Topic invertebrate facts: Delve into the fascinating world of invertebrates, a realm teeming with extraordinary diversity and intriguing biological secrets waiting to be uncovered.
Table of Content
- What are some interesting facts about invertebrates?
- Diversity of Invertebrates: A World Beyond Vertebrates
- Unique Biological Features of Invertebrates
- Ecological Importance of Invertebrates
- Invertebrates in Human Culture and Economy
- Innovations in Invertebrate Research and Technology
- Conservation Challenges and Strategies for Invertebrates
- YOUTUBE: Invertebrate Animals: Educational Video for Kids
- Interactive Learning: Invertebrate Galleries and Case Studies
- Emerging Trends in Invertebrate Studies
- Myths and Misconceptions About Invertebrates
- Resources for Further Learning and Exploration
What are some interesting facts about invertebrates?
Here are some interesting facts about invertebrates:
- Invertebrates make up the largest group in the animal kingdom, accounting for 97% of all animals.
- There have been around 1.25 million species of invertebrates described so far.
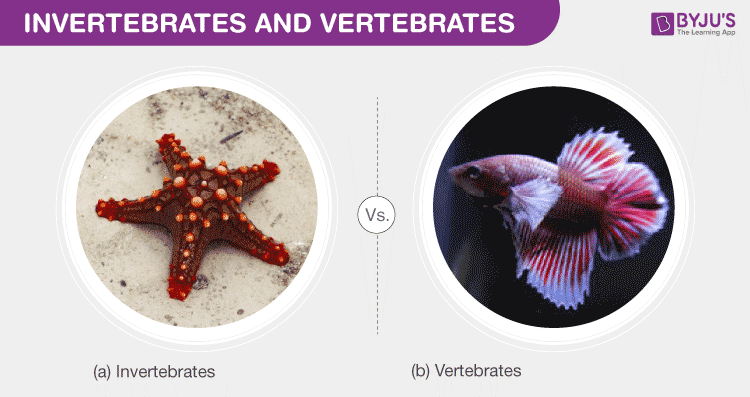
- Invertebrates do not have a vertebral column or backbone, distinguishing them from vertebrates.
- There are six basic groups of invertebrates: sponges, cnidarians, flatworms, roundworms, mollusks, and arthropods.
- Unlike vertebrates, invertebrates do not have skeletons or backbones.
- The first invertebrates appeared more than 600 million years ago.
- Invertebrates can be found in various habitats, including freshwater, marine environments, and land.
READ MORE:
Diversity of Invertebrates: A World Beyond Vertebrates
Invertebrates, lacking a vertebral column, represent an astonishing array of life forms. This diverse group encompasses over 95% of all animal species, making them the true rulers of the animal kingdom in terms of diversity. From microscopic nematodes to the majestic giant squid, invertebrates inhabit every conceivable environment on Earth.
- Classification Complexity: Invertebrates include numerous phyla such as Arthropoda (insects, spiders, crustaceans), Mollusca (snails, octopuses), Annelida (earthworms), and many more, each with unique characteristics.
- Size and Shape Variation: The size of invertebrates ranges from the almost invisible to the giant squid, which can reach lengths of over 40 feet. Their shapes are equally varied, from simple sponges to complex cephalopods.
- Adaptations: Invertebrates exhibit a wide range of adaptations, from the camouflage abilities of cephalopods to the social structures of ant colonies.
- Reproduction and Life Cycles: These creatures showcase diverse reproductive strategies, including asexual reproduction in some species, complex metamorphosis in insects, and intricate mating rituals in others.
- Habitats: Invertebrates are found in every habitat, from deep ocean trenches to the highest mountains, and from polar regions to tropical rainforests.
Understanding the vast diversity of invertebrates not only fascinates but also provides crucial insights into the functioning of ecosystems and the evolutionary history of life on Earth.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/149242726-56a007eb5f9b58eba4ae8e3e.jpg)
Unique Biological Features of Invertebrates
Invertebrates are a marvel of nature, boasting unique biological features that set them apart from their vertebrate counterparts. These characteristics not only define their survival in diverse environments but also highlight the evolutionary ingenuity of nature.
- Exoskeletons: Many invertebrates, like insects and crustaceans, possess exoskeletons made of chitin, providing protection and support without the need for internal bones.
- Radial Symmetry: Creatures such as jellyfish and sea anemones exhibit radial symmetry, enabling them to interact with their environment from all sides equally.
- Regeneration Abilities: Some invertebrates, like starfish and certain worms, can regenerate lost body parts, a feat few vertebrates can achieve.
- Variety in Sensory Organs: Invertebrates have evolved an array of sensory organs, from the compound eyes of insects to the tentacles of octopuses, each adapted to their specific ecological niches.
- Respiration Variations: Invertebrates employ various respiration methods, including through the skin, gills, or even tracheal systems, as seen in insects.
- Diverse Reproductive Strategies: Their reproductive methods are equally varied, ranging from simple binary fission in protozoans to complex life cycles involving multiple stages and host changes in parasites.
The study of these unique features not only enlightens us about invertebrate biology but also enhances our understanding of the broader principles of life and adaptation.
Ecological Importance of Invertebrates
Invertebrates play pivotal roles in maintaining ecological balance and supporting life on Earth. Their contributions are vast and varied, profoundly impacting ecosystems in multiple ways.
- Pollination: Insects like bees, butterflies, and many others are crucial for the pollination of numerous plants, including those vital for human agriculture.
- Soil Health and Fertility: Earthworms and other soil-dwelling invertebrates are essential in aerating the soil and decomposing organic matter, enriching soil fertility.
- Food Web Dynamics: Invertebrates form a significant part of the food web, serving as primary consumers of plant matter and as prey for numerous vertebrates.
- Biological Control: Many invertebrates help control pest populations, thereby maintaining the balance of various ecosystems.
- Nutrient Cycling: Their role in the decomposition process is vital for nutrient cycling, breaking down dead matter and returning nutrients to the ecosystem.
- Indicator Species: Certain invertebrates serve as indicator species, providing insights into the health of ecosystems and signaling environmental changes.
Their ecological significance extends far beyond their numbers, making invertebrates indispensable to the health and stability of the planet"s ecosystems.

Invertebrates in Human Culture and Economy
Invertebrates have a profound and often underappreciated impact on human culture and the economy. Their roles range from direct economic contributions to symbolic and cultural significance.
- Agricultural Impact: Invertebrates like bees play a critical role in pollinating crops, essential for the production of a significant portion of the world’s food supply.
- Silk and Honey Production: Silkworms and bees are prime examples of invertebrates used in the production of silk and honey, commodities with both economic and cultural value.
- Scientific Research and Medicine: Various invertebrates, such as fruit flies and nematodes, are key models in scientific research, leading to medical and genetic breakthroughs.
- Cultural Symbolism: Many invertebrates, like butterflies and beetles, hold symbolic meanings in different cultures, representing concepts like transformation and renewal.
- Art and Literature: Invertebrates have inspired countless works of art and literature, reflecting their intriguing forms and behaviors.
- Ecosystem Services: Beyond direct use, invertebrates provide essential ecosystem services such as waste decomposition and nutrient cycling, indirectly supporting economic activities.
From practical uses to symbolic representations, invertebrates are intertwined with many aspects of human life, highlighting their significance beyond their ecological roles.
Innovations in Invertebrate Research and Technology
The field of invertebrate research has seen remarkable technological advancements, leading to breakthroughs in our understanding and utilization of these diverse organisms.
- Genomic Research: Advances in genomics have allowed scientists to unravel the complex DNA of various invertebrates, leading to insights into their evolution, diversity, and unique biological mechanisms.
- Nanotechnology: Nanotechnology is being applied to study invertebrate systems at the molecular level, providing unprecedented insights into their physiology and potential medical applications.
- Environmental Monitoring: Invertebrates are increasingly used as bioindicators in environmental monitoring, utilizing their sensitivity to ecological changes to assess environmental health.
- Robotics and Biomimicry: The study of invertebrate locomotion and structure inspires innovations in robotics and biomimicry, leading to the development of new technologies and materials.
- Biomedical Applications: Research on invertebrates like cephalopods and jellyfish contributes to advancements in neuroscience and the development of new materials for medical use.
- Conservation Technology: Modern tracking and monitoring technologies are enhancing conservation efforts for endangered invertebrate species and habitats.
These innovations not only deepen our understanding of invertebrates but also pave the way for new technologies and applications in various fields.

Conservation Challenges and Strategies for Invertebrates
Conserving invertebrates presents unique challenges and requires targeted strategies due to their diverse nature and often overlooked status in conservation efforts.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: The primary threat to invertebrates is habitat destruction caused by human activities. Protecting and restoring natural habitats is crucial for their survival.
- Pollution Impact: Addressing pollution, especially pesticides and industrial chemicals, is vital as these substances can be lethal to invertebrates or disrupt their life cycles.
- Climate Change Effects: Climate change poses a significant threat, as many invertebrates are highly sensitive to temperature and weather changes. Conservation efforts must include climate resilience strategies.
- Overexploitation: Some species are threatened by overexploitation for commercial purposes. Sustainable practices and regulations are needed to manage this issue.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about the importance of invertebrates and their conservation is essential for garnering support for conservation initiatives.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring are necessary to understand invertebrate populations, their ecological roles, and the threats they face.
- Collaborative Conservation Efforts: Conservation of invertebrates requires collaboration between governments, NGOs, scientists, and communities to develop and implement effective strategies.
Through comprehensive and collaborative approaches, it is possible to address the conservation challenges facing invertebrates and ensure their continued role in our ecosystems.
Invertebrate Animals: Educational Video for Kids
\"Discover the mesmerizing world of invertebrates in this captivating video! From delicate butterflies to fascinating sea creatures, you\'ll be amazed by the incredible diversity and beauty of these spineless wonders. Join us on a journey through their hidden habitats and uncover the secrets of these remarkable creatures.\"
Invertebrate Animals for Kids: Arthropods, Worms, Cnidarians, Mollusks, Sponges, Echinoderms
\"Step into the extraordinary realm of arthropods with this thrilling video! Brace yourself to witness the astonishing strength and agility of these joint-legged creatures. Get ready to meet fierce spiders, stunning beetles, and graceful crustaceans as we dive into the enchanting world of arthropods. Prepare to be awestruck by their remarkable adaptations and unique behaviors.\"
Interactive Learning: Invertebrate Galleries and Case Studies
Interactive learning methods, such as invertebrate galleries and case studies, provide engaging ways to explore and understand the fascinating world of invertebrates.
- Virtual Invertebrate Galleries: Online galleries and virtual tours offer immersive experiences to explore diverse invertebrate species, their habitats, and behaviors.
- Educational Exhibits: Museums and educational centers often feature invertebrate exhibits, showcasing live specimens and providing hands-on learning experiences.
- Interactive Case Studies: Detailed case studies of specific invertebrates or ecosystems help in understanding the complex interactions and ecological roles of these creatures.
- Augmented Reality Experiences: Augmented reality (AR) apps and games bring invertebrates to life, allowing users to interact with digital models in a real-world context.
- Documentaries and Web Series: Educational documentaries and web series provide visual and narrative insights into the lives and importance of invertebrates.
- Community Science Projects: Participating in community science projects related to invertebrate monitoring encourages active learning and contribution to scientific research.
These interactive approaches not only educate but also inspire a deeper appreciation and curiosity about the diverse world of invertebrates.

Emerging Trends in Invertebrate Studies
Recent advancements in technology and research methodologies are driving exciting new trends in invertebrate studies, broadening our understanding and appreciation of these diverse organisms.
- Genetic and Genomic Research: Cutting-edge genomic research is unraveling the complex genetics of invertebrates, providing insights into their evolution, adaptation, and biodiversity.
- Environmental DNA (eDNA) Analysis: eDNA sampling is becoming a vital tool in studying invertebrate populations in their natural habitats, allowing for non-invasive monitoring and biodiversity assessments.
- Climate Change Impact Studies: Research is increasingly focusing on the impact of climate change on invertebrate species, particularly their adaptation and resilience to changing environmental conditions.
- Nanotechnology in Research: The application of nanotechnology is providing new ways to study invertebrate biology at a microscopic level, enhancing our understanding of their physiology and behavior.
- Behavioral and Neurological Studies: Advanced imaging and tracking technologies are enabling detailed studies of invertebrate behavior and neurology, revealing the complexity of their sensory and response systems.
- Conservation Genomics: Genomic tools are increasingly being used in conservation efforts, helping to identify genetically important populations and inform conservation strategies.
These emerging trends highlight the dynamic nature of invertebrate research, promising new discoveries and insights into the world of these fascinating creatures.
Myths and Misconceptions About Invertebrates
Invertebrates are often misunderstood, leading to various myths and misconceptions that overshadow their true nature and importance.
- "Invertebrates are Primitive": Contrary to the belief that invertebrates are primitive, they exhibit highly evolved and specialized adaptations suited to their environments.
- "All Insects are Pests": While some insects are pests, the vast majority play crucial roles in ecosystems, such as pollination, decomposition, and serving as food sources for other animals.
- "Invertebrates Don"t Feel Pain": Recent studies suggest that some invertebrates may have the capacity to experience pain or discomfort, challenging long-held assumptions about their sensory experiences.
- "Invertebrates are Not Important for Ecosystems": Invertebrates are vital for the health of ecosystems, involved in processes like pollination, soil formation, and nutrient cycling.
- "Invertebrates are Dangerous to Humans": While a small number of invertebrate species can be harmful, the vast majority are harmless and play beneficial roles in human environments.
- "Invertebrates are Easy to Keep as Pets": Some invertebrates require complex care and environments that mimic their natural habitats, making them not as easy to keep as some might think.
Debunking these myths is essential for fostering a greater appreciation and understanding of invertebrates and their critical roles in our world.

READ MORE:
Resources for Further Learning and Exploration
To deepen your understanding and appreciation of invertebrates, a wealth of resources is available for further learning and exploration.
- Books and Field Guides: Numerous books and field guides offer comprehensive information on various invertebrate species, their behaviors, and habitats.
- Online Databases and Websites: Websites like the Encyclopedia of Life and the Integrated Taxonomic Information System provide detailed information on invertebrate taxonomy and biology.
- Scientific Journals: Journals such as Invertebrate Biology and Journal of Insect Science publish the latest research findings in the field of invertebrate studies.
- Educational Videos and Documentaries: Documentaries and online video platforms offer visual insights into the world of invertebrates, making learning engaging and accessible.
- Museums and Zoos: Many museums and zoos have invertebrate exhibits, providing opportunities to observe these creatures up close and learn from experts.
- Workshops and Courses: Various institutions offer workshops, online courses, and lectures on invertebrate biology and ecology for both students and enthusiasts.
- Community Science Programs: Participating in community science projects related to invertebrates can provide hands-on experience and contribute to scientific research.
These resources serve as gateways to a deeper exploration of the fascinating and diverse world of invertebrates.
In exploring the astonishing world of invertebrates, we uncover the marvels of biodiversity and the intricate tapestry of life, reminding us of our shared responsibility to cherish and protect these vital creatures.