Topic animals in the grassland ecosystem: Discover the vibrant world of animals in the grassland ecosystem, where diverse species thrive in these expansive, vital habitats, shaping the earth"s biodiversity.
Table of Content
- What are the animals found in the grassland ecosystem?
- Overview of Grassland Ecosystems
- Key Animal Species in Grasslands
- Adaptations of Grassland Animals
- Role of Predators and Herbivores in Grassland Ecology
- Biodiversity and Conservation Efforts
- Human Impacts on Grassland Ecosystems
- YOUTUBE: Grassland Ecosystem Animation
- Grassland Ecosystems Around the World
- Future Challenges and Research Directions
What are the animals found in the grassland ecosystem?
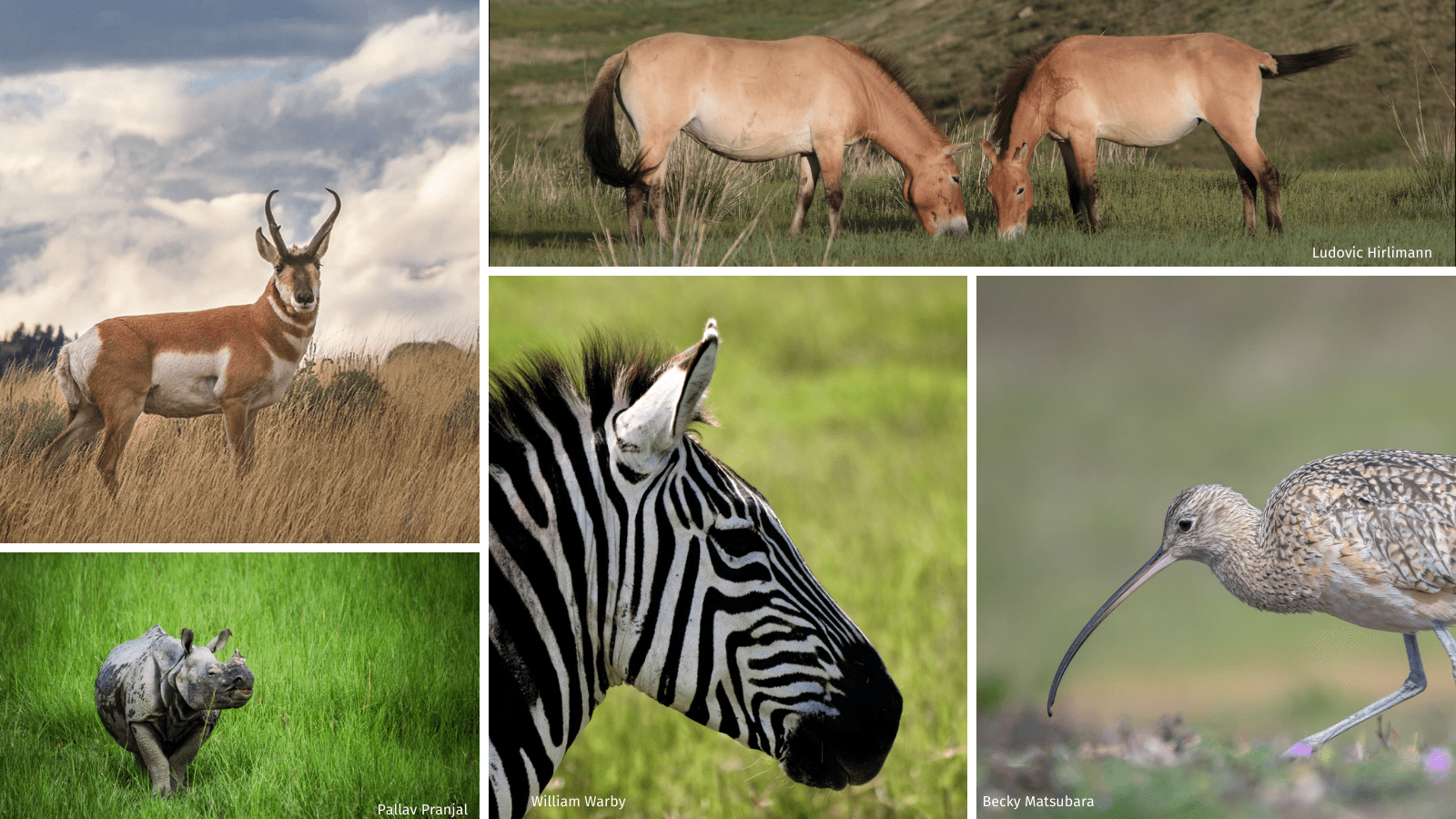
Animals found in the grassland ecosystem include:
- Giraffes
- African elephants
- Bison
- Black rhinoceros
- Black-footed ferrets
- Cheetahs
- Zebras
- Pronghorns
- Wildebeests
- Prairie dogs
- Warthogs
- Grasshoppers
- Ground squirrels
- Jackrabbits
These animals are well adapted to the grassland habitat and play important roles in maintaining the ecosystem\'s balance.
READ MORE:
Overview of Grassland Ecosystems
Grassland ecosystems, spanning across continents, are critical for supporting a wealth of wildlife and maintaining biodiversity. These ecosystems are characterized by vast open lands predominantly covered in grasses, herbs, and shrubs, with occasional trees. Grasslands can be found in various types, including savannas, prairies, and steppes, each with its unique climate, soil, and altitude conditions, influencing the diversity of life they support.
- Savannas: Warm year-round, with distinct wet and dry seasons, supporting a mix of grasses and sparse trees.
- Prairies: Known for their tall grasses, these regions experience moderate rainfall and have rich soils conducive to agriculture.
- Steppes: Characterized by short grasses, these areas have less rainfall and are often found in temperate zones.
Grasslands play a pivotal role in the ecosystem, serving as a habitat for numerous species, a source of food for herbivores, and a site for carbon storage which aids in climate regulation. Despite their importance, grasslands face threats from human activities such as agriculture, urbanization, and climate change, necessitating efforts for their conservation and sustainable management.

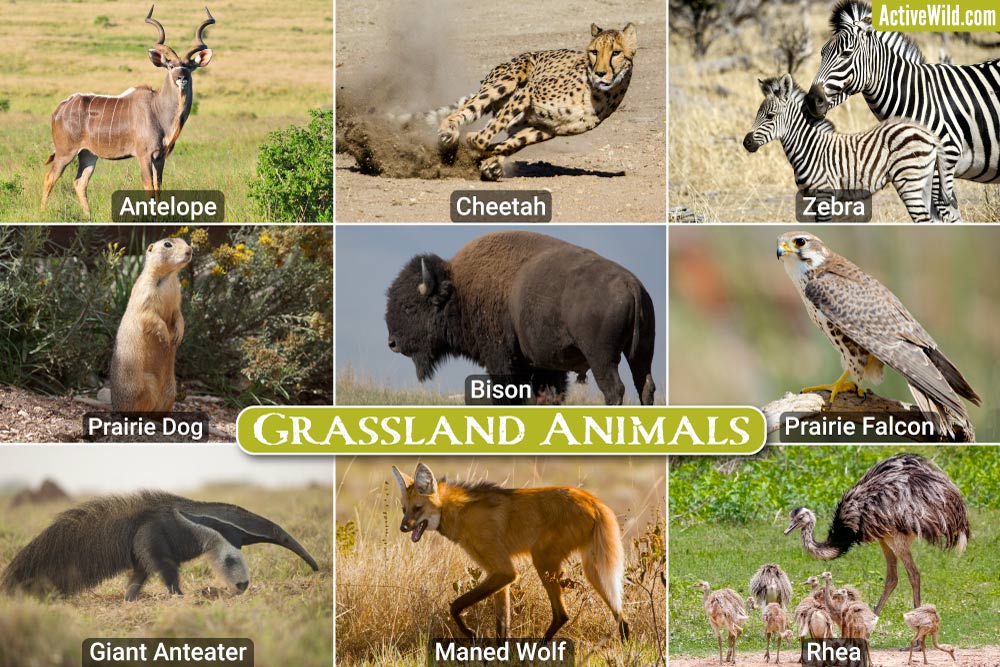
Key Animal Species in Grasslands
Grassland ecosystems are teeming with life, hosting a diverse array of animal species that play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance. These habitats are critical for the survival of many species, offering food, shelter, and breeding grounds. Here are some of the key animal species that inhabit grasslands across the globe:
- African Elephants: As the largest land animals, they help in shaping the savanna ecosystem by knocking down trees and trampling grasses, which helps maintain the grassland environment.
- American Bison: Once roaming the prairies of North America in vast herds, bison play a critical role in grassland ecology by grazing, which helps stimulate new grass growth.
- Cheetahs: The world"s fastest land animal, cheetahs are adapted to the open grasslands, where they can reach their top speed while hunting.
- Pronghorns: Native to the grasslands of North America, pronghorns are among the fastest mammals in the Western Hemisphere and are vital for maintaining the health of grassland ecosystems.
- Lions: As apex predators, lions play a key role in the grassland food chain, helping control the population of herbivores.
- Zebras: Their migration patterns are crucial for the dispersion of seeds and maintenance of grasslands" health and vitality.
These species, among others, illustrate the rich biodiversity found in grassland ecosystems and underscore the importance of these habitats for global biodiversity. Protecting these key animal species and their habitats is essential for preserving the intricate balance of grassland ecosystems.
Adaptations of Grassland Animals
Animals living in the grassland ecosystems have developed unique adaptations that enable them to survive and thrive in these environments. These adaptations range from physical characteristics to behavioral traits, helping animals cope with the challenges of grassland life, such as predation, climate extremes, and the search for food and water. Below are some of the notable adaptations:
- Speed and Agility: Many grassland predators and prey, like cheetahs and gazelles, have evolved to be incredibly fast and agile, enabling them to chase or evade in the open landscapes.
- Camouflage: Animals such as the grasshopper mouse and certain species of birds have coloring that blends into the grassland environment, helping them avoid predators.
- Digestive Adaptations: Herbivores like bison and zebras have complex digestive systems that allow them to efficiently process the tough, fibrous grasses that dominate their habitats.
- Social Structures: Species such as lions and wild dogs have developed complex social structures that enhance their ability to hunt and protect their members in the open grasslands.
- Migratory Behaviors: Many grassland animals, including various bird species, migrate seasonally to take advantage of different grazing areas and climates, ensuring their survival.
- Burrowing: Animals like prairie dogs and meerkats dig extensive burrow systems for protection from predators and extreme weather, as well as to store food.
These adaptations not only highlight the diversity of life in grassland ecosystems but also the intricate relationships and dependencies that have evolved over time. Understanding these adaptations is crucial for conserving these important habitats and their inhabitants.

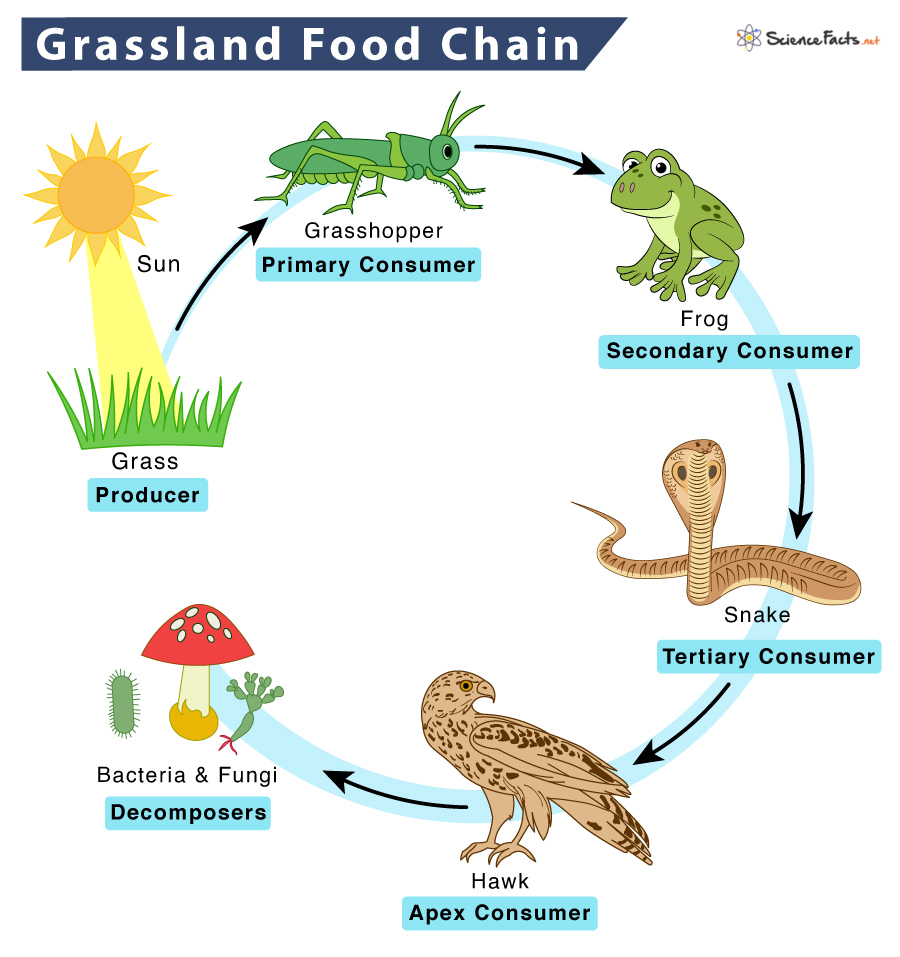
Role of Predators and Herbivores in Grassland Ecology
Predators and herbivores play pivotal roles in maintaining the health and stability of grassland ecosystems. Their interactions within these ecosystems drive ecological processes, influencing species diversity, population dynamics, and the overall structure of the community. Understanding the roles of these animals highlights the complexity and balance of grassland ecosystems.
- Herbivores as Landscape Shapers: Herbivores, such as bison, elephants, and zebras, shape the physical landscape by grazing. Their feeding habits control the height and spread of grasses, promoting biodiversity by allowing a variety of plant species to flourish.
- Predators Regulating Populations: Predators, including lions, wolves, and birds of prey, play a crucial role in controlling herbivore populations. This predation helps prevent overgrazing, ensuring that vegetation remains sustainable and diverse.
- Seed Dispersal and Fertilization: Many herbivores contribute to seed dispersal through their droppings, aiding in the spread of plant species. Additionally, their waste acts as a natural fertilizer, enriching the soil.
- Creating Niches for Other Species: The activities of predators and herbivores create niches for other species, such as burrowing animals and insects, by modifying the habitat and influencing the availability of resources.
- Maintaining Ecological Balance: The presence of both predators and herbivores ensures the maintenance of a balanced ecosystem by regulating species composition and preventing any one species from dominating the landscape.
These roles underscore the importance of preserving predator and herbivore populations in grasslands, as their decline can lead to significant ecological imbalances. Efforts to conserve these animals and their habitats are essential for the continued health and vitality of grassland ecosystems worldwide.
Biodiversity and Conservation Efforts
Grassland ecosystems are vital for their high biodiversity, supporting a vast array of plant and animal species. These ecosystems are under threat from human activities, leading to the need for concerted conservation efforts. Biodiversity in grasslands offers numerous ecological benefits, including habitat provision, climate regulation, and soil stabilization. Here"s how conservation efforts are being directed to protect these critical habitats:
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks and wildlife reserves to protect significant grassland habitats from agricultural expansion and urban development.
- Sustainable Management Practices: Promoting sustainable land use practices that balance the needs of wildlife with agriculture, such as rotational grazing and the restoration of native plant species.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting research to understand the complexities of grassland ecosystems and monitoring species populations to inform conservation strategies.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their role in stewardship of the land and the benefits of sustainable practices for their livelihoods.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Implementing strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change on grasslands, including conservation of carbon-rich soils and restoration of degraded lands.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders to protect migratory species and large ecosystems that span multiple countries, recognizing the global importance of grassland biodiversity.
The protection of grassland ecosystems is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the health of our planet. Through targeted conservation efforts, we can safeguard these habitats for future generations, maintaining the balance of life that they support.

Human Impacts on Grassland Ecosystems
Human activities have significantly impacted grassland ecosystems worldwide, with both negative and positive effects. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate damage and promote the health and sustainability of these vital habitats. Here are some of the main ways humans have influenced grassland ecosystems:
- Agricultural Expansion: The conversion of grasslands into agricultural land for crops and livestock grazing is one of the most significant threats, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation.
- Urbanization: The development of urban areas encroaches on grasslands, reducing available habitats for native species and altering the ecosystem"s natural balance.
- Introduction of Non-native Species: The introduction of invasive plant and animal species can outcompete native species, leading to decreased biodiversity and altered ecosystem dynamics.
- Pollution: Pollution from agricultural runoff, pesticides, and industrial activities can degrade grassland environments, affecting both plant and animal life.
- Climate Change: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns affect grassland ecosystems, potentially altering species distributions and ecosystem functions.
- Conservation Efforts: On the positive side, human-initiated conservation programs and sustainable management practices are helping to restore and protect grassland ecosystems, promoting biodiversity and ecological health.
Addressing the impacts of human activities on grassland ecosystems requires a multifaceted approach, including conservation, sustainable management, and education to ensure these habitats continue to thrive for future generations.
Grassland Ecosystem Animation
Animation: Dive into the mesmerizing world of animation and let your imagination run wild! Discover the extraordinary artistry and creativity behind captivating animated films, guaranteed to leave you in awe. Tune in to this video to witness the magic of animation come to life!
What are Grasslands Science for Kids
Science: Unveil the wonders of the universe with mind-blowing scientific discoveries! Explore the mysteries of our world, from the depths of the ocean to the vastness of outer space. Grasp the fascinating concepts and breakthroughs that shape our understanding of life. Join us on this captivating journey of knowledge and exploration!
Grassland Ecosystems Around the World
Grassland ecosystems are diverse and widespread, covering large portions of the globe. Each region"s grasslands have unique characteristics and support a wide range of flora and fauna. Here, we explore some of the most notable grassland ecosystems around the world:
- The Savannas of Africa: Home to iconic species such as lions, elephants, and giraffes, the African savannas are characterized by a mix of grasslands and scattered trees, thriving under warm temperatures and seasonal rainfall.
- The Prairies of North America: Once covering vast areas of the continent, these grasslands are known for their tall grasses and have been a critical habitat for bison, prairie dogs, and countless bird species.
- The Steppes of Eurasia: Stretching from Eastern Europe through Mongolia, the steppes are vast areas of grassland with extreme temperature variations, supporting unique species like the saiga antelope and Siberian tiger.
- The Pampas of South America: These fertile South American grasslands are important for agriculture but also host a variety of wildlife, including the rhea (a large flightless bird) and the pampas deer.
- The Australian Grasslands: Featuring both tropical and temperate grasslands, Australia"s landscapes support kangaroos, emus, and a unique array of flora and fauna adapted to the continent"s varied climates.
These grassland ecosystems, despite their differences, all play vital roles in their respective regions, supporting biodiversity, providing for human needs, and maintaining ecological balance. Protecting these grasslands from threats such as climate change and land conversion is crucial for their preservation and the well-being of our planet.

READ MORE:
Future Challenges and Research Directions
Grassland ecosystems face several future challenges that demand attention and action. Research plays a critical role in understanding these challenges and developing strategies for conservation and sustainable management. Here are key areas of focus for future research and the challenges that need to be addressed:
- Climate Change Impact: Investigating how changing climate conditions affect grassland ecosystems, including alterations in species distribution, biodiversity loss, and shifts in ecosystem services.
- Sustainable Land Use: Developing and promoting land use practices that balance agricultural productivity with the conservation of natural habitats to ensure the long-term health of grassland ecosystems.
- Invasive Species Control: Understanding the impact of invasive species on native biodiversity and ecosystem function, and developing effective management strategies to control their spread.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Identifying key species and habitats that require protection, and implementing conservation strategies to protect and restore biodiversity in grassland ecosystems.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Addressing conflicts between human activities and wildlife conservation, and finding solutions that benefit both local communities and grassland conservation efforts.
- Ecological Restoration: Researching restoration techniques to recover degraded grasslands, including reseeding native plants and reintroducing key animal species to restore ecological balance.
The future of grassland ecosystems depends on our ability to understand and address these challenges. Through targeted research and collaborative efforts, we can work towards sustainable solutions that preserve these vital habitats for future generations.
Exploring the majestic grassland ecosystems reveals a world where animals and nature coexist in delicate balance. By understanding and protecting these vital habitats, we ensure a richer, more diverse planet for generations to come.










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/164249141-56a006353df78cafda9fb0e5-be1ea8f1f1774e12bde868a948812d8d.jpg)

