Topic invertebrates and insects: Welcome to the enchanting realm of invertebrates and insects, a world brimming with diversity and wonder, where these spineless marvels play crucial roles in our ecosystems and offer endless fascination for nature enthusiasts and scientists alike.
Table of Content
- What are some examples of invertebrates and insects?
- Understanding Invertebrates: Definition and Characteristics
- Diversity of Invertebrates: Species Count and Classification
- Insects: The Largest Group of Invertebrates
- Unique Features of Insects: Wings, Reproduction, and Behavior
- Invertebrates in Different Habitats: Land, Water, and Marine Environments
- YOUTUBE: Invertebrate Animals Educational Video for Kids
- Role of Invertebrates in Ecosystems: Predators, Prey, and Decomposers
- Conservation Status: Endangered Invertebrates and Protection Efforts
- Parasitic Invertebrates: Impact on Humans and Other Animals
- Learning and Education: Resources on Invertebrates and Insects
- Invertebrates in Popular Culture: Myths, Misconceptions, and Facts
What are some examples of invertebrates and insects?
Some examples of invertebrates and insects include:
- Protozoa
- Porifera (sponges)
- Coelenterata (jellyfish, sea anemones, corals)
- Sea stars
- Sea urchins
- Earthworms
- Spiders
- Crustaceans (lobsters, crabs, shrimp)
- Insects (beetles, butterflies, mosquitoes, ants)
READ MORE:
Understanding Invertebrates: Definition and Characteristics
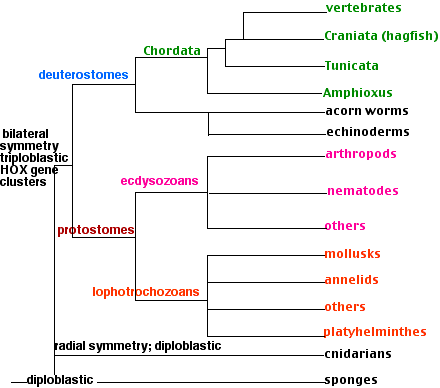
Invertebrates, encompassing a vast majority of animal species on Earth, are defined by their lack of a vertebral column, or backbone. This diverse group includes a range of organisms such as arthropods (like insects, crustaceans, and spiders), mollusks, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges.
- Arthropods, the most numerous invertebrate phylum, have a segmented body, paired limbs, an exoskeleton, and bilateral symmetry. This group includes insects, which are distinguished by their six legs and three-part body structure: head, thorax, and abdomen.
- Mollusca, the second-largest invertebrate phylum, are predominantly marine and include soft-bodied organisms like snails, slugs, clams, and octopuses, characterized by their unsegmented bodies and a nervous system with two main nerve cords.
- Annelids, or segmented worms, are another major group, featuring organisms with a nervous system, complete digestive tract, and a hydrostatic skeleton moved by their muscles.
Invertebrates vary vastly in size, ranging from tiny organisms barely visible to the naked eye to large species like the colossal squid. They inhabit diverse environments, from terrestrial to aquatic, playing crucial roles in ecosystems as predators, prey, decomposers, and pollinators.
Despite the lack of a backbone, many invertebrates have complex and efficient body systems, allowing them to thrive in various habitats and form an integral part of the natural world.

Diversity of Invertebrates: Species Count and Classification
Invertebrates, representing a vast majority of animal life on Earth, are a diverse group excluding those in the subphylum Vertebrata. This broad category includes numerous phyla like arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges.
Arthropods, encompassing insects, spiders, crustaceans, and others, form the largest phylum within invertebrates. Insects alone constitute more than half of all known organisms, with an estimated 10 million species, many of which are yet to be identified.
- Arthropods are known for their segmented bodies, exoskeletons, and bilateral symmetry, with over 80% of invertebrates belonging to this group.
- Mollusks, another significant invertebrate group, include species like snails, clams, and octopuses, known for their unsegmented bodies and diverse adaptations.
- Annelids, or segmented worms, are characterized by their complete digestive systems and hydrostatic skeletons.
These invertebrates occupy various roles in ecosystems, serving as primary and secondary consumers and decomposers. They have adapted to diverse habitats, from terrestrial to aquatic environments, illustrating the remarkable adaptability and evolutionary success of invertebrates.
Insects: The Largest Group of Invertebrates
Insects, members of the subphylum Hexapoda, constitute the largest and most diverse group of invertebrates, representing more than half of all known organisms. It is estimated that there may be over 10 million insect species worldwide, many yet to be discovered.
Insects vary significantly in size, ranging from less than a millimeter to as large as a human arm. Predominantly terrestrial, many insect species have also mastered flight, giving them advantages in mobility for food search and mate attraction.
- Body Structure: Insects typically have a segmented body comprising three main parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen. The thorax houses six legs, a distinctive feature of insects.
- Sensory Organs: Insects are equipped with a pair of antennae for sensing their environment, which can include chemical detection, tasting, and even sound perception. Their heads also feature compound eyes, allowing them to see images and, in some species like butterflies and bees, even perceive colors.
- Feeding: Insects exhibit a wide range of feeding habits, facilitated by specialized mouthparts adapted for various food sources.
Insects play crucial roles in ecosystems, including pollination, nutrient cycling, and serving as a food source for other animals. Their adaptability and evolutionary success make them a fascinating and integral part of the natural world.

Unique Features of Insects: Wings, Reproduction, and Behavior
Insects are renowned for their unique features which set them apart in the invertebrate world. These features include their wings, modes of reproduction, and diverse behaviors.
- Wings: Most insects possess two pairs of wings, forming an integral part of their exoskeleton and attached to the thorax. These wings vary greatly among different insect species, serving functions beyond flight, such as protection, communication, and mate attraction.
- Reproduction: The majority of insect species reproduce sexually, with some capable of asexual reproduction. Insects exhibit complex life cycles typically involving stages like larva, pupa, and adult, undergoing metamorphosis to transition between these stages.
- Behavior: Insect behavior ranges widely, with most being instinctive and genetically controlled. Certain behaviors, however, such as finding food, can be learned. Many insects, including ants, bees, and termites, exhibit complex social behaviors, living in organized colonies with specialized roles for different members.
These features contribute to the success and adaptability of insects in various environments, playing essential roles in ecosystems globally.
Invertebrates in Different Habitats: Land, Water, and Marine Environments
Invertebrates, the most diverse group of animals, inhabit various environments across the planet. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in land, freshwater, and marine ecosystems, each offering unique conditions and challenges.
- Land Invertebrates: Terrestrial invertebrates include insects, spiders, and worms. These creatures are adapted to life on land, with specializations like exoskeletons in insects to prevent water loss, and burrowing behaviors in earthworms for soil aeration.
- Marine Invertebrates: The marine environment is home to a plethora of invertebrates like corals, mollusks, and crustaceans. These species have adapted to the saline conditions, with some, like corals, playing vital roles in building reef ecosystems.
- Freshwater Invertebrates: Freshwater habitats, such as rivers and lakes, host invertebrates like certain species of snails and insects. These organisms often play crucial roles in the food web, serving as primary consumers and as food for larger aquatic animals.
Their presence in diverse habitats underscores the ecological importance of invertebrates, as they contribute significantly to biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems globally.

Invertebrate Animals Educational Video for Kids
This educational video provides a fascinating journey into the world of knowledge, offering a vibrant mix of facts and engaging visuals. Expand your understanding and immerse yourself in a captivating learning experience!
Insects Educational Videos for Kids
Discover the captivating world of insects in this mesmerizing video. Delve into their incredible adaptations, marvel at their intricate behaviors, and gain a deeper appreciation for the small wonders that make up our ecosystem. Join us in exploring the extraordinary world of insects!
Role of Invertebrates in Ecosystems: Predators, Prey, and Decomposers
Invertebrates play vital roles in ecosystems, functioning as predators, prey, and decomposers. They contribute significantly to the ecological balance and biodiversity across various habitats.
- Predators: Many invertebrates are predators, feeding on smaller organisms and helping to control their populations. For example, spiders and certain insect species prey on other invertebrates and help maintain ecological balance.
- Prey: Invertebrates also serve as essential food sources for a wide range of animals, including birds, mammals, and other insects. Their abundance makes them a critical link in food chains across ecosystems.
- Decomposers: Decomposing invertebrates, such as earthworms and certain insects, play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter. This process enriches the soil with nutrients and supports plant growth, thereby sustaining terrestrial ecosystems.
Their presence in different ecosystems, whether terrestrial, marine, or freshwater, demonstrates the indispensable role of invertebrates in maintaining ecological health and biodiversity.
Conservation Status: Endangered Invertebrates and Protection Efforts
The conservation status of invertebrates is a growing concern globally. Many invertebrate species, integral to biodiversity and ecosystem functioning, are facing threats leading to their endangerment or extinction.
- Global Decline: Studies have shown significant declines in invertebrate populations, including insects and butterflies, highlighting an urgent need for conservation efforts.
- Conservation Efforts: Organizations like the IUCN Invertebrate Conservation Committee and The Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation are actively working towards protecting invertebrates. Their efforts include habitat conservation, policy advocacy, and raising awareness about the ecological importance of invertebrates.
- Challenges in Conservation: Invertebrate conservation faces challenges like lack of public awareness, underrepresentation in policy-making, and gaps in biodiversity data. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for effective conservation strategies.
Effective conservation strategies are vital for invertebrates, considering their essential roles as pollinators, decomposers, and components of the food web. Their protection is critical to maintaining the health and balance of ecosystems worldwide.

Parasitic Invertebrates: Impact on Humans and Other Animals
Parasitic invertebrates play a significant role in various ecosystems, but they can also have substantial impacts on human and animal health. These organisms have developed complex relationships with their hosts, often leading to health issues.
- Morphological and Cellular Adaptations: Parasitic invertebrates exhibit unique adaptations that enable them to thrive as parasites. These include specialized structures for attachment to hosts and systems for nutrient uptake and processing.
- Health Impact on Humans and Animals: Parasitic invertebrates can cause a range of diseases and health issues in humans and animals. For example, certain invertebrates are responsible for transmitting diseases like malaria. The impact of these parasites can be severe, affecting millions of people worldwide.
- Challenges in Control and Prevention: Controlling parasitic invertebrates poses significant challenges, particularly in terms of developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Research is ongoing to understand the life cycles of these parasites better and to find new ways to mitigate their impact on human and animal health.
Understanding and managing the impact of parasitic invertebrates is crucial for public health and the well-being of animal populations. Continuous research and innovative control strategies are essential in this ongoing battle against parasitic diseases.
Learning and Education: Resources on Invertebrates and Insects
Educational resources on invertebrates and insects are abundant and cater to various age groups and learning styles. These resources can significantly enhance knowledge and understanding of these fascinating creatures.
- Online Educational Platforms: Websites like the Australian Museum"s Bugwise for Schools and Elephango offer interactive learning experiences about invertebrates. They provide engaging content, including identification guides and activities to explore the diversity of invertebrates.
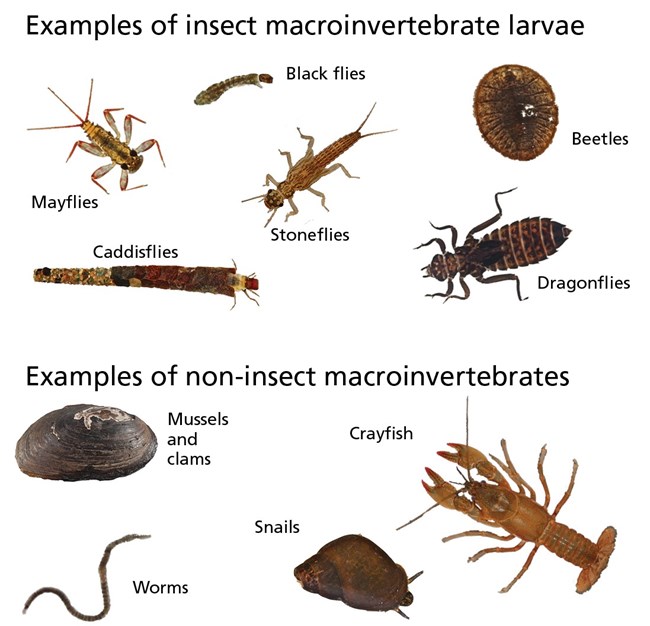
- Interactive Lesson Plans: Resources like Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Lesson Plans and Frontiers in Parasitology offer hands-on activities for students to learn about aquatic invertebrates and their roles in ecosystems.
- Educational Videos: YouTube channels and other video platforms offer a plethora of educational content on invertebrates, making learning visually engaging and accessible.
- Identification and Research Resources: Macroinvertebrates.org and similar websites provide detailed identification guides and taxonomic resources, aiding in the study and research of invertebrates.
- Books and Publications: A variety of books and scientific publications are available for those seeking more in-depth knowledge on specific invertebrate groups or topics.
These resources are invaluable for educators, students, and anyone interested in the world of invertebrates and insects, offering a blend of scientific information and interactive learning experiences.

READ MORE:
Invertebrates in Popular Culture: Myths, Misconceptions, and Facts
Invertebrates, though crucial to our ecosystems, are often surrounded by myths and misconceptions in popular culture. Understanding the facts helps in appreciating these diverse creatures and their roles in our world.
- Myths and Misconceptions: Common myths include beliefs that all spiders are dangerous or that insects are mostly harmful pests. These misconceptions often lead to unnecessary fear and misunderstanding of the vital roles these creatures play.
- Representation in Media: Invertebrates are frequently depicted in media and folklore, often in exaggerated or fantastical roles. While these representations can be entertaining, they sometimes perpetuate fears or misunderstandings about these creatures.
- Educational Efforts: Efforts by educators, naturalists, and scientists to dispel these myths are crucial. Accurate representation in documentaries, books, and educational programs helps in spreading awareness about the ecological importance of invertebrates.
- Facts: The truth is that most invertebrates are harmless to humans and play essential roles in our ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and a source of food in the food chain. Understanding and respecting their roles is vital for biodiversity conservation.
By separating fact from fiction, we can better understand and appreciate the diverse and fascinating world of invertebrates and their essential roles in the environment.
Unveiling the diverse and vibrant world of invertebrates and insects opens doors to understanding their crucial roles in our ecosystems. Embracing their fascinating life, we deepen our appreciation for nature"s intricacies and the delicate balance of life.