fauna: Hosts various animals like the Fennec Fox, Addax, Dromedary Camels, and diverse reptiles and birds.
- Adaptations: Sahara"s wildlife has evolved with unique traits for survival, such as water conservation, heat resistance, and sand mobility.
- Human Impact: The delicate balance of this ecosystem is increasingly disturbed by climate change and human activities.
- Conservation: Efforts are being made to protect endangered species and manage the impact of human encroachment.
This desert, though harsh and unforgiving, brims with life that demonstrates remarkable resilience and adaptability.

Adaptations of Sahara Desert Animals
The Sahara Desert, a vast and extreme environment, hosts a variety of animals uniquely adapted to survive in its harsh conditions. These adaptations are critical for managing the extreme temperatures, scarce water, and food availability.
- Dromedary Camels: Known for their fat-storing humps, these camels can go for days without water or food. They have thick lips for feeding on thorny plants and large footpads for traversing rocky and sandy terrain. Their slit nostrils and heavy eyebrows protect them from sandstorms.
- Ostriches: The largest and fastest birds in the world, ostriches have adapted to the desert with their long legs, which allow them to run at high speeds and evade predators. They can also survive without water for extended periods, obtaining moisture from the plants they eat.
- Death Stalker Scorpions: These venomous scorpions are adapted for survival in extreme heat and can cause respiratory failure in their prey and predators.
- Addax Antelopes: Adapted for crossing the Sahara sands with their flat feet, they"re endangered due to hunting and climate change.
- Scarab Beetles: Known for their strength, these beetles can lift over a thousand times their body weight. They play an important role in the desert ecosystem by recycling animal waste.
- Sidewinders: These snakes have a unique sideways movement that helps them move quickly over sand and reduces body contact with hot ground.
- Saharan Cheetahs: These cheetahs have adapted to hunt in the sparse desert environment but are critically endangered due to hunting and habitat loss.
- Gazelles: Gazelles are highly adapted to desert life, able to sustain themselves without direct water intake by extracting moisture from plants.
- Desert Monitors: These lizards are active during the day and have skin adapted to withstand extreme heat. They also have salt glands to manage water loss.
- Egyptian Gerbils: Nocturnal rodents that primarily feed on plants and occasionally bird eggs, adapting to the desert"s extreme conditions.
Each species in the Sahara Desert showcases unique adaptations, highlighting the diversity and resilience of life in one of the most challenging environments on Earth.
Mammals of the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, a vast and arid landscape, is home to a remarkable variety of mammals that have adapted to its challenging environment. These mammals showcase a diverse range of sizes, behaviors, and adaptations.
- Dromedary Camels: These camels are a crucial part of the desert ecosystem, providing transportation and resources for human inhabitants. They have adapted to the desert conditions with features like a single hump for fat storage and wide feet for sand travel.
- African Wild Dogs: Known for their hunting prowess and social structure, these dogs live in packs and are adept at endurance hunting in the harsh desert environment.
- Gazelles: Including species like the Dorcas, Rhim, and Dama gazelles, these mammals are known for their agility and ability to survive in arid conditions without direct water sources.
- Addax Antelopes: These antelopes are well-suited for desert life, with adaptations for sparse vegetation and water conservation.
- Fennec Foxes: Recognizable by their large ears, these small foxes have adapted to the desert with features for dissipating heat and conserving water.
- Saharan Cheetahs: A subspecies of the cheetah, these large cats are adapted for hunting in the desert, with a leaner build and a diet that allows for less frequent water consumption.
- Jerboas: These small rodents are known for their unique hopping movement and ability to thrive in desert environments.
- Hyraxes: Small, herbivorous mammals that live in large groups and forage together in the rocky regions of the Sahara.
These mammals not only survive but thrive in the Sahara, each with unique adaptations that allow them to overcome the challenges of this extreme environment.

Birds in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, despite its arid and harsh environment, is home to a diverse array of bird species that have adapted to its unique conditions.
- Desert Sparrow: A native bird of the Sahara, found in arid areas with sparse vegetation. They are known for their sandy color, which serves as camouflage, and their sociable nature around humans.
- Nubian Bustard: Found in the southern margins of the Sahara, this bird is an opportunistic omnivore, feeding on a varied diet that includes small vertebrates, invertebrates, seeds, and fruit.
- Egyptian Vulture: Known as Pharoah’s chicken, this vulture is one of the smaller Old World vultures, notable for its white plumage with black flight feathers and a yellow, featherless face.
- Pharoah Eagle-Owl: A silent nocturnal predator with tawny, cream, and brown mottled plumage and fiery orange eyes. They are adept at hunting a variety of desert prey.
- Desert Lark: Adapted to hot, dry environments, these birds are typically found in desert habitats, with adaptations allowing them to thrive in such harsh conditions.
- Greater Flamingo: These striking birds are found in the region, known for their distinctive pink coloring and social behavior.
- Golden Eagles: Apex predators in the Sahara, known for their size, speed, and ability to feed on small mammals and other birds.
- House Bunting: These birds are native to the Sahara, characterized by white and gray speckles on their neck and head, and are known to live close to humans in urban areas.
These bird species not only represent the biodiversity of the Sahara Desert but also demonstrate remarkable adaptability to one of the most extreme environments on Earth.
Reptiles and Amphibians of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, one of the most extreme environments on Earth, is home to a diverse range of reptiles and amphibians uniquely adapted to its arid conditions.
- West African Crocodile: Capable of reaching up to 10 feet in length, these crocodiles are known for their ability to survive extended dry seasons by aestivating in caves or burrows.
- Egyptian Tortoise: A small, endangered species, the Egyptian Tortoise is active at dawn and dusk during hot weather, and in the afternoon when it"s cold.
- Saharan Horned Viper: This venomous snake is recognizable by the horn-like scales above its eyes and is known for its ambush hunting style, often hiding beneath the sand.
- Saharan Spiny-Tailed Lizard/Uromastyx: These lizards, known for their spiny tails and flat bodies, are herbivores often found basking in the sun near rock formations.
- Sahara Sand Viper: A small viper, adept at both ambush hunting and active hunting, often buries itself in the sand with only its head protruding.
- Nubian Spitting Cobra: This cobra is known for its ability to spit venom as a defensive mechanism and for its neurotoxic and cytotoxic venom.
- Saw-Scaled Viper: Recognized as one of the deadliest snakes due to its aggressive nature and frequent interactions with humans.
- Desert Horned Viper: A distinct species with horn projections above each eye, known for being smaller in size but highly recognizable.
These reptiles and amphibians play crucial roles in the Sahara ecosystem, from controlling rodent populations to being key components in the food chain.

Insects and Arthropods in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert is not only home to a variety of mammal, bird, and reptile species but also hosts a diverse array of insects and arthropods, each uniquely adapted to the harsh desert environment.
- Ants: Including species like the Sahara desert ant, these insects are known for their incredible heat tolerance and navigational capabilities. They can endure extreme surface temperatures and are adept at foraging for food in the scorching desert.
- Beetles: Beetles are a prominent group in the Sahara, with adaptations that allow them to thrive in arid conditions. Some species, like the Microdera, are known to collect water droplets on their surfaces to survive.
- Butterflies and Moths: These insects are found in a variety of desert habitats, including the Sahara. They play crucial roles in pollination and the ecosystem"s health, with over 250 species of butterflies alone in some desert regions.
- Spiders: Various spiders, including the camel spider and tarantulas, are found in the Sahara. These arachnids are well-adapted to desert life, with some species known for their speed and hunting abilities.
- Flies: Flies in the Sahara have adapted to tolerate extreme heat and conserve water, playing important roles in pollination and decomposition within the desert ecosystem.
- Grasshoppers: These herbivorous insects, including the notorious desert locust, are well-adapted to the desert environment and are significant for their role in agriculture and food security in desert regions.
- Scorpions: Scorpions are a key part of the Sahara"s arthropod population, known for their venomous stingers and role in controlling other small creature populations.
These insects and arthropods not only display remarkable survival strategies but also contribute significantly to the Sahara"s ecological balance and biodiversity.
Sahara Desert Animals
Discover the fascinating world of Sahara Desert animals in this captivating video. Marvel at the stunning landscapes and learn about the incredible adaptations these creatures have developed to survive in this harsh environment. Don\'t miss out on this extraordinary wildlife spectacle!
Top 10 Animals in The Sahara Desert - Endangered & Unique Animals
Dive into the enchanting world of the Sahara Desert and explore the top 10 endangered and unique animals that call this place home. Witness their remarkable beauty and understand the importance of protecting these species to ensure their survival. Get ready for an eye-opening experience you won\'t want to miss!
Endangered Species in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, known for its harsh and arid conditions, is home to several species that are currently facing the threat of extinction. These species struggle to survive due to various factors, including habitat loss, poaching, and environmental changes.
- Saharan Cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus hecki): This elusive and critically endangered cheetah species has fewer than 250 adult individuals in the wild, primarily found in Algeria and Niger. Their survival is threatened by habitat loss, hunting, and reduced prey availability.
- Slender-Horned Gazelle (Gazella leptoceros): With only 250 to 300 individuals remaining in Algeria, Egypt, Libya, and Tunisia, this species is endangered, mainly due to poaching and habitat degradation.
- Egyptian Tortoise (Testudo kleinmanni): Also known as Kleinmann’s tortoise, this critically endangered species is nearly extinct in its natural habitat. It is threatened by habitat loss and the illegal pet trade.
- Sahara Aphanius (Aphanius saourensis): A critically endangered tiny fish found only in the Oued Saoura river basin near Mazzer, Algeria. It faces threats from drought, groundwater contamination, and competition with introduced species like the North American mosquito fish.
- Addax (Addax nasomaculatus): This antelope species is on the brink of extinction, with only a few individuals remaining in the wild. Factors contributing to its decline include habitat disturbance from oil installations, increased poaching, and regional insecurity.
The survival of these species is critically dependent on conservation efforts, including habitat protection, anti-poaching measures, and legal enforcement to prevent illegal wildlife trade.
Human Impact on Sahara Wildlife
Human activities have significantly impacted the wildlife of the Sahara Desert, leading to a range of environmental challenges. These impacts stem from various factors, including habitat encroachment, poaching, and climate change.
- Habitat Loss: Expansion of human settlements and agricultural practices have led to significant habitat loss for many Sahara species, encroaching on migration routes and natural habitats.
- Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: Iconic species such as elephants, rhinos, and lions have been targeted for their valuable parts, leading to drastic reductions in their populations. Poaching, driven by international demand for wildlife goods, continues to be a major threat.
- Climate Change: Climate change exacerbates the already harsh conditions of the Sahara, affecting the availability of water and food sources for wildlife.
- Conservation Efforts: Organizations like Sahara Conservation focus on species conservation and promote sustainable landscape management that integrates the needs of local communities with wildlife conservation. Successful reintroduction projects, like that of the scimitar-horned oryx, demonstrate the potential for recovery of species once thought to be on the brink of extinction.
It is evident that balancing human development with the needs of nature is crucial for the survival of Sahara"s wildlife. Efforts to protect and restore nature, reduce poaching, and manage climate change impacts are essential for the preservation of this unique ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts in the Sahara
Conservation efforts in the Sahara Desert are diverse and crucial due to the unique and fragile ecosystem it supports. These efforts are aimed at addressing challenges such as desertification, human encroachment, climate change, and the protection of endangered species.
- Habitat Restoration: Initiatives like the Great Green Wall aim to restore degraded land, sequester carbon, and create jobs by planting native species such as baobabs, gum acacias, and tamarinds. This not only combats desertification but also supports local communities economically.
- Wildlife Conservation: Organizations like the Sahara Conservation Fund focus on protecting endangered species like the Saharan cheetah, Dama Gazelle, and addax. Efforts include reintroduction programs, habitat management, and partnerships with local communities and governments.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation through sustainable practices and eco-tourism is key. This approach fosters a sense of responsibility and provides alternative income sources, ensuring long-term conservation success.
- Challenges and Adaptation: Conservation in the Sahara faces challenges such as security issues, water scarcity, and the effects of climate change. Adapting strategies to these conditions is crucial for the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
- Success Stories: The reintroduction of species like the Scimitar-horned oryx, previously extinct in the wild, demonstrates the potential positive impact of these conservation efforts.
These conservation efforts are essential for preserving the Sahara"s biodiversity, benefiting both the wildlife and the local communities dependent on this ecosystem.

READ MORE:
Interesting Facts about Sahara Desert Animals
The Sahara Desert is a unique ecosystem that hosts a variety of fascinating animals, each adapted to survive in one of the harshest environments on Earth. Here are some interesting facts about these incredible creatures:
- Deathstalker Scorpion: This dangerous scorpion is known for its highly venomous sting. Interestingly, its venom has potential medical uses, such as locating tumors in the human body.
- Dromedary Camel: This iconic desert animal can go long periods without water and stores fat and energy in its hump. It has special adaptations like bushy eyebrows and double-layered eyelashes to protect against sandstorms.
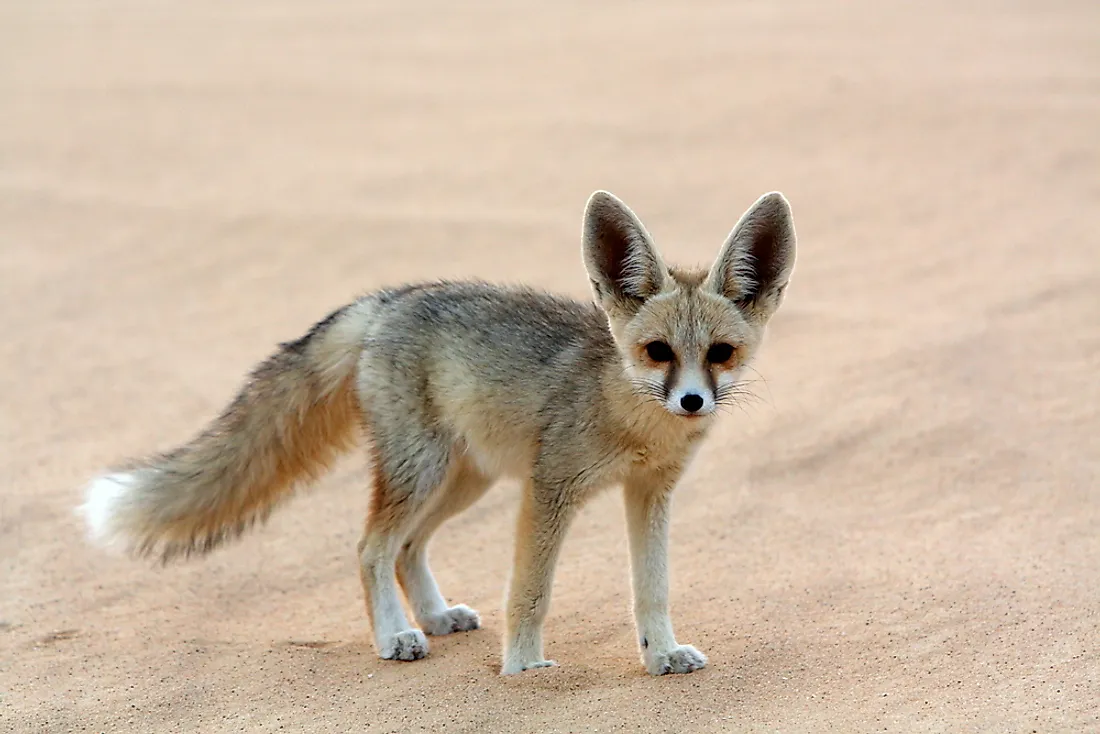
- Fennec Fox: The smallest member of the dog family, it is known for its large ears, which help in dissipating heat and provide sensitive hearing. Its thick fur helps keep it warm during the cold desert nights.
- Greater Flamingo: While not exclusively a desert animal, the greater flamingo visits shallow lakes and flood plains in desert regions, including the Sahara.
- Sand Cats: These small felines have adapted well to desert life with features like thick fur on their paws to protect them from hot sand and a sandy-colored coat for camouflage.
These animals demonstrate remarkable adaptability and resilience, making the Sahara Desert a place of both extreme conditions and extraordinary wildlife.
Discover the resilience and wonder of Sahara Desert animals, a testament to nature"s adaptability in the most extreme environments, revealing a world of remarkable survival and beauty.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ISS-42_Richat_Structure-5ae0e2bba18d9e00372f913e.jpg)



