Topic definition of desert ecosystem: Discover the vibrant life and ecological significance of desert ecosystems, where extreme conditions foster unique biodiversity and adaptive strategies.
Table of Content
- What are the main characteristics of a desert ecosystem?
- Definition and Importance of Desert Ecosystems
- Types of Deserts: Hot and Cold
- Characteristics: Climate, Flora, and Fauna
- Adaptations of Desert Plants and Animals
- Human Impact and Conservation Efforts
- Economic Importance of Deserts
- YOUTUBE: Desert Ecosystem Environmental Studies
- Challenges Facing Desert Ecosystems
- Research and Studies on Desert Ecology
What are the main characteristics of a desert ecosystem?
The main characteristics of a desert ecosystem include:
- Extreme dryness: Deserts are known for their minimal precipitation levels, resulting in arid conditions.
- Limited vegetation: Due to the lack of water, desert ecosystems have sparse plant life, with vegetation adapted to conserve water.
- Diverse adaptation: Plants and animals in deserts have evolved unique physiological and behavioral adaptations to survive in harsh conditions.
READ MORE:
Definition and Importance of Desert Ecosystems
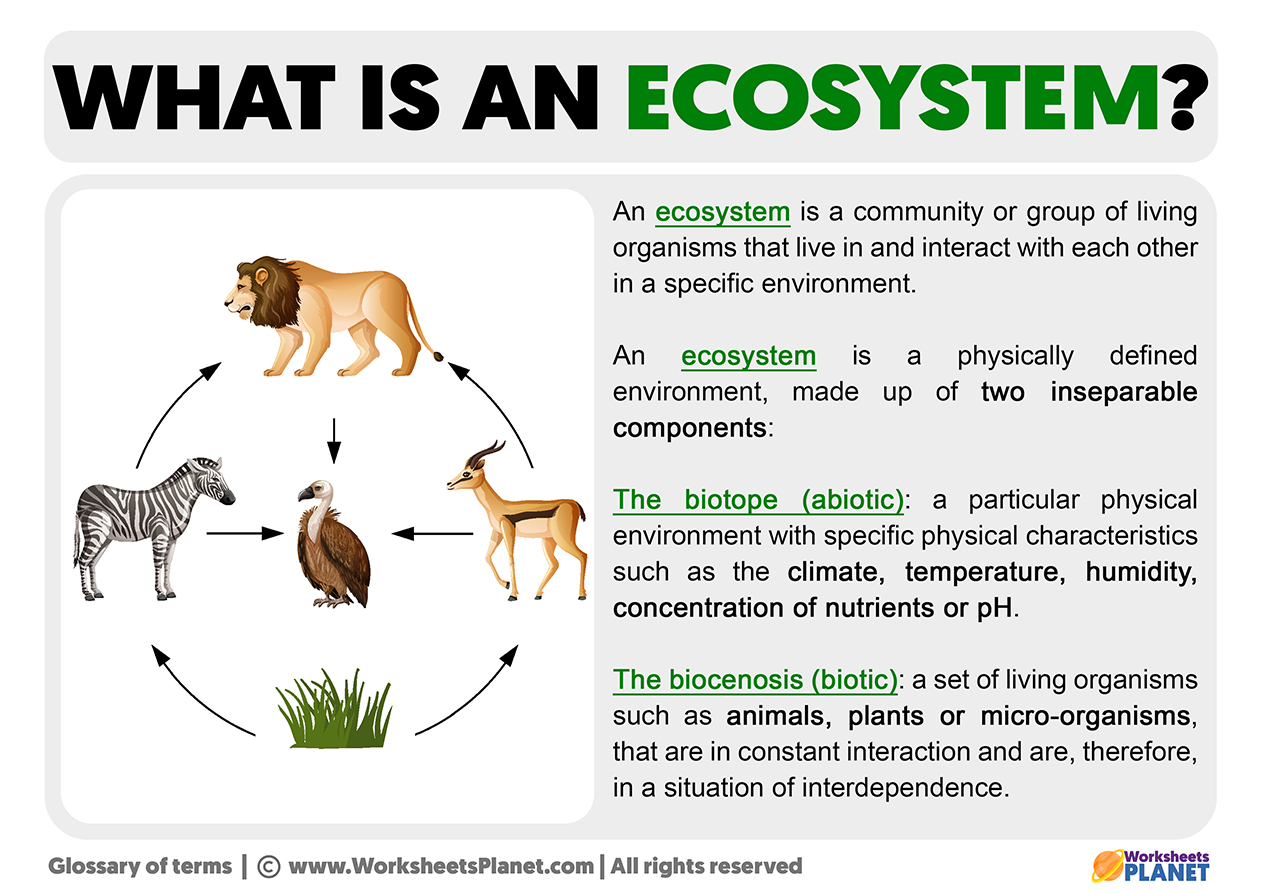
A desert ecosystem is characterized by low precipitation, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation. This ecosystem supports a unique variety of life adapted to harsh conditions, demonstrating remarkable resilience and biodiversity. Deserts cover about one-fifth of Earth"s surface, offering critical habitats, influencing global climate patterns, and sustaining cultural and economic activities.
- Biodiversity: Despite harsh conditions, deserts are home to a wide range of plants and animals specially adapted to survive with minimal water.
- Climate Regulation: Deserts play a crucial role in Earth"s climate system, reflecting sunlight and affecting global temperature and weather patterns.
- Economic Benefits: Deserts offer resources like minerals, solar energy potential, and unique tourism opportunities.
- Cultural Significance: Many civilizations have thrived in desert regions, developing unique ways of life and sustainable practices.
Understanding and preserving desert ecosystems is vital for biodiversity conservation, climate stability, and the well-being of human communities relying on these landscapes.

Types of Deserts: Hot and Cold
Deserts are diverse ecosystems classified mainly into hot and cold types, each with distinctive characteristics and adaptations.
- Hot Deserts: Known for their extreme heat during the day and significant temperature drops at night. These deserts, such as the Sahara and the Arabian, receive very little rainfall and are characterized by sand dunes, rocky landscapes, and sparse vegetation.
- Cold Deserts: Found in regions like the Gobi and the Great Basin, cold deserts experience more precipitation than hot deserts but have cold winters with snowfall. Vegetation is more abundant, and the landscape may feature steppes and salt flats.
Both hot and cold deserts are vital for their unique ecosystems, supporting a variety of life forms adapted to extreme conditions. Understanding these desert types helps in appreciating their ecological significance and the need for conservation efforts.
Characteristics: Climate, Flora, and Fauna
Desert ecosystems are distinguished by their unique climate, vegetation, and wildlife, each adapted to survive in extreme conditions.
- Climate: Deserts typically experience less than 250 mm of rainfall per year, with hot deserts featuring high temperatures and significant diurnal temperature variations, while cold deserts have cold winters and milder summers.
- Flora: Vegetation in deserts is sparse but highly specialized. Plants such as cacti, succulents, and hardy shrubs have adaptations like deep root systems, reduced leaf surfaces, and thick stems for water storage to survive the arid conditions.
- Fauna: Desert animals have evolved various adaptations to deal with the lack of water and extreme temperatures. Examples include nocturnal lifestyles to avoid daytime heat, water conservation mechanisms, and burrowing habits. Species such as reptiles, small mammals, birds, and insects are common.
These characteristics underscore the resilience and adaptability of life in desert ecosystems, highlighting the intricate balance between climate, flora, and fauna.

Adaptations of Desert Plants and Animals
The harsh conditions of deserts have led to remarkable adaptations in both plants and animals, enabling them to thrive in environments with extreme temperatures and limited water.
- Plants: Desert flora, such as cacti, have thick, fleshy parts for water storage, waxy coatings to reduce water loss, and deep root systems to access underground moisture. Some plants have small or no leaves to minimize evaporation.
- Animals: Desert fauna exhibit adaptations such as nocturnal activity patterns to avoid daytime heat, efficient water reabsorption systems, and camouflage to blend into the sandy environment. Many reptiles regulate body temperature through behavioral adaptations, while mammals often have thick fur on the bottoms of their feet to protect against hot surfaces.
These adaptations are essential for survival, illustrating the resilience and ingenuity of life in desert ecosystems.
Human Impact and Conservation Efforts
Human activities have significantly impacted desert ecosystems, leading to habitat degradation, biodiversity loss, and water scarcity. However, concerted conservation efforts are underway to protect these vital landscapes.
- Impact: Overgrazing, urbanization, mining, and unsustainable water use are major threats to desert environments, disrupting the natural balance and endangering native species.
- Conservation Initiatives: Protected areas, habitat restoration projects, sustainable management practices, and water conservation measures are key strategies to mitigate human impact and preserve desert ecosystems.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial. Educational programs and sustainable livelihood initiatives help foster a sense of stewardship towards desert environments.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring are essential to understand the impacts of climate change on deserts, guide conservation actions, and adapt strategies as needed.
Protecting desert ecosystems is imperative for maintaining biodiversity, supporting local communities, and ensuring the health of our planet.

Economic Importance of Deserts
Deserts hold significant economic value, contributing to local and global economies through various sectors.
- Natural Resources: Deserts are rich in minerals and fossil fuels, including oil, gas, and valuable ores, driving mining and energy industries.
- Renewable Energy: The vast, open lands and high solar irradiance make deserts ideal sites for solar energy production, contributing to sustainable energy solutions.
- Agriculture: Innovative irrigation techniques and desert agriculture practices, such as hydroponics, allow for the cultivation of crops in arid regions, promoting food security.
- Tourism: Deserts attract tourists with their unique landscapes, wildlife, and cultural heritage, supporting local businesses and conservation through eco-tourism.
- Research and Development: The unique conditions of deserts provide opportunities for scientific research, from studying biodiversity to testing space exploration technologies.
The economic activities in deserts, when managed sustainably, can provide substantial benefits while ensuring the preservation of these unique ecosystems.
Desert Ecosystem Environmental Studies
Sustainability: \"Discover the beauty of sustainable living in this eye-opening video. Learn practical ways to reduce your environmental footprint and make a positive impact on the planet. Watch and be inspired to join the movement towards a greener future.\" Adaptations: \"Dive into the fascinating world of animal adaptations in this captivating video. Explore how different species have evolved unique characteristics to survive and thrive in their environments. Witness the wonders of nature\'s ingenuity and resilience.\"
The Desert Biome Biomes 4
The Desert Biome. ☀️ In this biogeography video we look at the world\'s deserts, explain why they are that way, and what types ...
Challenges Facing Desert Ecosystems
Desert ecosystems face numerous challenges that threaten their sustainability and the biodiversity they support.
- Climate Change: Increased temperatures and changing precipitation patterns exacerbate water scarcity, impacting desert flora and fauna.
- Desertification: Unsustainable land use and overgrazing contribute to desertification, turning fertile land into desert and reducing biodiversity.
- Water Scarcity: The overuse of groundwater for agriculture and human consumption leads to the depletion of aquifers, further stressing desert environments.
- Habitat Loss: Expansion of urban areas and infrastructure development encroach on desert habitats, fragmenting ecosystems and endangering species.
- Pollution: Mining and industrial activities introduce pollutants into desert ecosystems, affecting soil, air, and water quality.
Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable management practices, and innovative solutions to protect and preserve desert ecosystems for future generations.

READ MORE:
Research and Studies on Desert Ecology
Scientific research and studies in desert ecology are crucial for understanding these complex ecosystems and addressing the challenges they face.
- Biodiversity Monitoring: Ongoing projects aim to catalog and monitor the diverse species living in desert environments, assessing the impacts of climate change and human activities.
- Climate Impact Assessment: Researchers study how global warming affects desert climates, precipitation patterns, and the frequency of extreme weather events.
- Conservation Strategies: Studies focus on developing effective conservation strategies to protect endangered species and restore degraded habitats.
- Sustainable Management: Research aims to improve land use and water management practices, promoting sustainable development in desert regions.
- Technological Innovations: Advances in technology, such as remote sensing and GIS, enhance the monitoring and management of desert ecosystems.
Through interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative approaches, research in desert ecology seeks to preserve the delicate balance of these ecosystems for the benefit of future generations.
Embracing the unique beauty and critical importance of desert ecosystems enriches our understanding of nature and underscores the urgency of conservation efforts for these remarkable landscapes.