Topic fish invertebrate: Dive into the enthralling realm of fish invertebrates, a world where spineless wonders of the marine ecosystem reveal their astonishing diversity and ecological significance.
Table of Content
- What is the relationship between fish and invertebrates?
- Diversity and Classification of Invertebrates
- Marine Invertebrates in Aquariums
- Role in Ecosystems and Human Impact
- Conservation and Management Efforts
- Invertebrates in Research and Education
- Invertebrate Fisheries: Trends and Economic Importance
- YOUTUBE: Invertebrate Animals for Kids: Arthropods, Worms, Cnidarians, Mollusks, Sponges, Echinoderms
- Interesting Facts About Invertebrates
- Techniques in Studying Invertebrates
What is the relationship between fish and invertebrates?
The relationship between fish and invertebrates is diverse and can vary depending on the specific species and their ecological interactions.
Some fish species feed on invertebrates, making them an important part of their diet. These fish are often referred to as \"invertebrate feeders\" and may include species such as angelfish, wrasses, and blennies. They rely on invertebrates like crustaceans, mollusks, and worms as a primary food source.
On the other hand, certain invertebrates can also interact with fish in a symbiotic relationship. For example, cleaner fish, such as cleaner wrasses, engage in mutualistic behavior with other fish species. They remove parasites and dead skin from the bodies of larger fish, benefiting both the cleaner and the host fish.
In some cases, invertebrates and fish may share the same habitat or depend on similar resources, leading to competition. This competition can occur for food, space, or other essential resources. However, the extent and outcome of competition between fish and invertebrates can vary depending on the specific ecological conditions.
In summary, the relationship between fish and invertebrates can range from predator-prey interactions to mutualistic symbiosis or competition for resources.
READ MORE:
Diversity and Classification of Invertebrates
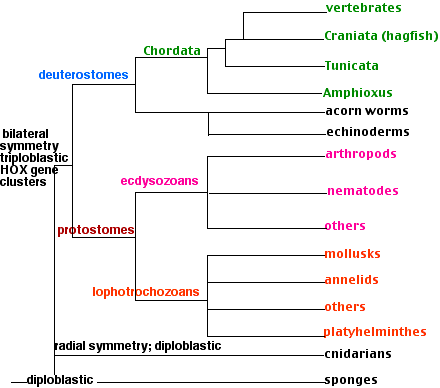
Invertebrates, encompassing a vast array of spineless creatures, form a significant portion of the animal kingdom. These fascinating creatures, devoid of a vertebral column, showcase a remarkable diversity across various habitats.
- Main Phyla: Invertebrates are categorized into several phyla, including arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges, each with unique characteristics and ecological roles.
- Marine Invertebrates: Marine invertebrates, such as corals, crustaceans, and mollusks, play pivotal roles in ocean ecosystems. They serve as key prey for fish and marine mammals and contribute to the creation of critical habitats like coral reefs.
- Aquarium Invertebrates: The world of aquariums brings a closer look at some of these species, such as various corals like torch coral, whisker coral, and finger leather coral, each with distinct care requirements and temperaments.
- Size and Form: The size of invertebrates varies dramatically, from microscopic species to the colossal squid, highlighting the incredible adaptability and evolutionary success of these organisms.
- Ecological Significance: Invertebrates are integral to many food chains and are crucial for the pollination of plants. They also serve as indicators of environmental health and play a role in nutrient cycling.
- Conservation Challenges: Despite their ecological importance, invertebrates face threats from human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing, necessitating focused conservation efforts.
Understanding the diversity and classification of invertebrates is vital for appreciating their role in our ecosystems and the challenges they face in the modern world.

Marine Invertebrates in Aquariums
Marine invertebrates offer an exotic and fascinating addition to aquariums, bringing diverse forms, colors, and behaviors. These creatures, ranging from corals to crustaceans, require specific care, making them an intriguing challenge for aquarists.
- Types of Marine Invertebrates: The marine invertebrates commonly found in aquariums include various corals like torch coral and whisker coral, soft corals like cabbage leather coral, and other species like clove polyps and pulse coral. Each species has unique care requirements and temperaments, from peaceful to aggressive.
- Care Requirements: The key to successfully keeping marine invertebrates lies in understanding their specific needs. This includes optimal water conditions, lighting, and dietary requirements. For instance, some corals require specific lighting and flow conditions for photosynthesis.
- Aquarium Setup: Creating the right environment is crucial. This involves setting up the aquarium with suitable substrates, providing adequate lighting, and ensuring the water chemistry is balanced. Some invertebrates, like snails and shrimps, also help maintain the aquarium ecosystem by consuming algae and waste.
- Benefits in the Ecosystem: In addition to their aesthetic appeal, many marine invertebrates play a functional role in aquariums. They help in cleaning by consuming algae and waste, thus maintaining the ecological balance within the tank.
- Choosing Invertebrates: When selecting invertebrates for an aquarium, it"s important to consider their compatibility with other tank inhabitants and the overall ecosystem of the aquarium. Researching and understanding the specific needs of each species is crucial for a healthy and thriving aquarium.
Marine invertebrates can transform an aquarium into a vibrant and dynamic ecosystem, offering both beauty and functional benefits. However, their care requires careful planning and understanding of their unique requirements.
Role in Ecosystems and Human Impact
Fish and invertebrate species are integral to the health and functioning of marine and freshwater ecosystems. They play critical roles in nutrient cycling, food webs, and the overall balance of aquatic environments.
- Ecological Roles: Invertebrates such as sponges and jellyfish significantly contribute to nutrient cycling, affecting the availability of essential elements like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous in marine ecosystems. This impact is crucial in maintaining the ecological balance and supporting diverse marine life.
- Impact on Food Webs: Many fish and invertebrates serve as vital links in food webs. For example, river herring are a key food source for predators like striped bass and birds like ospreys. The decline in their populations due to human activities disrupts these food webs.
- Human Activities and Consequences: Overfishing, habitat destruction, and environmental degradation caused by human activities have led to significant declines in various fish and invertebrate populations. This not only affects the species themselves but also the larger ecosystems they are part of.
- Conservation Efforts: Efforts to monitor and conserve these species are crucial. This includes studies like eDNA analysis for understanding distribution and abundance, as well as implementing sustainable fishing practices and habitat restoration projects.
- Management of Invertebrate Fisheries: The rapid expansion of invertebrate fisheries has raised concerns about their impact on marine ecosystems. Effective management and regulation of these fisheries are essential to mitigate negative impacts and ensure sustainable use of marine resources.
Understanding the role of fish and invertebrates in ecosystems and the impact of human activities on them is key to ensuring the health and sustainability of aquatic environments.

Conservation and Management Efforts
Conservation and management of fish and invertebrate species are vital for maintaining the ecological balance in both marine and freshwater ecosystems. These efforts are diverse and cover various aspects, from habitat restoration to sustainable fishing practices.
- Habitat Restoration and Creation: Efforts such as creating pollinator habitats and restoring marine nurseries are crucial. These initiatives focus on providing a healthy environment for various species, supporting their life cycles from birth to adulthood.
- Partnerships and Collaboration: Conservation success often relies on collaborations between government agencies, NGOs, and local communities. Programs like the Partners for Fish and Wildlife program in the U.S. offer technical and financial assistance for habitat improvements on private lands.
- Sustainable Management Practices: Sustainable management of fisheries, including invertebrate fisheries, is critical to prevent over-exploitation and ensure long-term viability. This involves implementing practices that balance ecological needs with economic interests.
- Research and Monitoring: Continuous research and monitoring are essential to understand the population dynamics and ecological roles of these species. Efforts like eDNA analysis and catch assessments help in making informed conservation decisions.
- Policy and Regulation: Effective policy frameworks and regulations play a key role in conservation efforts. Laws such as the Endangered Species Act and international agreements aim to protect vulnerable species and habitats.
- Addressing Climate Change: With climate change impacting marine ecosystems, efforts are also geared towards understanding and mitigating its effects on fish and invertebrate populations.
These conservation and management efforts are integral to preserving the biodiversity of our aquatic ecosystems and ensuring the sustainability of both fish and invertebrate species.
Invertebrates in Research and Education
Invertebrates play a significant role in both research and education, offering unique opportunities to study biodiversity, ecosystem dynamics, and the impact of environmental changes. Their use in educational and research settings provides valuable insights into marine and freshwater ecosystems.
- Research Importance: Invertebrates are vital for ecological studies, helping scientists understand the complexities of aquatic ecosystems. For instance, studies on river herring and blue crabs have provided essential data on species distribution and ecosystem interactions, using methods like eDNA analysis.
- Educational Value: Educational programs at institutions like Mote Marine Laboratory & Aquarium and the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center utilize invertebrates to teach about marine biology and conservation. These programs often include internships and hands-on experiences for students.
- Conservation Efforts: Research on invertebrates also informs conservation strategies. Studies on species like the blue crab have led to better understanding of their life cycles and migration patterns, essential for effective conservation planning.
- Public Engagement: Invertebrates are used to engage the public in science and conservation, through aquarium exhibits and citizen science projects. These initiatives help increase awareness and understanding of marine life and its conservation.
- Innovative Methodologies: Research on invertebrates often involves innovative methodologies, including genetics, habitat analysis, and population dynamics studies, contributing to broader scientific knowledge.
The study and display of invertebrates in research and educational settings are crucial for fostering a deeper understanding of marine ecosystems and highlighting the importance of their conservation.

Invertebrate Fisheries: Trends and Economic Importance
Invertebrates play a significant role in both research and education, offering unique opportunities to study biodiversity, ecosystem dynamics, and the impact of environmental changes. Their use in educational and research settings provides valuable insights into marine and freshwater ecosystems.
- Research Importance: Invertebrates are vital for ecological studies, helping scientists understand the complexities of aquatic ecosystems. For instance, studies on river herring and blue crabs have provided essential data on species distribution and ecosystem interactions, using methods like eDNA analysis.
- Educational Value: Educational programs at institutions like Mote Marine Laboratory & Aquarium and the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center utilize invertebrates to teach about marine biology and conservation. These programs often include internships and hands-on experiences for students.
- Conservation Efforts: Research on invertebrates also informs conservation strategies. Studies on species like the blue crab have led to better understanding of their life cycles and migration patterns, essential for effective conservation planning.
- Public Engagement: Invertebrates are used to engage the public in science and conservation, through aquarium exhibits and citizen science projects. These initiatives help increase awareness and understanding of marine life and its conservation.
- Innovative Methodologies: Research on invertebrates often involves innovative methodologies, including genetics, habitat analysis, and population dynamics studies, contributing to broader scientific knowledge.
The study and display of invertebrates in research and educational settings are crucial for fostering a deeper understanding of marine ecosystems and highlighting the importance of their conservation.
Invertebrate Animals for Kids: Arthropods, Worms, Cnidarians, Mollusks, Sponges, Echinoderms
Discover the fascinating world of invertebrates in this mesmerizing video! Watch as they gracefully navigate through their underwater habitats, showcasing their vibrant colors and intricate patterns. Prepare to be in awe of the diversity and beauty of these incredible creatures!
A Unique Jam-Packed Invertebrate Reef Tank!
Immerse yourself in the breathtaking beauty of the coral reef with this captivating video! Dive into an underwater paradise, where vibrant corals dance with a myriad of marine life. Experience the tranquility and wonder of the reef as you explore its vibrant ecosystem.
Interesting Facts About Invertebrates
Invertebrates play a significant role in both research and education, offering unique opportunities to study biodiversity, ecosystem dynamics, and the impact of environmental changes. Their use in educational and research settings provides valuable insights into marine and freshwater ecosystems.
- Research Importance: Invertebrates are vital for ecological studies, helping scientists understand the complexities of aquatic ecosystems. For instance, studies on river herring and blue crabs have provided essential data on species distribution and ecosystem interactions, using methods like eDNA analysis.
- Educational Value: Educational programs at institutions like Mote Marine Laboratory & Aquarium and the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center utilize invertebrates to teach about marine biology and conservation. These programs often include internships and hands-on experiences for students.
- Conservation Efforts: Research on invertebrates also informs conservation strategies. Studies on species like the blue crab have led to better understanding of their life cycles and migration patterns, essential for effective conservation planning.
- Public Engagement: Invertebrates are used to engage the public in science and conservation, through aquarium exhibits and citizen science projects. These initiatives help increase awareness and understanding of marine life and its conservation.
- Innovative Methodologies: Research on invertebrates often involves innovative methodologies, including genetics, habitat analysis, and population dynamics studies, contributing to broader scientific knowledge.
The study and display of invertebrates in research and educational settings are crucial for fostering a deeper understanding of marine ecosystems and highlighting the importance of their conservation.

READ MORE:
Techniques in Studying Invertebrates
In the study of fish invertebrates, various sophisticated techniques are employed to understand their diversity, ecology, and behavior. These methodologies are vital in assessing the health of aquatic ecosystems and in conservation efforts.
Environmental DNA (eDNA) Surveys
One cutting-edge technique is the use of eDNA. This involves filtering and extracting DNA from water samples and amplifying specific DNA regions. The amplified DNA is then sequenced and compared to reference genomes to identify the species present. This method allows for the detection of a wide range of species, including those that are elusive or rare.
Population Sampling Techniques
Various methods are used for population sampling of aquatic organisms. Techniques like snorkel surveys and electrofishing are common in shallow streams and rivers. Manta tows are used in marine environments, especially coral reefs, to monitor species populations and habitat conditions. This involves towing a snorkeler behind a boat to observe and record data on marine life.
Macroinvertebrate Ecology and Identification
Studying macroinvertebrates is crucial for understanding aquatic ecosystems. Techniques include hands-on fieldwork and lab analysis. Researchers collect samples from various habitats, such as streams and ponds, and identify species to understand their ecological roles. This includes understanding life history strategies, trophic groups, and patterns of abundance.
Invertebrate Monitoring Methods
Monitoring invertebrate populations is important for assessing water quality and ecological integrity. Techniques include collecting samples from terrestrial, pelagic, and benthic strata using various gears like traps and nets. The collected samples are then analyzed for species identification, enumeration, and biomass estimation.
These techniques collectively contribute to a comprehensive understanding of invertebrate diversity and their role in aquatic ecosystems, aiding in conservation and management efforts.
Exploring the wondrous world of fish invertebrates reveals a hidden realm of biodiversity and ecological significance, inviting us all to delve deeper into these fascinating creatures and their vital role in our planet"s aquatic ecosystems.