Topic invertebrate animals examples: Explore the captivating world of invertebrate animals, where spineless creatures showcase nature"s incredible diversity and adaptability, from ocean depths to forest floors.
Table of Content
- What are some examples of invertebrate animals?
- Overview of Invertebrates
- Examples of Marine Invertebrates
- Examples of Terrestrial Invertebrates
- Invertebrates in Freshwater Ecosystems
- Unique Features and Adaptations of Invertebrates
- Role of Invertebrates in Ecosystems
- YOUTUBE: The Diversity of Invertebrates
- Conservation Challenges for Invertebrates
- Invertebrates in Research and Medicine
- Interesting Facts about Invertebrates
- Resources for Learning More about Invertebrates
What are some examples of invertebrate animals?
Some examples of invertebrate animals include:
- Sea stars
- Snails
- Jellyfish
- Squid
- Octopuses
- Insects (such as ants, butterflies, and beetles)
- Spiders
- Worms
- Crustaceans (such as crabs, lobsters, and shrimp)
- Coral
Invertebrates make up more than 90 percent of all animal species on Earth. They can be found in a wide range of habitats, including oceans, forests, deserts, and even in your own backyard!
READ MORE:
Overview of Invertebrates
Invertebrates, a vast and diverse group of animals without a backbone, constitute over 95% of animal species on Earth. These creatures range from microscopic organisms to larger species, each playing a crucial role in their ecosystems.
- Classification: Invertebrates include various phyla such as Arthropoda (insects, spiders, crustaceans), Mollusca (snails, octopuses), Annelida (earthworms), and more.
- Habitats: They inhabit diverse environments, from deep ocean floors to the highest mountains, adapting remarkably to their surroundings.
- Biological Importance: Invertebrates are vital for ecological balance, participating in processes like pollination, decomposition, and serving as a food source for other species.
- Physical Characteristics: Despite lacking a vertebral column, many invertebrates have exoskeletons or hydrostatic skeletons for support and protection.
- Reproduction and Lifespan: These organisms exhibit a wide range of reproductive strategies and life spans, from short-lived insects to long-lived mollusks.
Invertebrates are not only essential for their ecological roles but also for their contribution to human life, including scientific research, agriculture, and even inspiring engineering designs through biomimicry.

Examples of Marine Invertebrates
Marine invertebrates are a fascinating and diverse group of animals that thrive in the world"s oceans. From the shallowest tidal pools to the deepest ocean trenches, these creatures exhibit incredible adaptations to marine life.
- Jellyfish: Known for their gelatinous bodies and stinging tentacles, jellyfish are a common sight in oceans worldwide.
- Octopuses: These intelligent mollusks are famous for their eight arms, camouflage abilities, and problem-solving skills.
- Starfish (Sea Stars): With their distinctive star-shaped bodies, starfish are important predators in many marine ecosystems.
- Crustaceans: This diverse group includes crabs, lobsters, and shrimps, known for their hard exoskeletons and varied habitats.
- Corals: Essential to marine ecosystems, corals build vast reefs that support a high biodiversity of marine life.
- Sea Urchins: These spiny creatures are part of the echinoderm family and play a vital role in controlling algae growth in marine environments.
- Squids: Fast and agile, squids are cephalopods known for their jet propulsion and ink defense mechanism.
- Sponges: As one of the simplest marine invertebrates, sponges filter feed and provide habitat for many other marine species.
These examples represent just a glimpse of the vast array of marine invertebrates, each contributing uniquely to the ocean"s complex ecosystems.
Examples of Terrestrial Invertebrates
Terrestrial invertebrates are a diverse group of spineless creatures that thrive on land. These organisms exhibit a remarkable range of sizes, shapes, and behaviors, adapting to various terrestrial habitats.
- Insects: Including butterflies, beetles, ants, and bees, insects are the most diverse group of terrestrial invertebrates.
- Arachnids: This group includes spiders, scorpions, and ticks, known for their eight legs and often misunderstood nature.
- Earthworms: Vital for soil health, earthworms play a key role in aerating the soil and breaking down organic matter.
- Centipedes and Millipedes: These multi-legged creatures are often found in moist, dark environments and play various ecological roles.
- Slugs and Snails: Known for their slow movement and unique feeding habits, these mollusks are important decomposers in many ecosystems.
- Termites: Essential for breaking down cellulose, termites are crucial for nutrient cycling but can also be pests in human habitats.
- Praying Mantises: With their distinctive appearance and predatory habits, mantises are fascinating examples of terrestrial invertebrates.
- Ladybugs: Admired for their colorful patterns, ladybugs are beneficial insects, feeding on plant pests like aphids.
These examples represent the vast array of terrestrial invertebrates that play critical roles in maintaining ecological balance and contributing to biodiversity on land.

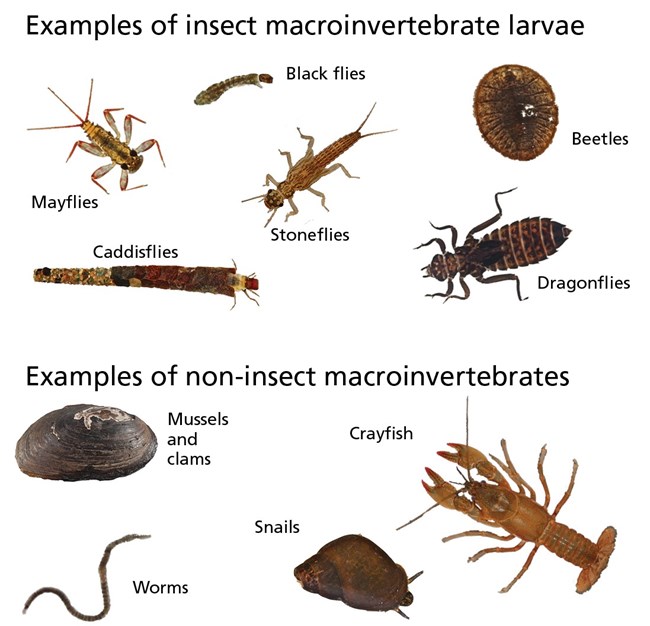
Invertebrates in Freshwater Ecosystems
Freshwater ecosystems are rich with a diverse array of invertebrate species. These organisms are crucial for maintaining the ecological balance of freshwater environments, from streams and rivers to lakes and ponds.
- Dragonflies and Damselflies: Known for their striking colors and agile flight, these insects spend their larval stage in water.
- Mayflies: Renowned for their short adult life, mayflies are important indicators of water quality in their nymph form.
- Freshwater Snails: These mollusks are vital for algae control and are a food source for many other species.
- Caddisflies: Caddisfly larvae construct protective cases from materials found in their aquatic surroundings.
- Water Beetles: Diverse in form, water beetles include predators, scavengers, and herbivores in freshwater ecosystems.
- Freshwater Sponges: These simple organisms filter water, playing a key role in maintaining water quality.
- Aquatic Worms: Including various species, these worms are crucial for nutrient cycling in freshwater habitats.
- Freshwater Crustaceans: Such as crayfish and daphnia, these crustaceans are important both as predators and prey in freshwater food webs.
Each of these invertebrates contributes uniquely to the health and biodiversity of freshwater ecosystems, showcasing the complexity and interdependence of life in these habitats.
Unique Features and Adaptations of Invertebrates
Invertebrates, encompassing a vast range of species, exhibit some of the most fascinating and unique features and adaptations in the animal kingdom. These adaptations have enabled them to thrive in almost every habitat on Earth.
- Exoskeletons: Many invertebrates, like insects and crustaceans, have exoskeletons, providing protection and support without the need for internal bones.
- Camouflage: Invertebrates such as cephalopods (like octopuses and squids) are masters of camouflage, changing color and texture to blend into their environments.
- Regeneration: Some invertebrates, like starfish and certain worms, can regenerate lost body parts, a remarkable adaptation for survival.
- Venom: Many invertebrates, including some species of spiders and jellyfish, use venom for defense and to capture prey.
- Flight: Insects were the first animals to evolve flight, an adaptation that opened up new ecological niches and modes of survival.
- Metamorphosis: Invertebrates like butterflies undergo complete metamorphosis, dramatically changing form from larva to adult.
- Sensory Adaptations: Invertebrates have developed various sensory adaptations; for example, ants communicate using pheromones, and moths can detect ultrasonic sounds.
- Aquatic Adaptations: Aquatic invertebrates, such as jellyfish and corals, have adaptations like flotation mechanisms and symbiotic relationships with algae.
These unique features highlight the incredible adaptability and diversity of invertebrates, making them integral to the Earth"s ecosystems.

Role of Invertebrates in Ecosystems
Invertebrates play critical and varied roles in ecosystems, contributing significantly to ecological balance and biodiversity. Their presence and activities are vital for the functioning of both terrestrial and aquatic habitats.
- Pollinators: Many invertebrates, especially insects like bees and butterflies, are essential pollinators for a multitude of plants, including those important for agriculture.
- Decomposers: Invertebrates such as earthworms, termites, and various beetles help break down organic matter, enriching soil nutrients and aiding in decomposition.
- Food Web Dynamics: Serving as both predators and prey, invertebrates are integral to food web structures, supporting a diversity of life in various ecosystems.
- Biological Control: Certain invertebrates help control pest populations, providing natural pest management in both natural ecosystems and agricultural settings.
- Soil Health: Soil-dwelling invertebrates contribute to soil aeration, structure, and fertility, crucial for plant growth and ecosystem health.
- Indicator Species: The presence and health of invertebrate populations, such as certain insects and mollusks, can indicate the overall health of an ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Support: Invertebrates support biodiversity by creating and maintaining habitats, such as coral reefs, which are home to numerous other species.
- Ecosystem Engineering: Some invertebrates like beavers (although semi-aquatic) significantly alter their environment, creating new habitats for other species.
The roles of invertebrates in ecosystems are multifaceted and essential, underlining their importance in maintaining ecological balance and supporting biodiversity.
The Diversity of Invertebrates
\"Experience the beauty of diversity like never before! Our video showcases a kaleidoscope of cultures, traditions, and perspectives that will leave you inspired and in awe of the world\'s richness. Join us on this journey of celebrating differences and fostering inclusivity!\"
Invertebrates - The Dr. Binocs Show - Learn Videos For Kids
\"Discover the mesmerizing world of invertebrates with our captivating video. Dive into the fascinating lives of these often-overlooked creatures and be amazed by their incredible adaptations and unique behaviors. Get ready for a close encounter with the intriguing world of invertebrates!\"
Conservation Challenges for Invertebrates
Invertebrates, despite their ecological importance, face numerous conservation challenges. These challenges stem from various human activities and environmental changes, impacting their populations and habitats globally.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation lead to the loss and fragmentation of habitats, crucial for the survival of many invertebrate species.
- Climate Change: Changes in temperature and weather patterns disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, affecting invertebrate life cycles and distribution.
- Pollution: Water and soil pollution from chemicals, plastics, and other pollutants pose serious threats to invertebrates, particularly aquatic species.
- Overexploitation: Overharvesting of certain species, whether for commercial, recreational, or scientific purposes, can lead to population declines.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced into ecosystems can outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native invertebrates.
- Pesticides and Herbicides: The widespread use of these chemicals in agriculture and landscaping harms invertebrates, particularly pollinators and soil dwellers.
- Lack of Awareness: Invertebrates often receive less attention in conservation efforts compared to vertebrates, leading to insufficient protection measures.
- Research Gaps: Limited research on many invertebrate species hinders understanding of their needs and effective conservation strategies.
Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts, increased awareness, and targeted conservation strategies to ensure the survival and health of invertebrate populations.
Invertebrates in Research and Medicine
Invertebrates play a significant role in research and medicine, contributing to advancements in various scientific fields. Their unique biological features make them ideal subjects for a range of studies.
- Model Organisms in Genetics: Fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) are extensively used in genetic research due to their short life cycles and genetic simplicity.
- Neurological Studies: The simplicity of the nervous system of nematodes like C. elegans allows scientists to study neurological diseases and development.
- Drug Testing and Development: Invertebrates like zebrafish are used in pharmacology for drug screening and understanding drug effects on biological systems.
- Studying Disease Mechanisms: Mosquitoes and ticks, which are vectors for diseases like malaria and Lyme disease, are crucial for understanding disease transmission and developing prevention strategies.
- Biomedical Research: Cephalopods and other mollusks are studied for their unique features, such as regeneration and camouflage abilities.
- Ecotoxicology: Aquatic invertebrates are used to assess the toxicity of environmental pollutants and their impact on ecosystems.
- Biomimicry in Engineering: The study of invertebrates has inspired innovations in materials science and engineering, mimicking structures like the adhesion abilities of geckos.
- Conservation Biology: Understanding the biology of invertebrates helps in conservation efforts, particularly for endangered species and habitats.
Through these roles, invertebrates not only enhance our understanding of biology and ecosystems but also contribute to medical and technological advancements.
Interesting Facts about Invertebrates
Invertebrates, with their vast diversity, offer a myriad of fascinating facts that highlight their uniqueness and importance in the natural world.
- Vast Diversity: Invertebrates make up about 97% of all animal species, showcasing an immense variety in forms, sizes, and colors.
- Ancient Lineage: Some invertebrates, like jellyfish, have been around for over 500 million years, predating dinosaurs.
- Extraordinary Abilities: Octopuses are known for their intelligence, including problem-solving skills and the ability to escape from enclosures.
- Incredible Migrations: Monarch butterflies undertake one of the longest migrations of any insect, traveling thousands of miles.
- Unique Reproductive Strategies: Some invertebrates, like aphids, can reproduce without mating, a process known as parthenogenesis.
- Bioluminescence: Many marine invertebrates, such as certain jellyfish and squids, can produce light, a phenomenon known as bioluminescence.
- Environmental Indicators: The presence and health of invertebrate species, like bees and freshwater mussels, can indicate the health of an ecosystem.
- Architectural Marvels: Termites and ants build complex structures, some of which are the equivalent of skyscrapers in human terms.
These facts barely scratch the surface of the intriguing world of invertebrates, a world full of wonders and vital ecological significance.

READ MORE:
Resources for Learning More about Invertebrates
For those interested in delving deeper into the world of invertebrates, a wealth of resources is available. These resources range from educational websites and books to documentaries and interactive experiences.
- Books: Numerous books offer in-depth knowledge about invertebrates, suitable for both beginners and advanced enthusiasts.
- Online Databases: Websites like the Encyclopedia of Life and the Integrated Taxonomic Information System provide comprehensive information on various invertebrate species.
- Documentaries: Educational documentaries on platforms like National Geographic and BBC Earth feature stunning visuals and insights into invertebrate life.
- Museums: Natural history museums often have extensive collections and exhibits dedicated to invertebrates, offering an up-close look at these creatures.
- University Courses: Many universities offer courses in zoology and biology that include modules on invertebrates.
- Conservation Organizations: Groups like the World Wildlife Fund and the National Wildlife Federation provide resources on invertebrate conservation efforts.
- Interactive Experiences: Aquariums and zoos often have sections dedicated to invertebrates, allowing for interactive learning experiences.
- Scientific Journals: Journals such as Invertebrate Biology and the Journal of Invertebrate Pathology publish the latest research in the field.
Exploring these resources can provide a deeper understanding of invertebrates, their roles in ecosystems, and the efforts to conserve them.
Delving into the world of invertebrates reveals a fascinating tapestry of life, highlighting their crucial roles in ecosystems and inspiring a deeper appreciation for these extraordinary creatures.