Topic sahara desert average temperature: Explore the Sahara Desert"s average temperature, a land of extreme beauty and contrast, where searing heat meets surprisingly cool nights, shaping one of Earth"s most fascinating environments.
Table of Content
- What is the average temperature of the Sahara Desert?
- Overview of Sahara Desert Climate
- Seasonal Temperature Variations
- Day and Night Temperature Fluctuations
- Monthly Temperature Averages
- Impact of Geography on Temperature
- Historical Temperature Records
- YOUTUBE: The temperature of Sahara desert
- Climate Change and Future Predictions
- Human and Ecological Impact
- Exploring the Sahara: Tips and Precautions
What is the average temperature of the Sahara Desert?
The average temperature of the Sahara Desert varies depending on the season and time of day. However, it is generally known to be one of the hottest regions in the world. Here are some key points about the average temperature of the Sahara Desert:
- The mean temperature in the Sahara Desert can sometimes exceed 30°C (86°F).
- The average high temperatures in the desert are quite high.
- The annual range in average daily temperatures is approximately 17.5°C (31.5°F).
- During the summer, the heat in the Sahara Desert can be the most intense, with temperatures sometimes exceeding 40°C (100°F) during the day.
- The desert tends to be somewhat cooler at night.
- Winter temperatures in the Sahara Desert are generally lower compared to summer.
Overall, the Sahara Desert maintains a hot and dry climate with high temperatures throughout the year, making it one of the hottest places on Earth.
READ MORE:
Overview of Sahara Desert Climate
The Sahara Desert, an emblem of extreme climate conditions, is characterized by its hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh). It"s one of the driest and hottest regions in the world, where temperatures can soar to extremes.
- Temperature Range: The desert experiences average high temperatures well over 30°C (86°F), often crossing 40°C (104°F) in summer. It"s not uncommon for temperatures to reach as high as 47°C (117°F).
- Night and Winter Variations: Despite the scorching daytime heat, nights in the Sahara can be surprisingly cool, with temperatures dropping significantly. In winter, northern parts of the desert can experience freezing conditions.
- Precipitation: Rainfall is exceedingly rare, with most of the Sahara receiving less than 100 mm (3.9 in) annually. Some areas may go for years without a single drop of rain.
- Geographical Influence: The Sahara"s vastness covers different geographical features like sand dunes, stone plateaus, and mountains, each influencing local climate conditions.
- Seasonal Winds and Storms: The desert is also known for its powerful winds, which can cause severe sandstorms, impacting visibility and temperature.
This extreme climate not only shapes the landscape of the Sahara but also profoundly affects the flora and fauna that inhabit this arid expanse.

Seasonal Temperature Variations
The Sahara Desert"s climate is marked by stark seasonal contrasts, shaped by geographical and atmospheric factors.
- Summer: This is the most intense season heat-wise, with daytime temperatures frequently exceeding 40°C (100°F), while nighttime temperatures offer slightly cooler conditions but still remain high. In some areas, temperatures have been recorded as high as 58°C (136°F).
- Winter: Winters bring milder days but cold nights. The northern Sahara experiences colder conditions compared to the central parts. In winter, average temperatures are around 13°C (55°F), but can drop much lower.
- Spring and Autumn: These seasons show the least temperature contrast. Days are hot and nights are moderately cool, making these seasons favorable for outdoor activities like trekking.
- Monthly Variations: Month-to-month, temperature fluctuations are significant. Starting from mild temperatures in January, around 18°C (64°F), and progressively heating up to peak in July and August with averages around 43°C (109°F), then cooling down towards the end of the year.
- Geographical Impact: Different regions of the Sahara, like the mountainous areas or the vast sand dunes, experience varied temperatures due to their elevation and landscape.
This stark variation in temperatures, influenced by the desert"s geographical location in the subtropical high-pressure zone, creates a unique environment that challenges both flora and fauna in the region.
Day and Night Temperature Fluctuations
The Sahara Desert is renowned for its extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night, a phenomenon influenced by several geographical and atmospheric factors.
- Daytime Heat: During the day, temperatures in the Sahara can soar, often reaching an average of 100°F (38°C). This intense heat results from the desert’s exposure to direct sunlight and the sand’s ability to absorb and radiate heat back into the atmosphere.
- Nighttime Cool Down: At night, temperatures drop dramatically, averaging around 25°F (-4°C). The absence of humidity and cloud cover, which could trap the heat, leads to this rapid cooling. The desert"s clear skies and dry air allow the accumulated heat to escape quickly into the atmosphere once the sun sets.
- Impact of Geography: The desert"s varying elevation also plays a role, with higher elevations experiencing cooler temperatures at night. Cloud cover, or the lack thereof, further influences these temperature changes.
- Seasonal Differences: While these day and night temperature fluctuations are a constant feature, the extent of the change can vary seasonally, with summer days being hotter and winter nights colder.
- Human and Wildlife Adaptation: Both humans and wildlife in the Sahara have adapted to these harsh conditions. For instance, many desert animals are nocturnal, avoiding the daytime heat.
This unique climate characteristic of the Sahara highlights the desert"s harsh environment and the remarkable adaptations of its inhabitants.
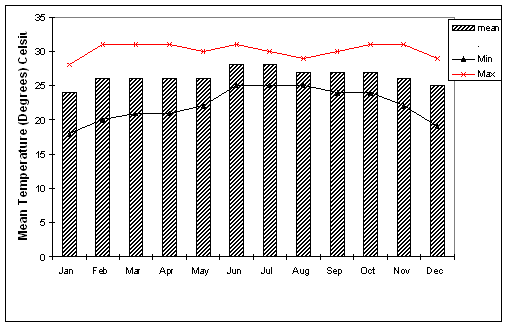
Monthly Temperature Averages
The Sahara Desert, with its expansive landscapes and diverse topography, exhibits a range of temperatures throughout the year. Here"s a general overview of the monthly temperature averages:
- January: Average temperatures hover around 18.5°C (65.3°F) in Dakhla, reflecting cooler conditions in winter.
- February: A slight increase in temperature, averaging 18.9°C (66.1°F) in Dakhla.
- March to May: Transition into warmer months with temperatures in March averaging 19.4°C (66.9°F) in Dakhla, gradually increasing to around 20.2°C (68.4°F) in May.
- June: Marking the onset of hotter days, temperatures rise to an average of 21.4°C (70.5°F) in Dakhla.
- July and August: Peak summer months, July averages 22.3°C (72.2°F), and August around 23.3°C (74°F) in Dakhla, with some regions experiencing extreme highs up to 45°C (113°F).
- September to November: A gradual decline in temperatures, September averages at 23.5°C (74.3°F), cooling down to 21.7°C (71.1°F) in November in Dakhla.
- December: Cooler winter temperatures return, averaging 19.5°C (67.2°F) in Dakhla.
Note that these averages are from the Dakhla region and can vary across different parts of the Sahara. The desert"s vastness and varied topography lead to significant temperature differences in its different regions.
Impact of Geography on Temperature
The geography of the Sahara Desert plays a crucial role in shaping its temperature profile. Here"s how various geographical features influence the desert"s climate:
- Topography: The Sahara consists of sand dunes (ergs), stone plateaus (hamadas), gravel plains (regs), dry valleys (wadis), and salt flats. These features affect how heat is absorbed and radiated.
- Altitude: In mountainous regions like the Tibesti and Hoggar, temperatures are slightly moderated due to higher elevations, ranging between 35-42°C (95-108°F) in summer.
- Proximity to Water Bodies: Regions closer to the Mediterranean Sea, like the northern fringes, receive some winter clouds and minimal rainfall due to low-pressure systems. This proximity can slightly moderate temperatures.
- Latitude: The Sahara"s location in the subtropical high-pressure zone results in high temperatures and dry conditions. Its vast size means that it spans several degrees of latitude, each with slightly different weather patterns.
- Human Influence: Human activities have also impacted the Sahara"s climate, contributing to its stability by increasing surface reflectivity and reducing evapotranspiration.
- Wind Patterns: The Sahara is known for its powerful winds, which can significantly affect temperature and weather patterns. These winds also contribute to distributing dust across vast distances, impacting global climate.
Understanding these geographical influences is key to comprehending the Sahara"s diverse and extreme climate conditions.
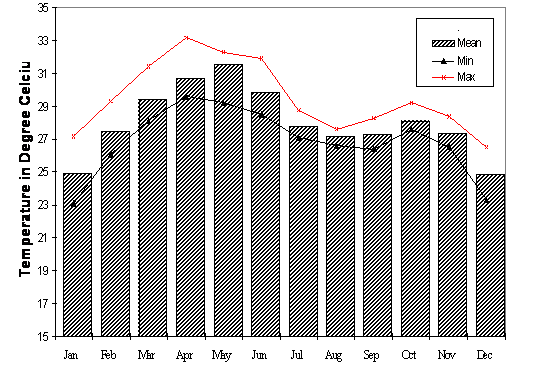
Historical Temperature Records
The Sahara Desert"s climate history reveals a fascinating journey from its formation to present-day conditions. Let"s explore some of these significant historical temperature records:
- Formation and Early Climate: Geological studies suggest that the Sahara became a climatic desert around 2-3 million years ago. The discovery of 7-million-year-old dune deposits in Chad indicates that the region may have become arid during the Miocene Epoch (23 to 5.3 million years ago).
- Climate Variability: Since its formation, the Sahara has experienced periods of drier and more humid conditions. For example, during the "Little Ice Age" in Europe (16th to 18th century), there was an increase in precipitation in the Sahara which lasted until the 19th century.
- Temperature Extremes: The Sahara is known for its extreme temperatures. The highest temperature ever recorded was approximately 58°C (136°F) in Aziziyah, Libya. In contrast, the coldest temperature recorded was -11.7°C (11°F) in Ksar Guilane, Tunisia, on February 11, 1935.
- Climate Stability: Over the past 2,000 years, the Sahara"s climate has been relatively stable. However, it has been subject to various climatic changes due to factors like Earth"s axial tilt, which influenced monsoon activity and transformed the Sahara into a green landscape every 20,000 years.
- Modern Day Climate: Today, the Sahara experiences extremely high temperatures during the day, often exceeding 100°F (38°C), and cool to cold temperatures at night, sometimes dropping below freezing.
This historical overview highlights the dynamic nature of the Sahara"s climate, characterized by significant changes over millions of years.
The temperature of Sahara desert
Discover the mesmerizing beauty of the Sahara desert in this captivating video! Immerse yourself in breathtaking landscapes, golden sand dunes, and endless horizons. Get ready for an extraordinary journey that will leave you awe-inspired and yearning for adventure!
The Sahara Desert can reach up to 136 degrees. Its average temperature is about 100 degrees.
Dive into the world of temperature with this enlightening video! Explore the fascinating science behind thermodynamics and learn how temperature affects our daily lives. From the freezing depths of winter to the scorching heat of summer, this captivating video will make you appreciate the power and impact of temperature.
Climate Change and Future Predictions
The Sahara Desert, already an emblem of extreme climate conditions, is likely to experience significant changes due to climate change. Here are some key aspects and predictions:
- Shift in Rainfall Patterns: There"s an expectation of altered rainfall patterns in the Sahara and Sahelian regions due to climate change. Some studies suggest potential increases in rainfall, which could transform certain areas from hyperarid to more mesic landscapes. However, these predictions come with uncertainties, and there"s a need for more research to understand the exact nature of these changes.
- Temperature Increases and Dust Reduction: NASA predicts that climate change and ocean warming will lead to reduced Saharan dust in the future. This reduction in dust could lead to more sunlight reaching the Earth"s surface and the ocean, further warming the climate. This change might also have implications for air quality and the formation of storms and hurricanes.
- Desert Expansion: Studies have shown that the Sahara Desert has expanded in size over the past century, likely influenced by climate change. This expansion into new regions could continue, further altering the desert"s landscape and its bordering ecosystems.
- Increased Temperature Extremes: Africa, including the Sahara, has experienced hotter and longer heatwaves in the 21st century. The continuation of this trend is expected, with longer periods without rain and more intense precipitation when rainfall does occur. The overall variability in weather patterns is likely to increase, which could have profound impacts on the desert"s ecosystem and surrounding areas.
- Global Implications: The changes in the Sahara"s climate not only affect the local environment but also have global implications. For instance, Saharan dust plays a crucial role in various ecological processes, including fertilizing the Amazon rainforest. Changes in the dust patterns could, therefore, have wide-reaching impacts.
Overall, while there are certain predictions about the Sahara"s future climate, there remains a high degree of uncertainty. Continued research and observation are essential to better understand these changes and their implications for both the local environment and the global climate system.
Human and Ecological Impact
The Sahara Desert"s climate and environmental changes have profound implications for both human societies and ecological systems. Here are some key aspects of these impacts:
- Historical Human Activities: Human activities have historically influenced the Sahara. For instance, overgrazing by cattle and land management practices have affected the desert"s environment, contributing to its current arid conditions. The use of fire as a land management tool and the reduction of atmospheric moisture by overgrazing grasses are some ways humans have historically impacted the Sahara"s climate and landscape.
- Impact of Climate Change: The Sahara is experiencing significant changes due to climate change. Increasing temperatures are leading to stronger evaporation and more intense rainfall in some areas. This change is contributing to the expansion of the desert, which affects the Sahel region by pushing back its grassland ecosystems and disrupting societies that depend on these ecosystems.
- Ecological Shifts: The Sahara has undergone ecological shifts from green, vegetated periods to the current desert conditions. These shifts have major consequences for species dispersal and evolution in Africa. Periodic wet phases in the Sahara, driven by Earth’s orbital changes, were crucial in providing vegetated corridors for the dispersal of various species, including early humans.
- Effects of Saharan Dust: Saharan dust plays a significant role in the Earth"s climate system. It affects marine life by depositing nutrients into the ocean and influences plant life when it makes landfall. However, changes in dust patterns due to climate change could have varied impacts, including potential benefits like improved air quality in regions like the Caribbean but also negative effects such as harmful algal blooms.
- Adaptation and Survival: Both human populations and wildlife in the Sahara have adapted to its extreme climate. For instance, many desert animals are nocturnal, avoiding the daytime heat. Similarly, human societies have developed unique ways to cope with the harsh desert conditions.
The Sahara Desert"s dynamic and changing environment continues to be a subject of scientific study, with ongoing implications for human societies and ecological systems in the region and beyond.
READ MORE:
Exploring the Sahara: Tips and Precautions
Adventuring into the Sahara Desert can be an exhilarating experience, but it requires careful preparation and awareness of the harsh environment. Here are some essential tips and precautions:
- Hydration: Carry ample water supplies as the desert heat can lead to rapid dehydration. It"s recommended to drink at least one gallon (approximately 4 liters) of water per day.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves, long pants, and a wide-brimmed hat to protect your skin from the sun. Light-colored clothing reflects sunlight and helps keep you cool.
- Sunscreen and Sunglasses: Use high-SPF sunscreen to prevent sunburn and sunglasses to protect your eyes from intense sunlight and blowing sand.
- Navigational Tools: GPS devices, maps, and compasses are crucial as it"s easy to get disoriented in the desert. Always inform someone about your travel plans and expected return.
- Weather Awareness: Understand the local weather patterns. Sandstorms can occur suddenly, and temperatures drop sharply at night, so be prepared for varying conditions.
- Camping and Shelter: If planning to camp, bring a sturdy tent that can withstand wind and sand. At night, temperatures can plummet, so warm sleeping gear is essential.
- Emergency Kit: Carry a first-aid kit, a multi-tool or knife, matches or a lighter, and a whistle or mirror for signaling in case of emergency.
- Local Knowledge: Consider hiring a local guide who knows the desert well. They can provide invaluable knowledge about safe routes, water sources, and areas to avoid.
- Respect the Environment: The Sahara is a fragile ecosystem. Minimize your environmental impact by following Leave No Trace principles.
- Health Precautions: Be aware of symptoms of heat exhaustion and heatstroke. Take regular breaks in the shade and eat salty snacks to replace lost electrolytes.
Preparation, respect for the desert environment, and understanding the risks are key to a safe and enjoyable Sahara exploration experience.
Embark on a journey through the Sahara"s shifting sands and soaring temperatures, where each step unveils the desert"s timeless allure and hidden mysteries, beckoning the adventurous spirit to explore and understand this magnificent and ever-changing landscape.








