Topic brown snake species: Explore the diverse world of brown snake species, delving into their unique behaviors, habitats, and intriguing facts, offering a captivating journey into the realm of these remarkable reptiles.
Table of Content
- What are the different species of brown snakes?
- Overview of Brown Snake Species
- Distinctive Features of Brown Snakes
- Habitat and Geographic Distribution
- Behavior and Diet of Brown Snakes
- Reproduction and Lifecycle
- Conservation Status and Human Impact
- YOUTUBE: 10 Things You Didn\'t Know About The Eastern Brown Snake
- Identification and Safety Tips
- Interesting Facts and Research Studies
- Myths and Misconceptions about Brown Snakes
- Medical Significance and First Aid for Bites
What are the different species of brown snakes?
There are several different species of brown snakes, including:
- The eastern brown snake (Pseudonaja textilis)
- Brown Snake (Storeria dekayi)
In addition, there are approximately 10 species of the genus Pseudonaja that are referred to as brown snakes in New Guinea and Australia.
READ MORE:
Overview of Brown Snake Species
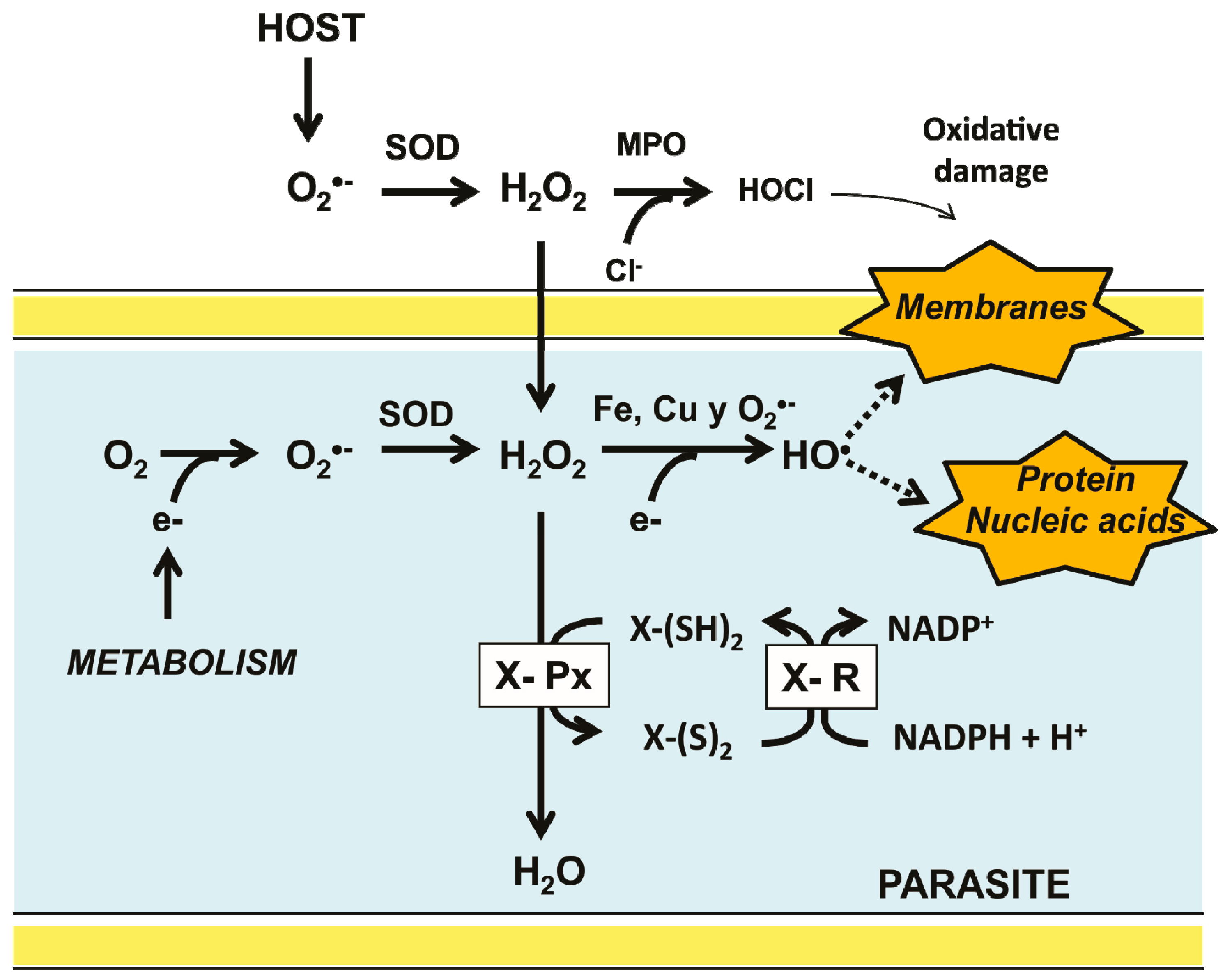
Brown snake species, encompassing a wide range of snakes, are notable for their diverse appearances and behaviors. Found in various habitats, they display a spectrum of brown and tan shades, making them both unique and challenging to identify. These species include non-venomous types such as the Dekay"s Brownsnake, known for its small size and distinct markings, and venomous types like the Eastern Brown Snake, notorious for its lethal bite.
- The Western Hognose Snake, with its rattlesnake-like appearance and upturned nose, is a notable non-venomous species.
- Chihuahuan Night Snakes and California Kingsnakes, each with unique color patterns and habitats, add to the diversity of brown snake species.
- Species like the Bullsnake, found in the central United States, exemplify the wide distribution of these reptiles.
- The Eastern Brown Snake, prevalent in Australia, is known for its high venom potency and varied diet, including mammals and other reptiles.
- Western Brown Snakes, with their complex taxonomic classification and color variations, are another significant group within the brown snake category.
These snakes, although sharing a common color palette, exhibit a wide range of sizes, dietary preferences, and reproductive behaviors, making them a fascinating subject for both herpetologists and enthusiasts alike.

Distinctive Features of Brown Snakes
Brown snakes, a diverse group of serpents, exhibit a range of distinctive features across different species. These snakes are primarily recognized for their varying shades of brown and tan, blending seamlessly into their natural habitats. They display unique color patterns, body sizes, and behaviors that set them apart from other snake families.
- The Western Hognose Snake, known for its upturned nose and rattlesnake-like color patterns, is a standout for its unique defense mechanism and digging capability.
- Chihuahuan Night Snakes possess thick reddish-brown bands, adapting their coloration to the environment, making them distinctive in their habitat.
- California Kingsnakes present two main color morphs, showcasing the diversity within a single species.
- The Eastern Brown Snake, one of the most venomous, shows genetic diversity with different clades found across various regions in Australia and New Guinea.
- Dekay"s Brownsnakes feature a checkerboard pattern of black spots along their back and distinctive markings on their head, making them easily identifiable.
- In terms of size, brown snake species can vary significantly, with some reaching over seven feet in length, while others remain much smaller.
These snakes not only vary in appearance but also in their behavior and habitat preferences, contributing to their distinctiveness among reptiles.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Brown snake species exhibit a wide range of habitats and geographic distributions, reflecting their adaptability and ecological diversity. These species are found in various environments, each with unique characteristics that influence their lifestyle and behavior.
- North America is home to several brown snake species like the Western Hognose Snake, Chihuahuan Night Snake, California Kingsnake, and Bullsnake. These species are found in environments ranging from deserts to forests, showcasing their adaptability.
- The Eastern Brown Snake, a prominent species in Australia and New Guinea, demonstrates distinct genetic lineages in different regions, indicating varied environmental adaptations.
- Dekay"s Brownsnake, commonly found in North America, prefers habitats such as forests, swamps, and grasslands, often near water sources.
- Brown tree snakes, another member of this diverse group, have been observed in both arboreal and ground environments, highlighting their versatile nature.
- The brown snakes" range spans from North America through parts of Central America, including Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Guatemala, into diverse biomes such as forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
This geographical and habitat diversity among brown snake species underscores their remarkable adaptability and ecological significance in various ecosystems.
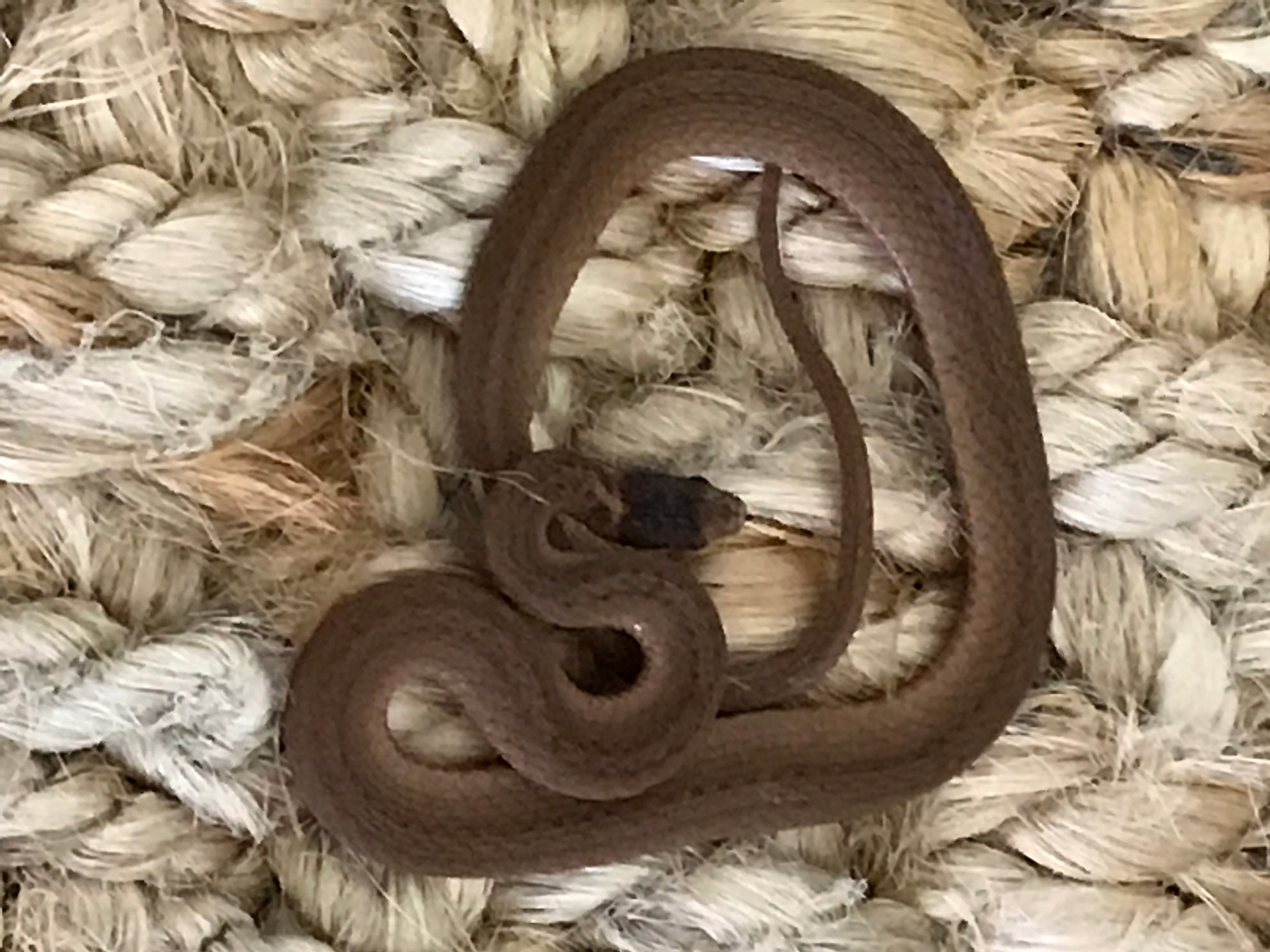

Behavior and Diet of Brown Snakes
The behavior and diet of brown snakes vary significantly across different species, reflecting their adaptability and ecological diversity. These snakes exhibit a range of behaviors and dietary preferences, influenced by their habitat and biological needs.
- Many brown snakes, like the Western Hognose and Chihuahuan Night Snake, are found in areas with water sources, often basking during the day and displaying unique foraging and defensive behaviors.
- The Eastern Brown Snake, found in various regions of Australia and New Guinea, is known for its diverse diet, including vertebrates like frogs, reptiles, birds, and mammals. These snakes are active hunters, using both venom and constriction to subdue prey.
- In North America, species like the Dekay"s Brownsnake are commonly found in habitats such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands, feeding on smaller prey such as earthworms and insects.
- Brown snakes display a range of reproductive behaviors, with some species engaging in ritual combat and others exhibiting unique courtship behaviors.
Understanding the behavior and diet of brown snakes is crucial for appreciating their role in various ecosystems and their interactions with other species.
Reproduction and Lifecycle
The reproductive behaviors and lifecycle of brown snakes vary across species, demonstrating fascinating aspects of their biology. From courtship rituals to hatching patterns, these snakes exhibit diverse reproductive strategies.
- Western Hognose Snakes and other North American species like the Chihuahuan Night Snake and California Kingsnake demonstrate unique mating behaviors, often influenced by environmental conditions.
- The Eastern Brown Snake, native to Australia and New Guinea, engages in ritual combat during the breeding season. Males wrestle for access to females, and the females lay eggs which hatch with distinct patterns.
- Dekay"s Brownsnakes, commonly found in North America, are known for their unique newborn markings and rapid development after hatching.
- Brown tree snakes exhibit interesting courtship behaviors, including tongue-flicking and chin-rubbing, which are distinct among snakes within their family.
- The reproductive cycle of brown snakes can be influenced by seasonal changes, with some species entering a period of dormancy or reduced activity during cooler months.
The diversity in reproductive and lifecycle patterns among brown snake species highlights their adaptability and the role of environmental factors in shaping their biology.
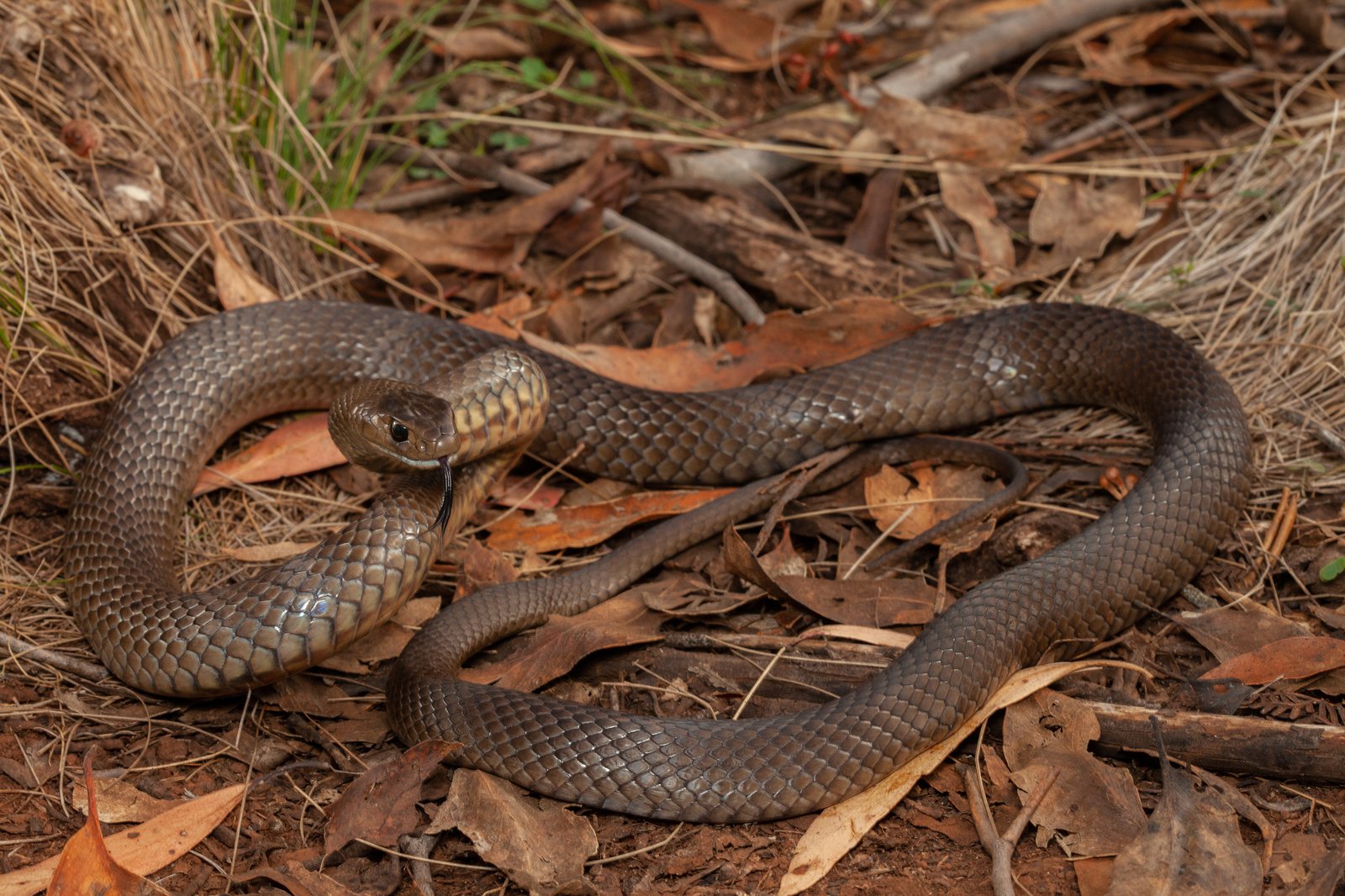

Conservation Status and Human Impact
The conservation status and human impact on brown snake species are diverse, reflecting the varied habitats and regions they inhabit. These species, ranging from North America to Australia, face different challenges and conservation efforts.
- In North America, species like the Western Hognose Snake, Chihuahuan Night Snake, and California Kingsnake are adapted to specific environments, such as deserts and forests. Human activities, including habitat destruction and pollution, can impact their populations.
- The Eastern Brown Snake, native to Australia and New Guinea, faces threats from habitat loss due to urbanization and agricultural expansion. Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection and understanding human-snake interactions to reduce conflicts.
- The invasive Brown Tree Snake, particularly in Guam, has had a significant ecological impact by preying on native bird species. Control methods have been implemented to manage its population and protect local ecosystems.
- Conservation statuses vary among brown snake species, with some classified as species of concern due to habitat loss, while others have stable populations but are monitored for potential threats.
Conservation efforts for brown snakes include habitat preservation, public education on snake safety, and research on ecological impact. These measures aim to balance human development with the protection of these unique reptiles.
10 Things You Didn\'t Know About The Eastern Brown Snake
Get a closer look at the mesmerizing Eastern Brown Snake in this captivating video! Learn about its impressive speed, dangerous venom, and fascinating camouflage abilities. Don\'t miss the chance to admire the beauty and grace of this remarkable creature in action.
Aussie Celebs\' Close Encounter With Deadly Eastern Brown Snake
Calling all fans of Australian celebrities! This video is your ultimate treat as it takes you behind the scenes of your favorite Aussie celebs\' glamorous lives. From red carpet events to exclusive interviews, get ready to indulge in the glitz and glamour of your beloved stars.
Identification and Safety Tips
Identifying brown snakes and ensuring safety around them is crucial given their diverse species and habitat ranges. Brown snakes vary in appearance and behavior, making identification and safety measures important for coexistence.
- Physical Identification: Brown snakes can vary in size and color patterns. For example, the Western Hognose Snake is known for its upturned nose and color patterns similar to rattlesnakes. The Eastern Brown Snake, found in Australia, requires close inspection to distinguish from other species in its genus due to variations in color and scale patterns.
- Behavioral Traits: Understanding the behavior of different brown snake species is key for identification. For instance, the Eastern Hognose Snake is known for its unique defensive behavior, which includes inflating its body and hissing.
- Safety Precautions: It"s essential to maintain a safe distance from all wild snakes. If encountered, do not attempt to handle or provoke the snake. Seek professional advice or assistance if a snake is found in a residential area or if there is a risk of conflict.
- Environment Awareness: Being aware of the snake"s native habitat can aid in identification and avoidance. For instance, many brown snakes are found in forested areas, grasslands, or near water sources.
- Emergency Response: In regions where venomous brown snakes are present, such as parts of Australia, it"s crucial to have knowledge of first aid procedures for snake bites and to seek immediate medical attention in case of an encounter.
Overall, respect for these reptiles and knowledge of their habits and habitats are key to safely coexisting with brown snakes.

Interesting Facts and Research Studies
The world of brown snakes is full of fascinating facts and ongoing research that sheds light on these intriguing reptiles. Each species of brown snake brings its own unique characteristics and behaviors to the table, making them a subject of interest for both herpetologists and enthusiasts alike.
- The Western Hognose Snake, for instance, is known for its distinctive upturned nose and color patterns that resemble rattlesnakes, a feature that helps it deter predators.
- In terms of diet, the Chihuahuan Night Snake, which inhabits the Chihuahuan Desert, preys on reptiles and salamanders, demonstrating a specific adaptation to its environment.
- California Kingsnakes, widely known for their color variation, display two main morphs: black-and-white and brown-and-cream, highlighting the diversity within a single species.
- The Eastern Brown Snake, native to Australia, is notable for its solitary nature and diurnal hunting habits. Its ability to raise its head like a periscope to survey for prey demonstrates a unique hunting strategy among snakes.
- Unique courtship behaviors have been observed in Brown Tree Snakes, with some females displaying behaviors traditionally seen in males, indicating a complex social structure within this species.
- Research has also highlighted the invasive nature of the Brown Tree Snake, particularly in areas like Guam, where it has significantly impacted local ecosystems.
These snippets of information represent just a glimpse into the diverse and fascinating world of brown snakes, a group that continues to captivate and inspire curiosity among researchers and snake enthusiasts worldwide.
Myths and Misconceptions about Brown Snakes
Brown snakes, encompassing a variety of species, are often subject to myths and misconceptions that can lead to misunderstandings about their nature and behavior. Addressing these misconceptions is essential for fostering a better understanding and coexistence with these reptiles.
- Aggressiveness: A common myth is that all brown snakes are highly aggressive and dangerous. While some species like the Eastern Brown Snake can be defensive when cornered, many brown snakes, such as the Western Hognose Snake, are known for their docile nature.
- Venomous vs. Non-Venomous: There"s a misconception that all brown snakes are venomous. In reality, the venomous nature varies significantly among species. For example, the Eastern Brown Snake is highly venomous, whereas species like the California Kingsnake and Chihuahuan Night Snake are non-venomous.
- Appearance: Another myth pertains to the identification of brown snakes. Some species are often misidentified due to similar color patterns with other snakes. For instance, the Western Hognose Snake has color patterns similar to rattlesnakes but can be distinguished by its upturned nose.
- Behavior in Captivity: Misconceptions also exist regarding their behavior in captivity. For example, the Eastern Brown Snake is known to exhibit cannibalistic tendencies in overcrowded conditions, a behavior not commonly expected from many snake species.
Debunking these myths is crucial for appreciating the diversity and ecological roles of brown snakes, promoting conservation efforts, and ensuring safe interactions between humans and these reptiles.

READ MORE:
Medical Significance and First Aid for Bites
The medical significance of brown snake species varies, with some being highly venomous, such as the Eastern Brown Snake, which is responsible for the highest number of snakebite fatalities in Australia. Understanding first aid for snakebites is crucial in regions where these snakes are prevalent.
- Identification of Venomous Species: It"s important to identify whether a brown snake is venomous. For example, the Eastern Brown Snake is venomous, and its bite requires immediate medical attention.
- First Aid for Snakebites: In case of a bite from a venomous brown snake, it is critical to remain calm, immobilize the bitten limb, and seek medical help immediately. Do not attempt to suck out the venom or apply a tourniquet. Applying a pressure immobilization bandage and keeping the bitten limb still can slow venom spread until medical help is received.
- Venom Effects: The venom of some brown snakes, like the Eastern Brown Snake, can cause severe symptoms, including bleeding disorders, collapse, and cardiac arrest. Immediate administration of the appropriate antivenom is necessary in such cases.
- Preventive Measures: To reduce the risk of snakebites, it is advisable to wear protective clothing such as boots and long trousers in snake-prone areas, especially in regions known for venomous brown snakes.
- Snakebite Education: Awareness and education about local snake species, their habitats, and behavior can help in preventing snakebites and enable appropriate response in case of an encounter.
Given the medical significance of some brown snake species, understanding their behavior, habitat, and appropriate first aid measures is vital for ensuring safety and effective treatment in case of snakebites.
Unraveling the mysteries of brown snake species reveals a world rich in diversity and ecological significance. These remarkable reptiles, varying from the harmless to the venomous, play a crucial role in our ecosystems. Understanding and respecting them is key to appreciating nature"s intricate balance.