Topic another word for ecosystem: Discover the richness of language surrounding our environment by exploring another word for ecosystem, broadening your understanding of the natural world.
Table of Content
- What are the synonyms for the term ecosystem?
- Synonyms for Ecosystem
- Understanding Ecosystems: Broader Definitions
- Environmental Contexts: Where Ecosystem Synonyms Are Used
- Biomes, Biospheres, and Bionetworks: Exploring Variations
- Ecology and Its Components: A Detailed Examination
- The Significance of Habitat Terminology in Scientific Studies
- YOUTUBE: Learn the word ECOSYSTEM
- Conservation Efforts and Ecosystem Management: A Lexical Perspective
- Nature and Natural Systems: Synonymous Terms and Their Importance
- Flora and Fauna: The Living Organisms of Ecosystems
- Climate Impact on Ecosystem Terminology: An Overview
What are the synonyms for the term ecosystem?
The synonyms for the term \"ecosystem\" are:
- biosphere
- environment
- habitat
- ecology
- environs
- flora and fauna
- ecological community
- ecosphere
- biota
- grassland
READ MORE:
Synonyms for Ecosystem
Understanding the variety of terms that mirror the concept of an ecosystem can enrich our dialogue about the natural world. Below are synonyms that capture the essence of what an ecosystem represents:
- Biome - A large community of plants and animals that occupies a major habitat.
- Biosphere - The global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships.
- Environment - The surroundings or conditions in which a person, animal, or plant lives or operates.
- Habitat - The natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
- Ecotone - A transition area between two biomes, where two communities meet and integrate.
- Biocommunity - A community of living organisms interacting with each other and their environment.
- Natural System - A system that exists in nature, which includes living organisms and the physical environment.
- Life System - A term used to describe the complex web of interactions among living organisms and their environment.
Each term offers a unique perspective on the interconnectivity and complexity of life on Earth, highlighting different aspects of ecological study and environmental conservation.

Understanding Ecosystems: Broader Definitions
Ecosystems are complex and dynamic environments where living organisms interact with each other and their physical surroundings. To fully appreciate the breadth of this concept, it"s essential to consider broader definitions that encompass various dimensions of ecological study:
- Ecological System: A broader term that emphasizes the interconnectedness of organisms and their physical environment, focusing on cycles of matter and energy flows.
- Biological Community: Highlights the focus on the diversity of species living together in a specific area and their interdependent relationships.
- Natural Environment: Encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally, stressing the holistic nature of ecosystems.
- Ecological Balance: Refers to the equilibrium between, and harmonious coexistence of, all living and non-living elements of an ecosystem.
- Conservation Biology: An aspect of broader ecosystem understanding that focuses on the preservation of biodiversity and natural resources.
- Sustainability: Looks at ecosystems from the perspective of maintaining ecological processes in a way that supports both current and future human needs and biodiversity.
These broader definitions underscore the importance of ecosystems not just as biological entities, but as fundamental components of our planet"s health, sustainability, and resilience. Understanding these concepts encourages a more comprehensive approach to environmental stewardship and conservation efforts.
Environmental Contexts: Where Ecosystem Synonyms Are Used
The terminology surrounding ecosystems is diverse and finds application across various environmental contexts. Understanding where and how these synonyms are used can enhance our comprehension of ecological concepts and their practical implications:
- Conservation Projects: Terms like "biosphere" and "biocommunity" are often used to emphasize the holistic approach needed for effective conservation efforts.
- Environmental Education: "Natural system" and "life system" are terms introduced to students to broaden their understanding of the interdependencies within nature.
- Urban Planning: "Green infrastructure" and "urban ecosystem" are applied to describe the integration of natural elements within urban environments.
- Climate Change Research: "Global ecosystem" or "biosphere" are used to discuss the earth"s ecological system"s responses to climate change.
- Agriculture and Forestry: "Agroecosystem" and "forest ecosystem" focus on the interaction between humans and the environment in the cultivation of crops and forest management.
- Wildlife Management: "Habitat" and "wildlife ecosystem" are key terms in strategies aimed at preserving animal populations and their natural habitats.
- Ecotourism: The concept of "ecotone," highlighting areas of transition between two biomes, is significant in promoting the conservation of unique natural environments through tourism.
These contexts reflect the adaptability and relevance of ecosystem-related terminology in addressing environmental challenges, promoting sustainability, and enhancing our engagement with the natural world.

Biomes, Biospheres, and Bionetworks: Exploring Variations
The terms biomes, biospheres, and bionetworks represent different aspects of ecological systems, each highlighting a unique scale and complexity of interactions within the natural world. By exploring these variations, we gain insights into the diversity of life and ecological processes:
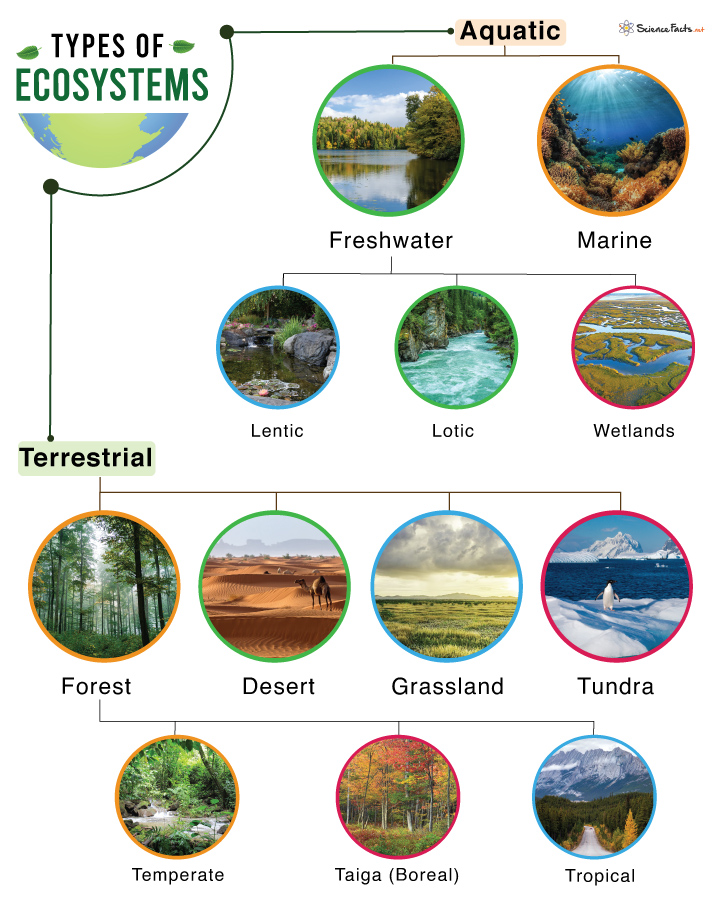
- Biomes: Large community units, such as forests, deserts, and grasslands, characterized by distinct climatic conditions and life forms. Biomes demonstrate the adaptability of ecosystems to various environmental conditions.
- Biospheres: Encompasses all ecosystems on Earth, representing the global sum of all living beings and their relationships with the physical earth. The biosphere is a testament to the interconnectedness of life across the planet.
- Bionetworks: Focuses on the intricate networks of interactions among organisms within an ecosystem. This term highlights the complexity of ecological relationships and the flow of energy and nutrients.
Understanding these concepts enriches our appreciation for the vastness and complexity of life on Earth and emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts to maintain the balance within these systems.
Ecology and Its Components: A Detailed Examination
Ecology, the scientific study of interactions among organisms and their environment, is a broad field that encompasses numerous components. Understanding these elements provides insight into the complexity and interdependence of life processes. Here’s a detailed examination of key components within ecology:
- Organisms: The individual life forms that are the basic units of ecology. Their interactions and survival strategies are fundamental to ecological studies.
- Populations: Groups of individuals belonging to the same species that live in a specific area. Population dynamics, including growth, density, and patterns of reproduction, are crucial for understanding ecological balance.
- Communities: All the different populations that live together in a defined area. Community ecology looks at how species interactions, such as predation and competition, affect the structure and diversity of communities.
- Ecosystems: Systems that include all the organisms in an area along with the physical environment, operating as a unit. Ecosystem studies focus on energy flow and nutrient cycling.
- Biomes: Large-scale ecological zones that classify regions based on climate, flora, and fauna. Biomes are essential for understanding global ecological patterns.
- Biosphere: The global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships. The biosphere is the sum of all ecosystems, highlighting the global interconnectivity of life and its environments.
This examination reveals the depth and breadth of ecology, showcasing the intricate web of life and the importance of each component in maintaining ecological equilibrium.

The Significance of Habitat Terminology in Scientific Studies
The precise use of habitat terminology is crucial in scientific studies for accurate communication, research, and conservation efforts. Understanding the distinctions and applications of various habitat-related terms allows for a more nuanced approach to ecological and environmental studies:
- Habitat: The natural environment in which a species or group of species lives and grows. It includes both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors.
- Niche: Describes the role or function of an organism or species within an ecosystem, including its interactions with other species and its contributions to energy flow and nutrient cycling.
- Microhabitat: A smaller, specific area within a habitat that provides unique conditions for certain species.
- Ecotone: A transitional zone between two distinct ecosystems or habitats, which often supports species from both areas as well as unique biodiversity.
- Biotope: A term used to describe a region with uniform environmental conditions and specific communities of plants and animals.
These terms are integral to ecological research, guiding the study of species distribution, behavior, and the effects of human impact on natural environments. The significance of habitat terminology extends beyond academic discourse, influencing conservation policies and practices aimed at preserving biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Learn the word ECOSYSTEM
Diversity: \"Explore the beauty and strength of diversity in our latest video, showcasing the vibrant tapestry of cultures, backgrounds, and perspectives that make our world truly unique and enriching. Join us on a journey of celebration and unity!\" Explanation: \"Curious minds, this is for you! Dive into our engaging video providing clear and insightful explanations on a fascinating topic. Let us unlock the secrets and complexities in a way that is easy to understand and truly captivating.\"
Unraveling the Ecosystem Definition Meaning Pronunciation and Examples
Explore the meaning, pronunciation, and usage of the word \'Ecosystem\' in English. Uncover its definition with clear examples in ...
Conservation Efforts and Ecosystem Management: A Lexical Perspective
The language we use to describe conservation efforts and ecosystem management plays a vital role in shaping public understanding and policy direction. By examining key terms and concepts, we can better appreciate the complexities and strategies involved in preserving our natural world:
- Sustainable Development: Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, emphasizing the balance between economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The practice of protecting and preserving the diversity of species, ecosystems, and genetic diversity within an area. It"s crucial for maintaining ecosystem services and resilience.
- Restoration Ecology: The scientific study and practice of renewing and restoring degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems and habitats in the environment by active human intervention and management.
- Ecosystem Services: The benefits that humans freely gain from the natural environment and from properly-functioning ecosystems, such as clean water, pollination, and disease control.
- Protected Areas: Regions of land or sea dedicated to the protection and maintenance of biological diversity, natural resources, and cultural values, managed through legal or other effective means.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Efforts to reduce or prevent the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, aiming to limit the magnitude or rate of long-term climate change.
Understanding and using these terms accurately can enhance the effectiveness of conservation efforts and ecosystem management, fostering a more informed and engaged public committed to preserving our planet"s natural heritage.

Nature and Natural Systems: Synonymous Terms and Their Importance
The terms "nature" and "natural systems" often overlap in meaning but bring unique perspectives on the ecological world. Their importance in scientific, educational, and conservation contexts cannot be overstated, as they encapsulate the essence of our planet"s living and non-living components:
- Nature: Often refers to the physical world collectively, including plants, animals, landscapes, and other features and products of the earth, as opposed to humans or human creations.
- Natural Systems: These are the complex networks of plants, animals, and microorganisms and their abiotic environment interacting as a functional unit. This term emphasizes the interconnectedness and interdependence of all elements within an ecosystem.
- Wilderness: Areas that remain largely unaffected by human activity, highlighting the importance of untouched natural environments in biodiversity conservation.
- Ecological Integrity: A measure of the completeness of an ecosystem and its capacity to maintain ecological processes and functions, supporting biodiversity and resilience.
- Earth Systems Science: An interdisciplinary study that looks at the Earth as a complex, dynamic system, integrating various fields such as geology, meteorology, hydrology, and biology to understand global environmental changes.
These terms underscore the intrinsic value of the natural world and the critical role it plays in sustaining life on Earth. Recognizing and respecting the complexity of nature and natural systems is fundamental to our survival and the health of the planet.
Flora and Fauna: The Living Organisms of Ecosystems
Flora and fauna represent the plant and animal life that populate the ecosystems of our planet. These living organisms play integral roles in their habitats, contributing to the biodiversity and balance within ecosystems. Understanding their diversity, interrelationships, and the challenges they face is crucial for conservation efforts:
- Flora: Refers to all the plant life present in a particular region or time, usually the naturally occurring (indigenous) plants. The study of flora includes understanding species diversity, distribution, and adaptations to their environment.
- Fauna: Encompasses all the animal life in any particular region or time. The term includes birds, mammals, insects, reptiles, amphibians, and other wildlife. Fauna studies focus on species behavior, habitat requirements, and ecological roles.
- Endemic Species: Species that are native to a specific location and are not naturally found elsewhere. Both flora and fauna can have endemic species, which are often of particular interest in conservation biology.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species that are introduced to a new environment where they become established and begin to displace native flora and fauna, often causing ecological harm.
- Conservation Status: Categories used to evaluate the risk of extinction faced by flora and fauna, guiding conservation actions to protect vulnerable and endangered species.
Protecting the flora and fauna of ecosystems is essential for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the health and sustainability of our environment. Their study not only reveals the beauty and complexity of nature but also highlights the importance of ecological stewardship.
READ MORE:
Climate Impact on Ecosystem Terminology: An Overview
Climate change has a profound effect on ecosystems, influencing both the physical environment and the terminology used to describe ecological processes and components. As the climate continues to change, understanding these impacts is crucial for adapting conservation strategies and ecological studies:
- Shifting Biomes: Climate change can lead to the relocation of biomes, as temperature and precipitation patterns change. This shift affects the distribution of flora and fauna, requiring updated terminology and classification systems.
- Altered Phenology: Changes in the timing of natural events, such as flowering, migrations, and breeding seasons, impact ecosystems. Phenological shifts necessitate new descriptors for these changing patterns.
- Increased Extremes: More frequent and severe weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and floods, challenge existing ecosystem resilience and terminology, pushing for terms that describe increased variability and disturbance.
- Acidification and Ocean Warming: Oceans are experiencing warming temperatures and increased acidification, affecting marine ecosystems. New terms like "ocean deoxygenation" are emerging to describe these phenomena.
- Carbon Sequestration: The process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide is a critical ecosystem service. Terminology related to carbon sinks and sequestration practices is evolving in response to climate change.
As the climate impacts ecosystems globally, the terminology used to discuss these changes must also evolve. This adaptation ensures accurate communication of research findings and the effective implementation of conservation measures.
Exploring alternative terms for "ecosystem" enriches our understanding of Earth"s intricate life networks, emphasizing the importance of conservation and our role in sustaining planetary health for future generations.