Topic vertebrate vs invertebrate: Explore the fascinating world of biology through the lens of "Vertebrate vs Invertebrate," delving into the unique characteristics and roles of these diverse animal groups in our ecosystem.
Table of Content
- What is the difference between vertebrates and invertebrates?
- Definition and Key Differences Between Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- Anatomy and Physiology: Distinguishing Characteristics
- Diversity of Species in Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- Evolutionary Perspectives: Understanding the Development of Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- Ecological Roles and Environmental Impact of Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- YOUTUBE: The Animal Kingdom: Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- Behavioral Traits and Life Cycles in Vertebrate and Invertebrate Species
- Adaptation Strategies: How Vertebrates and Invertebrates Survive and Thrive
- Medical and Scientific Research: Contributions of Vertebrate and Invertebrate Studies
- Conservation Efforts and the Future of Vertebrate and Invertebrate Populations
- Interactive Learning Resources and Further Reading on Vertebrates vs Invertebrates
What is the difference between vertebrates and invertebrates?
The main difference between vertebrates and invertebrates lies in their skeletal structure. Vertebrates have an internal skeleton made up of bones or cartilage, while invertebrates lack a backbone or any internal skeleton. This fundamental distinction leads to various other contrasting characteristics between the two groups.
Here are some key points differentiating vertebrates and invertebrates:
- Skeletal Structure: Vertebrates have a well-developed internal skeleton, while invertebrates lack a backbone.
- Size and Diversity: Invertebrates comprise around 97% of all animal species, showcasing significant diversity in shape, size, and habitat adaptations. Vertebrates make up the remaining 3% but still exhibit a great range of forms.
- Nervous System: Vertebrates possess a more complex nervous system, including a brain and a spinal cord. In contrast, most invertebrates have simpler nervous systems, with varying degrees of complexity.
- Respiratory System: Vertebrates primarily respire using lungs or gills, allowing them to live in various environments. Invertebrates use a wide range of respiratory organs such as spiracles, tracheae, gills, or diffusion through their body wall.
- Circulatory System: Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system with a heart and blood vessels, facilitating efficient oxygen and nutrient transport. Invertebrates exhibit diverse circulatory systems, including open circulatory systems where the blood directly bathes tissues.
- Reproduction: Vertebrates generally have internal fertilization and give birth to live young, although some lay eggs. Invertebrates employ various reproductive strategies, including external fertilization and both sexual and asexual reproduction.
- Habitat: Vertebrates can be found in various habitats, including terrestrial, aquatic, and aerial environments. Invertebrates occupy an even broader range of habitats, including virtually all ecosystems on Earth.
These differences between vertebrates and invertebrates contribute to the incredible diversity of animal life on our planet.
READ MORE:
Definition and Key Differences Between Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Vertebrates and invertebrates represent two broad categories of animals, each with distinct characteristics. Vertebrates are animals with a backbone or spinal column, a feature absent in invertebrates. This fundamental difference leads to several other distinctions:
- Skeletal Structure: Vertebrates have an internal skeleton made of bone or cartilage, whereas invertebrates may have an external shell or no hard supporting structure.
- Nervous System: Vertebrates generally have a more complex nervous system, with a well-developed brain and spinal cord.
- Size and Complexity: Vertebrates tend to be larger and more complex organisms compared to invertebrates.
- Reproduction: Most vertebrates have advanced reproductive systems, often involving internal fertilization, while invertebrates exhibit a wider range of reproductive methods.
- Diversity: Invertebrates account for a vast majority of animal diversity, with numerous species spread across various phyla.
- Habitat: Both vertebrates and invertebrates inhabit diverse environments, but invertebrates, being more numerous, are found in virtually every habitat on Earth.
Understanding these differences not only highlights the incredible diversity of life on our planet but also helps in studying biological evolution and ecosystem dynamics.
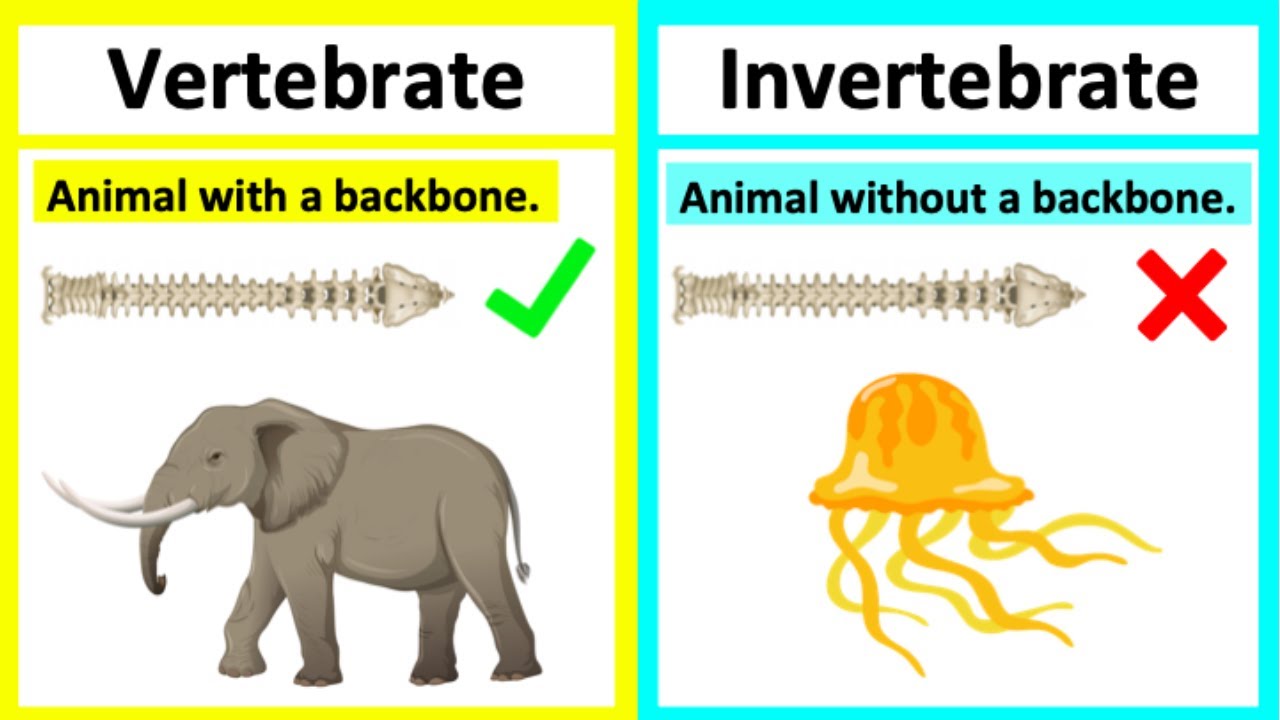
Anatomy and Physiology: Distinguishing Characteristics
The anatomy and physiology of vertebrates and invertebrates reveal key differences that highlight their evolutionary paths and ecological roles:
- Body Structure: Vertebrates possess a well-defined internal skeletal structure, supporting a complex body plan. Invertebrates, lacking this, often have simpler body structures.
- Skin and Coverings: Vertebrates typically have skin with specialized structures like scales, feathers, or fur. Invertebrates may have exoskeletons, shells, or soft outer coverings.
- Organ Systems: Vertebrates usually have highly developed organ systems, including respiratory, circulatory, and nervous systems. Invertebrates have less complex, sometimes decentralized, systems.
- Movement: The vertebrate muscular and skeletal systems allow for diverse and complex movements. Invertebrates exhibit varied movement mechanisms, often related to their body structures.
- Sensory Organs: Vertebrates generally have advanced sensory organs for vision, hearing, and smell. Invertebrates have varied sensory adaptations, which may be less complex.
- Reproduction and Development: Vertebrates predominantly reproduce sexually with significant embryonic development stages. Invertebrates show a wider array of reproductive and developmental strategies.
These anatomical and physiological traits illustrate the vast diversity within the animal kingdom, offering insights into the adaptability and survival strategies of different species.
Diversity of Species in Vertebrates and Invertebrates
The anatomy and physiology of vertebrates and invertebrates reveal key differences that highlight their evolutionary paths and ecological roles:
- Body Structure: Vertebrates possess a well-defined internal skeletal structure, supporting a complex body plan. Invertebrates, lacking this, often have simpler body structures.
- Skin and Coverings: Vertebrates typically have skin with specialized structures like scales, feathers, or fur. Invertebrates may have exoskeletons, shells, or soft outer coverings.
- Organ Systems: Vertebrates usually have highly developed organ systems, including respiratory, circulatory, and nervous systems. Invertebrates have less complex, sometimes decentralized, systems.
- Movement: The vertebrate muscular and skeletal systems allow for diverse and complex movements. Invertebrates exhibit varied movement mechanisms, often related to their body structures.
- Sensory Organs: Vertebrates generally have advanced sensory organs for vision, hearing, and smell. Invertebrates have varied sensory adaptations, which may be less complex.
- Reproduction and Development: Vertebrates predominantly reproduce sexually with significant embryonic development stages. Invertebrates show a wider array of reproductive and developmental strategies.
These anatomical and physiological traits illustrate the vast diversity within the animal kingdom, offering insights into the adaptability and survival strategies of different species.
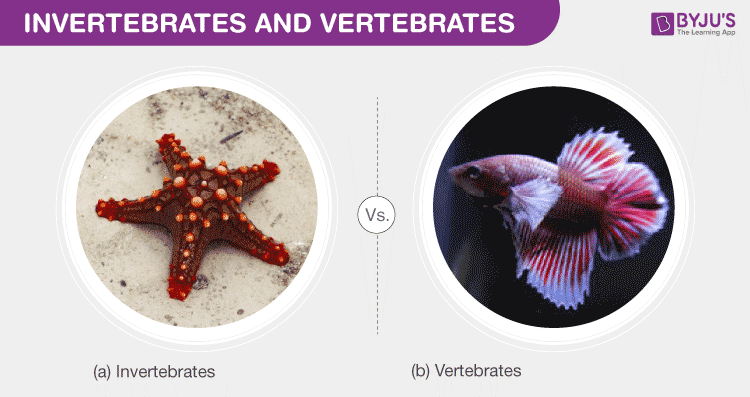
Evolutionary Perspectives: Understanding the Development of Vertebrates and Invertebrates
The anatomy and physiology of vertebrates and invertebrates reveal key differences that highlight their evolutionary paths and ecological roles:
- Body Structure: Vertebrates possess a well-defined internal skeletal structure, supporting a complex body plan. Invertebrates, lacking this, often have simpler body structures.
- Skin and Coverings: Vertebrates typically have skin with specialized structures like scales, feathers, or fur. Invertebrates may have exoskeletons, shells, or soft outer coverings.
- Organ Systems: Vertebrates usually have highly developed organ systems, including respiratory, circulatory, and nervous systems. Invertebrates have less complex, sometimes decentralized, systems.
- Movement: The vertebrate muscular and skeletal systems allow for diverse and complex movements. Invertebrates exhibit varied movement mechanisms, often related to their body structures.
- Sensory Organs: Vertebrates generally have advanced sensory organs for vision, hearing, and smell. Invertebrates have varied sensory adaptations, which may be less complex.
- Reproduction and Development: Vertebrates predominantly reproduce sexually with significant embryonic development stages. Invertebrates show a wider array of reproductive and developmental strategies.
These anatomical and physiological traits illustrate the vast diversity within the animal kingdom, offering insights into the adaptability and survival strategies of different species.
Ecological Roles and Environmental Impact of Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Vertebrates and invertebrates play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance and contribute significantly to environmental health. River herring, including alewife and blueback herring, serve as a vital part of coastal food webs. Their decline due to overfishing and habitat loss has notable ecological impacts. The preservation of these species is crucial for ecosystem stability.
Fishing, an important sector of coastal economies, greatly influences marine ecosystems. Sustainable fishing practices are essential to maintain biodiversity and productivity in these habitats. Understanding the ecology of fisheries helps in crafting effective conservation strategies to protect these vital resources.
Invertebrates, often overlooked, are pivotal in various ecological processes. They act as key players in nutrient cycling, soil formation, and as indicators of environmental health. Their conservation is vital for maintaining ecological integrity and resilience.
Overall, both vertebrates and invertebrates are integral to sustaining ecological systems. Their roles range from being food sources to ecosystem engineers, underlining the importance of their conservation for a healthy environment.

The Animal Kingdom: Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Classification: Discover the power of classification in this groundbreaking video! Uncover the secrets behind organizing complex data and unlock a world of possibilities. Dive into the fundamentals and watch your understanding soar!
Behavioral Traits and Life Cycles in Vertebrate and Invertebrate Species
Vertebrates and invertebrates exhibit diverse behavioral traits and life cycles that are crucial for their survival and ecological roles. Understanding these differences enriches our knowledge of the animal kingdom.
Vertebrate Behavioral Traits and Life Cycles
- Vertebrates, such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, possess a centralized nervous system with a brain and spinal cord, facilitating sophisticated behaviors, communication, and learning abilities.
- They typically have an internal skeleton made of bone or cartilage, providing support and enabling a wide range of movements.
- Many vertebrates undergo significant developmental changes from birth to adulthood, marked by various stages of growth and maturation.
Invertebrate Behavioral Traits and Life Cycles
- Invertebrates, including insects, spiders, crustaceans, mollusks, and worms, have decentralized nervous systems with ganglia or nerve nets, resulting in varying degrees of behavioral complexity.
- Some invertebrates exhibit complex life cycles, like the coelenterate Obelia, which transitions from a sessile polyp stage to a motile medusa stage.
- Most invertebrates, except insects, are aquatic, and their behaviors are often adapted to their specific environmental niches.
The study of these traits and life cycles offers insights into the adaptability and evolution of various species within these two broad classifications of the animal kingdom.
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals
Diversity: Celebrate the beauty of diversity! Join us on this inspiring journey as we explore the different faces, voices, and cultures that make our world vibrant. Embrace the richness of diversity and learn how it strengthens our communities and fosters unity.
Adaptation Strategies: How Vertebrates and Invertebrates Survive and Thrive
Vertebrates and invertebrates have evolved a fascinating array of adaptation strategies to survive and thrive in diverse environments. These adaptations are crucial for their survival, reproduction, and maintenance of their ecological roles.
Vertebrate Adaptation Strategies
- Vertebrates, such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, have developed complex nervous systems, including a centralized brain and spinal cord, enabling sophisticated behaviors and environmental interactions.
- Some vertebrates, like certain species of fish and amphibians, have evolved mechanisms to withstand extreme environmental conditions, such as the ability of wood frogs to tolerate freezing.
- Vertebrate species have also adapted various reproductive strategies and developmental stages to ensure survival and continuation of their species in different habitats.
Invertebrate Adaptation Strategies
- Invertebrates, including insects, crustaceans, mollusks, and worms, often possess decentralized nervous systems, with adaptations like nerve nets in radially symmetric animals, allowing for basic environmental responses.
- Many invertebrates have evolved complex life cycles, such as certain coelenterates that transition from a polyp stage to a medusa stage, demonstrating an incredible adaptability to their living conditions.
- Invertebrates have adapted to terrestrial life with features for gas exchange without desiccation, crucial for survival in varying environmental conditions.
These adaptation strategies highlight the remarkable diversity and resilience of life in our planet"s ecosystems, showcasing the evolutionary ingenuity of both vertebrates and invertebrates.
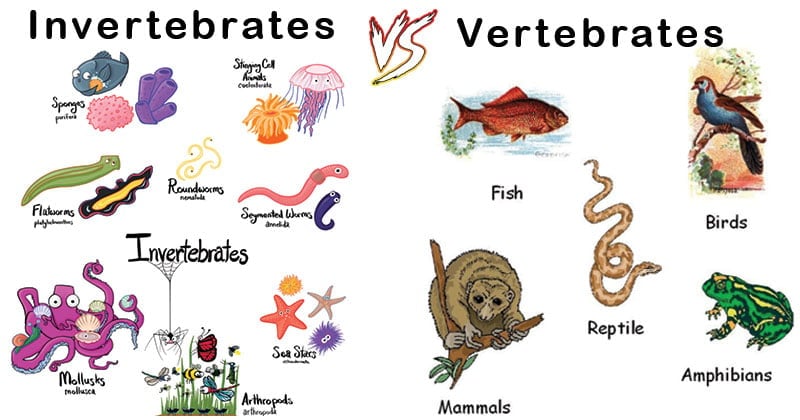
Medical and Scientific Research: Contributions of Vertebrate and Invertebrate Studies
Medical and scientific research has greatly benefited from studies involving both vertebrates and invertebrates, each offering unique insights into biological processes and disease mechanisms.
Contributions of Vertebrate Studies
- Vertebrates, due to their more complex nervous systems and similarities to humans, are often used in neuroscience research. For instance, studies on the mouse brain have provided valuable insights into cerebral cortex functions and neurological diseases.
- The spinal cord of vertebrates, with its distinct arrangement of gray and white matter, is crucial in understanding nerve impulse transmission and spinal injuries.
- Vertebrates have been instrumental in studying various aspects of human health, including the development of new pharmacological strategies for neurodegenerative conditions.
Contributions of Invertebrate Studies
- Invertebrates like Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) have been pivotal in understanding genes and neuronal circuits controlling behaviors such as courtship and aggression, due to their simpler and genetically tractable nervous systems.
- Studies on invertebrates have advanced our knowledge in areas like the immune response, cardiac diseases, and host-pathogen interactions, contributing to breakthroughs in medical research.
- The use of invertebrates in research also raises important ethical considerations, highlighting the need for oversight and public trust in scientific practices.
Together, vertebrate and invertebrate studies continue to be essential in advancing our understanding of biology and medicine, offering complementary perspectives that enrich scientific knowledge and healthcare innovations.
Conservation Efforts and the Future of Vertebrate and Invertebrate Populations
Conservation efforts for vertebrate and invertebrate populations are critical for preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance. Both groups face unique challenges and require specific strategies for their conservation.
Conservation of Vertebrates
- Vertebrate conservation often focuses on habitat protection and restoration, addressing issues such as deforestation and urbanization that directly impact these species.
- Conservation programs for vertebrates also include measures against overhunting and illegal wildlife trade.
- Climate change is a significant threat to vertebrates, and conservation efforts are increasingly incorporating strategies to mitigate its impact.
Conservation of Invertebrates
- Invertebrate conservation is challenged by the general lack of awareness about their crucial ecological roles, such as pollination and soil aeration.
- Efforts to conserve invertebrates include protecting critical habitats like coral reefs and addressing pollution, which can have devastating effects on these species.
- Marine invertebrates, for instance, are particularly affected by ocean acidification and require conservation efforts that tackle these environmental changes.
Future conservation strategies will need to be adaptive and multifaceted, focusing not only on preserving species but also on maintaining the integrity of entire ecosystems. Public education and scientific research are key components in driving effective conservation efforts for both vertebrates and invertebrates.

READ MORE:
Interactive Learning Resources and Further Reading on Vertebrates vs Invertebrates
Engaging in interactive learning resources and exploring further reading materials can significantly enhance understanding of the differences and similarities between vertebrates and invertebrates. Here are some valuable resources and activities:
Interactive Learning Resources
- Interactive presentations and quizzes on vertebrates vs invertebrates can be found in online educational platforms, offering an engaging way for learners to understand these animal groups.
- Activities such as sorting games and Venn diagrams allow students to classify and compare the characteristics of vertebrates and invertebrates in an interactive manner.
- Hands-on activities like creating models of vertebrates and invertebrates using playdough, clay, and other materials can help visualize and reinforce learning.
Further Reading and Educational Materials
- Educational websites provide detailed descriptions and examples of vertebrates and invertebrates, often accompanied by illustrative images and diagrams.
- Lesson plans and teaching resources, including worksheets and foldables, are available for educators to facilitate structured learning on this topic.
- Digital resources like Google Slides and PowerPoint presentations offer comprehensive information and are ideal for both classroom and distance learning setups.
These resources not only provide factual information but also engage learners in a more interactive and enjoyable way of learning about the fascinating world of vertebrates and invertebrates.
Explore the fascinating world of vertebrates and invertebrates, where each creature, big or small, plays a unique role in our ecosystem. Join us in uncovering the mysteries and marvels of these diverse life forms!










