Topic categories of invertebrates: Delve into the fascinating world of invertebrates, a realm teeming with diversity and wonder. Explore the intricate categories that reveal the hidden marvels of these spineless wonders.
Table of Content
- What are the different categories of invertebrates?
- Main Characteristics of Invertebrates
- Classification of Platyhelminthes
- Classification of Nematodes
- Classification of Echinoderms
- Diversity and Distribution of Invertebrates
- Common Types of Invertebrates
- YOUTUBE: Invertebrate Classification
- Role and Importance of Invertebrates
What are the different categories of invertebrates?
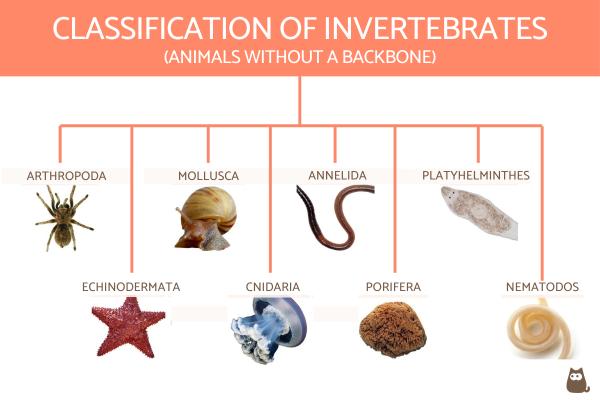
The different categories of invertebrates include:
- Protozoa
- Porifera
- Coelenterata
- Platyhelminthes
- Nematoda
- Annelida
- Echinodermata
- Mollusca
- Arthropoda
READ MORE:
Main Characteristics of Invertebrates
Invertebrates, encompassing a vast array of animal species, share the defining trait of lacking a vertebral column. They form an incredibly diverse group, with body plans ranging from fluid-filled hydrostatic skeletons to hard exoskeletons. Representing a majority of animal life on Earth, invertebrates can be found in various environments, from deserts to deep oceans.
- Body Structure: Most invertebrates possess an exoskeleton, a protective outer shell, as seen in arthropods like insects and crustaceans. This feature compensates for the absence of a backbone, providing rigidity and form.
- Size and Complexity: Typically smaller in size, invertebrates vary greatly in complexity, from single-celled organisms to more intricate forms like mollusks and echinoderms.
- Respiration: Lacking lungs, many invertebrates respire through their skin or other specialized structures.
- Nutrition: As heterotrophs, invertebrates obtain their nutrition from various sources, ranging from absorbing nutrients to consuming other organisms.
- Reproduction: Invertebrate reproduction methods vary, with some species reproducing through fission, while others have more complex reproductive systems.
- Habitats: Invertebrates are adaptable, inhabiting diverse environments including terrestrial, freshwater, and marine ecosystems.
Understanding these characteristics provides a window into the biology and ecology of the numerous invertebrate species that play crucial roles in Earth"s ecosystems.

Classification of Platyhelminthes
Platyhelminthes, commonly known as flatworms, represent a diverse phylum of acoelomate, bilaterally symmetrical organisms. These flatworms are characterized by their dorsoventrally flattened bodies, absence of internal body cavities, and a lack of circulatory and respiratory systems. Their excretion is facilitated by flame-bulb protonephridia.
- Class Turbellaria: This class primarily includes free-living marine species, though some are parasitic. Turbellarians are known for their ciliated epidermis and simple life cycle. Examples include planarians, which are non-parasitic and mostly predators or scavengers.
- Class Monogenea: Monogeneans are ectoparasites, primarily infesting fish. They are characterized by a large posterior adhesive disk and a simple life cycle without host alternation.
- Class Trematoda: Trematodes, also known as flukes, are mostly parasitic, often possessing hooks and suckers for attachment to hosts. These include species like Fasciola hepatica.
- Class Cestoda: Cestodes or tapeworms are exclusively parasitic, lacking a digestive system and consisting of a series of segments called proglottids. They attach to hosts using hooks and suckers. Examples include Taenia spp.
Platyhelminthes exhibit diverse reproductive strategies, including both sexual and asexual methods. Most are monoecious and have complex reproductive systems with internal fertilization. They play significant roles in ecosystems and include many species that are harmful parasites to humans and other animals.
Classification of Nematodes
Nematodes, also known as roundworms, are a highly diverse phylum of worms, Nematoda, characterized by their tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. They inhabit a wide range of environments and include both free-living and parasitic species. Their classification involves two major classes, each with distinct characteristics.
- Class Chromadorea: This class includes nematodes with a smooth or ringed cuticle and a posterior pharyngeal bulb. Many species within this class are free-living, though some are parasitic.
- Class Enoplea: Enopleans are often distinguished by a thick, multi-layered cuticle and a muscular pharynx without a bulb. They include both free-living and parasitic species, inhabiting various environments.
- Class Secernentea: These nematodes are mostly parasitic and characterized by the absence of caudal glands and presence of plasmids, which are unicellular, pouch-like sense organs. The excretory system in this class has paired lateral canals.
The nematodes" morphology is cylindrical and pseudocoelomate, lacking a true coelom. They are known for their simple nervous and excretory systems and lack a well-developed circulatory or respiratory system. Their reproduction is predominantly sexual, with internal fertilization. Nematodes are known for their ability to adapt to various ecosystems, contributing significantly to soil health and nutrient recycling but also causing diseases in plants and animals.

Classification of Echinoderms
Echinoderms, characterized by their radial symmetry and spiny skin, are a diverse marine phylum. This group includes species that are important ecologically and economically. The classification of echinoderms is based on their unique features, such as water vascular systems, tube feet, and endoskeletal plates.
- Class Asteroidea: This class includes sea stars or starfishes, known for their star-shaped body and usually five arms, though some species have more. They are mostly predators or scavengers.
- Class Ophiuroidea: Brittle stars and basket stars fall under this class. They have a central disc and long, flexible arms, which are distinct from the central body.
- Class Echinoidea: This class comprises sea urchins and sand dollars. They have a globular or disc-shaped body covered with spines and move using their tube feet.
- Class Crinoidea: Members of this class include sea lilies and feather stars. They are characterized by their feathery arms surrounding the central disc, and many species are filter feeders.
- Class Holothuroidea: This class includes sea cucumbers. They have an elongated body and reduced endoskeleton. Many sea cucumbers are detritivores, feeding on debris in the water.
Echinoderms play crucial roles in marine ecosystems, from the tidal zones to the deep sea. Their unique features, such as regeneration abilities and calcareous endoskeletons, contribute to their ecological significance.
Diversity and Distribution of Invertebrates
Invertebrates, encompassing over 95% of all animal species, exhibit an astonishing diversity in morphology, habitat, and behavior. Their distribution spans nearly every environment on Earth, showcasing their adaptability and evolutionary success.
- Global Distribution: Invertebrates are found in diverse habitats ranging from deep ocean trenches to the highest mountains, from polar ice caps to tropical rainforests. Their adaptability to extreme conditions is remarkable.
- Marine Invertebrates: The oceans are teeming with a vast array of invertebrates like mollusks, echinoderms, and cnidarians. Coral reefs, in particular, are biodiversity hotspots, supporting thousands of invertebrate species.
- Terrestrial Invertebrates: Land-based ecosystems host numerous invertebrates, including insects, spiders, and worms. They play crucial roles in soil formation, pollination, and as a food source for other animals.
- Freshwater Invertebrates: Lakes, rivers, and streams are home to diverse invertebrate species, such as crustaceans and aquatic insects, crucial for maintaining ecological balance in freshwater systems.
- Role in Ecosystems: Invertebrates are vital for ecological functions like pollination, decomposition, and as a part of the food web. They are indicators of environmental health and play a key role in nutrient cycling.
The diversity and distribution of invertebrates reflect their evolutionary success and their critical role in sustaining ecosystems worldwide.

Common Types of Invertebrates
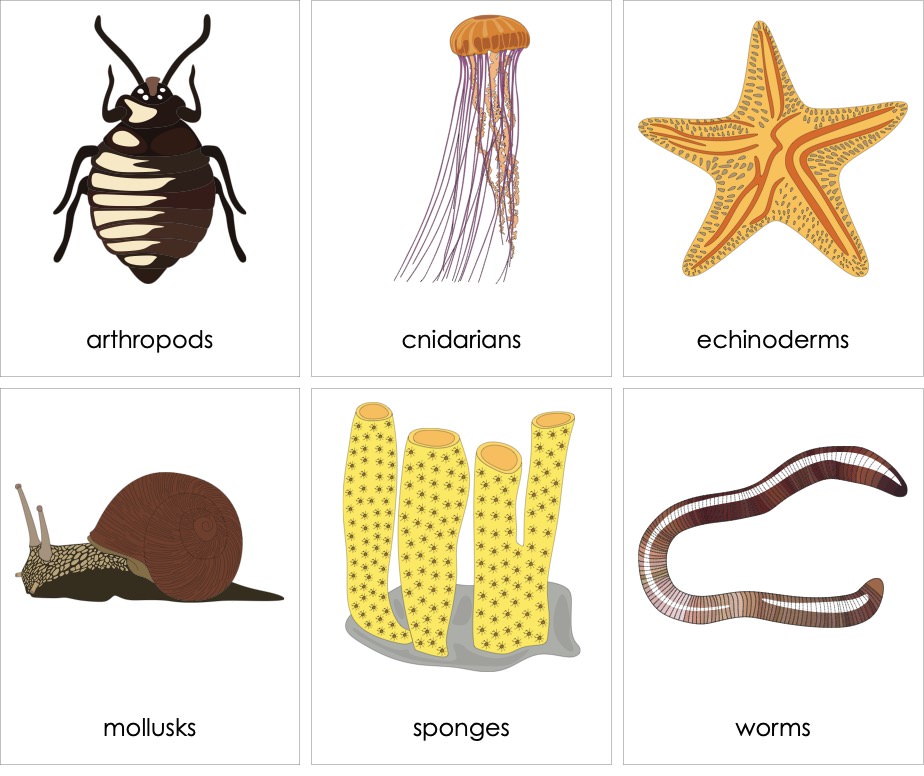
Invertebrates, which comprise a majority of the animal kingdom, display a stunning array of forms and functions. This diverse group includes creatures ranging from microscopic organisms to larger, more complex beings. Their classification spans multiple phyla, each with distinct characteristics.
- Phylum Arthropoda: This is the largest phylum in the animal kingdom and includes insects, arachnids (like spiders and scorpions), and crustaceans (such as crabs, lobsters, and shrimp). Arthropods are characterized by their segmented bodies, exoskeleton made of chitin, and jointed appendages.
- Phylum Mollusca: Mollusks are a diverse group, including snails, slugs, clams, octopuses, and squid. They are known for their soft bodies, and many have a hard shell for protection.
- Phylum Annelida: This group includes segmented worms like earthworms and leeches. They have a body divided into ring-like segments and play vital roles in soil health and ecology.
- Phylum Nematoda: Also known as roundworms, nematodes are found in a variety of habitats, including soil, water, and as parasites in plants and animals. They have a cylindrical shape and are known for their resilience in diverse environments.
- Phylum Echinodermata: Echinoderms, such as starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers, are primarily marine animals known for their radial symmetry and spiny skin.
- Phylum Cnidaria: This group includes jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones, known for their stinging cells used in capturing prey and defense.
- Phylum Porifera: Commonly known as sponges, these are simple, sessile animals mainly found in marine environments. They have porous bodies and are filter feeders.
Invertebrates play crucial roles in ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and food sources for other animals. Their study offers insights into biodiversity, ecology, and evolutionary biology.
Invertebrate Classification
Invertebrates: Discover the fascinating world of invertebrates! Watch our video to learn about the incredible variety of these spineless creatures, from beautiful butterflies to peculiar octopuses. Get ready to be amazed by their remarkable adaptations and diverse lifestyles!
Introduction to Invertebrates
Introduction: Are you ready for an exciting journey into the unknown? Join us in this video introduction where we\'ll delve into captivating topics and unlock mysteries you never thought possible. Get ready to embark on an enlightening adventure that will leave you craving for more knowledge!
READ MORE:
Role and Importance of Invertebrates