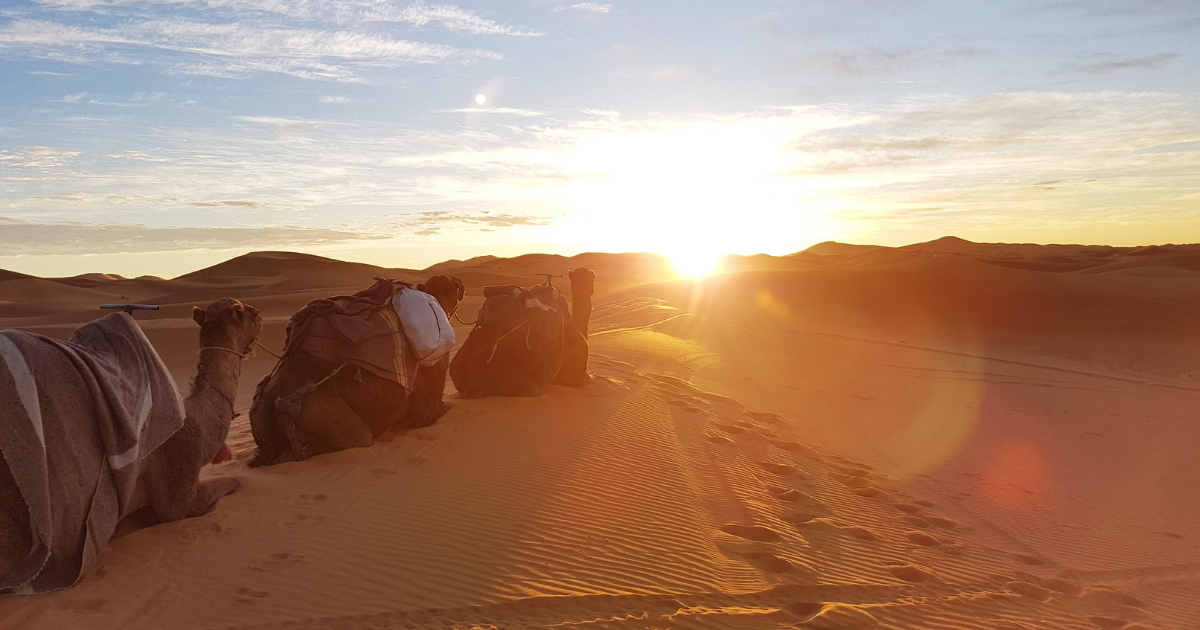
Topic sahara desert temperature at night: Explore the enchanting Sahara Desert, where nighttime reveals a dramatic shift in temperature, transforming the landscape into a surprisingly chilly realm, a stark contrast to its daytime blaze.
Table of Content
- What is the typical temperature at night in the Sahara Desert?
- Overview of Sahara Desert Climate
- Temperature Variations: Day vs. Night
- Causes of Drastic Night Temperature Drop
- Impact of Sand and Lack of Humidity
- Seasonal Temperature Fluctuations
- Geographical Influence on Night Temperatures
- YOUTUBE: The Science behind the Desert\'s Temperature Shifts: Hot Days and Cold Nights
- Wildlife Adaptations to Extreme Temperatures
- Human Experience and Preparation for Sahara Nights
- Interesting Facts: Snowfall and Record Temperatures
- Exploring the Sahara: Activities and Survival Tips
What is the typical temperature at night in the Sahara Desert?
The typical temperature at night in the Sahara Desert can vary, but it is generally known for experiencing significant temperature drops. The desert\'s arid climate and lack of vegetation contribute to the rapid cooling effect during the night.
According to various sources, the average nighttime temperature in the Sahara Desert can drop as much as 75 degrees Fahrenheit (42 degrees Celsius). This temperature drop is quite significant and can make the nights in the Sahara Desert extremely cold, especially when compared to the scorching daytime temperatures that can reach up to 50 degrees Celsius.
It\'s important to note that the exact nighttime temperature in the Sahara Desert can vary depending on the time of year, location within the desert, and other factors. These variations can also be influenced by altitude, with lower-lying areas experiencing slightly higher temperatures compared to elevated regions.
- During the night in the Sahara Desert:
- Temperatures can drop an average of 75 degrees Fahrenheit (42 degrees Celsius) overnight.
- The rapid cooling effect is due to the desert\'s arid climate and lack of vegetation.
- Nighttime temperatures are significantly colder compared to the scorching daytime temperatures.
- Exact temperatures can vary based on factors such as time of year, location, and altitude.
Overall, the Sahara Desert experiences a considerable drop in temperature during the night, making it a challenging environment for survival without proper preparation.
READ MORE:
Overview of Sahara Desert Climate
The Sahara Desert, known for its vast, arid landscape, exhibits one of the most extreme climates on Earth. Dominating North Africa, it is the world"s largest hot desert, characterized by scorching daytime temperatures, scarce rainfall, and surprisingly cold nights.
- Daytime temperatures often exceed 100°F (38°C), creating a sun-baked environment with minimal shade.
- Night temperatures can plummet to around 25°F (-4°C), a stark contrast to the daytime heat.
- The desert"s aridity is due to its location in the subtropical ridge, an area of high pressure where moisture is scarce.
- Seasonal variations include hotter summers with temperatures soaring above 120°F (49°C), and milder winters, with cooler but still significant daytime warmth.
- Geographical factors like altitude and proximity to the equator play a critical role in these temperature extremes.
- Lack of cloud cover and low humidity levels contribute significantly to the rapid cooling at night.
The Sahara"s climate presents a unique challenge for its inhabitants and wildlife, necessitating remarkable adaptations to survive in such harsh conditions.

Temperature Variations: Day vs. Night
The Sahara Desert showcases one of the most extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night, an intriguing phenomenon that defines its unique climate.
- Daytime Heat: During the day, the Sahara becomes intensely hot. Temperatures often soar above 100°F (38°C), peaking at times near 120°F (49°C) in summer. This is due to direct solar radiation, minimal cloud cover, and the heat-retaining properties of sand.
- Nighttime Chill: Contrary to its daytime heat, nighttime in the Sahara sees a dramatic drop in temperatures. It"s not uncommon for the temperature to plummet to around 25°F (-4°C), and even lower in winter months. This rapid cooling occurs due to the desert"s dry air and the sand"s inability to retain heat after sunset.
- Factors Influencing Temperature Shifts: Several factors contribute to these dramatic shifts, including the desert"s low humidity, the high thermal emissivity of the sand, and the clear skies which facilitate rapid heat loss at night.
- Seasonal Variations: While these temperature shifts are observed year-round, they are more pronounced during certain seasons. In summer, the temperature difference between day and night can be even more extreme.
This remarkable temperature swing from the scorching heat of the day to the cold of the night makes the Sahara Desert a fascinating subject for climatologists and travelers alike.
Causes of Drastic Night Temperature Drop
The Sahara Desert"s night-time temperature drop is a result of several key environmental factors that interact in unique ways.
- Sand as a Poor Heat Retainer: The Sahara"s sandy terrain heats up quickly under the sun but doesn"t retain that heat. Once the sun sets, the heat stored in the sand dissipates rapidly into the atmosphere, leading to a sharp decrease in temperature.
- Low Humidity: The Sahara"s air is extremely dry, with minimal humidity. Humid air retains heat more effectively than dry air. Therefore, in the absence of moisture, the desert cannot hold onto the day"s heat, resulting in a steep temperature decline at night.
- Clear Skies: Cloud cover can act as an insulating layer, trapping heat close to the Earth"s surface. However, the Sahara typically has clear skies, which means there is no cloud cover to retain heat during the night, contributing to the temperature plunge.
- Radiational Cooling: This process occurs when the Earth"s surface loses its heat by radiation. The desert sands and rocks, having absorbed heat during the day, radiate it back into the atmosphere at night, leading to a cooler environment.
- Geographical Location: The Sahara"s proximity to the equator means it receives intense and direct sunlight during the day but also contributes to rapid cooling when the sun sets.
These factors together create the unique and extreme climate of the Sahara, where temperatures can swing dramatically from day to night.

Impact of Sand and Lack of Humidity
The Sahara Desert"s night-time temperature drop is a result of several key environmental factors that interact in unique ways.
- Sand as a Poor Heat Retainer: The Sahara"s sandy terrain heats up quickly under the sun but doesn"t retain that heat. Once the sun sets, the heat stored in the sand dissipates rapidly into the atmosphere, leading to a sharp decrease in temperature.
- Low Humidity: The Sahara"s air is extremely dry, with minimal humidity. Humid air retains heat more effectively than dry air. Therefore, in the absence of moisture, the desert cannot hold onto the day"s heat, resulting in a steep temperature decline at night.
- Clear Skies: Cloud cover can act as an insulating layer, trapping heat close to the Earth"s surface. However, the Sahara typically has clear skies, which means there is no cloud cover to retain heat during the night, contributing to the temperature plunge.
- Radiational Cooling: This process occurs when the Earth"s surface loses its heat by radiation. The desert sands and rocks, having absorbed heat during the day, radiate it back into the atmosphere at night, leading to a cooler environment.
- Geographical Location: The Sahara"s proximity to the equator means it receives intense and direct sunlight during the day but also contributes to rapid cooling when the sun sets.
These factors together create the unique and extreme climate of the Sahara, where temperatures can swing dramatically from day to night.
Seasonal Temperature Fluctuations
The Sahara Desert"s night-time temperature drop is a result of several key environmental factors that interact in unique ways.
- Sand as a Poor Heat Retainer: The Sahara"s sandy terrain heats up quickly under the sun but doesn"t retain that heat. Once the sun sets, the heat stored in the sand dissipates rapidly into the atmosphere, leading to a sharp decrease in temperature.
- Low Humidity: The Sahara"s air is extremely dry, with minimal humidity. Humid air retains heat more effectively than dry air. Therefore, in the absence of moisture, the desert cannot hold onto the day"s heat, resulting in a steep temperature decline at night.
- Clear Skies: Cloud cover can act as an insulating layer, trapping heat close to the Earth"s surface. However, the Sahara typically has clear skies, which means there is no cloud cover to retain heat during the night, contributing to the temperature plunge.
- Radiational Cooling: This process occurs when the Earth"s surface loses its heat by radiation. The desert sands and rocks, having absorbed heat during the day, radiate it back into the atmosphere at night, leading to a cooler environment.
- Geographical Location: The Sahara"s proximity to the equator means it receives intense and direct sunlight during the day but also contributes to rapid cooling when the sun sets.
These factors together create the unique and extreme climate of the Sahara, where temperatures can swing dramatically from day to night.

Geographical Influence on Night Temperatures
The Sahara Desert"s night temperatures are profoundly influenced by its geography, which plays a key role in its unique climatic conditions.
- Desert"s Location: The Sahara, located near the equator, receives intense sunlight, contributing to its high daytime temperatures and subsequent rapid cooling at night.
- Altitude Variations: Varying elevations in the Sahara lead to different temperature experiences. Higher altitudes typically have cooler temperatures, which are more pronounced at night.
- Proximity to Seas: Areas of the Sahara closer to the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean can experience milder temperatures due to the influence of these large water bodies.
- Diverse Topography: The Sahara"s diverse landscape, including mountains, plateaus, and dunes, affects local temperature variations, with mountainous areas often experiencing more significant temperature drops at night.
- Wind Patterns: Winds like the Sirocco and Harmattan, can move hot air during the day and cooler air at night across the desert, affecting the night temperatures in different regions of the Sahara.
This complex geographical interplay contributes to the Sahara"s dramatic temperature variations, particularly at night, adding to its mystique and allure as a natural wonder.
The Science behind the Desert\'s Temperature Shifts: Hot Days and Cold Nights
\"Discover the fascinating world of temperature shifts in this captivating video! Explore how different elements react to changes in temperature and witness the incredible transformations that occur. Get ready for mind-blowing revelations that will leave you in awe!\"
Understanding the Chilling Phenomenon: Why Deserts Turn Cold at Night
\"Prepare to be chilled to the core as we unravel the haunting mysteries behind this chilling phenomenon. Step into the unknown and experience spine-tingling encounters that will send shivers down your spine. Brace yourself for an unforgettable journey into the chilling depths of the unexplained!\"
Wildlife Adaptations to Extreme Temperatures
The Sahara Desert"s extreme temperatures have led to fascinating adaptations among its wildlife, enabling them to thrive in this harsh environment.
- Adaptations for Heat and Cold: Many Sahara animals are nocturnal, active during cooler night temperatures to avoid daytime heat. Species like the dromedary camel have developed physiological adaptations, such as fluctuating body temperatures and features to protect against sand and heat.
- Water Conservation: Animals such as the dorcas gazelle have evolved to sustain themselves without direct water consumption, getting hydration from their food. Camels, known for their ability to travel long distances without water, can drink large quantities when available, preparing for dry conditions.
- Camouflage and Hunting Strategies: The sand viper, for example, uses its coloration for camouflage and a unique hunting strategy mimicking a worm to attract prey. Animals like the Saharan cheetah have adapted to the limited availability of prey due to the desert"s harsh conditions.
- Physical Adaptations: The fennec fox, with its large ears, dissipates heat and has excellent hearing to detect prey. The gerbil"s large eyes enhance its night vision, crucial for nocturnal life.
- Plant Adaptations: Sahara plants like date palms and acacias have long roots to access water, while other plants complete their life cycle quickly after rare rainfalls.
- Threats and Conservation: Many Sahara species face threats from habitat loss, climate change, and human activities. Conservation efforts focus on habitat preservation and combating illegal wildlife trade to protect these unique desert dwellers.
These adaptations highlight the resilience and ingenuity of life in one of the world"s most extreme environments.
Human Experience and Preparation for Sahara Nights
Experiencing the Sahara Desert at night requires understanding and preparation for its extreme temperature variations. Here"s how visitors and locals adapt:
- Understanding Temperature Swings: The Sahara Desert experiences a dramatic temperature drop at night, often falling to around 25°F (-4°C) after daytime highs above 100°F (38°C). Awareness of this dramatic shift is crucial for anyone planning to stay overnight in the desert.
- Appropriate Clothing: Due to the significant drop in temperature, it"s essential to carry warm clothing for the night, including a winter jacket, despite the desert"s daytime heat.
- Staying Hydrated and Protected During the Day: During the day, the intense heat and sun exposure require ample hydration and sun protection, including hats, sunscreen, and sunglasses.
- Shelter and Sleeping Arrangements: Adequate shelter, such as tents or desert camps, is vital for protection against the cold and potential wind at night.
- Adapting to Dry Conditions: The Sahara is extremely arid, with low humidity levels, which contributes to the rapid cooling at night. Visitors should be prepared for these dry conditions both during the day and night.
- Navigating the Terrain: Knowledge of the Sahara’s diverse terrain, including sand dunes and rocky areas, is important for safe navigation, especially during the cooler, more manageable night hours.
- Respecting Wildlife: The Sahara is home to wildlife that has adapted to these extreme conditions. Visitors should respect the natural habitat and be aware of potential wildlife encounters during nighttime explorations.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding and respecting the local culture and practices of Sahara"s inhabitants is essential for a harmonious experience.
Preparation and respect for the desert’s extreme conditions are key to a safe and enjoyable experience in the Sahara at night.
Interesting Facts: Snowfall and Record Temperatures
The Sahara Desert, known for its extreme heat, also presents some surprising climatic anomalies and record-setting temperatures.
- Snowfall in the Sahara: While a rare phenomenon, snow has been recorded in the Sahara Desert, highlighting its climatic diversity. These instances, like the snowfall in 2022, astonish both locals and scientists, given the desert"s reputation for heat.
- Record High Temperatures: The Sahara is home to some of the hottest recorded temperatures on Earth. In some areas, temperatures have soared to around 136°F (58°C), pushing the limits of human and environmental endurance.
- Extreme Winter Lows: Contrary to popular belief, winter in the Sahara can be harsh, especially in northern regions, with temperatures plummeting well below freezing, reaching as low as -36 to -52°F (-33 to -47°C).
- Temperature Variability: The Sahara experiences one of the most significant temperature variations between day and night, sometimes nearing an 80-degree difference, a testament to its unique geographical and climatic conditions.
- Historical Climate Changes: Over centuries, the Sahara has witnessed various climatic shifts, including periods of increased precipitation and colder eras, like during the Little Ice Age from the 16th to 18th centuries.
- Climate Change Impact: Studies indicate that the Sahara is witnessing shifts in its traditional weather patterns due to global climate change, with predictions of even hotter and drier conditions in the future.
These intriguing facts about the Sahara"s temperature extremes and occasional snowfall add to the mystique of this vast and seemingly inhospitable desert.

READ MORE:
Exploring the Sahara: Activities and Survival Tips
Embarking on an adventure in the Sahara Desert requires careful planning and preparation to safely enjoy its unique beauty and challenges. Here are some essential tips and activities for an unforgettable Sahara experience:
- Acclimatization to Heat: Gradually get used to the desert"s extreme temperatures by spending time in hot environments, like saunas, before your trip. Plan your activities during the cooler hours of early morning and late afternoon to avoid the midday heat.
- Appropriate Clothing: Wear a complete desert outfit covering your entire body, including a head covering, to protect against the sun and sand. Polarized sunglasses are recommended for eye protection.
- Water Management: Drinking adequate water is crucial. Carry enough water, and if possible, boil any found water before drinking. Limiting physical activity during peak heat hours helps in conserving water.
- Navigation Tools: Consider carrying a satellite phone, GPS device, or personal locator beacon for emergency communication and navigation in the vast desert.
- Enjoying Desert Activities: Try sand surfing on the dunes, sit around a campfire during chilly nights, spot wildlife like the elusive Fennec fox, and watch the breathtaking Sahara sunsets and sunrises.
- Packing Essentials: Include items like warm clothes for the night, a first-aid kit, a flashlight, and protection for your electronics. During winter, pack extra warm clothing, and for summer, opt for loose, long-sleeved shirts to protect from the sun.
With the right preparation and respect for its natural environment, the Sahara Desert offers an adventure like no other, filled with awe-inspiring landscapes and unique experiences.
Embarking on an adventure in the Sahara Desert requires careful planning and preparation to safely enjoy its unique beauty and challenges. Here are some essential tips and activities for an unforgettable Sahara experience:
With the right preparation and respect for its natural environment, the Sahara Desert offers an adventure like no other, filled with awe-inspiring landscapes and unique experiences.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ISS-42_Richat_Structure-5ae0e2bba18d9e00372f913e.jpg)










