Updating information and knowledge about where is sahara desert located in africa in detail and most comprehensive, this article is currently a topic of great interest compiled by the editorial team.
Table of Content
- Geographic Location and Size of the Sahara Desert
- Where is the Sahara Desert situated in Africa?
- Climate and Environmental Conditions in the Sahara
- Flora and Fauna: Life in the Sahara Desert
- Human Settlements and Cultures of the Sahara
- Historical Significance and Changes Over Time
- Ecological Regions and Variations within the Sahara
- Geopolitical and Economic Factors in Sahara Countries
- YOUTUBE: Faces of Africa: The Sahara
Geographic Location and Size of the Sahara Desert

READ MORE:
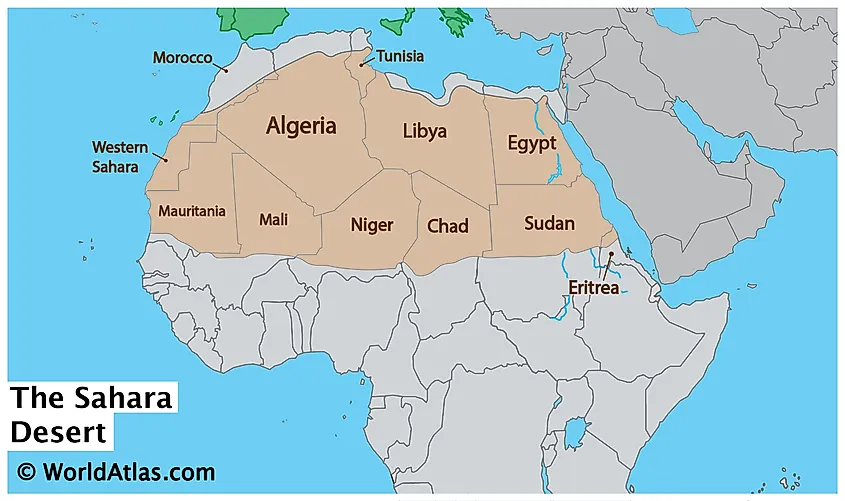
Where is the Sahara Desert situated in Africa?
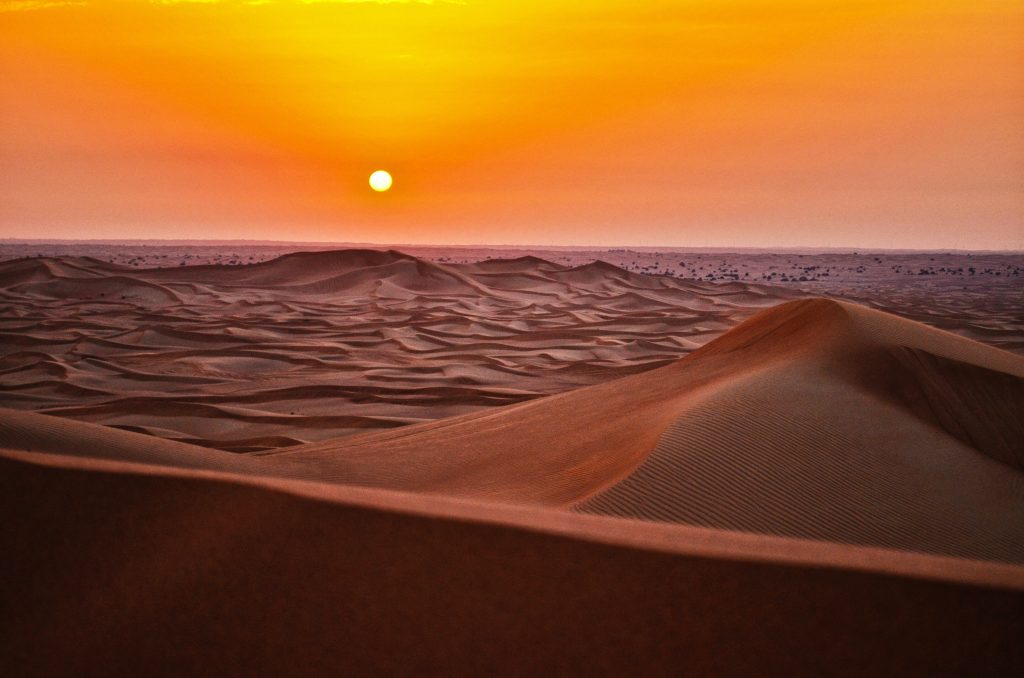
The Sahara Desert is located in northern Africa.
Here are the detailed steps to find the location of the Sahara Desert:
- Open a map of Africa or use an online map service.
- Locate the continent of Africa on the map.
- Identify the northern portion of Africa.
- Within the northern portion, you will find a vast desert stretching across the region.
- This desert is the Sahara Desert.
The Sahara Desert is known for its vast size, stretching approximately 3,000 miles (4,800 km) from east to west and covering an area of 9,200,000 square kilometers (3,600,000 square miles).
Climate and Environmental Conditions in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert is characterized by a distinctive climate that varies greatly across its vast expanse. This climate is primarily defined by its extreme aridity and wide temperature fluctuations.
- Two Climatic Regimes: The Sahara features two major climatic regimes. The northern part experiences a dry subtropical climate with high temperature ranges and two rainy seasons, while the southern part has a dry tropical climate with one rainy season.
- Temperature Extremes: Daytime temperatures can soar above 50°C (122°F) in summer, dropping dramatically at night. Winters can be relatively cold, especially in the northern Sahara.
- Minimal Rainfall: Rainfall in the Sahara is scarce and sporadic, with many areas receiving less than 100 mm (3.9 inches) annually. Some central parts of the Sahara may receive only 0.04 inches of rain per year.
- Environmental Changes: Historically, the Sahara has undergone significant environmental changes, alternating between desert and savanna grassland in a 20,000-year cycle influenced by Earth"s axial precession.
- Wind Patterns: The Sahara is known for its strong winds, which can cause severe dust storms. These winds often carry dust from the Sahara to distant locations across the globe.
- Impact on Global Climate: The Sahara plays a significant role in the global climate system, influencing regional atmospheric circulation patterns and having far-reaching impacts.
Understanding the complex climate and environmental conditions of the Sahara is crucial for grasping its influence on both local and global scales.
Flora and Fauna: Life in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, despite its harsh conditions, supports a unique array of flora and fauna, each adapted to the extreme environment.
- Resilient Flora: The Sahara"s flora includes hardy species like acacia trees, date palms, various grasses, and succulents. These plants have adapted to the arid conditions by developing features like deep roots, water-storing capabilities, and small leaves to minimize water loss.
- Diverse Fauna: The Sahara is home to a range of animals uniquely adapted to the desert climate. This includes mammals like the fennec fox, addax, and various species of gazelles; reptiles like the desert monitor lizard and various snake species; and birds such as the ostrich and Namaqua dove.
- Survival Strategies: Many Sahara animals are nocturnal, venturing out during the cooler nights to forage and then taking shelter during the heat of the day. Others have physical adaptations like large ears for heat dissipation (fennec fox) or the ability to store fat in humps (camels).
- Endemic Species: The Sahara hosts several endemic species, which are found nowhere else in the world. This includes certain types of jerboas, skinks, and the critically endangered addax.
- Human Impact: Human activities, such as hunting and habitat destruction, pose significant threats to the Sahara"s wildlife. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these unique species and their habitats.
The flora and fauna of the Sahara Desert showcase the incredible adaptability and resilience of life in one of the most extreme environments on Earth.
Human Settlements and Cultures of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, though predominantly arid and inhospitable, has been home to various human cultures and settlements for thousands of years. These communities have adapted to the challenging environment in remarkable ways.
- Nomadic Tribes: The Sahara is known for its nomadic tribes like the Tuareg and the Berbers. These groups have historically traveled across the desert, herding camels and goats, and are renowned for their rich cultural traditions and deep knowledge of the desert.
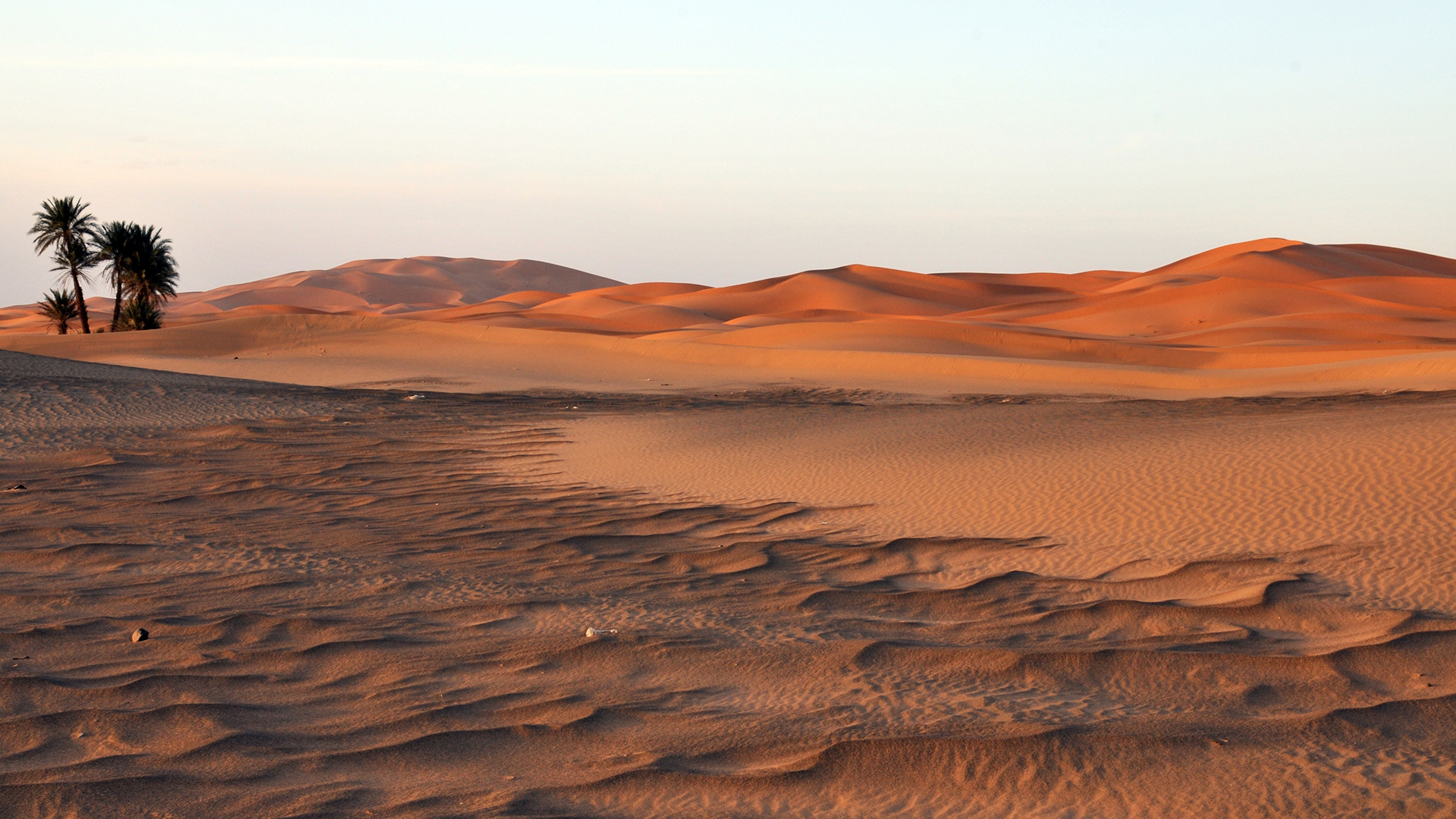
- Settled Communities: Along the edges of the Sahara, there are more settled communities. These are often located near oases, where water is available for agriculture and settlement. Dates, millet, and other crops are typically grown in these areas.
- Historical Trade Routes: The Sahara was once a bustling network of trade routes, where caravans of camels transported salt, gold, and other goods across the desert. This trade played a significant role in the cultural and economic exchanges between North and Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Cultural Heritage: The Sahara is rich in cultural heritage, including music, art, and traditional crafts. This cultural diversity reflects the adaptations and interactions of the various peoples who have lived in and traversed the desert over millennia.
- Modern Changes: In recent times, some nomadic tribes have become more sedentary, partly due to changing environmental conditions and the discovery of resources like oil and minerals in the desert. This has led to the growth of urban areas and a shift in traditional lifestyles.
Despite the harsh conditions, the Sahara Desert continues to be a vibrant tapestry of human cultures and communities, each with its unique way of life and traditions.
Historical Significance and Changes Over Time
The Sahara Desert has a rich and varied history that reflects significant changes over time, influencing both the landscape and the human activities within it.
- Ancient Climate Shifts: Thousands of years ago, the Sahara was much greener and more hospitable than it is today. Evidence from archaeological discoveries, including cave paintings and artifacts, suggests that it was once a savanna with abundant wildlife and vegetation.
- Early Human Settlements: This greener Sahara supported early human settlements, with communities engaged in hunting, fishing, and cattle herding. The gradual desertification of the Sahara led to migrations and significant changes in lifestyle for these early inhabitants.
- Historical Trade Routes: The Sahara has been a conduit for trade across Africa for centuries. The Trans-Saharan trade routes facilitated the exchange of goods like gold, salt, and ivory, as well as ideas and culture between North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Islamic and European Influence: Over the centuries, the Sahara witnessed the expansion of Islamic influence, followed by European colonialism. These periods brought significant cultural and political changes to the region.
- Environmental Changes: The Sahara is still subject to environmental changes. Studies suggest that it undergoes natural cycles of aridity and humidity, with the last major humid period occurring around 10,000 years ago.
- Modern Challenges: In contemporary times, the Sahara faces challenges such as climate change, resource exploitation, and geopolitical issues, impacting both the environment and the local communities.
The Sahara Desert"s history is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of its landscapes and peoples, revealing a dynamic interplay between the environment and human civilization over millennia.
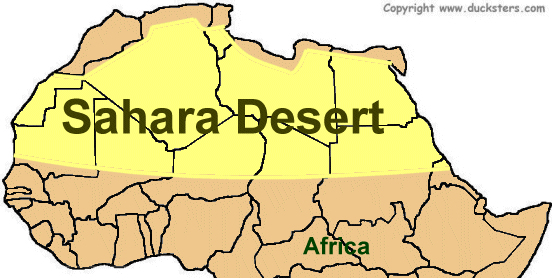
Ecological Regions and Variations within the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, spanning across North Africa, is not only the world"s largest hot desert but also a mosaic of diverse ecological regions. Each of these regions has distinct environmental characteristics and supports unique life forms.
- Atlantic Coastal Desert: This region lies along the Atlantic coast and is characterized by fog and haze. It has a very dry climate with minimal annual precipitation and is known for its lichens and drought-resistant shrubs.
- North Saharan Steppe and Woodlands: Located in the northern part of the Sahara, this ecoregion receives more winter rainfall and has a diverse habitat including sandy areas, rocky areas, wadis, and depressions, supporting a variety of wildlife such as snakes, lizards, and birds.
- Sahara Desert Ecoregion: Covering the arid center of the desert, this region is characterized by sand dunes, salt flats, and sandy plains. It is one of the driest and hottest places in the world, with extremely low annual rainfall and temperatures often exceeding 30°C.
- South Saharan Steppe and Woodlands: Between the Sahara Desert and the Sahel grasslands, this ecoregion experiences extreme climate variations and is home to endemic species of flora and fauna.
- West Saharan Montane Xeric Woodlands: Covering highland areas in the Sahara, this region is relatively cooler and receives more rainfall. It hosts a diversity of vegetation and animal species, including barbary sheep and cheetahs.
- Tibesti-Jebel Uweinat Montane Xeric Woodlands: Found in the eastern Sahara, this ecoregion encompasses mountain ranges that receive more rainfall and cooler temperatures compared to the surrounding desert.
These ecoregions collectively illustrate the Sahara"s environmental diversity, ranging from hyper-arid central areas to more vegetated steppe and woodland regions at its peripheries.
Geopolitical and Economic Factors in Sahara Countries
The Sahara region, encompassing several African countries, is influenced by various geopolitical and economic factors that shape its development and international relations.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: The Sahara-Sahel region has experienced episodes of instability, particularly in countries like Libya and Mali. These instabilities have restructured the geopolitical dynamics, affecting security and development in the region.
- Resource Richness: Many Sahara countries are rich in natural resources like oil and minerals, which play a significant role in their economies. However, dependence on these resources also makes them vulnerable to global market fluctuations.
- Environmental Challenges: The Sahara faces environmental challenges such as desertification, which impact agriculture and livelihoods. Climate change exacerbates these challenges, posing a threat to sustainable development.
- Economic Development: The Sahara countries exhibit diverse economic profiles, with some showing rapid growth and others struggling with poverty and underdevelopment. Economic policies and international partnerships significantly influence these trends.
- Regional Cooperation: Cross-border and regional cooperation is essential in addressing shared challenges like security, migration, and resource management in the Sahara-Sahel region.
Overall, the geopolitical and economic landscape of Sahara countries is complex, influenced by a mix of domestic and international factors, requiring holistic and collaborative approaches for stability and growth.
Discover the Sahara"s captivating secrets—from its vast landscapes to rich cultures and dynamic history—unveiling the heart of Africa"s grandest desert.

Faces of Africa: The Sahara
Explore the breathtaking beauty of Africa and witness its rich diversity in wildlife, stunning landscapes, and vibrant cultures. Get ready for an awe-inspiring adventure that will leave you in awe of this magical continent. Watch our video to immerse yourself in the wonders of Africa!
READ MORE:
Where is the Sahara Desert located in Africa?
Embark on a captivating journey through the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, where endless golden dunes stretch as far as the eye can see. Experience the serenity and magnificence of this breathtaking natural wonder, as our video takes you on a mesmerizing expedition through this mesmerizing desert landscape.









