Topic how do humans impact aquatic ecosystems: Exploring how humans impact aquatic ecosystems reveals our profound influence and the potential for positive environmental stewardship.
Table of Content
- How do humans impact aquatic ecosystems?
- Conservation Efforts and Restoration Projects
- Reduction in Pollution through Policy and Innovation
- Community Engagement and Education on Aquatic Health
- Implementation of Sustainable Fishing Practices
- Advancements in Waste Management to Protect Waterways
- Climate Change Mitigation Strategies Affecting Oceans
- YOUTUBE: Human Impact on Aquatic Environments
- Technological Innovations for Monitoring Aquatic Ecosystems
- Protection of Endangered Marine Species and Habitats
- International Agreements and Policies for Ocean Conservation
- Public Awareness Campaigns and their Impact on Aquatic Life
How do humans impact aquatic ecosystems?
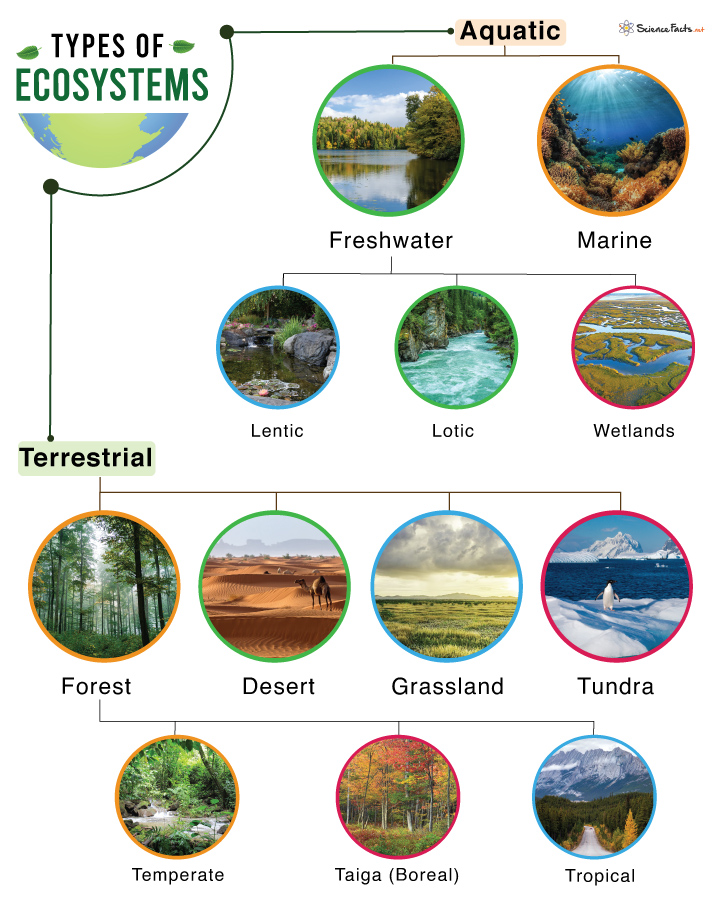
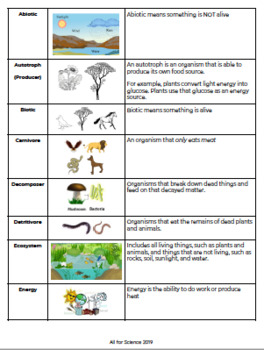
Humans have a significant impact on aquatic ecosystems through various activities and behaviors. These impacts can affect the overall health and balance of the ecosystem, as well as the species that depend on it for survival. Some key ways in which humans impact aquatic ecosystems include:
- Habitat Destruction: Human activities such as the construction of dams, dredging, and coastal development can lead to the destruction and alteration of aquatic habitats. This can disrupt the natural flow of water, destroy spawning grounds, and reduce the availability of food and shelter for aquatic organisms.
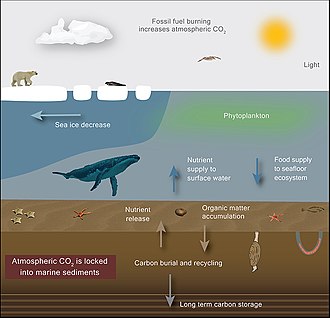
- Carbon Emissions: The release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases from human activities such as burning fossil fuels contributes to climate change. This can lead to rising sea levels, increased ocean acidification, and changes in temperature, which can negatively impact the survival and biodiversity of marine organisms.
- Chemical Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities often result in the release of pollutants into water bodies. Pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals can contaminate aquatic ecosystems, leading to reduced water quality, the disruption of ecosystems, and harm to aquatic organisms and their habitats.
- Oil Spills: Accidental oil spills from offshore drilling or transportation can have devastating effects on marine ecosystems. Oil spills can contaminate water, coat the surfaces of plants and animals, suffocate marine life, and disrupt the food chain.
- Noise Pollution: Underwater noise from human activities such as shipping, sonar systems, and oil exploration can stress or disorient marine mammals, affect their communication and feeding patterns, and lead to behavioral changes.
- Plastic Pollution: The improper disposal and excessive use of plastic products have led to widespread plastic pollution in marine environments. Marine animals can become entangled in plastic debris, mistake it for food, and suffer from ingestion or suffocation. This not only affects individual organisms but also disrupts the overall balance of the ecosystem.
It is crucial for humans to be aware of their impact on aquatic ecosystems and take actions to minimize negative consequences. Implementing sustainable practices, reducing the use of pollutants, properly managing waste, and supporting conservation efforts are some ways individuals and communities can contribute to the preservation and restoration of these vital ecosystems.
READ MORE:
Conservation Efforts and Restoration Projects
Conservation and restoration initiatives are crucial in mitigating human impacts on aquatic ecosystems. These efforts aim to preserve biodiversity, restore degraded habitats, and ensure sustainable use of aquatic resources.
- Wetland Restoration: Projects focus on reestablishing the natural hydrology and plant communities of wetlands, which are critical for water purification, flood control, and habitat provision.
- Coral Reef Rehabilitation: Techniques such as coral gardening and artificial reefs help in the recovery of these biodiverse ecosystems, essential for marine life and coastal protection.
- Removal of Invasive Species: Managing invasive species helps in restoring the balance of aquatic ecosystems, allowing native species to thrive.
- River and Stream Restoration: Efforts include removing barriers like dams, reinstating natural flow regimes, and enhancing riparian zones to improve water quality and habitat connectivity.
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): Establishing MPAs helps in conserving marine biodiversity by restricting activities that can harm marine environments, such as overfishing and resource exploitation.
- Community Engagement and Education: Involving local communities and educating the public on the importance of aquatic ecosystems can lead to more sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
These initiatives, supported by global cooperation and local action, highlight humanity"s capacity to positively influence aquatic ecosystems and ensure their health for future generations.

Reduction in Pollution through Policy and Innovation
Efforts to reduce pollution in aquatic ecosystems are anchored in innovative policies and technological advancements. These strategies aim to minimize adverse human impacts and foster sustainable interactions with water environments.
- Stricter Regulations: Implementing rigorous environmental policies and regulations helps control emissions and discharges from industries, agriculture, and urban areas into water bodies.
- Green Technology: Adoption of green technologies in waste treatment, energy production, and manufacturing processes reduces pollutants entering aquatic systems.
- Plastic Waste Management: Initiatives like plastic bans, recycling programs, and the development of biodegradable materials combat plastic pollution in oceans and rivers.
- Chemical Use Reduction: Policies limiting the use of harmful chemicals in agriculture and industry decrease the risk of toxic substances contaminating waterways.
- Community-Based Initiatives: Local community actions, such as clean-up campaigns and pollution monitoring, play a significant role in maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystems.
- International Agreements: Global cooperation through agreements like the Paris Accord helps address transboundary pollution and climate change, indirectly benefiting aquatic environments.
Together, these policies and innovations represent a comprehensive approach to reducing pollution, ensuring the resilience and vitality of aquatic ecosystems for future generations.
Community Engagement and Education on Aquatic Health
Empowering communities through engagement and education is pivotal for the health of aquatic ecosystems. These initiatives foster a deeper understanding of the ecological significance of water bodies and the impact of human activities.
- Environmental Stewardship Programs: Programs aimed at educating individuals about the importance of aquatic ecosystems and their role in conservation.
- Public Workshops and Seminars: Interactive sessions providing practical knowledge on reducing pollution, conserving water, and protecting aquatic life.
- School Curriculum Integration: Incorporating aquatic health topics into school curriculums to instill a sense of responsibility towards water conservation from a young age.
- Community Clean-Up Events: Organizing local clean-up events to remove trash from beaches, rivers, and lakes, enhancing community involvement in conservation efforts.
- Citizen Science Projects: Engaging the public in data collection and monitoring of local water bodies to contribute to scientific research and conservation strategies.
- Awareness Campaigns: Launching campaigns to raise public awareness about issues like plastic pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction, and promoting sustainable practices.
Such collective actions and educational efforts play a crucial role in safeguarding aquatic ecosystems and ensuring their resilience against environmental challenges.
Implementation of Sustainable Fishing Practices
Adopting sustainable fishing practices is key to minimizing human impact on aquatic ecosystems. These practices ensure the long-term health and viability of marine life and habitats.
- Eco-Friendly Gear: Utilizing fishing gear designed to reduce bycatch and habitat damage, such as turtle excluder devices and biodegradable nets.
- Fish Stock Management: Implementing quotas and size limits based on scientific assessments to prevent overfishing and allow fish populations to recover.
- Protected Areas: Designating marine protected areas where fishing is restricted or prohibited to allow ecosystems to regenerate and maintain biodiversity.
- Responsible Aquaculture: Developing and following best practices for aquaculture to prevent pollution and the spread of diseases to wild fish populations.
- Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers about sustainable seafood choices to drive demand for responsibly sourced fish and seafood products.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local fishing communities in conservation efforts and decision-making processes to ensure sustainable livelihoods and the protection of aquatic resources.
Through these measures, we can significantly reduce the negative impacts of fishing on aquatic ecosystems, ensuring the health and abundance of marine life for future generations.
Advancements in Waste Management to Protect Waterways
Innovations in waste management have significantly contributed to protecting aquatic ecosystems. These advancements aim to reduce the direct discharge of pollutants into waterways, enhancing water quality and aquatic life health.
- Improved Sewage Treatment: Advanced sewage treatment technologies, such as tertiary treatment, effectively remove contaminants before water is released back into the environment.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: The development and use of biodegradable and compostable packaging materials help reduce plastic pollution in aquatic ecosystems.
- Stormwater Management Systems: Green infrastructure, like rain gardens and permeable pavements, helps manage stormwater runoff, preventing harmful pollutants from reaching water bodies.
- Chemical Waste Reduction: Stricter regulations and better practices in industries have led to a decrease in the amount of hazardous chemicals being released into waterways.
- Recycling and Upcycling: Enhanced recycling programs and upcycling initiatives reduce waste and its impact on aquatic environments by diverting materials from landfills.
- Community-Based Projects: Local waste collection and waterway cleanup efforts engage communities in directly protecting their aquatic resources.
Together, these waste management advancements form a comprehensive approach to preserving the health and diversity of aquatic ecosystems for future generations.

Climate Change Mitigation Strategies Affecting Oceans
Addressing climate change is crucial for protecting ocean health. Mitigation strategies are designed to reduce the impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems and enhance the resilience of these vital habitats.
- Carbon Emission Reductions: Implementing policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from industries, transportation, and energy production to slow ocean warming and acidification.
- Renewable Energy Adoption: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydro, to decrease dependence on fossil fuels and reduce ocean warming impacts.
- Marine Carbon Sequestration: Promoting natural processes such as oceanic carbon uptake and protecting blue carbon ecosystems like mangroves, seagrasses, and salt marshes that absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Improved Ocean Governance: Strengthening international cooperation and governance frameworks for ocean conservation to address climate change impacts effectively.
- Ocean-Based Renewable Energy: Developing sustainable ocean-based energy solutions like tidal and wave energy, which have minimal environmental footprints.
- Climate-Resilient Marine Protected Areas: Designing MPAs to be resilient to climate change by considering current and future climate impacts in their planning and management.
These strategies, combined with global efforts to address climate change, are essential for maintaining the health and biodiversity of our oceans in the face of environmental challenges.
Human Impact on Aquatic Environments
Aquatic ecosystems are a mesmerizing world full of diverse marine life, vibrant corals, and breathtaking seascapes. Dive into the depths of this enchanting underwater universe and discover the beauty and fragility of aquatic ecosystems through this captivating video.
Human Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystem Health
Uncover the profound effects of human impacts on our planet\'s delicate ecosystems. From deforestation to pollution, this eye-opening video showcases the consequences of our actions on nature. Gain a deeper understanding of the importance of preserving and restoring our environment for a sustainable future.
Technological Innovations for Monitoring Aquatic Ecosystems
Recent technological advancements have revolutionized the monitoring of aquatic ecosystems, offering new insights into their health and the impacts of human activities. These innovations enable more precise and real-time data collection, crucial for effective management and conservation efforts.
- Remote Sensing Technologies: Satellite imagery and aerial drones provide comprehensive overviews of aquatic ecosystems, allowing for the monitoring of changes in habitat, water quality, and land use.
- Underwater Drones and ROVs: Remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) explore areas that are difficult for humans to reach, collecting data on water conditions, marine life, and the ocean floor.
- Acoustic Monitoring: Uses sound waves to track the movement of fish and marine mammals, assess biodiversity, and monitor the impacts of noise pollution on aquatic life.
- Environmental DNA (eDNA): Analyzing water samples for DNA traces allows scientists to identify the species present in a water body without seeing or capturing them, offering a non-invasive way to monitor biodiversity.
- Water Quality Sensors: Automated sensors placed in water bodies continuously measure temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and pollutants, providing real-time data on water quality.
- Citizen Science Apps: Mobile applications engage the public in data collection, significantly expanding the geographic and temporal scope of environmental monitoring.
These technologies not only enhance our understanding of aquatic ecosystems but also empower conservation efforts with actionable, data-driven insights.

Protection of Endangered Marine Species and Habitats
Protecting endangered marine species and their habitats is a key focus of conservation efforts worldwide. Initiatives are designed to safeguard these vital components of the marine ecosystem, ensuring their survival and the overall health of aquatic environments.
- Species-Specific Conservation Programs: Tailored programs addressing the unique needs of endangered species, such as breeding programs, habitat restoration, and anti-poaching measures.
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): Designation of MPAs to conserve critical habitats, provide refuge for marine life, and allow ecosystems to recover and thrive without human interference.
- Habitat Restoration Projects: Efforts to restore coral reefs, mangroves, seagrass beds, and other crucial marine habitats that support biodiversity and protect coastlines.
- Bycatch Reduction Techniques: Implementation of fishing gear modifications and practices to minimize bycatch, protecting non-target species from unintentional capture.
- Legal Protections and Enforcement: Strengthening of laws and regulations to protect endangered species and their habitats, coupled with strict enforcement against illegal activities.
- Community Involvement and Livelihood Alternatives: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts and providing sustainable livelihood alternatives to reduce reliance on destructive practices.
Through collaborative efforts, innovative strategies, and global commitments, the protection of endangered marine species and habitats continues to advance, offering hope for the future of our oceans.
International Agreements and Policies for Ocean Conservation
International agreements and policies play a pivotal role in the collective global effort to conserve oceanic ecosystems. These frameworks facilitate cooperation among nations to address the complex challenges facing aquatic environments.
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS): Often referred to as the "Constitution for the Oceans," this agreement sets out the legal framework within which all activities in the oceans and seas must be carried out.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): This global agreement fosters conservation of biodiversity, sustainable use of its components, and fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources.
- Paris Agreement: Although primarily focused on climate change, the Paris Agreement has significant implications for ocean conservation, addressing issues like ocean warming and acidification.
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): MPAs are established under various international and regional frameworks to protect critical marine habitats and biodiversity.
- International Whaling Commission (IWC): The IWC works to regulate whaling practices, ensuring the conservation of whale populations through agreements and regulations.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES): CITES regulates international trade in endangered species, including marine species, to ensure that such trade does not threaten their survival.
These and other agreements underscore the global commitment to preserving the health and diversity of the world"s oceans, ensuring they remain vibrant and life-sustaining for generations to come.
READ MORE:
Public Awareness Campaigns and their Impact on Aquatic Life
Public awareness campaigns play a crucial role in safeguarding aquatic ecosystems by enlightening the public on the importance of these habitats and the myriad of life they support. These initiatives aim to shift perceptions, inspire positive behavior changes, and foster a collective responsibility towards aquatic conservation.
- Informing and Educating: Campaigns utilize various platforms, including social media, documentaries, and educational programs, to disseminate information on the threats facing aquatic ecosystems, such as pollution, overfishing, and climate change. By making this knowledge accessible, individuals are better equipped to make informed decisions that benefit aquatic environments.
- Encouraging Community Involvement: Many campaigns focus on engaging communities in conservation activities like beach cleanups, restoration projects, and citizen science initiatives. This hands-on involvement not only aids in the direct improvement of aquatic habitats but also strengthens the connection between individuals and their local environments.
- Promoting Sustainable Practices: Awareness efforts often highlight sustainable alternatives to harmful practices, such as advocating for sustainable seafood choices, reducing plastic use, and supporting eco-friendly companies. As consumers become more conscious of their impact, demand shifts towards more sustainable products and services, driving positive change in industries affecting aquatic life.
- Influencing Policy Change: Public support galvanized through awareness campaigns can lead to significant policy changes. Successful campaigns have led to the creation or enforcement of regulations aimed at protecting aquatic ecosystems, such as bans on harmful chemicals, the establishment of marine protected areas, and stricter fishing regulations.
- Raising Funds for Conservation: Awareness campaigns also play a vital role in fundraising for conservation efforts. Public donations contribute to research, habitat restoration, and the protection of endangered species, providing essential resources for ongoing conservation work.
In conclusion, public awareness campaigns are a powerful tool in the conservation of aquatic ecosystems. By informing, engaging, and inspiring the public, these campaigns harness the collective power of individuals and communities to enact positive change, ensuring the health and vitality of aquatic environments for future generations.
Exploring human impacts on aquatic ecosystems reveals our power to harm or heal, urging us to adopt practices that nurture these vital habitats for the enduring health of our planet.