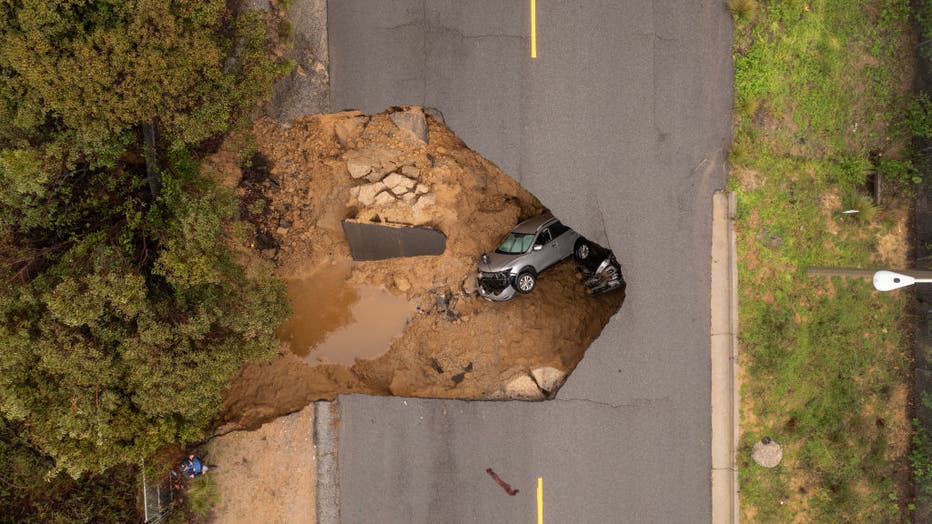
Topic california sinkhole map: Explore the essential California Sinkhole Map to uncover the hidden geological phenomena shaping the landscape, ensuring safety and awareness for all residents and visitors alike.
Table of Content
- What areas in California are prone to sinkholes and where can I find a map indicating their locations?
- Overview of Sinkholes in California
- Mapping Sinkholes in California
- YOUTUBE: Sinkhole Closes Highway 92 in San Mateo County
- Introduction to Sinkholes in California
- Understanding the Causes of Sinkholes
- Mapping California"s Sinkholes: An Overview
- Interactive Sinkhole Maps: Features and Access
- Areas in California Most Affected by Sinkholes
- Prevention and Safety Measures for Sinkholes
- Recent Sinkhole Events in California
- Resources for Residents: Reporting and Repairing Sinkholes
- Future Trends: Sinkhole Monitoring and Research
- FAQs: Common Questions About California"s Sinkholes
What areas in California are prone to sinkholes and where can I find a map indicating their locations?
California is a state with a variety of geological features, some of which are prone to sinkholes. Areas in California that are more susceptible to sinkholes include regions with soluble rock formations such as limestone, gypsum, or salt beds. These areas are more likely to develop sinkholes due to the dissolution of the rock by groundwater over time. Some regions known for sinkhole activity in California include:
- Central Valley
- Central Coast
- Desert regions
- Sierra Nevada foothills
If you are looking for a map indicating specific locations of sinkholes in California, you may want to reach out to geological agencies or departments that specialize in such information. The California Department of Conservation or the United States Geological Survey (USGS) may have resources or maps available for public access. Additionally, local county or city geological surveys may also provide information on sinkhole-prone areas within their jurisdiction.
READ MORE:
Overview of Sinkholes in California
Sinkholes form when the ground below the land surface cannot adequately support it, often due to water erosion of soluble rock layers beneath. While more rare in California, recent heavy rains have led to several notable occurrences.
Areas Prone to Sinkholes
- Regions with karst terrain are more susceptible to sinkhole formation. These areas contain soluble rocks such as carbonates and evaporites, which can dissolve over time, creating underground cavities that eventually collapse.
- Volcanic regions may also develop sinkholes, not from dissolution of rock but from the collapse of lava tubes left after volcanic activity.
Recent Incidents
Recent heavy rainfall in California has triggered the formation of dangerous sinkholes across the state, highlighting the importance of monitoring and preparedness in vulnerable areas.
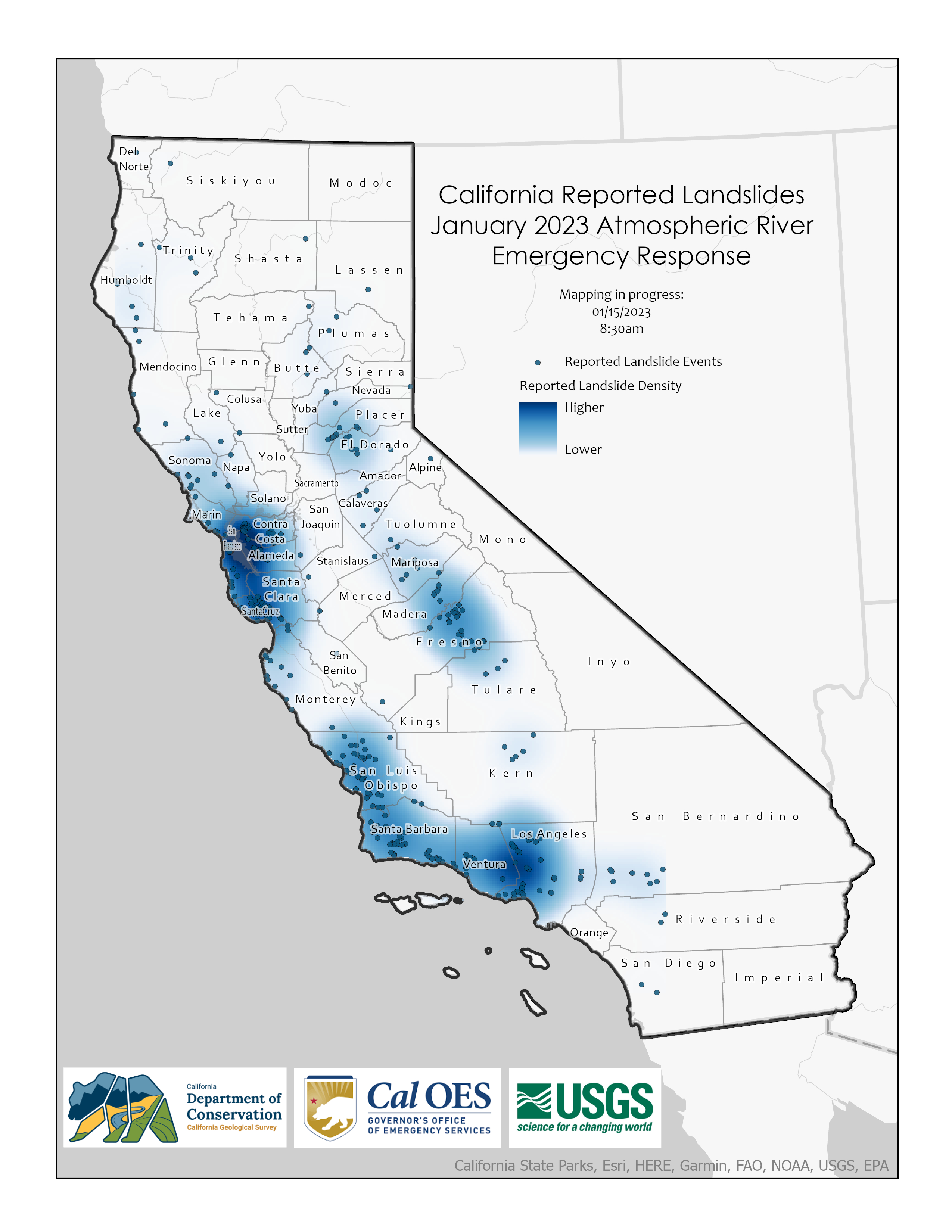
Mapping Sinkholes in California
Maps and data analysis by the California Geological Survey, part of the California Department of Conservation, provide valuable resources for identifying areas at risk of sinkholes and other geologic hazards.
| Resource | Description |
| California Geological Survey Maps | Includes data on seismic and geologic hazards, including areas prone to sinkholes. |
| USGS Karst Map | Shows areas of the United States with karst terrain susceptible to sinkhole formation. |
Preventive Measures and Safety Tips
- Stay informed about the geological risks in your area.
- Avoid building or residing in areas known to be at high risk for sinkholes without proper geological assessments.
- Monitor your property for signs of subsidence or new depressions in the land surface.
While sinkholes can be concerning, understanding their causes, recognizing the signs, and knowing the areas at risk can help mitigate their impact. The state of California and geological experts continue to monitor and study these phenomena to ensure public safety and awareness.
Sinkhole Closes Highway 92 in San Mateo County
Sinkholes are fascinating natural phenomena that occur unexpectedly, revealing the mysterious subterranean world beneath our feet. Watch our video to learn more about how these geological wonders form and the stunning landscapes they create. Rainfall is the lifeblood of the Earth, bringing nourishment to plants, replenishing rivers, and refreshing the air. Join us in exploring the beauty and power of rainfall in our video, showcasing the mesmerizing sights and sounds of a rainstorm.
Rainfall Triggers Sinkholes and Mudslides in Southern California
The latest round of rainfall in Southern California is opening up more sinkholes and causing dangerous mudslides across the ...
Introduction to Sinkholes in California
Sinkholes in California, though less common than in other regions, present a unique challenge due to the state"s diverse geological makeup and variable climate conditions. Understanding these natural occurrences is vital for ensuring public safety and maintaining infrastructure.
Sinkholes occur when water erodes underlying rock layers, causing the land surface to collapse. In California, this process is influenced by factors such as heavy rainfall, drought conditions, and human activities. The state"s geological diversity, including areas with soluble rocks like limestone, contributes to the formation of sinkholes.
- Geological Conditions: California"s varied geology, including sedimentary basins and volcanic areas, creates conditions conducive to sinkhole formation.
- Climate Impact: Periods of heavy rain following droughts can accelerate the erosion of underground cavities, leading to sinkholes.
- Human Factors: Urban development and water management practices can affect groundwater levels and increase sinkhole risk.
This section provides an overview of sinkholes in California, emphasizing the importance of awareness and preparedness to mitigate their impacts. By mapping sinkhole-prone areas and understanding the underlying causes, residents and authorities can take proactive measures to protect property and ensure public safety.

Understanding the Causes of Sinkholes
Sinkholes in California can form due to a variety of natural and human-induced factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring the safety of communities and infrastructure.
- Natural Erosion: Water gradually dissolves certain types of rock such as limestone, gypsum, and salt beds, creating underground cavities that can collapse to form sinkholes.
- Heavy Rainfall: Intense or prolonged periods of rain can saturate the ground, increasing pressure on subterranean voids and triggering collapses.
- Groundwater Withdrawal: Excessive pumping of groundwater for agriculture, drinking water, or industrial use can create voids below the surface, leading to sinkholes.
- Urban Development: Construction and development can alter water drainage patterns and increase the load on the ground, contributing to sinkhole formation.
- Seismic Activity: Earthquakes and other seismic events can fracture the ground and underlying rock layers, precipitating sinkholes.
Effective sinkhole prevention and mitigation strategies involve careful monitoring of risk factors, responsible water management, and adherence to building codes designed to minimize impacts on susceptible land. By addressing the underlying causes, California aims to reduce the frequency and severity of sinkholes, safeguarding both natural landscapes and urban environments.
Mapping California"s Sinkholes: An Overview
The initiative to map sinkholes in California represents a critical step towards understanding and mitigating the risks associated with these geological phenomena. Through advanced technology and comprehensive data collection, scientists and researchers are able to provide valuable insights into sinkhole-prone areas across the state.
- Geological Surveys: Detailed geological surveys form the foundation of sinkhole maps, identifying areas with soluble rock layers that are susceptible to erosion and collapse.
- Remote Sensing Technology: Satellite imagery and aerial photography offer wide-ranging perspectives, enabling the identification of sinkhole formations even in remote areas.
- Groundwater Monitoring: Monitoring groundwater levels helps to predict the conditions that may lead to sinkhole development, particularly in regions heavily reliant on groundwater extraction.
- Public Contributions: Reports from local residents and municipal authorities provide crucial, up-to-date information on new or expanding sinkholes.
This mapping effort not only aids in emergency preparedness and urban planning but also enhances public awareness about the locations and potential triggers of sinkholes. As a living document, the California Sinkhole Map is continually updated to reflect new discoveries and changes in the landscape, serving as a vital resource for homeowners, developers, and policymakers alike.
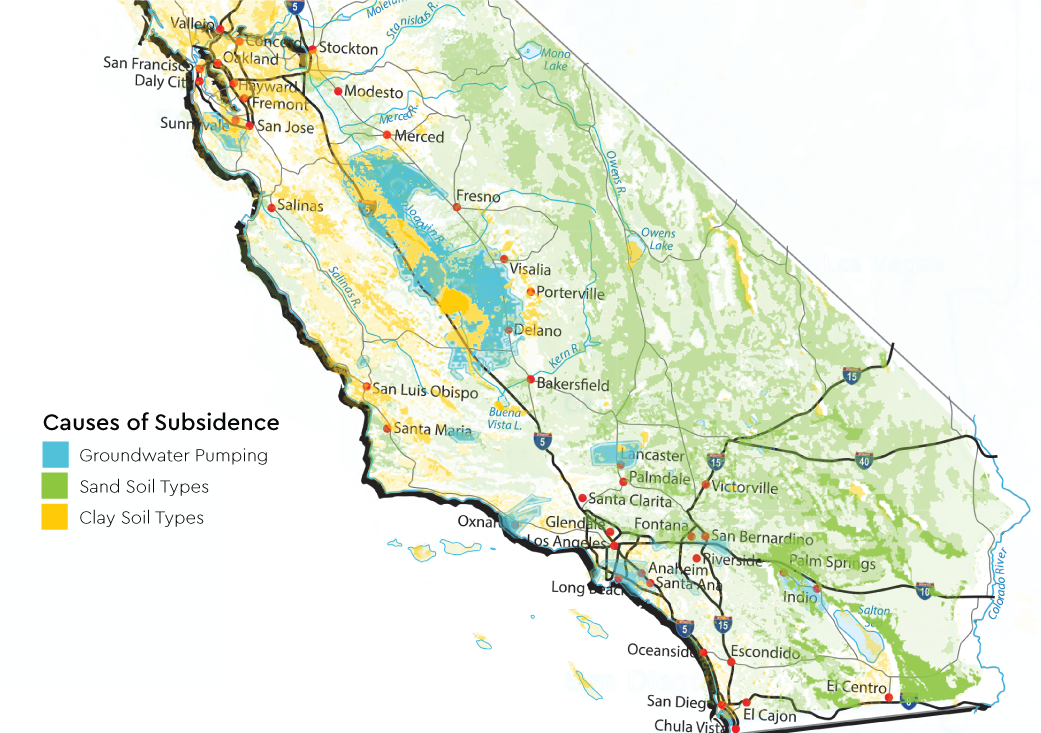
Interactive Sinkhole Maps: Features and Access
Interactive sinkhole maps are a crucial tool for understanding and managing the risk of sinkholes in California. These digital platforms offer detailed, real-time information, helping individuals, communities, and professionals to identify areas of concern and take preventative measures.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed for ease of use, these maps allow users to navigate and zoom into specific regions to view sinkhole locations and affected areas.
- Real-Time Data: Incorporating the latest data, interactive maps provide up-to-date information on sinkhole occurrences and potential risk zones.
- Historical Records: Access to historical sinkhole data helps to identify patterns and areas with recurrent issues, aiding in long-term planning and prevention strategies.
- Resource Links: Maps often include links to resources for those affected by sinkholes, including how to report new sinkholes and access repair and mitigation services.
- Geological Information: Detailed geological layers and information can be overlaid on the maps, offering insights into the underlying causes of sinkholes.
Access to interactive sinkhole maps is typically provided through governmental and environmental agencies" websites. These tools are invaluable for enhancing public awareness, facilitating research, and guiding policy and infrastructure decisions aimed at minimizing the impact of sinkholes in California.
Areas in California Most Affected by Sinkholes
California"s diverse geography means that sinkhole occurrence varies across the state. Identifying areas most affected by sinkholes is key to understanding regional risks and preparing mitigation strategies.
- Central Valley: Known for its agricultural productivity, this region also faces sinkhole risks due to groundwater depletion and soil subsidence.
- San Joaquin Valley: Intensive agriculture and water extraction have led to notable ground subsidence and increased sinkhole formation risks.
- Los Angeles Basin: Urban development and water management issues contribute to the risk of sinkholes in this densely populated area.
- San Francisco Bay Area: Natural factors and human activities, including construction and groundwater pumping, heighten sinkhole risks.
- Coastal Regions: Coastal erosion, along with the impact of heavy rains and storms, can lead to sinkhole occurrences in these areas.
Monitoring and mapping efforts continue to evolve, offering better insights into sinkhole-prone areas. This knowledge is crucial for planning, development, and emergency preparedness, aiming to minimize the impact of sinkholes on California"s communities and landscapes.
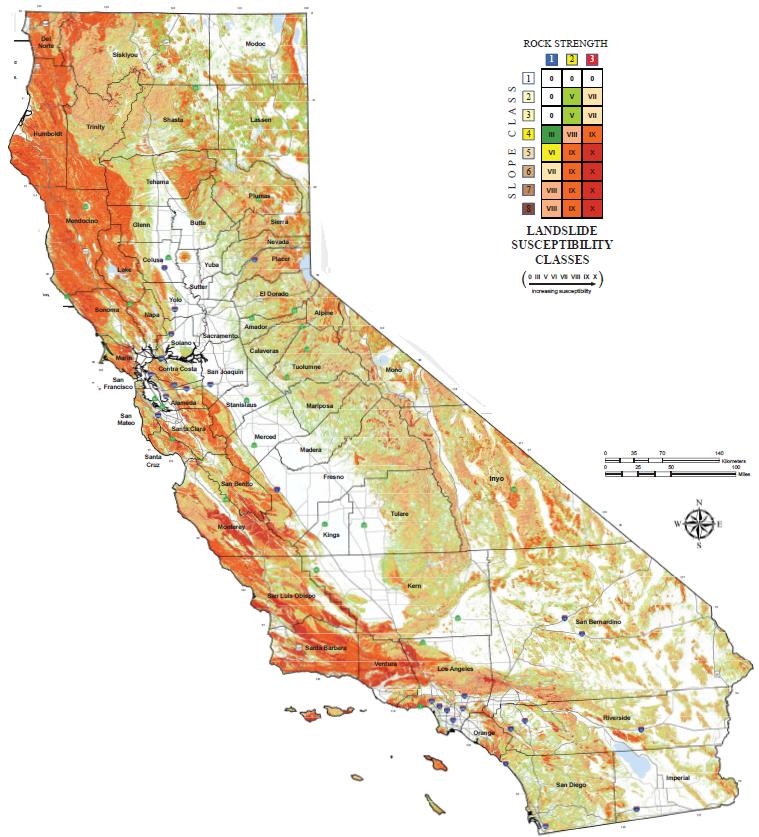
Prevention and Safety Measures for Sinkholes
Ensuring safety and minimizing damage from sinkholes in California involves a combination of prevention strategies and preparedness measures. Awareness and proactive actions can significantly reduce the risks associated with sinkholes.
- Regular Monitoring: Utilize geological surveys and sinkhole maps to monitor areas prone to sinkholes, especially if located near known vulnerable zones.
- Water Management: Practice responsible water use and management to prevent excessive groundwater withdrawal, which can lead to sinkhole formation.
- Construction Practices: Adhere to building codes and guidelines that consider sinkhole risks, including proper site assessment and using techniques to stabilize the ground.
- Emergency Preparedness: Develop emergency plans that include evacuation routes and contact information for local emergency services in case of a sinkhole occurrence.
- Public Awareness: Educate the community about sinkholes, their signs, and how to respond, enhancing overall safety and preparedness.
By implementing these measures, California aims to protect its residents, infrastructure, and natural landscapes from the potential damages caused by sinkholes, ensuring a safer environment for all.
Recent Sinkhole Events in California
California has witnessed several significant sinkhole events in recent years, highlighting the importance of ongoing vigilance and preparedness. These incidents underscore the unpredictable nature of sinkholes and the need for effective monitoring and response strategies.
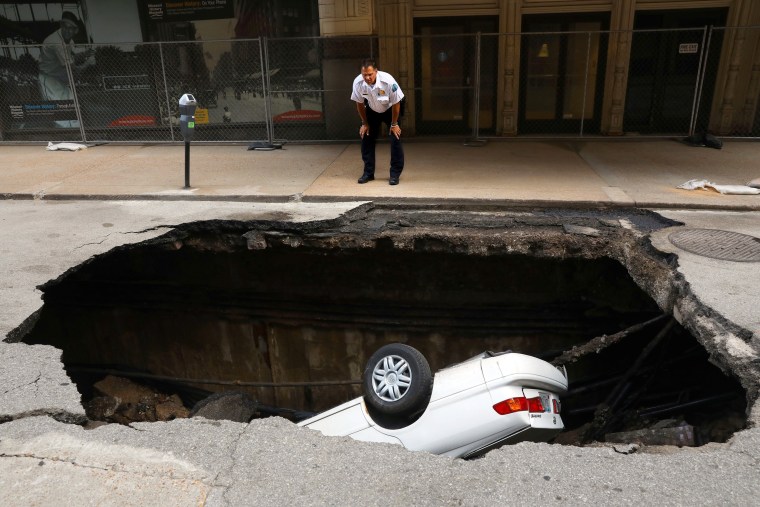
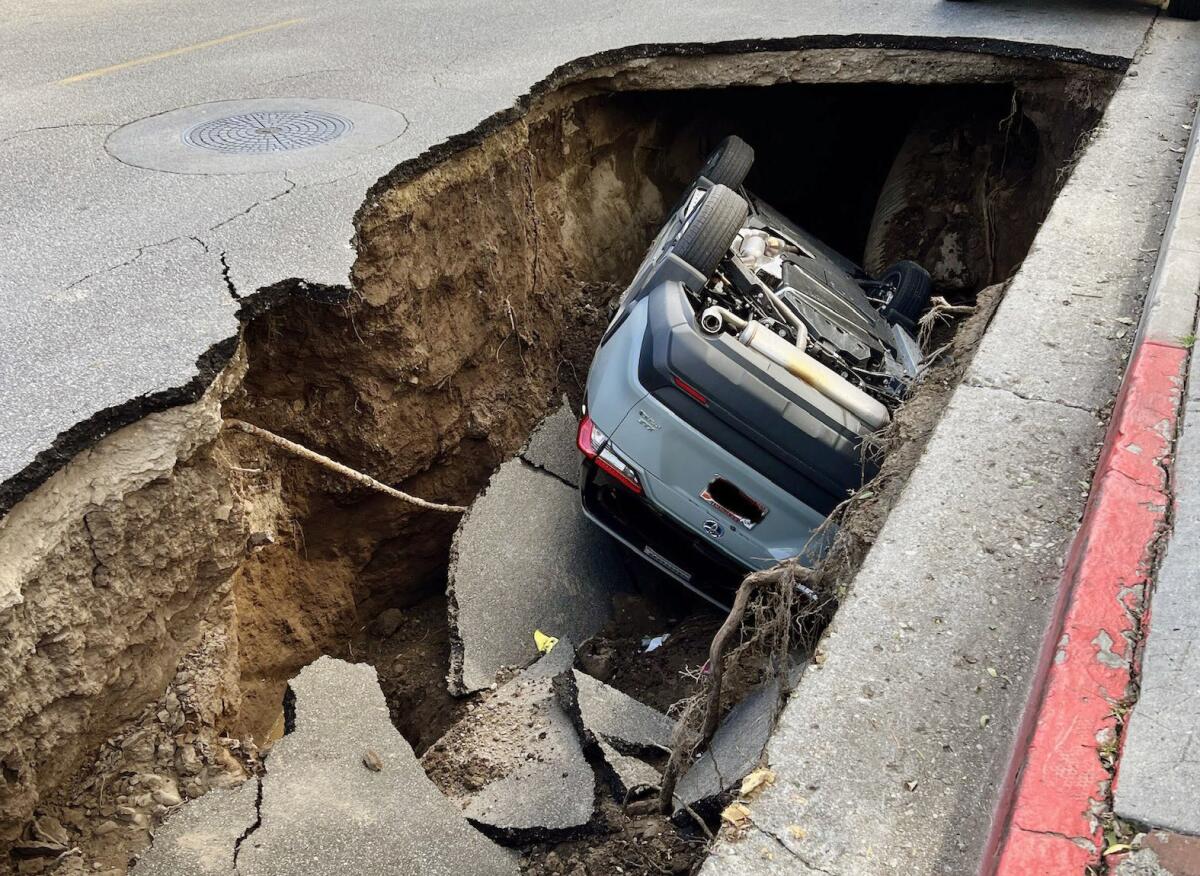
- Los Angeles, 2020: A massive sinkhole opened up in a residential area, causing property damage but thankfully no injuries. The event prompted a review of local water drainage systems.
- San Francisco, 2019: A sinkhole caused by a broken sewer line led to the evacuation of several homes and extensive repairs. It served as a reminder of the aging infrastructure in many cities.
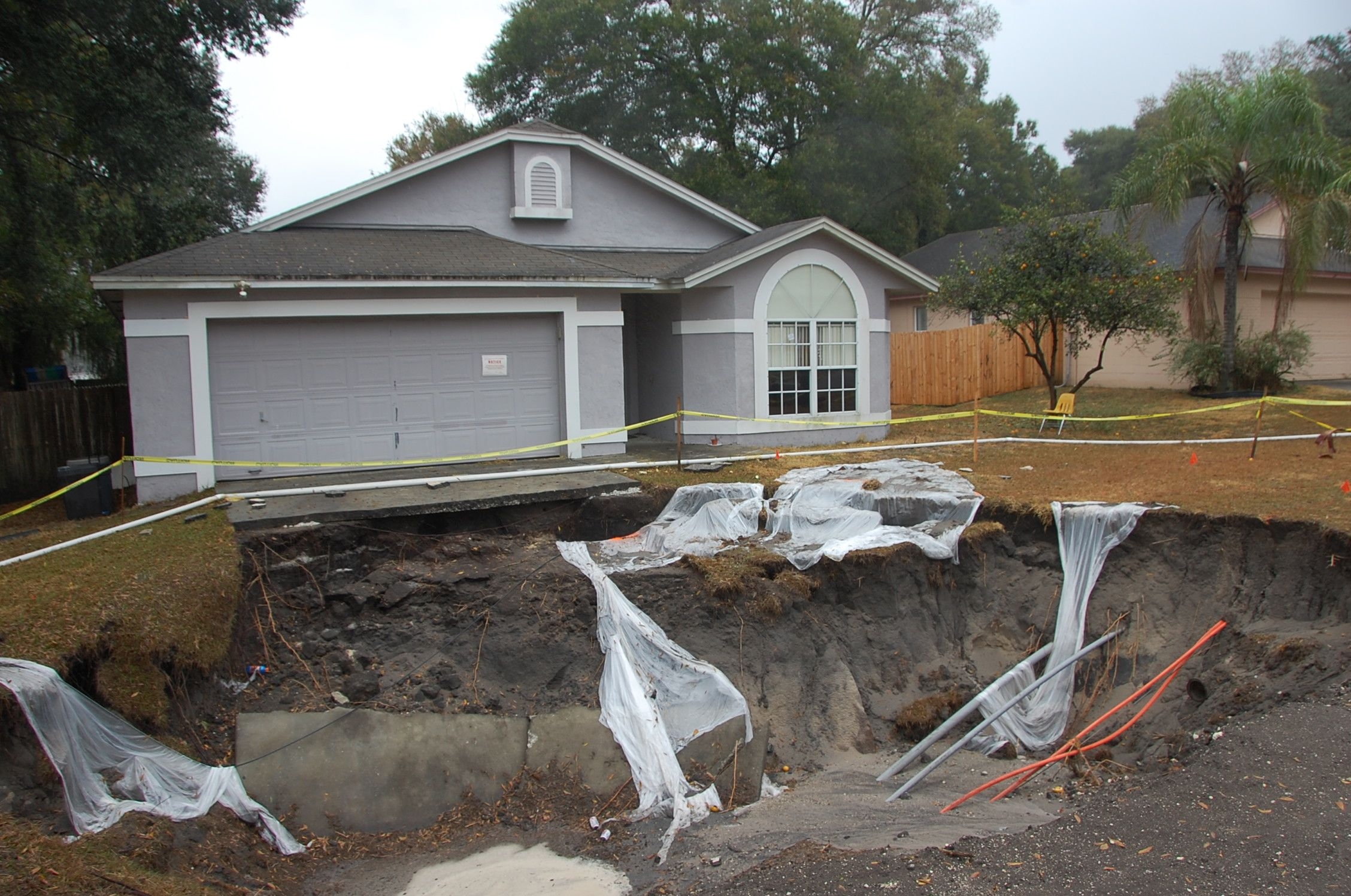
- Central Valley, 2018: Agricultural water usage contributed to a sinkhole that disrupted local farming operations, illustrating the impact of groundwater depletion.
- San Diego, 2017: Heavy rains triggered a sinkhole that swallowed part of a street, emphasizing the need for improved stormwater management.
These events have spurred efforts to enhance sinkhole prediction, prevention, and management throughout California. By learning from each occurrence, the state aims to better protect its citizens and infrastructure from future sinkhole incidents.
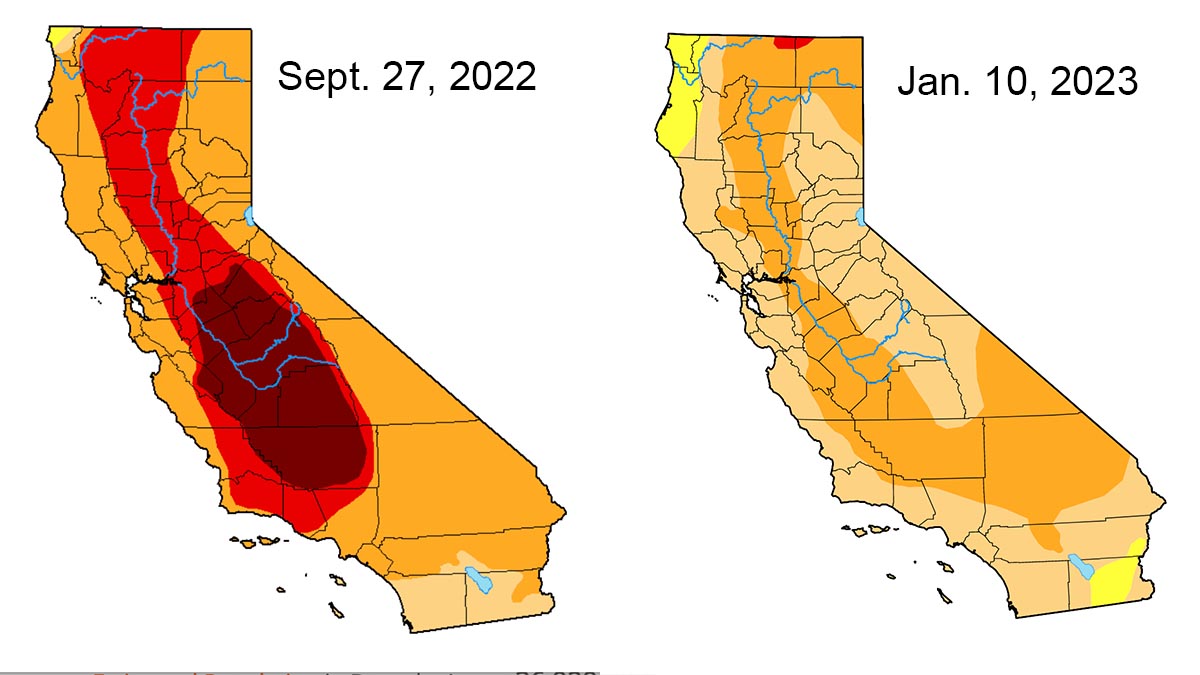
Resources for Residents: Reporting and Repairing Sinkholes
California provides various resources and guidelines for residents to report and address sinkholes, ensuring community safety and infrastructure integrity. Knowing how to respond to sinkhole incidents is critical for effective management and repair.
- Local Government Agencies: Residents should report any suspected sinkhole activity to their local city or county public works department, which can assess the situation and coordinate necessary actions.
- California Geological Survey: Offers information on sinkholes, including mapping and risk assessment resources, to help residents understand potential vulnerabilities.
- Emergency Services: In case of an immediate danger from a sinkhole, contacting emergency services is crucial to ensure swift action and safety.
- Insurance Companies: Property owners should consult with their insurance providers about coverage for sinkhole damage and the process for filing claims.
- Professional Engineers: For sinkhole repair, hiring a professional engineer with experience in geotechnical assessments is recommended to ensure proper remediation and stabilization.
By utilizing these resources, Californians can take proactive steps to manage sinkhole risks, contributing to the safety and resilience of their communities.
Future Trends: Sinkhole Monitoring and Research
Advancements in technology and research are paving the way for innovative approaches to sinkhole monitoring and management in California. These future trends are expected to enhance the state"s ability to predict, prevent, and respond to sinkhole events.
- Remote Sensing Technologies: The use of satellite imagery and drones for detecting early signs of sinkholes is becoming more prevalent, offering a broader view and early warning capabilities.
- Geotechnical Investigation Tools: Advanced ground-penetrating radar and other subsurface imaging techniques are improving the accuracy of underground assessments.
- Data Analytics and AI: Machine learning algorithms are being developed to analyze geological data, predict potential sinkhole formations, and optimize response strategies.
- Public Engagement Platforms: Online portals and mobile apps for reporting suspected sinkholes are enhancing community involvement and awareness.
- Environmental and Urban Planning: Integrating sinkhole risk assessments into planning and development processes to ensure safer infrastructure and land use.
These trends represent a proactive shift towards a more informed and technologically equipped approach to dealing with sinkholes. By investing in research and embracing innovation, California is working to safeguard its landscapes, communities, and infrastructure against the challenges posed by sinkholes.

READ MORE:
FAQs: Common Questions About California"s Sinkholes
- What causes sinkholes in California? Sinkholes in California are primarily caused by natural erosion of soluble rocks beneath the surface, heavy rainfall, groundwater withdrawal, and urban development.
- How can I find out if my area is prone to sinkholes? Checking the California Sinkhole Map and consulting local geological surveys can provide insights into whether your area is at risk.
- What should I do if I spot a potential sinkhole? Report any suspected sinkholes to local authorities or emergency services immediately to ensure timely assessment and response.
- Are there any preventive measures for sinkholes? Yes, responsible water management, adhering to building codes in sinkhole-prone areas, and regular monitoring can help mitigate risks.
- Can sinkholes be repaired? Yes, sinkholes can often be repaired through methods such as filling with graded material or constructing underground supports, depending on the severity and size of the sinkhole.
Understanding sinkholes in California is key to preventing and managing their impact. By staying informed and prepared, residents can significantly reduce the risks posed by these natural occurrences.
Discovering California"s sinkhole map not only enlightens but empowers us to navigate the challenges posed by nature with informed decisions, ensuring the safety and resilience of our communities against the unpredictable.







