Topic sinkholes in virginia: Discover the enigmatic world of Virginia"s sinkholes, where geological wonders reveal a hidden landscape shaping both history and future.
Table of Content
- What are the main areas in Virginia affected by sinkholes?
- Impact of Sinkholes
- Geographical Distribution
- Conservation Efforts
- YOUTUBE: Sinkhole in Virginia Beach
- Introduction to Sinkholes in Virginia
- Geographical Areas Prone to Sinkholes
- Impact on Infrastructure and Environment
- Regulatory Framework and Agencies
- Prevention, Monitoring, and Management Strategies
- Historical Incidents and Case Studies
- Conservation Efforts and Public Safety Measures
- Advancements in Sinkhole Prediction and Research
- Community Engagement and Education
- Conclusion and Future Directions
What are the main areas in Virginia affected by sinkholes?
The main areas in Virginia affected by sinkholes are:
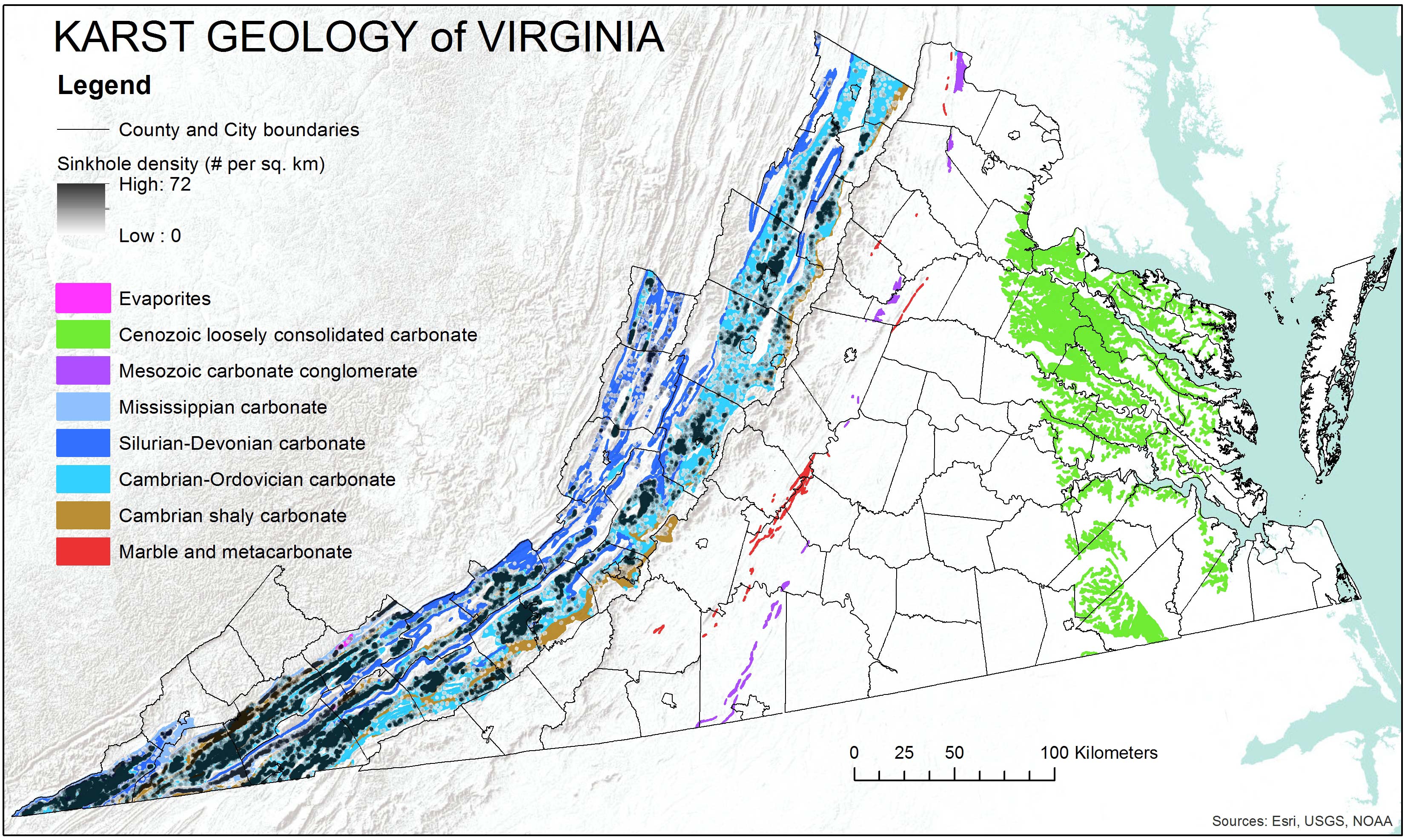
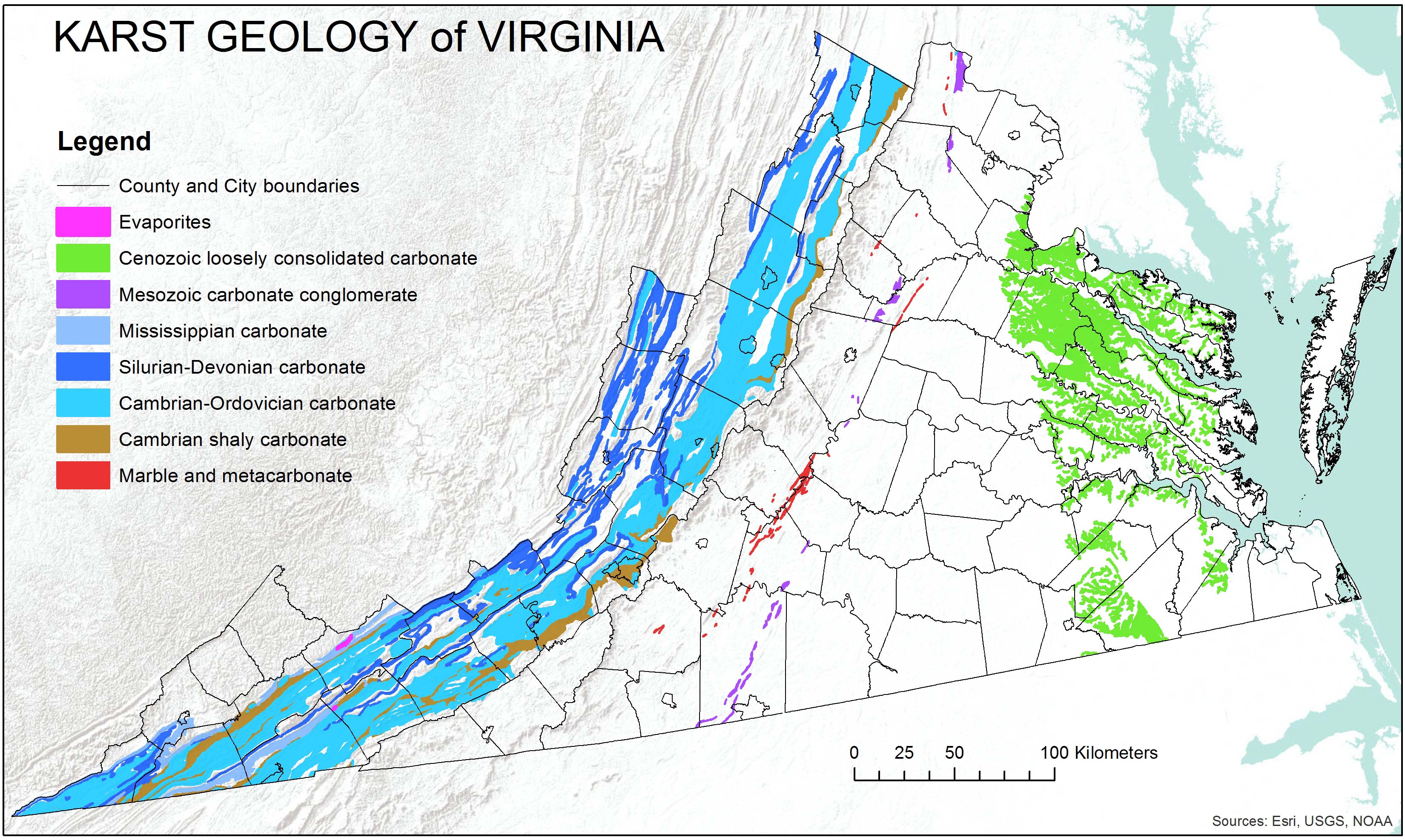
- Valley and Ridge Province
The Valley and Ridge Province in Virginia is the principal area affected by sinkholes. This region is characterized by extensive karst terrain underlain by limestone and dolomite, making it more prone to sinkhole formation.
READ MORE:
Impact of Sinkholes
Sinkholes can lead to various concerns, including groundwater contamination, structural damage, and human safety hazards. They act as direct channels for pollutants to enter groundwater systems, posing risks to both human and ecological health. The presence of sinkholes necessitates careful consideration in stormwater management, building construction, and land use planning to mitigate potential damages and safety risks.
Regulatory Framework
Virginia addresses sinkhole-related concerns through a comprehensive regulatory framework involving multiple agencies. The Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation, Virginia Cave Board, Department of Mines, Minerals and Energy, and Department of Environmental Quality are among the key entities that oversee aspects related to cave and karst management, geological mapping, water quality, and stormwater management.

Geographical Distribution
The Valley and Ridge Province is the principal area in Virginia affected by sinkholes, characterized by extensive karst terrain. However, sinkholes can also occur in the Coastal Plain Province and the Piedmont Province, where certain geological conditions exist. Notable incidents have demonstrated the potential for dramatic collapses, though such events are rare.
Prevention and Management
Monitoring and managing sinkholes involve recognizing early signs of formation, such as slumping fence posts, wilting vegetation, and structural cracks. Advanced techniques like LiDAR are being employed to map sinkholes and assess geological units prone to collapse, aiding in prevention and early intervention efforts.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts focus on protecting the unique ecosystems associated with karst terrains, including the rare and endemic species found within Virginia"s caves. Public education and responsible land use practices are crucial for preserving these delicate ecosystems and ensuring the quality of groundwater resources.
- Groundwater Quality: The sensitivity of karst aquifers to contamination is a significant environmental issue, with human activities posing the greatest threat.
- Subsidence and Ground Instability: Human-induced changes can trigger sudden collapses, posing risks to structures and requiring careful engineering and land use planning.
Understanding and responsibly managing sinkholes are essential for safeguarding Virginia"s natural and built environments, ensuring public safety, and preserving the state"s unique geological heritage.

Sinkhole in Virginia Beach
Sinkhole: Explore the mysterious world of sinkholes in this captivating video, uncovering the fascinating natural phenomena and the breathtaking beauty that lies beneath the surface. Watch to witness nature\'s incredible power unfold before your eyes.
Introduction to Sinkholes in Virginia
Sinkholes are a natural phenomenon in Virginia, particularly prevalent in areas with limestone and other soluble rocks. They form when mildly acidic groundwater dissolves these rocks, creating underground cavities. When the land surface collapses into these voids, sinkholes appear. This process is common in karst terrains, characterized by unique features like sinkholes, caves, and underground drainage systems. Virginia"s karst regions, notably the Valley and Ridge Physiographic Province, are rich in such geological formations.
Environmental concerns with sinkholes include groundwater contamination, as they provide direct channels for pollutants from the surface to the aquifer systems. This makes the karst aquifers in Virginia particularly vulnerable to contamination from various sources, including agricultural runoff, waste disposal, and urbanization. Additionally, sinkholes can cause structural damage and pose safety risks to humans and property. Effective management and awareness are crucial to mitigate these risks and protect the delicate karst ecosystems and groundwater quality in Virginia.
Proper management practices include monitoring and preventing the introduction of contaminants into sinkholes, establishing natural buffer zones around them, and educating the public about the importance of protecting these natural features and the broader karst landscape.
Geographical Areas Prone to Sinkholes
In Virginia, sinkholes are a natural and prevalent feature, especially in areas underlain by limestone and other soluble rocks. The formation and evolution of sinkholes in Virginia are influenced by both natural processes and human activities. Geographically, the Valley and Ridge Province is the principal area affected by sinkholes, characterized by extensive karst terrain underlain by limestone and dolomite. Additionally, narrow marble belts in the Piedmont Province and areas underlain by shelly beds in the Yorktown Formation of the Chesapeake Group in the Coastal Plain Province also exhibit sinkhole activity.
- The Valley and Ridge Province is known for its well-developed karst terrain, where sinkholes form chains known as solution valleys, and streams frequently disappear underground.
- In the Piedmont Province, marble belts contribute to the formation of sinkholes, albeit less frequently than in the Valley and Ridge Province.
- The Coastal Plain Province experiences sinkholes in areas with shelly beds, part of the Yorktown Formation.
Sinkholes in Virginia can cause significant damage to infrastructure, including buildings, highways, and water management systems. They also provide direct pathways for surface water to enter groundwater aquifers, increasing the potential for pollution. Understanding the geographical distribution of sinkholes is crucial for effective management and mitigation of their impact on the environment and human activities.
Impact on Infrastructure and Environment
Sinkholes in Virginia present significant challenges to both infrastructure and the environment, impacting communities and natural ecosystems in various ways. These geological phenomena can cause substantial damage to public and private properties, disrupt transportation networks, and pose risks to water quality and biodiversity.
- Infrastructure Damage: Sinkholes can lead to the collapse of roadways, damage to buildings and homes, and disruptions to underground utilities. The sudden appearance of sinkholes often requires emergency repairs and can lead to significant economic costs for maintenance and rehabilitation.
- Transportation Disruptions: Major roads and highways, particularly in karst regions, are susceptible to sinkhole formations, leading to closures, detours, and hazardous driving conditions. The Virginia Department of Transportation monitors and addresses these challenges to ensure public safety and minimize disruption.
- Water Contamination: Sinkholes provide direct pathways for surface runoff to enter groundwater systems, increasing the risk of contamination. This poses a threat to drinking water supplies and can affect water quality in surrounding areas.
- Environmental Impact: The formation of sinkholes can disrupt local ecosystems, damage habitats, and threaten the survival of species. Conservation efforts focus on protecting sensitive areas, particularly where rare or endangered species may be affected.
- Community and Economic Effects: Beyond the physical damage, sinkholes can affect property values, increase insurance premiums, and lead to costly legal challenges. Communities in prone areas require effective planning, education, and resources to mitigate these impacts.
Addressing the impacts of sinkholes in Virginia involves a multi-faceted approach, including geological surveys, land-use planning, public education, and infrastructure resilience. By understanding and anticipating the challenges posed by sinkholes, Virginia can better protect its communities, economy, and natural environments.
Regulatory Framework and Agencies
In Virginia, the management and oversight of sinkholes involve several regulatory frameworks and agencies. These entities work together to ensure public safety, environmental protection, and effective land use in areas prone to sinkholes. The following outlines the primary agencies and their roles in sinkhole management and regulation:
- Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation (DCR): DCR is responsible for overseeing karst landscapes in Virginia. This includes monitoring sinkhole activity, managing the impacts on water quality and natural habitats, and promoting conservation efforts in karst areas.
- Virginia Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ): DEQ plays a key role in regulating activities that may affect water quality, including those that could lead to sinkhole formation. This involves oversight of stormwater management, wastewater discharge, and pollution prevention measures.
- Virginia Department of Mines, Minerals, and Energy: This department provides geological expertise and mapping services that help identify areas susceptible to sinkholes. It also offers guidance on land use and construction practices in karst regions.
- Local County and City Governments: Local governments enforce zoning, building codes, and land-use planning measures that consider sinkhole risks. They may also have specific ordinances related to sinkhole management and mitigation.
- Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT): VDOT is involved in monitoring and repairing transportation infrastructure affected by sinkholes. This includes roads, bridges, and highways in sinkhole-prone areas.
Effective management of sinkholes in Virginia requires collaboration across these agencies and adherence to regulatory frameworks that protect both people and the environment. Through proactive planning, regulation, and education, Virginia aims to mitigate the impacts of sinkholes and ensure the safety and well-being of its residents.

Prevention, Monitoring, and Management Strategies
Effective management of sinkhole risks in Virginia involves a comprehensive approach that includes prevention, monitoring, and response strategies. These efforts aim to minimize the impact of sinkholes on communities, infrastructure, and the environment. The following are key components of a proactive sinkhole management strategy:
- Geological Surveys and Mapping: Conducting detailed geological surveys to identify areas with karst features and potential sinkhole risks. Mapping these areas helps in planning and risk assessment for land use and development.
- Land Use Planning: Implementing zoning regulations and building codes that consider the risk of sinkholes. This may include restricting certain types of development in high-risk areas or requiring specific construction practices to mitigate risk.
- Monitoring and Early Warning Systems: Developing and utilizing technology to monitor ground movement and water levels in sinkhole-prone areas. Early warning systems can alert communities and authorities to potential sinkhole formation, allowing for timely evacuation and response.
- Public Education and Awareness: Informing the public about sinkhole risks and what actions to take in the event of a sinkhole. Education campaigns can help prevent activities that exacerbate sinkhole formation, such as improper water management or construction practices.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response: Establishing clear protocols for responding to sinkhole incidents, including evacuation plans, emergency repairs, and public safety measures. Coordination among local, state, and federal agencies is crucial for an effective response.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Designing and constructing infrastructure with sinkhole risks in mind. This includes engineering buildings, roads, and utilities to withstand potential ground subsidence and incorporating features that can prevent or limit damage from sinkholes.
- Research and Innovation: Supporting ongoing research into sinkhole prediction, prevention, and remediation techniques. Innovations in geological science and engineering can improve the ability to manage sinkhole risks effectively.
Together, these strategies form a multifaceted approach to managing sinkhole risks in Virginia. Through prevention, monitoring, and management, it is possible to reduce the impacts of sinkholes and protect both people and the environment.
Historical Incidents and Case Studies
The history of sinkholes in Virginia is marked by several notable incidents that have had significant impacts on communities, infrastructure, and the environment. These historical events serve as important case studies for understanding sinkhole dynamics and improving future sinkhole management and response strategies.
- Staunton Sinkhole Events: The city of Staunton has experienced multiple significant sinkhole events, including one that resulted in the loss of several homes and a firehouse due to a series of sinkholes opening up on Baldwin Street and Central Avenue. Another event led to the formation of a large chasm on Lewis Street, highlighting the unpredictable nature of sinkholes in urban areas.
- Interstate Highway Closures: Virginia"s transportation infrastructure has also been affected by sinkholes, with instances of sudden sinkhole formations leading to the closure of major highways. These incidents necessitate emergency responses and illustrate the challenges of managing sinkhole risks in areas with heavy traffic.
- Environmental Impacts: Beyond structural damage, sinkholes in Virginia have also posed risks to the environment, including groundwater contamination and habitat disruption. Studying these incidents helps in developing strategies to mitigate environmental impacts.
- Community Responses and Adaptations: Historical sinkhole incidents have spurred communities and local governments to adapt and improve preparedness and response strategies. Case studies from affected areas provide valuable lessons in community resilience and the importance of public education on sinkhole risks.
These historical incidents and case studies underscore the importance of ongoing research, monitoring, and preparedness to mitigate the risks and impacts of sinkholes in Virginia. By learning from the past, Virginia can better safeguard its communities, infrastructure, and natural landscapes against future sinkhole events.
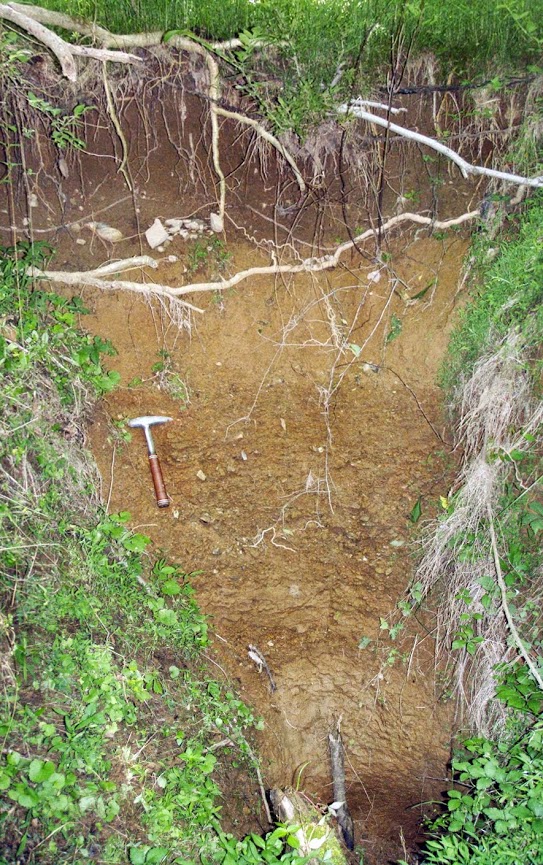

Conservation Efforts and Public Safety Measures
Addressing the challenges posed by sinkholes in Virginia involves a combination of conservation efforts aimed at protecting the environment and public safety measures designed to safeguard communities. These initiatives are vital for maintaining the integrity of natural landscapes and ensuring the well-being of Virginia"s residents.
- Protected Natural Areas: Designating karst regions and sinkhole-prone areas as protected natural habitats to conserve biodiversity and prevent activities that could trigger sinkhole formation. Conservation programs focus on maintaining the ecological balance and protecting water quality in these sensitive areas.
- Public Education Programs: Implementing educational initiatives to raise awareness among residents and property owners about the risks associated with sinkholes, preventive measures, and what to do in the event of a sinkhole. These programs aim to empower communities with knowledge and resources for sinkhole preparedness and response.
- Building and Zoning Regulations: Enforcing stringent building codes and zoning regulations in areas known to be at risk for sinkholes. These measures ensure that construction practices are adapted to mitigate risks, including proper land use planning and engineering solutions that account for the unique geological features of karst landscapes.
- Monitoring and Early Warning Systems: Developing and implementing monitoring systems to detect early signs of sinkhole formation, such as ground subsidence or changes in groundwater levels. Early warning systems can alert authorities and the public to potential sinkhole threats, facilitating timely evacuation and response actions.
- Emergency Response Plans: Establishing comprehensive emergency response and evacuation plans tailored to sinkhole incidents. These plans involve coordination among local, state, and federal agencies to ensure rapid and effective response to protect public safety during sinkhole emergencies.
Through these conservation efforts and public safety measures, Virginia aims to manage the risks associated with sinkholes effectively. By prioritizing the health of its natural environments and the safety of its communities, Virginia continues to develop and refine strategies to address the complex challenges posed by sinkholes.
Advancements in Sinkhole Prediction and Research
Recent advancements in sinkhole prediction and research have significantly contributed to understanding and mitigating the risks associated with sinkholes in Virginia. These innovations offer new tools and methodologies for early detection, prevention, and management of sinkhole events.
- Geotechnical Investigation Techniques: The development of advanced geotechnical investigation methods, such as ground penetrating radar (GPR) and electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), allows for detailed subsurface mapping. These technologies can identify potential sinkhole-forming conditions before they manifest on the surface.
- LiDAR Mapping: Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology has been instrumental in identifying and mapping karst features across Virginia. LiDAR provides high-resolution topographical data, revealing subtle ground deformations indicative of sinkhole activity.
- Machine Learning Models: Researchers are now applying machine learning algorithms to analyze geological data, predict sinkhole formation, and assess risks. These models can process vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict sinkhole development with greater accuracy.
- Public Participation GIS: The use of Public Participation Geographic Information Systems (PPGIS) enables communities to contribute to sinkhole monitoring efforts. Citizens can report signs of potential sinkholes, providing valuable data that enhances prediction and response strategies.
- Interdisciplinary Studies: Collaborations between geologists, engineers, and environmental scientists have led to comprehensive studies on sinkhole formation mechanisms. This interdisciplinary approach improves understanding of how various factors, including human activities and climate change, influence sinkhole dynamics.
These advancements in sinkhole prediction and research not only enhance our ability to address sinkhole-related challenges but also contribute to safer land-use practices and more resilient infrastructure in Virginia. Ongoing research and innovation continue to play a critical role in minimizing the impact of sinkholes on communities and the environment.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(779x730:781x732)/virginia-sinkhole-2-c86b18e164c0463084104aa375230197.jpg)
Community Engagement and Education
Community engagement and education are pivotal in managing sinkhole risks in Virginia. By fostering a collaborative approach, stakeholders can work together to mitigate the impact of sinkholes on society and the environment. The following initiatives highlight the importance of community involvement and public awareness:
- Sinkhole Awareness Programs: Implementing awareness programs to educate the public about the causes and dangers of sinkholes. These programs aim to inform residents about how to identify potential sinkhole activity and the appropriate steps to take if a sinkhole is suspected.
- Public Workshops and Seminars: Hosting workshops and seminars led by experts in geology, civil engineering, and emergency management. These events provide forums for residents to learn about sinkhole prevention, land-use practices, and emergency preparedness.
- School Curriculum Integration: Integrating sinkhole education into school curriculums, particularly in regions prone to sinkholes. Educating students about the geological processes that cause sinkholes and the importance of conservation efforts can foster a culture of awareness from an early age.
- Community-Based Monitoring Programs: Encouraging community participation in monitoring and reporting sinkhole activity. These programs leverage local knowledge and observations, which are invaluable for early detection and response efforts.
- Collaboration with Local Governments and Agencies: Strengthening partnerships between communities, local governments, and state agencies to develop cohesive strategies for sinkhole risk management. Collaboration ensures that community needs are addressed in policy-making and emergency response planning.
Through these community engagement and education efforts, Virginia can enhance its resilience to sinkhole challenges. Active participation and informed decision-making empower communities, reduce vulnerabilities, and contribute to the overall safety and well-being of the state"s residents.
READ MORE:
Conclusion and Future Directions
Virginia"s approach to managing sinkholes has evolved significantly over the years, thanks to advancements in geological research, technology, and community engagement. The state"s efforts to understand and mitigate the impacts of sinkholes have led to the development of comprehensive strategies encompassing prevention, monitoring, and management. As Virginia looks to the future, several key directions will be crucial in continuing to protect its landscapes, communities, and infrastructure from sinkhole-related challenges:
- Enhanced Prediction and Monitoring Technologies: Ongoing investment in cutting-edge technologies, such as remote sensing and machine learning models, will improve the accuracy of sinkhole predictions and the effectiveness of monitoring programs.
- Integrated Land Use Planning: Developing and enforcing land-use practices that consider sinkhole risks will be essential in minimizing future impacts. This includes stricter building codes in sinkhole-prone areas and sustainable development practices that reduce the likelihood of sinkhole formation.
- Community-Centric Approaches: Engaging communities through education and participation remains a cornerstone of effective sinkhole management. Future efforts will likely focus on expanding public awareness programs and enhancing community resilience through preparedness training.
- Interdisciplinary Research Collaboration: Collaborative research across disciplines will continue to shed light on the complex processes that lead to sinkhole formation. Partnerships between geologists, engineers, environmental scientists, and policymakers will drive innovations in sinkhole management.
- Policy and Regulatory Developments: Adapting policies and regulations to reflect the latest scientific understanding and technological advancements will ensure that sinkhole management strategies remain effective and responsive to emerging challenges.
In conclusion, Virginia"s journey toward effective sinkhole management is ongoing. By building on current knowledge, embracing technological advancements, and fostering community resilience, Virginia can continue to mitigate the risks posed by sinkholes and safeguard the well-being of its residents and the natural beauty of its landscapes.
Discover the intricate world of sinkholes in Virginia, where cutting-edge research and community engagement pave the way for safer and more resilient futures. Join us in exploring the dynamic strategies that safeguard the beauty and well-being of our landscapes.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__mnn__images__2019__03__CenoteIkKilStairwellSwimmingHole-d99e791c5c2242f680c5b143c04fd056.jpg)