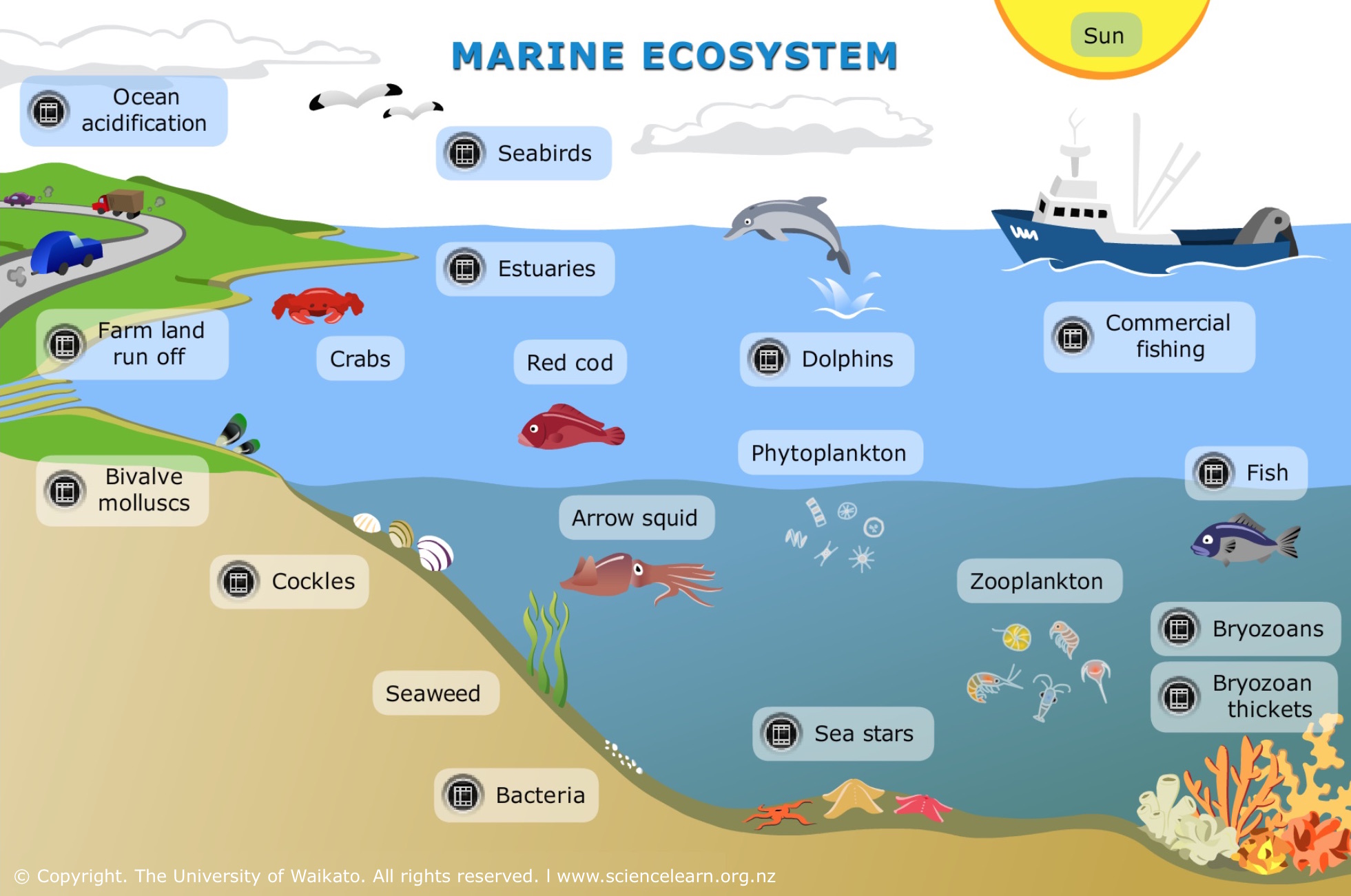
Topic ecosystem grassland animals: Discover the vibrant world of ecosystem grassland animals, where diverse species thrive in harmony, shaping the ecological balance of our planet"s vast grasslands.
Table of Content
- What types of animals are found in grassland ecosystems?
- Overview of Grassland Ecosystems
- Key Animals in Grassland Ecosystems
- Adaptations of Grassland Animals
- The Role of Predators in Grassland Ecosystems
- Migratory Patterns of Grassland Animals
- Impact of Human Activities on Grassland Animals
- YOUTUBE: Grassland Ecosystem Animation
- Conservation Efforts for Grassland Ecosystems
- Interactions Among Grassland Animals
- Grassland Ecosystems Around the World
- Future of Grassland Ecosystems and Their Inhabitants
What types of animals are found in grassland ecosystems?
Grassland ecosystems are home to a wide variety of animals. Some of the common types of animals found in grassland ecosystems include:
- Giraffes
- African elephants
- Bison
- Black rhinoceros
- Black-footed ferrets
These animals play important roles in the grassland ecosystem. They interact with the grasses and other organisms, contributing to the overall balance and functioning of the ecosystem.
Additionally, grassland ecosystems support a diverse range of smaller animals such as insects, rodents, rabbits, snakes, and various bird species. These organisms play vital roles in nutrient cycling, pollination, seed dispersal, and pest control within the ecosystem.
The presence of these animals within the grassland ecosystem is crucial for maintaining the ecological balance and promoting the overall health and sustainability of these habitats.
READ MORE:
Overview of Grassland Ecosystems
Grassland ecosystems, encompassing vast expanses of open and semi-open landscapes, are critical to the biodiversity of our planet. These ecosystems are defined by their dominant vegetation—grasses, herbs, and shrubs—that support a rich variety of life. Grasslands are found across the globe, from the prairies of North America to the savannas of Africa, each with unique species adapted to the local climate and soil conditions.
- Characteristics of Grassland Ecosystems: Predominantly covered by grasses, these areas receive enough rainfall to prevent deserts from forming but not enough for forests to grow.
- Types of Grasslands: Includes temperate grasslands, tropical savannas, and subtropical grasslands, each distinguished by climate, flora, and fauna.
- Importance of Grasslands: They play a vital role in carbon storage, flood mitigation, and providing habitats for numerous species.
- Threats to Grasslands: Despite their importance, grasslands face threats from land conversion, overgrazing, and climate change, impacting their biodiversity and ecological functions.
Understanding the dynamics of grassland ecosystems is crucial for their conservation and the sustainability of their animal populations. By protecting these landscapes, we safeguard a significant part of Earth"s biodiversity and maintain the ecological services they provide.

Key Animals in Grassland Ecosystems
Grassland ecosystems are teeming with a diverse array of animal life, each species playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of these environments. From the vast savannas of Africa to the prairies of North America, these habitats support a range of key animal species that are essential for the ecosystem"s health and stability.
- African Savannas: Home to iconic species such as elephants, lions, zebras, and giraffes, which are integral to the savanna"s ecological dynamics.
- North American Prairies: Host to bison, prairie dogs, and various bird species like the greater prairie-chicken, which contribute to the prairie"s biodiversity.
- Asian Steppes: Roamed by species like the Saiga antelope and the Siberian tiger, showcasing the unique fauna adapted to these regions.
- South American Pampas: Inhabited by the guanaco, rhea, and many bird species, highlighting the rich biodiversity of the grassland ecosystems in South America.
These animals are not only vital for the ecological balance but also for the cultural and economic aspects of human societies surrounding these ecosystems. They play key roles in pollination, seed dispersal, and controlling the populations of other species, thereby maintaining the health of grasslands worldwide.
Adaptations of Grassland Animals
Animals inhabiting grassland ecosystems have evolved a variety of adaptations to survive in these open habitats, where environmental conditions can be extreme and food availability varies seasonally. These adaptations not only enable them to thrive in their respective ecosystems but also play a significant role in the ecological balance of grasslands.
- Speed and Endurance: Many grassland predators and prey, such as cheetahs and antelopes, have developed remarkable speed and endurance to escape predators or catch their prey.
- Camouflage: Species like the grasshopper and certain bird species have adapted their coloration to blend in with the grassland environment, making it difficult for predators to spot them.
- Diet Specialization: Herbivores such as bison and zebras have specialized digestive systems to efficiently process the tough, fibrous grasses that dominate their habitats.
- Social Structures: Many grassland animals, including elephants and wolves, form complex social structures that help in protection, foraging, and raising young.
- Burrowing and Digging: Animals like prairie dogs and aardvarks have developed burrowing abilities to escape predators and extreme weather, as well as to access underground food sources.
These adaptations are crucial for the survival of grassland animals, allowing them to exploit different niches within the ecosystem and maintain the diversity and productivity of grassland habitats around the world.

The Role of Predators in Grassland Ecosystems
Predators play a vital role in maintaining the health and balance of grassland ecosystems. Through their interactions with prey species, they help regulate animal populations, maintain biodiversity, and influence the structure of the community.
- Population Control: Predators such as lions, wolves, and birds of prey help keep herbivore populations in check, preventing overgrazing and ensuring vegetation remains abundant for other species.
- Promoting Biodiversity: By preying on the most abundant species, predators prevent any single species from dominating the ecosystem, thus maintaining a diverse range of plant and animal life.
- Encouraging Healthy Prey Populations: Predation pressure can lead to the survival of the fittest prey individuals, promoting healthy and genetically robust populations.
- Impact on Ecosystem Structure: Predators influence the spatial distribution of herbivores, which can affect plant community composition and the physical structure of the habitat.
Understanding the intricate role of predators within grassland ecosystems underscores the importance of conserving these keystone species to ensure the stability and diversity of these habitats worldwide.
Migratory Patterns of Grassland Animals
Migratory patterns are a critical aspect of the survival strategies of many grassland animals, allowing them to navigate the vast expanses of their habitats in search of food, water, and breeding grounds. These movements are essential for the dispersal of species and the transfer of energy within the ecosystem.
- Seasonal Migrations: Animals such as wildebeest, zebras, and antelopes undertake long-distance migrations to follow the seasonal availability of food and water resources.
- Breeding Migrations: Species like certain birds migrate to grasslands for breeding purposes, taking advantage of the optimal conditions and abundant resources for raising their young.
- Altitudinal Migrations: Some species, including certain herds of sheep and goats, move between different elevations within grassland ecosystems in response to seasonal weather changes.
- Impact on Ecosystems: These migratory movements help in the pollination of plants, the distribution of seeds, and the control of local populations of pests and other animals.
The migratory patterns of grassland animals are a remarkable demonstration of nature"s adaptability and resilience, highlighting the interconnectedness of species within these ecosystems and the importance of preserving migratory corridors for their survival.

Impact of Human Activities on Grassland Animals
Human activities have significantly impacted grassland ecosystems worldwide, affecting the habitats and populations of grassland animals. These activities range from land conversion and agriculture to pollution and climate change, each with its consequences on the delicate balance of these ecosystems.
- Land Conversion: The transformation of grasslands into agricultural lands, urban areas, and for other developmental purposes reduces the available habitat for native species, leading to population declines.
- Overgrazing: Livestock farming often leads to overgrazing, which degrades the quality of grassland habitats, affecting the food sources for wild herbivores.
- Pollution: Chemical runoff from agriculture and industrial activities contaminates water sources and soil, impacting the health and reproductive success of grassland animals.
- Climate Change: Altered rainfall patterns and increased temperatures affect the growth of vegetation, water availability, and consequently the survival of many species dependent on grassland ecosystems.
- Conservation Efforts: In response to these challenges, conservation initiatives aim to protect and restore grassland habitats, promote sustainable land-use practices, and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
The collective effort to understand and reduce the impact of human activities on grassland ecosystems is crucial for preserving the biodiversity and ecological services these habitats provide.
Grassland Ecosystem Animation
This animation will take you on a magical journey filled with captivating visuals and heartwarming characters. Get ready to be enchanted and entertained like never before!
Let\'s Explore the Grassland Biome
Get ready to explore uncharted territories and discover a whole new world in this fascinating video. Join us on this adventure as we delve into unknown realms and uncover hidden treasures.
Conservation Efforts for Grassland Ecosystems
Conservation efforts for grassland ecosystems are crucial for preserving their biodiversity and the ecological services they provide. These initiatives aim to protect and restore these vital habitats, ensuring the survival of the myriad species that depend on them.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, reserves, and wildlife sanctuaries to protect grassland habitats from development and degradation.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agricultural and grazing practices to minimize impact on grasslands, including rotational grazing and the use of native plant species in restoration efforts.
- Species Reintroduction: Reintroducing native species to restore ecological balances, such as the bison in North America or the Przewalski"s horse in Mongolia"s steppes.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts through education and participatory management programs to ensure the sustainable use of grassland resources.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Implementing strategies to reduce the impact of climate change on grasslands, including carbon sequestration projects and habitat connectivity to facilitate species migration.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting ongoing research and monitoring to understand the impacts of human activities on grasslands and to inform conservation strategies.
Through these and other efforts, conservationists are working to ensure that grassland ecosystems continue to thrive, supporting the incredible diversity of life they harbor and the human communities that rely on them.

Interactions Among Grassland Animals
The interactions among grassland animals are complex and multifaceted, playing a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance and health of these ecosystems. These interactions range from predation and competition to symbiosis and mutualism, each contributing to the dynamic nature of grassland ecosystems.
- Predation: Predators and prey engage in a constant struggle for survival, which regulates populations and helps maintain species diversity.
- Competition: Animals compete for resources such as food, water, and territory, which influences their behavior, distribution, and population dynamics.
- Mutualism: Some species form mutually beneficial relationships, such as certain birds that feed on parasites found on large mammals, keeping them healthy.
- Symbiosis: Symbiotic relationships between species, such as those between pollinators and flowering plants, are critical for the reproduction of many grassland species.
- Social Interactions: Social species form groups that help protect members from predators, increase foraging efficiency, and assist in rearing young.
Understanding the intricate web of interactions among grassland animals is essential for grasping the full complexity of these ecosystems and the importance of each species within it. These relationships highlight the interconnectedness of life and the need for comprehensive conservation strategies to preserve these dynamic habitats.
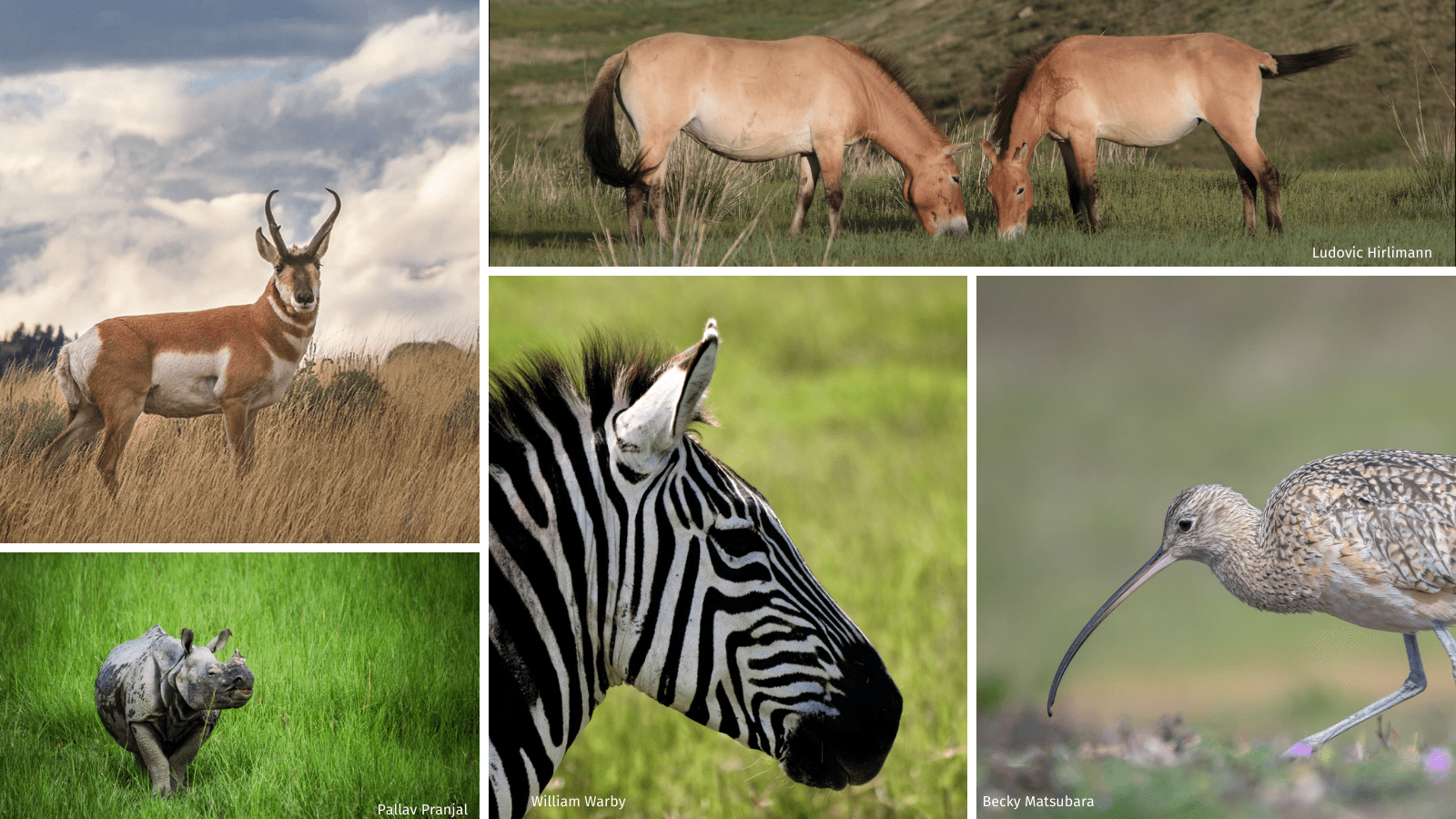
Grassland Ecosystems Around the World
Grassland ecosystems, with their vast expanses and rich biodiversity, are found across every continent except Antarctica. Each region hosts unique grassland environments that support a wide array of flora and fauna, adapted to local conditions. Here, we explore some of the most notable grassland ecosystems around the world.
- The Great Plains of North America: Spanning multiple U.S. states and Canadian provinces, this area is home to species such as the American bison, pronghorn antelope, and hundreds of bird species.
- The Savannas of Africa: Iconic for their large herds of wildebeest, zebras, elephants, and predators like lions and cheetahs, these ecosystems are crucial for Africa"s biodiversity.
- The Steppes of Central Asia: These vast grasslands are home to unique species like the Saiga antelope and the Siberian crane, adapted to the extreme climatic conditions.
- The Pampas of South America: These fertile plains are inhabited by a variety of species, including the guanaco, rhea, and many endemic bird species.
- The Australian Grasslands: Supporting kangaroos, emus, and a multitude of bird and plant species, these grasslands are adapted to Australia"s variable climate.
Each of these ecosystems not only supports wildlife but also plays a critical role in the culture and economy of the local human populations. Preserving these grassland ecosystems is essential for maintaining global biodiversity and ecological balance.

READ MORE:
Future of Grassland Ecosystems and Their Inhabitants
The future of grassland ecosystems and their diverse inhabitants hinges on the balance between human activities and conservation efforts. These vital habitats face challenges, but with strategic actions and global cooperation, we can ensure their preservation for future generations.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Implementing strategies to help grassland ecosystems adapt to changing climates, including preserving water resources and preventing desertification.
- Conservation and Restoration: Expanding protected areas, restoring degraded grasslands, and reintroducing native species to strengthen ecosystem resilience.
- Sustainable Management: Encouraging sustainable agriculture and grazing practices that support both human livelihoods and wildlife conservation.
- Research and Monitoring: Investing in research to understand ecosystem dynamics and the impacts of human activities, guiding effective conservation strategies.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their role as stewards of grassland ecosystems and their biodiversity.
By prioritizing these efforts, we can protect the delicate balance of grassland ecosystems, ensuring they continue to support a rich diversity of life and provide ecological services that are crucial for our planet.
Embracing the wonders of grassland ecosystems and their animals invites us to a world of discovery, underscoring the urgent need for conservation to preserve these vital habitats for future generations.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/164249141-56a006353df78cafda9fb0e5-be1ea8f1f1774e12bde868a948812d8d.jpg)