Topic what is an ecosystem function: Discover the essence of ecosystem functions, the backbone of our planet"s biodiversity and ecological balance, vital for sustaining life.
Table of Content
- What are ecosystem functions and how are they related to ecosystem services?
- Definition and Importance of Ecosystem Functions
- Key Ecosystem Processes: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycling
- Types of Ecosystem Services: Provisioning, Regulating, Supporting, and Cultural
- Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
- YOUTUBE: Biodiversity and Ecosystem Function
- Examples of Ecosystem Functions: Pollination, Decomposition, and Water Purification
- Human Impact on Ecosystem Functions and Services
- Conservation and Restoration Strategies for Ecosystem Functions
- Future Challenges and Research Directions in Ecosystem Functioning
What are ecosystem functions and how are they related to ecosystem services?
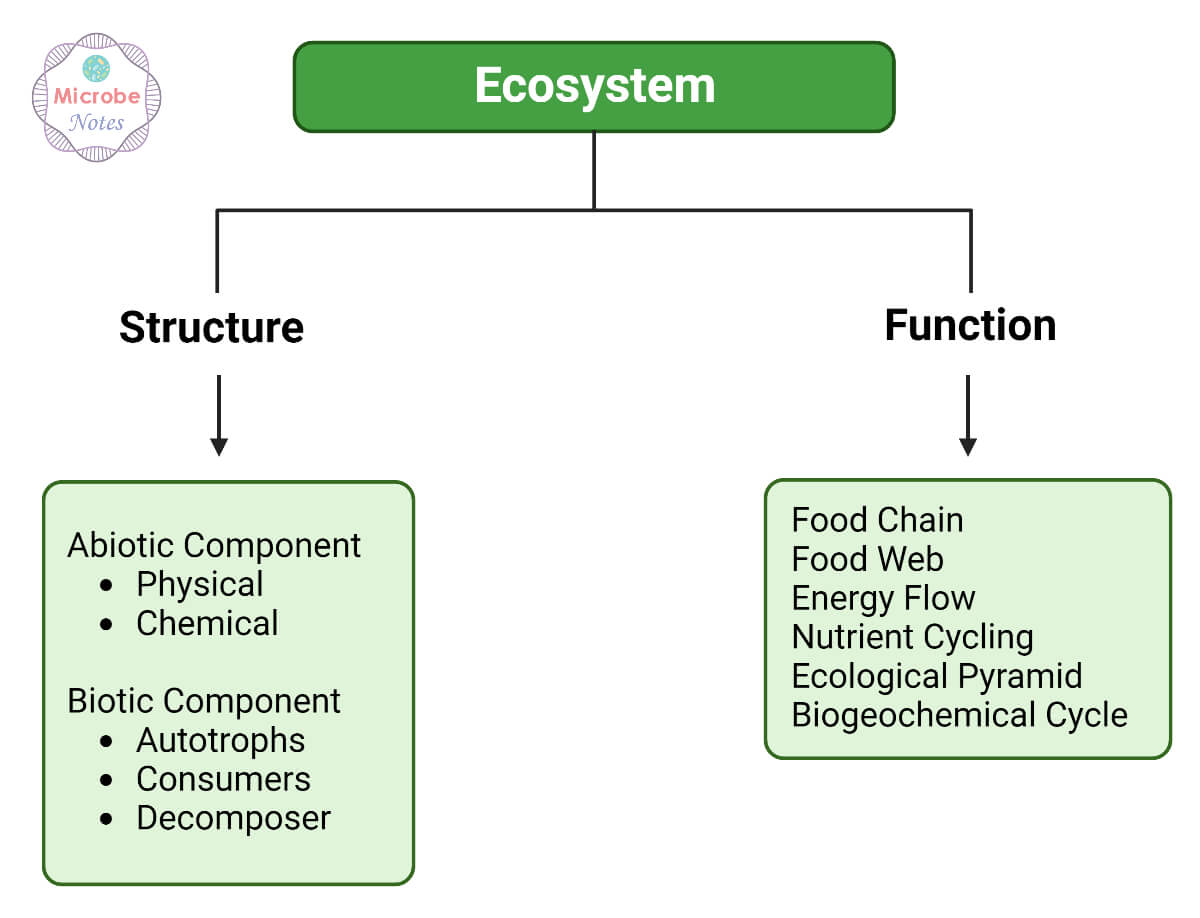
Ecosystem functions refer to the processes and interactions that occur within an ecosystem, contributing to the overall health, stability, and productivity of the system. These functions are essential for the maintenance of biodiversity, nutrient cycling, energy flow, and other ecosystem processes.
Ecosystem services, on the other hand, are the benefits that humans derive from ecosystem functions. These services can include provisioning services (such as food, water, and raw materials), regulating services (such as climate regulation, water purification, and pest control), cultural services (such as recreation, spiritual fulfillment, and cultural heritage), and supporting services (such as soil formation, nutrient cycling, and primary production).
The relationship between ecosystem functions and ecosystem services is crucial because the functions of an ecosystem determine the services it can provide. For example, the ability of an ecosystem to regulate water quality (function) can directly impact the provision of clean drinking water to humans (service). Understanding and managing ecosystem functions are therefore essential for sustaining the flow of ecosystem services that benefit both humans and the environment.
READ MORE:
Definition and Importance of Ecosystem Functions
Ecosystem functions encompass the natural processes and interactions within ecosystems that support life on Earth. These include biological, geochemical, and physical processes such as nutrient cycling, energy flow, and biodiversity maintenance, which are essential for the survival of organisms and the stability of environments.
- Nutrient Cycling: The movement of nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus through an ecosystem, vital for plant growth and energy transfer.
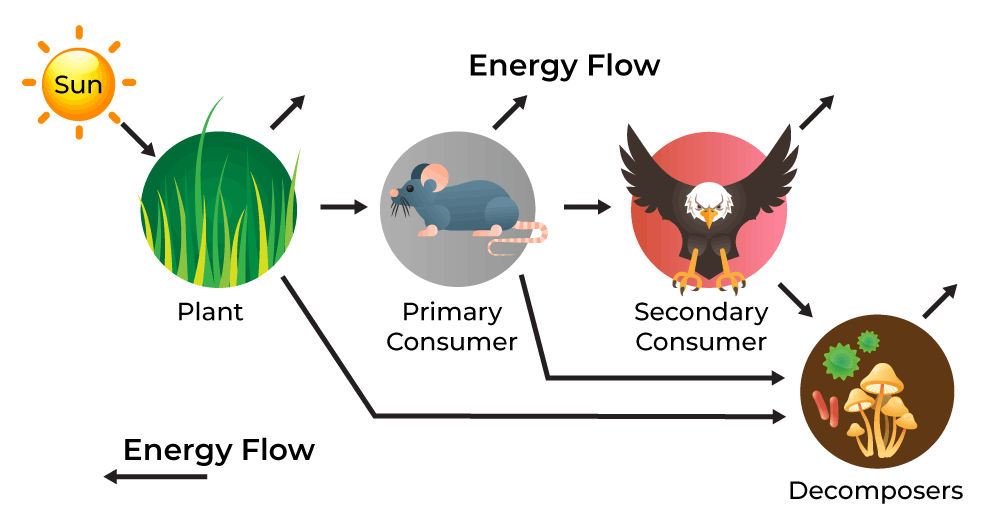
- Energy Flow: The transfer of energy from the sun through photosynthesis to various trophic levels, driving the ecosystem"s food web.
- Biodiversity Maintenance: The variety of life forms within an ecosystem, which contributes to resilience against disturbances and supports a wide range of ecosystem services.
The importance of ecosystem functions lies in their ability to provide ecosystem services, which directly or indirectly benefit human well-being. These services include provisioning services like food and water; regulating services such as climate regulation and disease control; supporting services like soil formation and nutrient cycling; and cultural services, which provide recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem functions are crucial for sustainable development and human survival, as these functions underpin the health of the planet and the resources we depend on.

Key Ecosystem Processes: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycling
Energy flow and nutrient cycling are fundamental processes that drive ecosystem functions, ensuring the survival and stability of ecosystems worldwide.
Energy Flow
Energy flow in an ecosystem starts with sunlight being captured by producers, usually plants and algae, through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred through the ecosystem via the food chain, from primary consumers (herbivores) to secondary consumers (carnivores) and decomposers, with each transfer being less efficient due to energy loss as heat.
Nutrient Cycling
Nutrient cycling involves the recycling of nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus from the environment to living organisms and back. This process is critical for the maintenance of soil fertility and the health of the ecosystem. Decomposers play a vital role in breaking down dead organisms, thus returning nutrients to the soil, which are then taken up by plants, and the cycle continues.
- Carbon Cycle: Involves the exchange of carbon among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth, crucial for regulating the Earth"s climate.
- Nitrogen Cycle: Essential for converting nitrogen available in the atmosphere into forms usable by living organisms, and vice versa, critical for protein synthesis in all living organisms.
- Phosphorus Cycle: Moves phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere, essential for cell function, DNA, and energy transfer in living organisms.
The interplay between energy flow and nutrient cycling is what sustains life, supports biodiversity, and maintains the health and resilience of ecosystems. Understanding these processes is key to addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainable management of natural resources.
Types of Ecosystem Services: Provisioning, Regulating, Supporting, and Cultural
Ecosystem services are the benefits that ecosystems provide to humanity, which are essential for our survival and well-being. These services are broadly categorized into four types:
- Provisioning Services: These are the products obtained from ecosystems, including food, fresh water, wood, fiber, genetic resources, and medicines. Provisioning services are the tangible goods that we can directly utilize for our needs.
- Regulating Services: These services include the regulation of ecosystem processes, such as climate regulation, flood control, disease regulation, water purification, and pollination. Regulating services help maintain the balance and quality of the Earth"s environment, mitigating natural and anthropogenic impacts.
- Supporting Services: Fundamental to the production of all other ecosystem services, supporting services include nutrient cycling, soil formation, primary production, and habitat provision. These services underpin the functioning of ecosystems and enable their productivity and diversity.
- Cultural Services: These are the non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems, which include aesthetic inspiration, cultural identity, sense of home, and spiritual experience related to the natural environment. Recreational, educational, and tourism opportunities also fall under this category, enriching human culture and experiences.
Understanding and valuing these services is crucial for sustainable ecosystem management and conservation efforts, ensuring that we maintain the health and resilience of our planet"s ecosystems for future generations.
Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
Biodiversity, the variety of life in all its forms, plays a pivotal role in maintaining ecosystem functions and services. It encompasses the diversity of genes, species, and ecosystems, which contribute to the resilience and adaptability of ecological systems.
- Genetic Diversity: Variability in the genetic makeup among individuals within a species ensures adaptability to changing environmental conditions, contributing to ecosystem resilience.
- Species Diversity: A higher number of species ensures a wider range of ecosystem services and functions, from pollination and seed dispersal to water purification and nutrient cycling.
- Ecosystem Diversity: Diverse ecosystems, such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands, provide varied habitats that support a wide range of biological communities.
The interconnectedness of biodiversity and ecosystem functioning is evident in the way complex ecological interactions among species influence productivity, stability, and resilience against disturbances. For instance, diverse plant communities lead to higher productivity and stability due to complementary and redundant roles in ecosystems.
Moreover, biodiversity is critical in regulating the spread of diseases and pests, with more diverse ecosystems often exhibiting greater resistance to outbreaks. It also enhances ecosystem adaptability to climate change, with a broader range of species having a higher likelihood of surviving and thriving under new environmental conditions.
Ultimately, the conservation of biodiversity is essential for sustaining ecosystem functions that humans rely on for food, clean water, and air, and overall well-being. Preserving biodiversity is not just an ecological necessity but also a critical strategy for ensuring sustainable development and resilience to environmental changes.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Function
Diversity: \"Embrace the beauty of diversity in this eye-opening video showcasing the power of different perspectives and experiences coming together. Witness the strength in unity and understanding. Don\'t miss out!\" Productivity: \"Unlock the secrets to skyrocketing your productivity in this inspiring video filled with practical tips and strategies. Learn how to maximize your efficiency and achieve your goals like never before. Watch now!\"
Functions of Ecosystem: Productivity, Decomposition, Energy Flow, Nutrient Cycling
In this short video we will discuss 4 Functions Of Ecosystem - Productivity, Decomposition, Energy Flow & Nutrient Cycling ...
Examples of Ecosystem Functions: Pollination, Decomposition, and Water Purification
Ecosystem functions are crucial for the sustainability of life on Earth, providing essential services that maintain ecological balance and support human well-being. Here are some examples:
Pollination
Pollination is a vital ecosystem function performed by various animals, including bees, butterflies, birds, and bats, which transfer pollen from one flower to another, facilitating plant reproduction. This not only ensures the survival of a wide variety of plant species but also supports agricultural productivity and biodiversity.
Decomposition
Decomposition is the process by which decomposers, such as bacteria, fungi, and certain insects, break down dead organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil and making them available for uptake by plants. This recycling of nutrients is fundamental to soil health and plant growth, supporting ecosystems" productivity.
Water Purification
Wetlands, forests, and riparian zones play a critical role in purifying water through natural filtration processes. As water moves through these ecosystems, pollutants are filtered out, and sediments are settled, resulting in cleaner water for ecosystems and human use. This function is crucial for maintaining the quality of freshwater resources and supporting aquatic life.
Understanding these functions highlights the intricate connections within ecosystems and underscores the importance of conserving natural habitats to ensure the continuity of these vital services.
Human Impact on Ecosystem Functions and Services
Human activities have profound impacts on ecosystem functions and services, often leading to significant ecological changes and challenges. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing sustainable practices and mitigating negative consequences.
Land Use Change
Conversion of natural habitats into agricultural lands, urban areas, and industrial sites reduces biodiversity, alters nutrient cycling, and disrupts habitats. This leads to a decline in ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, water filtration, and soil fertility.
Pollution
Emission of pollutants into the air, water, and soil affects ecosystem functions by contaminating water sources, degrading soil quality, and impacting the health of wildlife. Chemical pollutants can disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems, leading to loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Climate Change
Climate change, driven by the release of greenhouse gases from human activities, affects ecosystems by altering temperature and precipitation patterns. This can lead to shifts in species distributions, changes in flowering and migration timings, and increased vulnerability of ecosystems to invasive species and diseases.
Overexploitation
Overfishing, overhunting, and overharvesting of natural resources can deplete populations of key species, disrupt food webs, and reduce ecosystem resilience. This threatens the sustainability of provisioning services like food, medicine, and raw materials.
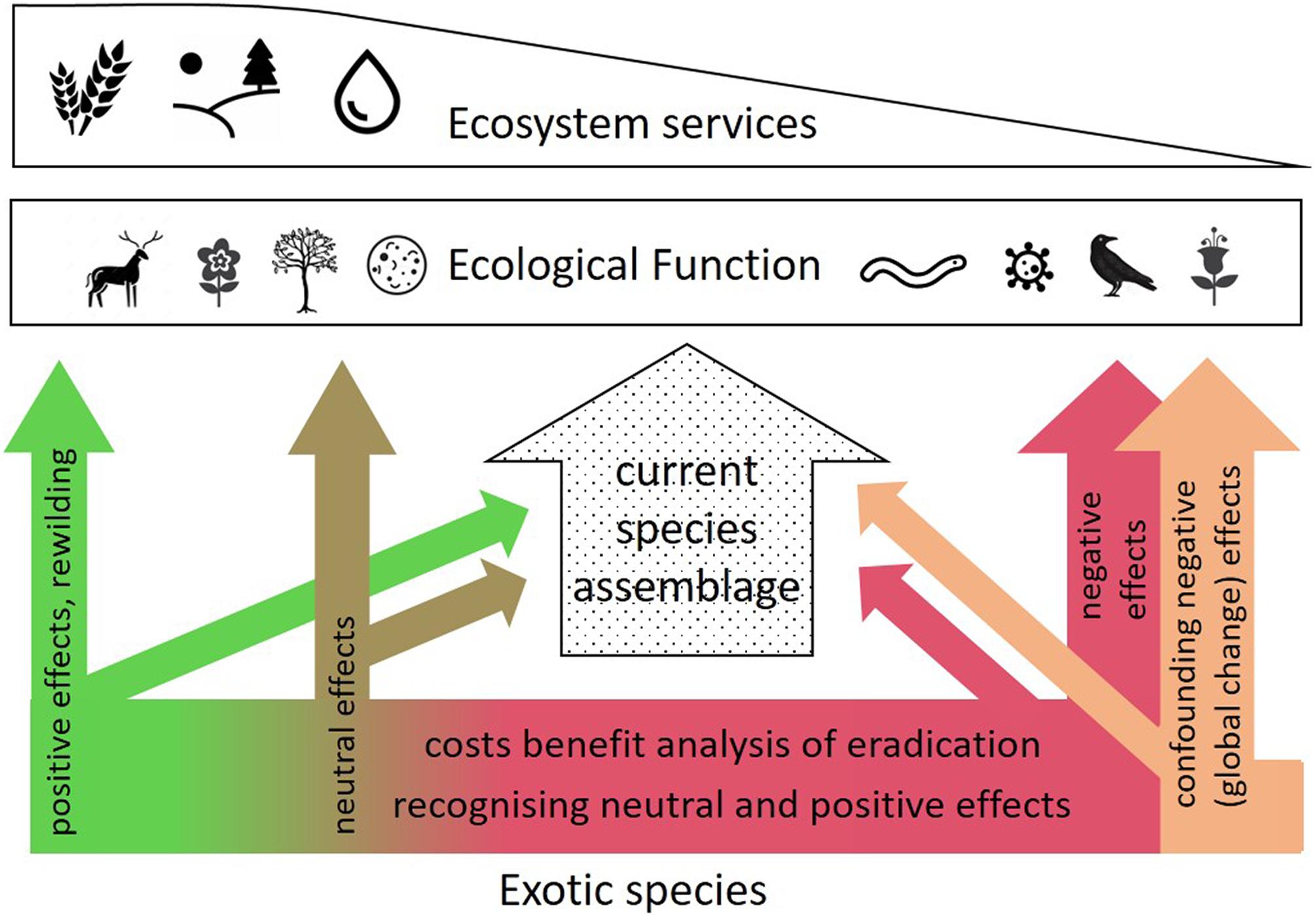
Introduction of Invasive Species
Human activities have facilitated the spread of invasive species, which can outcompete native species, alter ecosystem functions, and lead to the loss of native biodiversity. This affects the balance and health of ecosystems, reducing their ability to provide essential services.
Addressing these impacts requires concerted efforts in conservation, sustainable management of natural resources, and global cooperation to mitigate climate change. By understanding the intricate connections between human activities and ecosystem functions, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Conservation and Restoration Strategies for Ecosystem Functions
Conservation and restoration of ecosystem functions are vital for maintaining biodiversity, supporting sustainable development, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Here are some strategies:
Protected Areas and Biodiversity Conservation
Establishing and managing protected areas such as national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine sanctuaries to safeguard habitats and species. These areas serve as refuges for biodiversity, helping to maintain ecosystem functions and services.
Restoration Ecology
Restoring degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetland restoration, and rehabilitation of coral reefs and other habitats. These efforts aim to recover ecosystem functions and enhance biodiversity.
Sustainable Land and Water Use Practices
Implementing sustainable agricultural, forestry, and fisheries practices that conserve soil, water, and biological resources. Techniques such as agroforestry, conservation tillage, and sustainable harvesting maintain ecosystem productivity and resilience.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing ecosystem resilience to climate change through strategies like carbon sequestration in forests and wetlands, and protecting coastal zones with natural barriers.
Community Engagement and Indigenous Knowledge
Engaging local communities and integrating indigenous knowledge and practices in conservation and restoration efforts. Local stewardship and traditional ecological knowledge can provide valuable insights for sustainable ecosystem management.
These strategies, supported by scientific research and policy measures, are crucial for preserving ecosystem functions and ensuring that future generations inherit a healthy and vibrant planet.

READ MORE:
Future Challenges and Research Directions in Ecosystem Functioning
The study of ecosystem functioning faces several challenges and opportunities for future research that are crucial for biodiversity conservation, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development.
Understanding Complex Interactions
Research needs to further elucidate the complex interactions within ecosystems, including the synergies and trade-offs between different ecosystem functions and services. This includes understanding the effects of biodiversity loss, invasive species, and climate change on ecosystem resilience.
Impact of Climate Change
Assessing the impacts of climate change on ecosystem functions is critical. Future research should focus on predicting changes in ecosystem services under various climate scenarios and identifying vulnerable ecosystems and services.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology, such as remote sensing, bioinformatics, and ecological modeling, offer new opportunities to monitor and understand ecosystems at a global scale. Integrating these technologies can enhance our ability to assess changes in ecosystem functions and services.
Human-Environment Interactions
Understanding the socio-economic dimensions of human-environment interactions is essential. Research should integrate ecological, social, and economic sciences to develop strategies that balance human needs with the sustainability of ecosystem functions.
Restoration Ecology
Developing effective restoration strategies for degraded ecosystems is a key challenge. Research should focus on identifying the most effective methods for restoring ecosystem functions and services, considering the local ecological and socio-economic contexts.
Addressing these challenges through interdisciplinary research and collaboration among scientists, policymakers, and local communities is essential for the conservation and sustainable management of ecosystems globally.
Understanding ecosystem functions illuminates the intricate web of life, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices to preserve our planet"s vitality for future generations.