Topic define ecosystem biodiversity: Explore the vibrant world of ecosystem biodiversity, where life in all its forms interconnects to create a rich, resilient tapestry essential for our planet"s health and future.
Table of Content
- What is the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystems?
- Understanding Ecosystem Biodiversity
- The Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
- Types of Biodiversity: Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem
- Measuring Biodiversity: Methods and Indicators
- Threats to Ecosystem Biodiversity
- YOUTUBE: Intro to Biodiversity - Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem Biodiversity
What is the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystems?
Biodiversity and ecosystems are closely interlinked, with biodiversity playing a crucial role in the health and functioning of ecosystems. Here is a breakdown of the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystems:
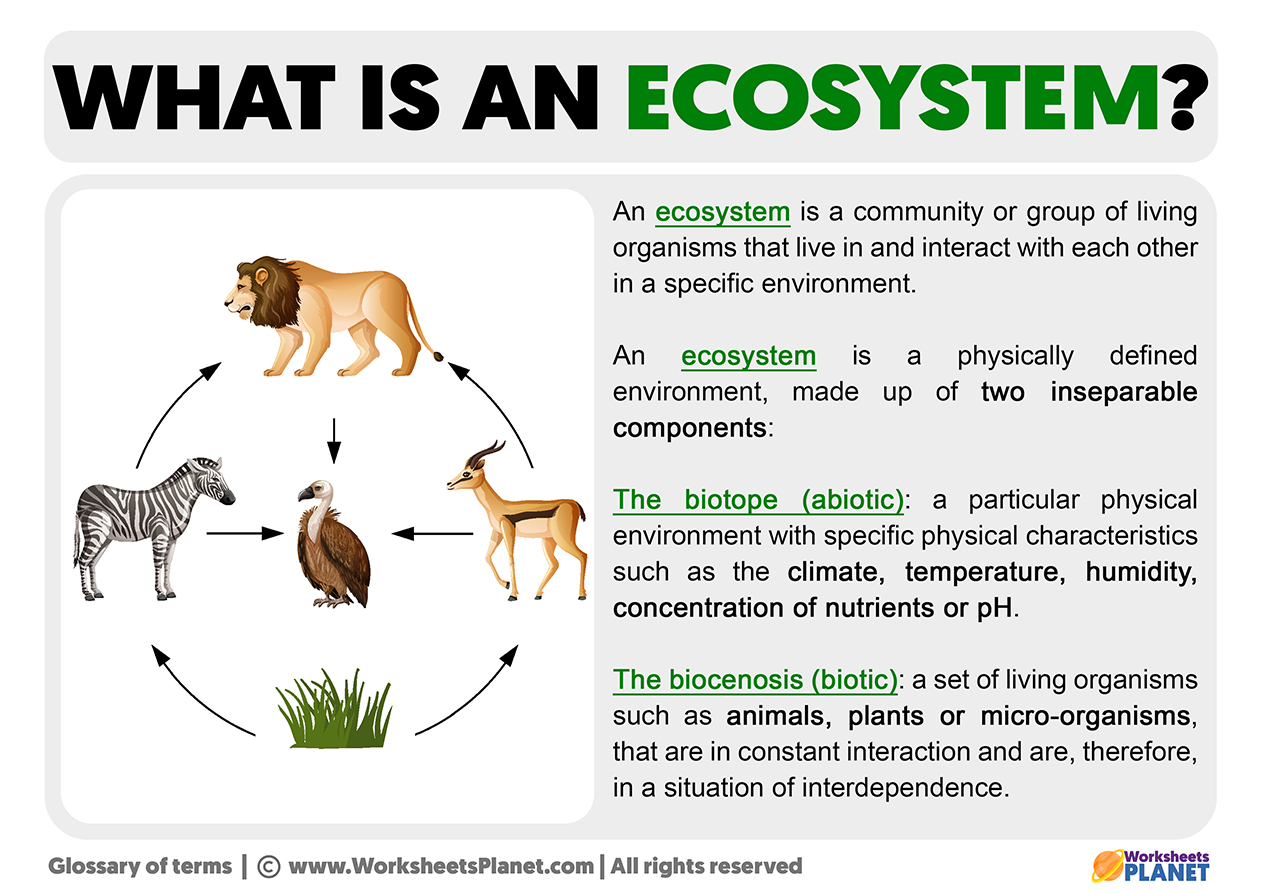
- Species Interdependence: Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in an ecosystem, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. These diverse species interact with each other in complex ways, forming intricate food webs and relationships.
- Ecosystem Stability: A high level of biodiversity in an ecosystem generally leads to greater stability. This is because diverse species can compensate for each other\'s fluctuations and help maintain balance in the ecosystem.
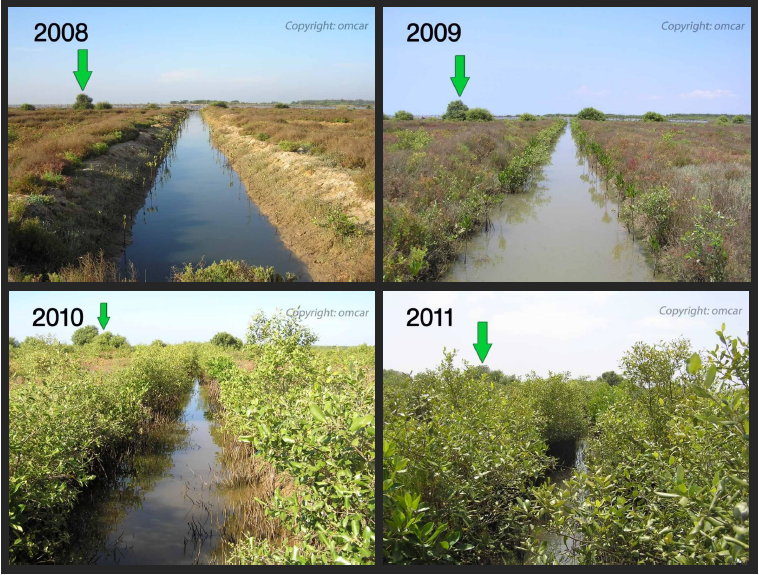
- Resilience to Disturbances: Ecosystems with higher biodiversity are often more resilient to disturbances such as climate change, pollution, and habitat destruction. A variety of species provide a natural buffer against environmental changes.
- Productivity and Nutrient Cycling: Biodiversity is essential for the efficient cycling of nutrients and energy within ecosystems. Different species perform specific functions that contribute to the overall productivity of the ecosystem.
- Supporting Services: Biodiversity supports various ecosystem services that benefit humans, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and natural pest control. Healthy ecosystems rely on diverse species to provide these services.
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystem Biodiversity
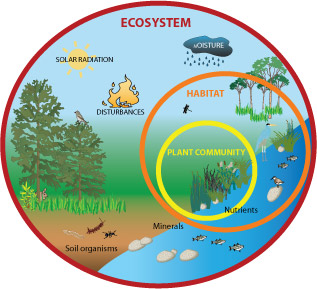
Ecosystem biodiversity is the variety and variability of life forms within a given ecosystem, encompassing the diversity of species, their genes, and the ecosystems they form. This concept is crucial for maintaining ecosystem health and resilience, offering a wide range of services to humanity, from clean air and water to pollination and climate regulation.
- Species Diversity: Refers to the variety of species within a region or ecosystem, highlighting the importance of each species in contributing to ecological balance.
- Genetic Diversity: The genetic variation within species, ensuring adaptability and resilience to changes or threats in the environment.
- Ecosystem Diversity: The variety of habitats, biotic communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere, including terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems.
Understanding the interconnectedness of these components is key to grasifying the full scope of biodiversity. It involves recognizing how species interact within ecosystems, the roles they play, and how ecosystems function as a whole. Conservation efforts focus on protecting this diversity to ensure ecosystem services continue to support life on Earth.

The Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
Biodiversity plays a pivotal role in maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems, influencing their stability, productivity, and resilience. It contributes to ecosystem services that are fundamental for life on Earth, including oxygen production, water purification, and climate regulation.
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity is at the heart of many ecosystem services that benefit humanity, such as pollination of crops, natural pest control, and genetic resources for medicine.
- Enhances Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to withstand environmental stress and recover from disturbances, thereby ensuring ecosystem stability and sustainability.
- Promotes Productivity: A rich variety of species can lead to higher productivity, as different species often perform unique roles in nutrient cycling, soil formation, and primary production.
- Facilitates Adaptation: Genetic diversity within and across species enhances their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions, crucial for survival amid climate change.
Understanding the role of biodiversity in ecosystem functioning is essential for conservation efforts, as it underscores the interconnectedness of life and the importance of preserving diverse biological communities for the health of the planet.
Types of Biodiversity: Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem
Biodiversity encompasses the variety of life on Earth, manifesting in different forms. Understanding its types—genetic, species, and ecosystem—is crucial for grasping the complexity and importance of biodiversity in sustaining ecological balance and providing essential services to humanity.
- Genetic Diversity: Refers to the variation of genes within species. This diversity allows species to adapt to changing environments, resist diseases, and contribute to the resilience and health of populations.
- Species Diversity: The diversity among species in an ecosystem. This includes all living organisms, from plants and animals to fungi and microorganisms. High species diversity increases ecosystem resilience and productivity.
- Ecosystem Diversity: Encompasses the variety of habitats, living communities, and ecological processes in the natural world. It includes forests, deserts, wetlands, grasslands, rivers, lakes, coral reefs, and many other habitats. Each ecosystem has its own unique assemblage of species and plays a critical role in providing ecosystem services.
Together, these types of biodiversity form a complex web of life that supports ecosystem functions and services critical to our survival. They offer a framework for conservation efforts, highlighting the need to protect diverse biological resources at all levels.

Measuring Biodiversity: Methods and Indicators
Accurately measuring biodiversity is fundamental for understanding its status, trends, and the impact of human activities. Various methods and indicators are employed to quantify and monitor the diversity of life across genetic, species, and ecosystem levels.
- Species Richness and Evenness: These metrics assess the number of species within a particular area and the distribution of individuals across those species, providing a snapshot of species diversity.
- Genetic Diversity Measures: Techniques such as DNA sequencing are used to evaluate the genetic variation within and between species, crucial for conservation genetics.
- Ecosystem Diversity Assessments: This involves mapping habitats and ecosystems, using satellite imagery and field surveys to understand the distribution and condition of ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Indices: Several indices, like the Shannon Diversity Index or Simpson"s Diversity Index, combine species richness and evenness to give a more comprehensive view of biodiversity.
- Indicator Species: The presence or absence of certain species, known as bioindicators, can reveal the health of an ecosystem and the impact of environmental changes.
These methods and indicators are essential tools for biodiversity research, conservation planning, and policy-making, helping to prioritize efforts to protect the most vital and vulnerable aspects of the natural world.
Threats to Ecosystem Biodiversity
Ecosystem biodiversity faces numerous threats that can lead to the degradation of habitats, loss of species, and disruption of ecological balance. Addressing these threats is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the continued provision of ecosystem services vital to human well-being.
- Habitat Destruction: The leading cause of biodiversity loss, driven by deforestation, urban expansion, agriculture, and mining activities, which fragment and degrade natural habitats.
- Climate Change: Alters temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting species distributions, breeding seasons, and migration routes, and leading to habitat loss.
- Pollution: Contaminants in the air, water, and soil can harm wildlife and disrupt delicate ecological processes, reducing biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystems and leading to species extinction.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable hunting, fishing, and logging practices deplete species at a rate faster than their natural replenishment, leading to population declines and extinction.
Combating these threats requires coordinated global efforts, including habitat protection, sustainable resource management, pollution control, and climate action. Protecting biodiversity is not only about preserving the natural world but also about safeguarding our own future.

Intro to Biodiversity - Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem Biodiversity
Biodiversity: \"Discover the beauty and importance of biodiversity in our world! Watch as diverse species interact and thrive in their natural habitats, showcasing the harmony of life on Earth.\" Ecosystem: \"Delve into the fascinating world of ecosystems and witness the intricate connections between plants, animals, and the environment. Explore the delicate balance that sustains life in this captivating video.\"
READ MORE:
What is an Ecosystem? Different Types of Ecosystem - Environmental Science - EVS - Letstute
Hello Friends, Check out this video on \"What is Ecosystem? | Different types of Ecosystem\" in #Environmental Science (EVS) by ...