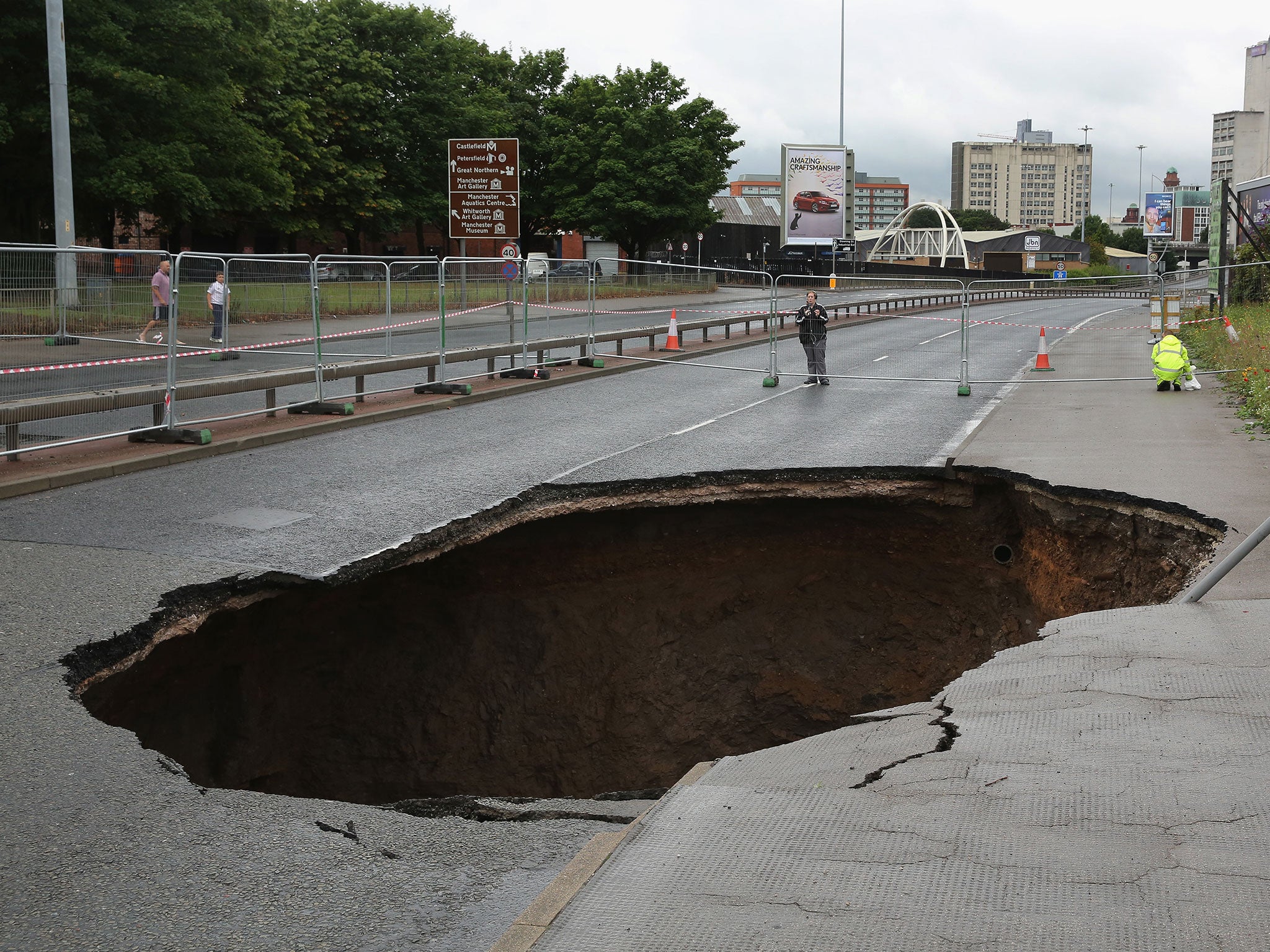
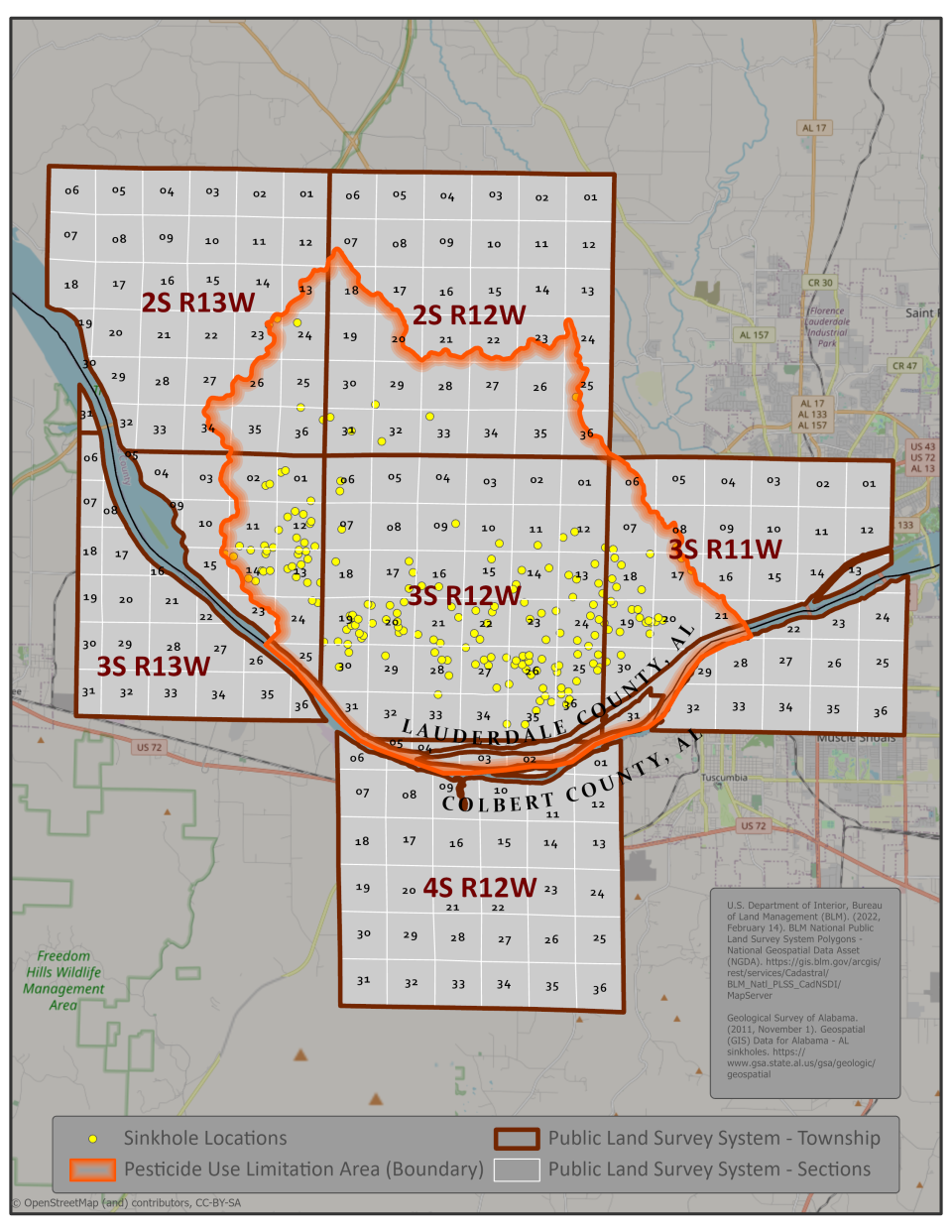
Topic sinkhole alabama: Discover the mesmerizing world of Alabama"s sinkholes, where nature"s hidden marvels reveal the fascinating interplay between geology and the environment.
Table of Content
- What town in Alabama is known for having a large pit called Neversink Cave Preserve or Neversink Pit?
- The Golly Hole: A Monumental Sinkhole
- Understanding Sinkholes
- Preservation and Safety Measures
- YOUTUBE: What\'s causing sinkholes in central Alabama?
- Introduction to Alabama Sinkholes
- Historical Sinkhole Events in Alabama
- Geological Causes of Sinkholes
- Impact of Sinkholes on Communities
- Notable Sinkholes in Alabama
- Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
- Future Research and Monitoring Efforts
- Resources and Support for Affected Residents
What town in Alabama is known for having a large pit called Neversink Cave Preserve or Neversink Pit?
The town in Alabama known for having a large pit called Neversink Cave Preserve or Neversink Pit is Fackler.
Neversink Cave Preserve, also known as Neversink Pit, is located in Fackler, Alabama.
READ MORE:
The Golly Hole: A Monumental Sinkhole
In December 1972, Alabama witnessed the formation of its largest sinkhole near Calera in Shelby County, famously known as the "Golly Hole." This colossal sinkhole, discovered by local hunters, measures approximately 325 feet in length and 300 feet in width, akin to a football field, and presents a breathtaking spectacle of nature"s might.
Notable Sinkhole Incidents
- In 1974, a 26-ton well-drilling rig was completely engulfed by a sinkhole at Glovers Point on Logan Martin Lake, showcasing the unpredictable power of these natural phenomena.
- Residents of Talladega County, including Sylacauga, have reported an uptick in sinkhole appearances in recent months, signaling an increased geological activity in the area.

Understanding Sinkholes
Sinkholes are intriguing geological features with no natural external surface drainage, meaning water that enters a sinkhole drains into the subsurface. They can vary greatly in size and depth, forming spectacular landscapes and, at times, posing challenges to human habitation and infrastructure.
Geological Composition and Formation
Alabama"s landscape, rich in karst terrain characterized by soluble rocks like limestone and dolomite, is particularly susceptible to sinkhole formation. These underlying rocks dissolve over time due to natural water flow, leading to the eventual collapse of the surface layer and the creation of sinkholes.
Preservation and Safety Measures
The study and monitoring of sinkholes are crucial for understanding their formation and mitigating potential hazards. Alabama"s geological community, including the Alabama Geological Survey, plays a vital role in researching and educating the public about these natural wonders and their impact on the environment and society.
Contact and Support
For more information on sinkholes and geological formations in Alabama, or to report a sinkhole, residents are encouraged to reach out to the Alabama Geological Survey. Their expertise and resources are invaluable in ensuring the safety and preservation of Alabama"s natural heritage.

What\'s causing sinkholes in central Alabama?
Geological: Embark on an exciting journey through the fascinating world of geological wonders in this video. Explore stunning landscapes, learn about the Earth\'s history, and marvel at the beauty of nature\'s incredible creations. Disaster: Gain valuable insights on disaster preparedness and mitigation in this informative video. Discover how communities come together in the face of adversity, learn about resilience, and find hope in the midst of challenges.
Lawrence County Alabama Sinkhole
Man describes a sinkhole in Lawrence County, Alabama.
Introduction to Alabama Sinkholes
Alabama"s landscape is punctuated by the enigmatic presence of sinkholes, natural geological formations that have intrigued and impacted the region for decades. The largest recorded sinkhole in Alabama, known as the "Golly Hole," was discovered near Calera in Shelby County in December 1972, measuring an astonishing 325 feet in length and 300 feet in width.
Sinkholes in Alabama are formed due to the state"s rich karst terrain, where soluble rocks like limestone and dolomite underlie the surface. The dissolution of these rocks by groundwater creates voids, leading to the eventual collapse of the surface layer and the formation of a sinkhole.
- Sinkholes vary in size and depth, creating unique landscapes and, at times, posing challenges to human habitation and infrastructure.
- The unpredictable nature of sinkholes has led to several notable incidents, including the swallowing of a 26-ton well-drilling rig at Glovers Point on Logan Martin Lake in 1974.
- Recent reports from residents in Talladega County, including Sylacauga, indicate an increase in sinkhole appearances, highlighting the ongoing geological activity in the region.
The study and monitoring of sinkholes are crucial for understanding their formation and mitigating potential hazards. Alabama"s geological community, including the Alabama Geological Survey, plays a vital role in researching and educating the public about these natural phenomena and their impact on the environment and society.
Historical Sinkhole Events in Alabama
Alabama has a rich history of notable sinkhole events that highlight the state"s dynamic geological landscape. One of the most significant occurrences was the formation of the "Golly Hole," the largest recorded sinkhole in Alabama, near Calera in Shelby County in December 1972. It was discovered by local hunters after a resident heard what sounded like trees crashing during the night, measuring approximately 325 feet in length and 300 feet in width, akin to a football field.
- In 1974, a remarkable incident occurred when a 26-ton well-drilling rig, valued at $120,000, was swallowed by a sinkhole at Glovers Point on Logan Martin Lake, owned by Fair Park Well Drilling Co. of Talladega.
- Recent times have seen an uptick in sinkhole appearances in Talladega County, including Sylacauga, with the Alabama Geological Survey confirming an increase in reports, underscoring the ongoing geological activity in the area.
These events serve as a reminder of the ever-present forces of nature at work beneath Alabama"s surface, shaping the landscape in unexpected and sometimes dramatic ways.
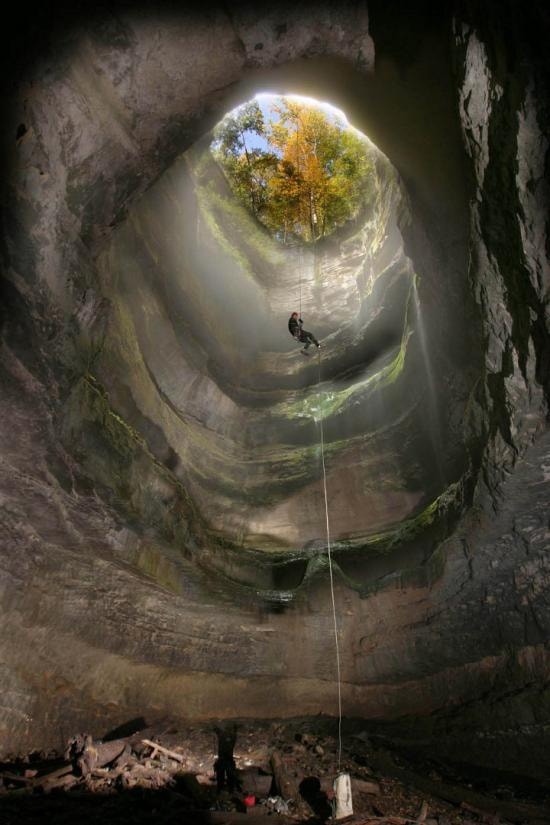

Geological Causes of Sinkholes
Sinkholes in Alabama are primarily the result of the state"s unique geological composition. The landscape is characterized by karst terrain, underlain by soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and chalk, which are easily dissolved by groundwater. This dissolution process creates underground cavities and voids.
- When the structural integrity of these cavities is compromised, the overlying surface layer can no longer support its weight, leading to sudden collapses that form sinkholes.
- Rainwater, which is slightly acidic due to dissolved carbon dioxide, accelerates the dissolution of carbonate rocks, further contributing to the formation of these geological features.
- The variability in the size and depth of sinkholes is influenced by factors such as the thickness of the soluble rock layer, the rate of dissolution, and the stability of the overlying surface materials.
This natural process, coupled with human activities such as groundwater withdrawal and construction, can exacerbate the conditions that lead to sinkhole formation, making certain areas more prone to these events.
Impact of Sinkholes on Communities
The occurrence of sinkholes in Alabama has significant impacts on local communities, affecting both the natural landscape and human infrastructure. These geological events can lead to disruptions in transportation, property damage, and even pose safety risks to residents.
- Sinkholes can cause road closures and detours, as seen in Shelby County where a massive sinkhole led to the shutdown of a major highway, disrupting daily commutes and local traffic flow.
- Residential areas are not immune to the effects of sinkholes, with properties in Talladega County and Sylacauga experiencing an increase in sinkhole formations, raising concerns among homeowners about property values and safety.
- The local economy can also be impacted by sinkholes, as they may affect businesses, tourism, and the overall attractiveness of the area for potential new residents and investors.
Despite the challenges posed by sinkholes, communities in Alabama continue to adapt and respond to these natural occurrences, working closely with geological experts and local authorities to mitigate risks and ensure public safety.

Notable Sinkholes in Alabama
Alabama"s landscape is peppered with remarkable sinkholes, each with its own story and impact on the local environment and communities. Among the most significant is the "Golly Hole," the largest recorded sinkhole in the state, which appeared suddenly in 1972 near Calera in Shelby County.
- The "Golly Hole" measures approximately 325 feet in length and 300 feet in width, with an estimated depth of 120 feet, making it a geological marvel and a subject of study and fascination.
- In 1974, another significant event occurred when a 26-ton well-drilling rig was engulfed by a sinkhole at Glovers Point on Logan Martin Lake, highlighting the unpredictable nature of these phenomena.
- Neversink Pit, known for its stunning fern-covered ledges and majestic waterfalls, is not only Alabama"s but also one of the world"s most photographed sinkholes, showcasing the beauty that can be found within these natural formations.
These notable sinkholes exemplify the diverse and dynamic geological landscape of Alabama, offering valuable insights into the natural processes that shape our world.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the challenges posed by sinkholes in Alabama involves a combination of prevention and mitigation strategies, aimed at reducing their impact on communities and infrastructure. Understanding the underlying geological conditions and human activities that contribute to sinkhole formation is key to developing effective solutions.
- Geological Surveys and Mapping: Regular geological surveys, including detailed mapping of karst features, help identify areas at higher risk of sinkhole formation, guiding land use and development decisions.
- Water Management: Proper management of groundwater extraction and surface water drainage can reduce the risk of sinkhole development by minimizing the alteration of natural water flow paths that can lead to the dissolution of soluble rocks.
- Building and Construction Guidelines: Implementing building codes and construction guidelines that take into account the local geological conditions can help minimize damage and ensure the stability of structures in sinkhole-prone areas.
- Public Awareness and Education: Educating the public about the causes and signs of sinkholes can lead to earlier detection and reporting, reducing potential hazards and allowing for timely intervention.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response Plans: Developing and maintaining emergency response plans for sinkhole events can enhance community resilience and ensure a coordinated response to mitigate risks and manage impacts.
Through these strategies, Alabama aims to safeguard its communities and preserve the state"s natural beauty and geological heritage.

Future Research and Monitoring Efforts
Alabama is committed to advancing the understanding and management of sinkholes through ongoing research and monitoring efforts. These initiatives are crucial for developing more effective strategies to predict, prevent, and mitigate the impacts of sinkholes on the environment and communities.
- Enhanced Geological Mapping: Future efforts will focus on the use of advanced technology, such as LiDAR and remote sensing, to improve the accuracy of geological maps, allowing for the identification of potential sinkhole-prone areas with greater precision.
- Groundwater Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of groundwater levels and quality will help in understanding the dynamics of aquifer systems and their relationship with sinkhole formation, enabling more proactive management of water resources.
- Community Engagement and Education: Increasing public awareness and involvement in sinkhole research and monitoring can lead to earlier detection and reporting, fostering a collaborative approach to sinkhole management.
- Collaboration with Academic Institutions: Partnerships with universities and research institutions will be strengthened to facilitate innovative studies on karst geology, sinkhole formation processes, and mitigation technologies.
- Development of Predictive Models: Investment in the development of predictive models using historical data and current observations will aid in forecasting sinkhole occurrences, enhancing preparedness and response strategies.
Through these concerted efforts, Alabama aims to enhance its resilience to sinkhole events, protecting both its natural landscapes and the communities that call it home.
READ MORE:
Resources and Support for Affected Residents
Residents affected by sinkholes in Alabama have access to a variety of resources and support systems designed to assist in dealing with the impacts of these geological events. From informational guidance to practical assistance, these resources aim to provide comprehensive support to those impacted.
- The Alabama Geological Survey (AGS) offers extensive information on sinkholes, including their causes, prevention, and mitigation. The AGS is a key resource for residents seeking to understand sinkhole risks and how to address them.
- Local government agencies often provide assistance with property assessments and advice on structural safety, helping homeowners navigate the challenges posed by sinkhole damage.
- Community support groups and online forums can offer valuable advice and emotional support from individuals who have experienced similar situations, fostering a sense of community and shared resilience.
- Educational programs and workshops, frequently conducted by geological experts and environmental organizations, aim to raise awareness about sinkholes and teach residents how to recognize early warning signs.
- Emergency response services are equipped to respond to sinkhole-related incidents, ensuring public safety and coordinating necessary interventions to mitigate immediate hazards.
By leveraging these resources, Alabama residents can better prepare for and respond to sinkhole occurrences, enhancing community safety and resilience against these natural phenomena.
Alabama"s journey with sinkholes unveils the intricate dance between nature and humanity, inviting us to explore, understand, and coexist with the geological wonders beneath our feet.