Topic names of invertebrate animals: Embark on an enthralling journey to explore the diverse world of invertebrates, uncovering the vast array of species and their fascinating characteristics that make them nature"s hidden gems.
Table of Content
- What are the names of invertebrate animals?
- Overview of Invertebrate Animal Kingdom
- Popular Invertebrate Animals: Examples and Characteristics
- Invertebrates in Different Habitats: Aquatic, Terrestrial, and Aerial
- Role of Invertebrates in Ecosystems and Human Life
- YOUTUBE: Invertebrate Animals | Educational Video for Kids
- Classification of Invertebrates: From Sponges to Arthropods
- Conservation Status of Various Invertebrate Species
- Invertebrates in Research and Science: Contributions and Discoveries
- Interactive Section: Fun Facts About Invertebrates
- Photographic Gallery of Diverse Invertebrate Animals
- Resources and Further Reading on Invertebrates
What are the names of invertebrate animals?
There are numerous names of invertebrate animals. Some of the commonly known names include:
- Octopus
- Squid
- Jellyfish
- Snail
- Slug
- Worm
- Insect (such as ants, bees, butterflies, and beetles)
- Crab
- Lobster
- Shrimp
- Starfish
- Sea Urchin
- Anemone
- Corals
These are just a few examples of invertebrate animals. There are many more species within this diverse group of animals.
READ MORE:
Overview of Invertebrate Animal Kingdom
The invertebrate kingdom, comprising animals without a backbone, showcases the most diverse range of organisms on Earth. This group includes over 1.3 million known species, with possibly millions more yet to be discovered. They inhabit various environments, including land, marine, and freshwater habitats, and represent Earth"s largest source of biodiversity.
- Arthropods: The most populous group, consisting primarily of insects, arachnids, and crustaceans. Arthropods alone account for about 85% of all known invertebrate species.
- Mollusks: This varied group includes snails, octopi, squid, and clams. Mollusks are known for their unique nervous systems and the mantle, a significant body part in their anatomy.
- Echinoderms: Such as starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers, these species are characterized by their radial symmetry and often inhabit marine environments.
- Annelids: Including earthworms and leeches, these segmented worms play a crucial role in soil health and ecology.
- Protozoans: Single-celled organisms like amoebas, which are among the simplest invertebrates.
Some invertebrates, like the giant squid, are known for their astonishing sizes, while others, like amoebas, are single-cell organisms. Invertebrates exhibit a wide range of body plans, from fluid-filled, hydrostatic skeletons in jellyfish and worms, to hard exoskeletons in insects and crustaceans. The vastness and diversity of this group underscore the complexity and adaptability of life without a backbone.

Popular Invertebrate Animals: Examples and Characteristics
Invertebrates, animals without backbones, represent a vast and diverse group within the animal kingdom. This section highlights some of the most well-known and interesting invertebrate species, each unique in its own right.
- Ant (Family: Formicidae): Commonly found across various environments, ants are social insects known for their organized colonies and complex behaviors.
- Jellyfish (Class: Scyphozoa): These marine animals are known for their gelatinous bodies and stinging tentacles, playing a crucial role in ocean ecosystems.
- Termite (Order: Isoptera): Termites are eusocial insects, mainly living in tropical and subtropical regions, and are famous for their wood-eating habits.
- Butterfly (Order: Lepidoptera): Known for their striking wing patterns and colors, butterflies undergo a remarkable transformation from caterpillar to adult.
- Octopus (Order: Octopoda): Octopuses are highly intelligent mollusks, recognized for their eight arms and ability to change color and texture.
- Starfish (Class: Asteroidea): Starfish, or sea stars, are famous for their star-shaped appearance and regenerative abilities, mostly found in ocean floors.
- Cricket (Order: Orthoptera): Crickets are jumping insects, known for their distinctive chirping sound, which is produced by rubbing their wings together.
- Snail (Class: Gastropoda): Snails are known for their slow movement and protective spiral shells, inhabiting a wide range of environments from gardens to ocean depths.
- Spider (Order: Araneae): Spiders are skilled predators, using their webs to catch prey, and are characterized by their eight legs and multiple eyes.
- Scorpion (Order: Scorpiones): Scorpions are arachnids known for their venomous sting, used for hunting prey and self-defense.
Each of these invertebrates plays a vital role in their respective ecosystems, showcasing the incredible diversity and adaptability of life without a backbone.
Invertebrates in Different Habitats: Aquatic, Terrestrial, and Aerial
Invertebrates, lacking a backbone, are remarkably adaptable and inhabit diverse environments. This section explores their presence across various habitats: aquatic, terrestrial, and aerial.
Aquatic Invertebrates
- Clams: These bivalve mollusks thrive in both saltwater and freshwater, feeding by filtering nutrients from algae or organic matter.
- Coral: Found in oceans globally, corals feed on tiny plankton, living in shallow waters or on ocean floors.
- Cuttlefish: Inhabiting cold to tropical seas, cuttlefish are carnivorous, eating fish, crabs, and mollusks near coral reefs or rocky areas.
Terrestrial Invertebrates
- Caterpillars: These herbivores consume leaves, flowers, or fruits, inhabiting diverse environments from forests to tree trunks.
- Centipedes: Predominantly found in warmer areas, centipedes feed on dead animals and plants.
- Cockroaches: Omnivores that adapt to various environments, including dark, moist places like sewers or basements.
Aerial Invertebrates
- Dragonflies: Found in freshwater, saltwater, or terrestrial habitats, these insects primarily eat other smaller insects.
- Crickets: Omnivores that live mostly underground, they consume plant matter and are commonly found in moist environments.
- Butterflies: Known for their migration and diverse habitats, they thrive in environments where they can find flowers for nectar.
From the depths of the oceans to the forest floors and the skies above, invertebrates demonstrate a remarkable ability to adapt to a wide range of ecological niches, contributing significantly to the biodiversity of each habitat.

Role of Invertebrates in Ecosystems and Human Life
Invertebrates, which make up a significant portion of the Earth"s biodiversity, play crucial roles in various ecosystems and in human life. Their contribution ranges from environmental impact to their role in human activities.
- Ecosystem Services: Invertebrates contribute significantly to ecosystem services such as pollination, soil aeration, and decomposition. Bees, for example, are vital pollinators for many crops and wild plants.
- Food Web Dynamics: As prey and predators, invertebrates are integral to food webs. Their presence affects the population dynamics of other species, thereby maintaining ecological balance.
- Scientific Research: Invertebrates like fruit flies and nematodes are widely used in scientific research due to their simple body plans and genetic tractability.
- Human Economy: Many invertebrates, such as mollusks (like clams and oysters) and crustaceans (like crabs and lobsters), are key to the fishing industry. Their economic value extends to sectors like pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Environmental Indicators: The presence or absence of certain invertebrates can indicate the health of an ecosystem. For instance, the diversity of insect species can reflect the quality of an environment.
- Waste Decomposition: Earthworms and other detritivores play a vital role in decomposing organic matter, enriching soil fertility and aiding in waste management.
In conclusion, invertebrates, despite their often unnoticed presence, are fundamental to the functioning of ecosystems and have a profound impact on human life and the environment.
Invertebrate Animals | Educational Video for Kids
Explore the captivating world of invertebrate animals in this eye-opening video! Discover the incredible diversity and unique adaptations of these spineless creatures that inhabit our planet, and prepare to be amazed by their extraordinary survival strategies. Get ready to be drawn into the intriguing and mysterious world of invertebrates!
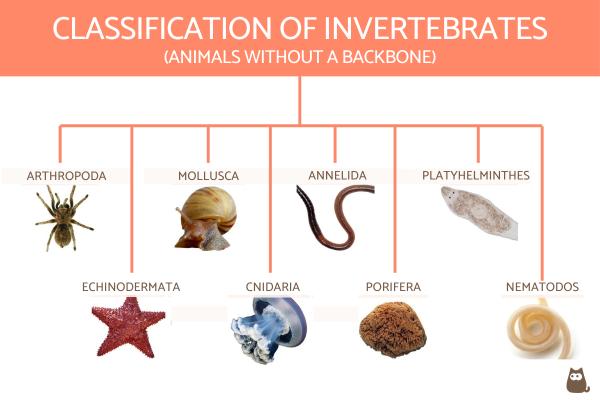
Classification of Invertebrates: From Sponges to Arthropods
Invertebrates encompass a vast array of animals without backbones, constituting a major part of Earth"s biodiversity. They are classified into various phyla based on their distinct characteristics.
- Porifera (Sponges): The simplest invertebrates, sponges lack true tissues and organs. They filter nutrients from water using a system of canals and pores.
- Cnidaria: This phylum includes jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones. These invertebrates are known for their stinging cells and radial symmetry.
- Platyhelminthes (Flatworms): Flatworms, including tapeworms, are characterized by their flattened bodies and lack of specialized respiratory and circulatory systems.
- Nematoda (Roundworms): Roundworms have a complete digestive system and are often parasitic.
- Annelida (Segmented Worms): This group includes earthworms and leeches, known for their segmented bodies.
- Mollusca: Mollusks, including snails, octopuses, and bivalves, have a soft body, usually with a hard shell.
- Arthropoda: The largest phylum, arthropods include insects, arachnids, and crustaceans. They are characterized by their exoskeleton, segmented body, and jointed appendages.
- Echinodermata: Including starfish and sea urchins, echinoderms have a unique water vascular system and radial symmetry.
Each of these phyla represents a unique evolutionary pathway, showcasing the incredible diversity of life forms in the invertebrate world.

Invertebrates without Backbone | Science for Kids
Dive deep into the wonders of the backbone in this fascinating video! Uncover the significance and marvel at the intricate structure that forms the basis of vertebrate life. Journey through the evolution of the backbone, from its origins to the incredible abilities it grants its possessors. Immerse yourself in the remarkable world of the backbone!
Conservation Status of Various Invertebrate Species
The conservation status of invertebrate species is a critical aspect of biodiversity and ecosystem health. Invertebrates, which form the majority of animal life on Earth, face various threats that impact their survival.
- Threats to Invertebrates: Habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation are major threats to invertebrate populations. These factors can lead to declines in species numbers and diversity.
- Endangered Species: Some invertebrate species are now endangered or threatened. For example, certain species of bees and butterflies, crucial for pollination, are facing significant challenges due to habitat destruction and pesticides.
- Conservation Efforts: Efforts to conserve invertebrates include habitat preservation, pollution control, and legal protection. Conservationists and scientists work to understand and mitigate the impacts of human activities on these species.
- Role in Ecosystems: Invertebrates play vital roles in ecosystems, such as pollination, soil aeration, and as part of the food chain. Protecting them is essential for maintaining ecological balance.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring are crucial to assess the conservation status of invertebrates and implement effective strategies for their protection.
It is important to recognize the significance of invertebrates and to continue efforts to protect them for the health of global ecosystems and biodiversity.
Invertebrates in Research and Science: Contributions and Discoveries
Invertebrates have made significant contributions to research and scientific discoveries, playing a vital role in our understanding of biology and the environment.
- Model Organisms: Certain invertebrates like fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) and nematodes (Caenorhabditis elegans) are used as model organisms in genetic research due to their simple genetic makeup and short lifecycles.
- Medical Research: Invertebrates are used in medical research, such as studying the nervous system in squids and octopuses due to their large neurons.
- Environmental Indicators: Many invertebrates, like certain species of bivalves and insects, are used as indicators of environmental health, helping to monitor pollution levels and ecosystem changes.
- Biological Innovation: Research on invertebrates has led to discoveries in biomimicry, inspiring new technologies and materials based on the unique physical structures and abilities of invertebrates, such as the adhesion properties of gecko feet.
- Ecological Studies: Invertebrates are crucial in ecological studies, helping scientists understand food webs, biodiversity, and the effects of climate change on different ecosystems.
The contributions of invertebrates to research and science are immense, providing critical insights into genetics, ecology, and much more.

Interactive Section: Fun Facts About Invertebrates
Delve into the fascinating world of invertebrates with these intriguing facts that highlight the diversity and uniqueness of these spineless wonders.
- Diverse Diet: Caterpillars, a type of invertebrate, have a varied diet including leaves, flowers, or fruits, and their habitats range from forest floors to inside tree trunks.
- Unique Survival: Cockroaches, known for their resilience, can survive in diverse environments from moist, dark areas to surviving an atomic bomb.
- Amazing Adaptability: Crabs, part of the invertebrate family, have a diverse diet and habitat, living in both freshwater and saltwater environments around the world.
- Versatile Habitats: Dragonflies, another invertebrate, are found in various habitats, including freshwater, saltwater, and terrestrial areas, feeding primarily on insects.
- Hydrostatic Skeletons: Many invertebrates like jellyfish and worms have fluid-filled, hydrostatic skeletons, while others like insects and crustaceans have hard exoskeletons.
These fun facts offer a glimpse into the intriguing and diverse world of invertebrates, revealing the incredible adaptability and resilience of these animals.
Photographic Gallery of Diverse Invertebrate Animals
Explore the captivating world of invertebrates through a photographic journey, showcasing the incredible diversity and unique characteristics of these spineless creatures.
- Luna Moths: Known for their striking bright green wings, measuring up to 7 inches across.
- Black Widow Spiders: Recognizable by their red hourglass marking, these spiders are found on every continent except Antarctica.
- Banana Slug: Typically bright yellow, these slugs thrive in cool, damp habitats in western United States and British Columbia.
- Moon Jellyfish: Often displayed in aquariums, these jellyfish drift in ocean currents, thriving in cool temperatures.
- Giant Squid: Mysterious deep-sea dwellers, they can grow up to 43 feet long.
- Blue Morpho Butterfly: Notable for their iridescent blue wings, found in the Amazon rainforest.
- Coconut Crab: The largest terrestrial invertebrate, known for its rigid exoskeleton and can weigh up to 9 pounds.
- American Horseshoe Crab: More closely related to ticks and spiders than crabs, found along the Atlantic Coast of the United States.
- Mosquito: Known for their ability to carry and transmit diseases like Malaria and Dengue Fever.
- Yellowjacket: Predatory wasps important for controlling pest insects, found almost all over the world.
Each of these invertebrates presents a unique aspect of the natural world, highlighting the diversity and beauty of life without a backbone.

READ MORE:
Resources and Further Reading on Invertebrates
For those intrigued by the diverse world of invertebrates, a wealth of resources is available to deepen your understanding and knowledge. Below are some recommended sources for further exploration.
- Visual Dictionary: Offers a comprehensive list of invertebrate animals, from microscopic organisms to giant octopuses, providing insight into their varied shapes and sizes.
- Fauna Facts: A resource with extensive information on a wide range of invertebrates, detailing their scientific names, diets, habitats, and other interesting facts.
- Encyclopedia Britannica: Provides a detailed overview of invertebrates, discussing their taxonomic significance, characteristics, and the vast number of extant species, along with educational articles for various age groups.
- Wikipedia: Offers extensive information on invertebrates, covering their characteristics, diversity, and the role they play in ecosystems, along with a list of the number of described species for major invertebrate groups.
These resources are ideal for anyone looking to expand their knowledge on invertebrates, from students to enthusiasts.
Embarking on the journey through the realm of invertebrates opens a window into the vast and vibrant tapestry of life, revealing the intricate roles and fascinating diversity of these spineless wonders that thrive in every corner of our planet.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/149242726-56a007eb5f9b58eba4ae8e3e.jpg)




