Topic definition of ecosystem biodiversity: Explore the essence of ecosystem biodiversity, where the interplay of life forms creates a resilient and vibrant Earth.
Table of Content
- What is the definition of ecosystem biodiversity?
- What is Ecosystem Biodiversity?
- Importance of Ecosystem Biodiversity
- Components of Ecosystem Biodiversity
- Threats to Ecosystem Biodiversity
- Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Biodiversity
- Role of Ecosystem Services in Biodiversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Biodiversity
- Impact of Climate Change on Ecosystem Biodiversity
- Case Studies of Ecosystem Biodiversity
- Future Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Biodiversity
- How Individuals Can Contribute to Biodiversity Conservation
What is the definition of ecosystem biodiversity?
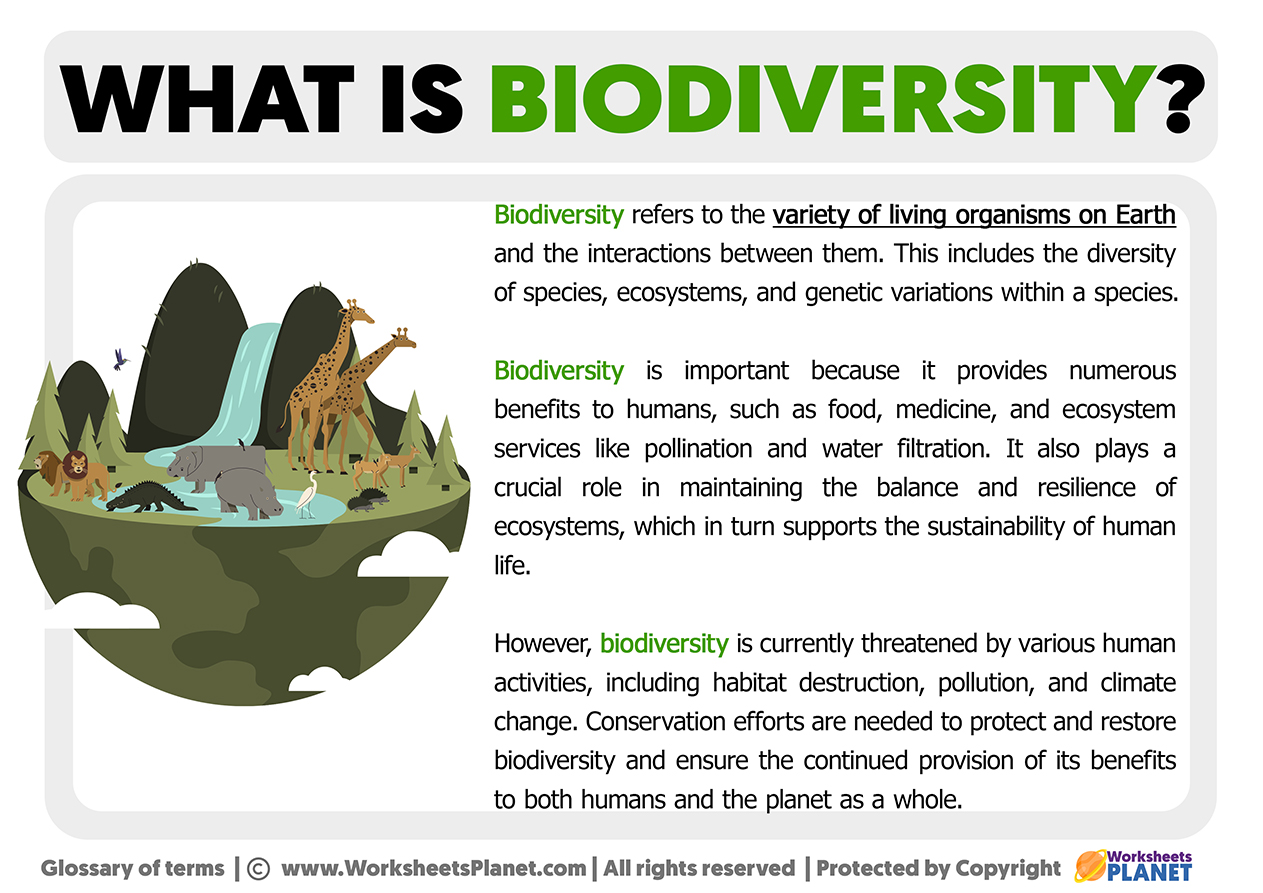
The definition of ecosystem biodiversity refers to the variety and abundance of different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms that inhabit an ecosystem. It includes all levels of biodiversity, from the genetic diversity within a species to the diversity of different habitats and ecosystems.
Ecosystem biodiversity is a measure of the richness and complexity of life forms within a particular ecosystem and is influenced by factors such as climate, geographical location, and interactions between different species. It encompasses both the biological diversity (biodiversity) and the abiotic properties (geodiversity) of an ecosystem.
At the genetic level, ecosystem biodiversity includes the variety of alleles and genetic traits within a species, which is important for adaptation and resilience to environmental changes. It also encompasses the diversity of species present in an ecosystem, ranging from plants and animals to microorganisms like bacteria and fungi.
Ecosystem biodiversity is not limited to a specific area but extends to the interactions and relationships between different ecosystems. It recognizes the interconnectedness and interdependence of various habitats and ecosystems, highlighting the importance of conserving and sustaining these diverse natural environments.
In summary, ecosystem biodiversity refers to the variety and abundance of species and their interactions within an ecosystem, covering genetic diversity, species diversity, and the diversity of habitats and ecosystems.
READ MORE:
What is Ecosystem Biodiversity?
Ecosystem biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of natural environments and the ecological complexes they are part of. It encompasses the diversity of living organisms, their interactions, and the physical contexts in which they exist, ranging from small local habitats to the global aggregate of ecosystems.
- It includes variations in ecosystems within a geographical location, reflecting the complex network of life forms and their environments.
- Emphasizes the importance of different habitats, such as forests, deserts, wetlands, and oceans, contributing to the overall diversity of life on Earth.
- Considers both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components and their interrelations within ecosystems.
This diversity is crucial for ecosystem resilience, providing essential services like air and water purification, pollination, and climate regulation, which are fundamental for life on Earth.

Importance of Ecosystem Biodiversity
Ecosystem biodiversity is vital for sustaining life on Earth, providing essential services that maintain balance and resilience in natural environments. This diversity ensures the functionality of ecosystems, supporting everything from nutrient cycling and water filtration to climate regulation and disease control.
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity underpins crucial ecosystem services like pollination, water purification, and soil fertility, directly impacting food security and human health.
- Enhances Resilience: A diverse ecosystem can better withstand environmental stress and adapt to changes, thereby contributing to the stability and sustainability of habitats.
- Drives Economic Benefits: Biodiversity is a key resource for industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and tourism, contributing significantly to economies worldwide.
- Promotes Health and Well-being: Natural ecosystems have been shown to improve mental and physical health, offering spaces for recreation and relaxation.
- Facilitates Adaptation and Evolution: The genetic diversity within ecosystems is the foundation for species adaptation and evolution, ensuring survival amidst changing environmental conditions.
Preserving ecosystem biodiversity is not just about protecting nature; it"s about safeguarding our future on this planet, ensuring a healthy, productive, and resilient environment for generations to come.
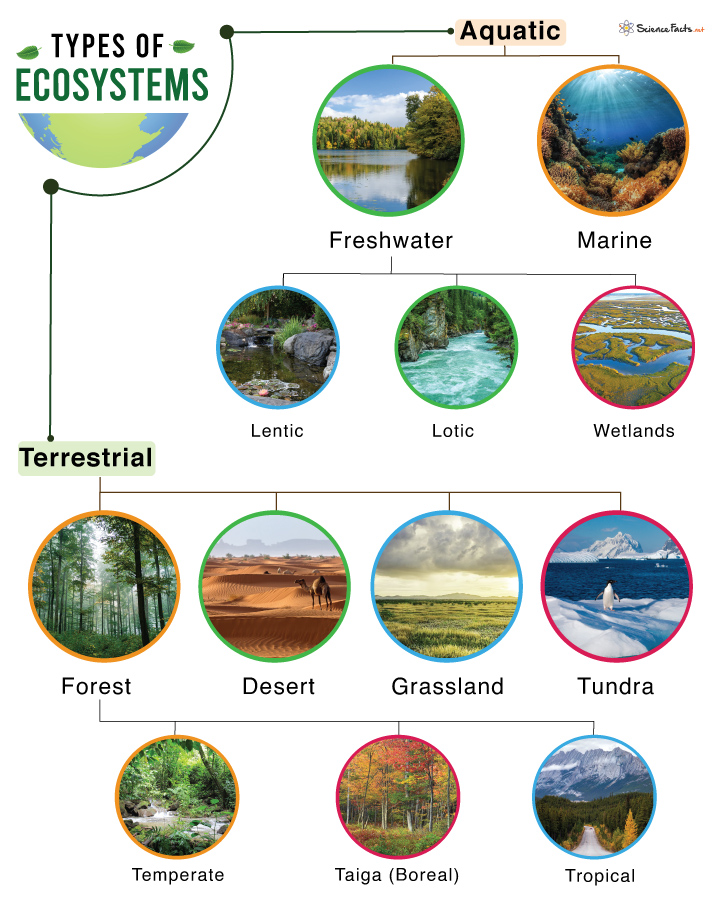
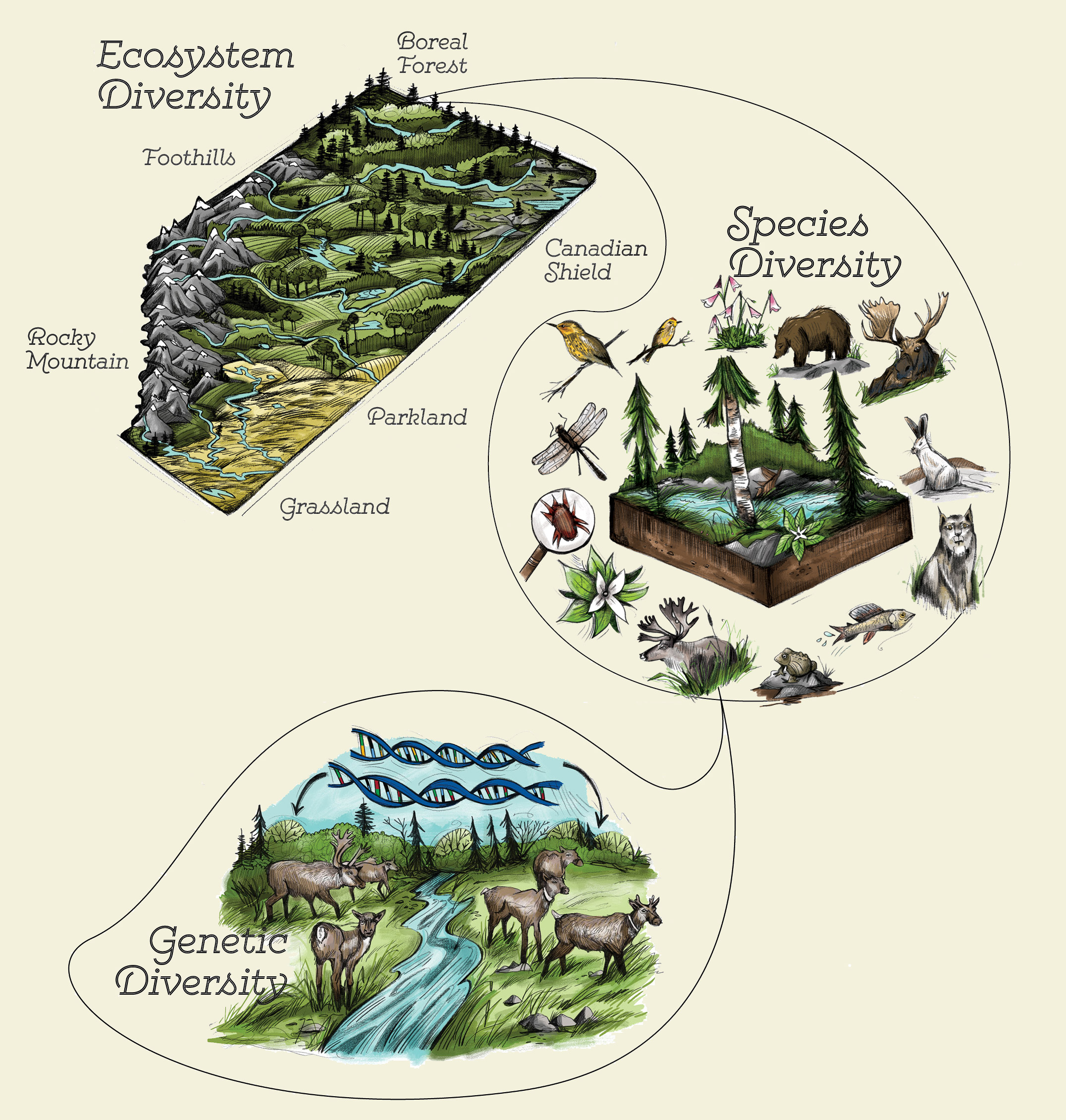
Components of Ecosystem Biodiversity
Ecosystem biodiversity is composed of three fundamental layers that interconnect to form the intricate web of life on our planet:
- Genetic Diversity: This refers to the variety of genes within species, ensuring adaptability and resilience to changes in the environment.
- Species Diversity: The assortment of species within an ecosystem, contributing to a complex and balanced ecological network.
- Ecosystem Diversity: The variety of habitats, biotic communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere, from deserts and forests to freshwater and marine ecosystems.
Each component plays a critical role in maintaining ecological balance, supporting ecosystem services, and ensuring survival and adaptability in the face of environmental changes.

Threats to Ecosystem Biodiversity
The delicate balance of ecosystem biodiversity faces numerous threats that can disrupt the intricate web of life, leading to irreversible consequences:
- Habitat Destruction: Urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture expansion are fragmenting and reducing natural habitats, eroding biodiversity at an alarming rate.
- Climate Change: Altering weather patterns, rising temperatures, and increased frequency of extreme weather events disrupt ecosystems, affecting species distribution and survival.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from chemicals, plastics, and waste runoff degrade natural habitats and poison wildlife, reducing biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced by human activities outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to indigenous species, disrupting local ecosystems.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable fishing, hunting, and logging deplete species faster than they can recover, leading to population declines and extinction.
Addressing these threats requires global cooperation and sustainable practices to protect the invaluable asset of ecosystem biodiversity for future generations.
Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Biodiversity
Protecting the rich tapestry of ecosystem biodiversity is crucial for our planet"s health and our own survival. Implementing effective conservation strategies can mitigate threats and promote the resilience and recovery of ecosystems:
- Establishment of Protected Areas: Creating national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to safeguard habitats and species from human exploitation.
- Restoration of Natural Habitats: Rehabilitating degraded areas, reforesting cleared lands, and restoring wetlands to their natural states to encourage biodiversity.
- Community-Based Conservation: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their traditional knowledge and incentivizing sustainable practices.
- Legislative Measures: Enforcing laws and regulations that limit pollution, restrict invasive species introduction, and control land use to protect ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Action Plans: Developing and implementing comprehensive strategies that address the specific needs of endangered species and critical habitats.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Adopting practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase carbon sequestration to lessen the impact of climate change on ecosystems.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting understanding and appreciation of biodiversity through education, fostering a culture of conservation among the public and policymakers.
By integrating these strategies, we can preserve the integrity and functionality of ecosystems, ensuring a sustainable future for all living beings.
Role of Ecosystem Services in Biodiversity
Ecosystem services play a crucial role in supporting and enhancing biodiversity. These services, which arise from the complex interactions within ecosystems, are fundamental to the health and functionality of our planet"s diverse habitats:
- Nutrient Cycling: The process of recycling nutrients, essential for plant growth and soil fertility, supports diverse plant and animal life.
- Water Regulation: Ecosystems like forests and wetlands regulate water flow and quality, creating stable environments for various species.
- Pollination: Bees, birds, and bats among others, facilitate the reproduction of many plants, contributing to genetic diversity and food production.
- Habitat Provision: Natural habitats provide shelter and breeding grounds, crucial for species survival and biodiversity.
- Climate Regulation: Ecosystems influence climate conditions by sequestering carbon and regulating local temperatures, supporting diverse climatic zones.
These services are not only essential for the survival of countless species but also for the ecological balance and resilience of ecosystems, illustrating the interdependence of ecosystem services and biodiversity.
Ecosystem Biodiversity
Discover the wonders of the ecosystem in this captivating video! Immerse yourself in the beauty of nature as you learn about the intricate web of life that exists in our planet. From lush forests to vast oceans, explore the diverse habitats and fascinating creatures that make up our ever-changing ecosystem.
What Is Biodiversity? Definition, Types And Importance - Learning Junction
Uncover the extraordinary world of biodiversity in this awe-inspiring video. Delve into the staggering variety of life forms - from tiny microorganisms to majestic animals - that thrive in our planet. Witness the stunning adaptations and interconnections that form the foundation of our delicate ecosystem, highlighting the importance of protecting and preserving biodiversity.
Impact of Climate Change on Ecosystem Biodiversity
Climate change significantly impacts ecosystem biodiversity, altering habitats, species distribution, and ecosystem services. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to shifts in species ranges and behaviors. These changes can result in mismatches in species interactions, such as pollination and predation, which are critical for ecosystem functioning and biodiversity maintenance.
- Alteration of Habitats: Climate change can transform habitats through increased temperatures, sea-level rise, and more frequent and intense extreme weather events. These transformations can make habitats inhospitable for existing species, forcing them to migrate, adapt, or face extinction.
- Species Distribution Shifts: As temperatures rise, many species move towards higher altitudes or latitudes in search of more suitable climate conditions. This shift can lead to the fragmentation of populations and reduce genetic diversity, making species more vulnerable to other threats.
- Changes in Ecosystem Services: Ecosystem services, such as carbon sequestration, water purification, and pollination, are directly affected by climate change. The disruption of these services can have far-reaching effects on human well-being and biodiversity conservation.
- Increased Vulnerability to Invasive Species: Climate change can provide new opportunities for invasive species to establish and outcompete native species, further threatening ecosystem biodiversity.
To mitigate the impact of climate change on ecosystem biodiversity, it is crucial to implement adaptive management strategies, promote habitat restoration, and strengthen conservation efforts. By addressing the root causes of climate change and enhancing the resilience of ecosystems, we can help protect and preserve biodiversity for future generations.

Case Studies of Ecosystem Biodiversity
Ecosystem biodiversity encompasses the variety of life in all its forms and interactions in natural habitats. The following case studies illustrate the significance of ecosystem biodiversity and the efforts to conserve it across different regions and ecosystems.
- The Amazon Rainforest, South America:
- The Amazon Rainforest is one of the most biodiverse areas on Earth, hosting millions of species. Conservation efforts focus on protecting habitats from deforestation and climate change impacts. Sustainable practices and indigenous community involvement are key to preserving its biodiversity.
- The Great Barrier Reef, Australia:
- As the world"s largest coral reef system, the Great Barrier Reef supports a vast array of marine life. Threats include coral bleaching caused by global warming and water pollution. Conservation initiatives aim to reduce carbon emissions and improve water quality to safeguard its diverse marine species.
- Serengeti National Park, Tanzania:
- Renowned for its large mammal populations and the annual wildebeest migration, Serengeti"s ecosystem is a focus of ecological studies and conservation efforts. Protecting the area from poaching and encroachment is vital for maintaining its biodiversity and ecological processes.
- The Galápagos Islands, Ecuador:
- These islands are famous for their unique species and the role they played in Charles Darwin"s theory of evolution. Conservation strategies include strict regulations on tourism and invasive species management to protect its endemic species.
- The Sundarbans, Bangladesh and India:
- The largest mangrove forest in the world, the Sundarbans, is critical for protecting against climate change impacts like cyclones and sea-level rise. Efforts to conserve its rich biodiversity include tiger protection initiatives and habitat restoration projects.
These case studies demonstrate the global importance of ecosystem biodiversity and the need for concerted conservation efforts. By learning from these examples, we can apply best practices to protect other vital ecosystems around the world.
Future Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Biodiversity
Preserving ecosystem biodiversity is essential for the health of the planet and the well-being of future generations. However, several challenges lie ahead that require global cooperation, innovative solutions, and sustained commitment. These challenges include:
- Climate Change:
- Climate change poses a significant threat to ecosystems worldwide, altering habitats and species distribution. Adapting to these changes while mitigating their effects is a critical challenge for biodiversity conservation.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation:
- Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation continue to reduce and fragment habitats, making it more difficult for species to survive and thrive. Efforts to preserve and restore habitats are essential for maintaining biodiversity.
- Invasive Species:
- The spread of invasive species disrupts local ecosystems, outcompeting, predating, or bringing diseases to native species. Managing these invasions requires vigilant monitoring and control strategies.
- Pollution:
- Pollution from plastic, chemicals, and other waste products affects land, air, and water ecosystems. Reducing pollution and its impact on biodiversity is a pressing challenge.
- Overexploitation:
- The unsustainable harvest of resources, including fishing, hunting, and logging, threatens species with extinction. Sustainable management practices are crucial to balance human needs with ecological preservation.
- Policy and Legislation:
- Developing and enforcing laws that protect ecosystems and biodiversity is challenging, especially when economic interests conflict with conservation goals. Global and local policies must align to effectively address biodiversity loss.
- Public Awareness and Engagement:
- Increasing public awareness and participation in biodiversity conservation efforts is essential. Education and community involvement can foster a culture of conservation and stewardship.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach that integrates science, policy, education, and community action. By working together, we can overcome obstacles and ensure a biodiverse and sustainable future for all living beings.
READ MORE:
How Individuals Can Contribute to Biodiversity Conservation
Every individual has the power to make a positive impact on biodiversity conservation. Through simple, everyday actions, we can help protect and preserve the variety of life on our planet. Here are some ways individuals can contribute:
- Support Conservation Organizations:
- Donate to or volunteer with organizations dedicated to conserving biodiversity. Your time, skills, or financial support can make a significant difference in conservation efforts.
- Practice Sustainable Living:
- Reduce, reuse, and recycle to minimize waste and decrease your carbon footprint. Choose sustainable products and reduce your consumption of resources like water and energy.
- Create Wildlife-Friendly Spaces:
- Whether you have a garden, balcony, or windowsill, you can create habitats for local wildlife. Plant native species to provide food and shelter for birds, insects, and other animals.
- Reduce Use of Chemicals:
- Minimize the use of pesticides and fertilizers that can harm wildlife. Opt for organic and natural alternatives to protect soil and water quality and support biodiversity.
- Advocate for Conservation:
- Use your voice to advocate for policies and actions that protect biodiversity. Engage with your community and elected officials to support conservation initiatives.
- Educate Yourself and Others:
- Learn about local and global biodiversity issues and share your knowledge with friends, family, and your community. Awareness is the first step towards change.
- Participate in Citizen Science Projects:
- Get involved in biodiversity monitoring and research projects. Your observations can help scientists track changes in species distribution and health, informing conservation strategies.
- Choose Sustainable Foods:
- Support sustainable agriculture by choosing local, organic, and fair-trade food products. Reducing meat consumption can also lessen the pressure on biodiversity.
- Responsible Recreation:
- When enjoying outdoor activities, stay on marked trails, respect wildlife, and follow leave-no-trace principles to minimize your impact on natural habitats.
By integrating these actions into our daily lives, we can all play a part in conserving biodiversity and ensuring a healthy planet for future generations.
Exploring ecosystem biodiversity reveals the intricate web of life that sustains our planet. Understanding its importance, challenges, and how we can contribute empowers us to protect this vital treasure for future generations.