Topic abiotic factors in the ecosystem: Explore the pivotal role of abiotic factors in ecosystems, understanding how elements like sunlight, water, and soil fundamentally shape biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Table of Content
- What are the main abiotic factors in the ecosystem?
- Understanding Abiotic Factors and Their Importance in Ecosystems
- Types of Abiotic Factors: Light, Temperature, Water, and Soil
- How Abiotic Factors Affect Biotic Components in Ecosystems
- Role of Climate and Weather as Abiotic Factors
- Influence of Abiotic Factors on Ecosystem Diversity and Productivity
- YOUTUBE: Abiotic Factors in Ecosystems: Water
- Adaptations of Organisms to Abiotic Environmental Stresses
- Human Impact on Abiotic Factors and Ecosystem Health
- Monitoring and Managing Abiotic Factors for Conservation
- Future Challenges in Understanding the Impact of Abiotic Factors
What are the main abiotic factors in the ecosystem?
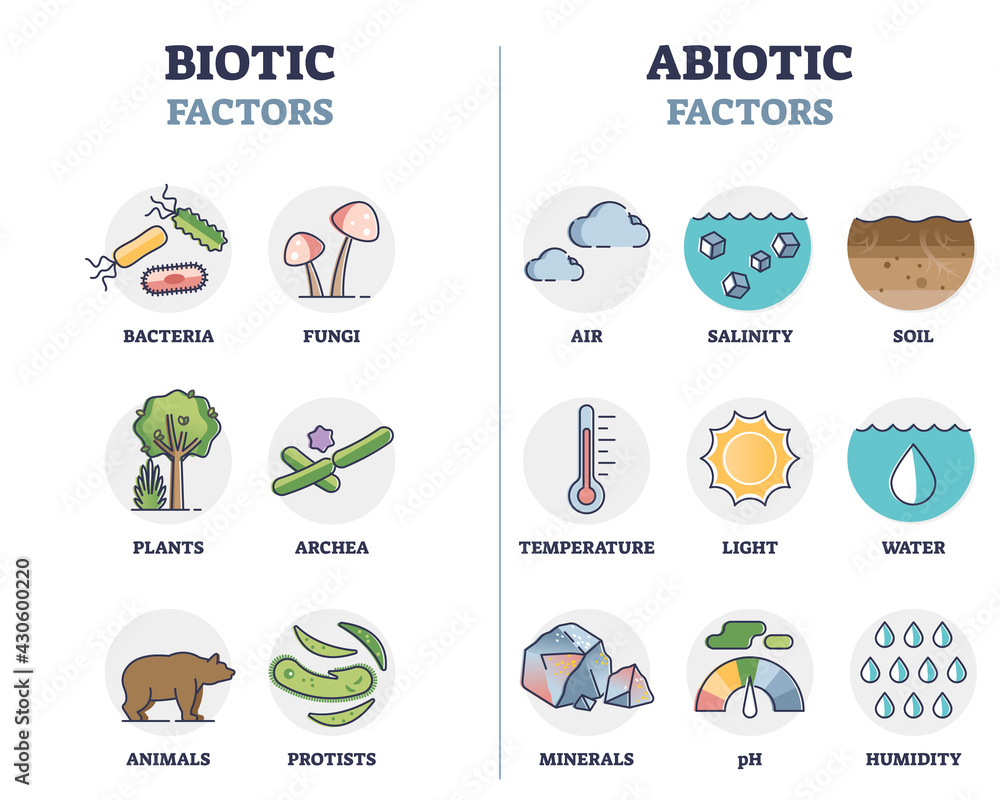
Abiotic factors are non-living components of the ecosystem that greatly influence its functioning and the organisms that inhabit it. These factors can be divided into several categories:
- Climate: Climate encompasses factors such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind patterns. These elements determine the overall weather conditions in an ecosystem.
- Topography: Topography refers to the physical features of the land, including elevation, slope, and relief. It affects factors like drainage patterns, water availability, and soil formation.
- Soil: Soil characteristics, such as texture, pH level, nutrient content, and organic matter, play a crucial role in determining what types of plants can grow in a particular area.
- Light: Sunlight availability and intensity impact photosynthesis, which influences the growth and development of both plants and algae in the ecosystem. It also affects various ecological processes, such as the availability of food and the behavior of organisms.
- Water: The presence and availability of water are vital for the survival of organisms in an ecosystem. It affects nutrient transport, hydration, and overall ecosystem productivity.
- Air: Air composition, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and pollutants, is essential for the respiration of organisms and influences their metabolic processes.
- Chemical factors: These encompass elements such as minerals, gases, and pollutants present in the ecosystem. They can significantly impact the physiological processes of organisms.
These abiotic factors interact in complex ways, shaping the ecological characteristics and potential biodiversity of an ecosystem. They provide the foundation upon which the biotic components of the ecosystem depend.
READ MORE:
Understanding Abiotic Factors and Their Importance in Ecosystems
Abiotic factors are the non-living elements that play a key role in the environment and the functioning of ecosystems. These factors include but are not limited to sunlight, temperature, water, and soil, each contributing significantly to the health and sustainability of ecosystems. Unlike biotic factors, which are living components such as plants and animals, abiotic factors shape the habitat and influence the conditions for life in various environments.
The importance of abiotic factors cannot be overstated. They determine the types of organisms that can survive in an ecosystem, influence their rates of growth, reproduction, and the structure of communities. For example, the availability of water directly affects the survival of all organisms, while sunlight is crucial for photosynthesis, a process that forms the basis of most food chains.
- Light: Essential for photosynthesis, light intensity and duration influence plant growth and the types of species that can exist in an area.
- Temperature: Affects metabolic rates of organisms and determines the geographic distribution of species.
- Water: A critical resource for all living organisms, water availability shapes ecosystems and influences species diversity.
- Soil: The composition, pH, and nutrient content of soil determine the types of plants that can grow, which in turn supports various animal species.
Understanding abiotic factors is crucial for conservation efforts, as changes in these elements can lead to significant impacts on ecosystem health and biodiversity. Human activities, such as pollution and deforestation, can alter abiotic factors, leading to habitat degradation and loss of species. Monitoring and managing these factors is essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and ensuring the survival of diverse species on Earth.
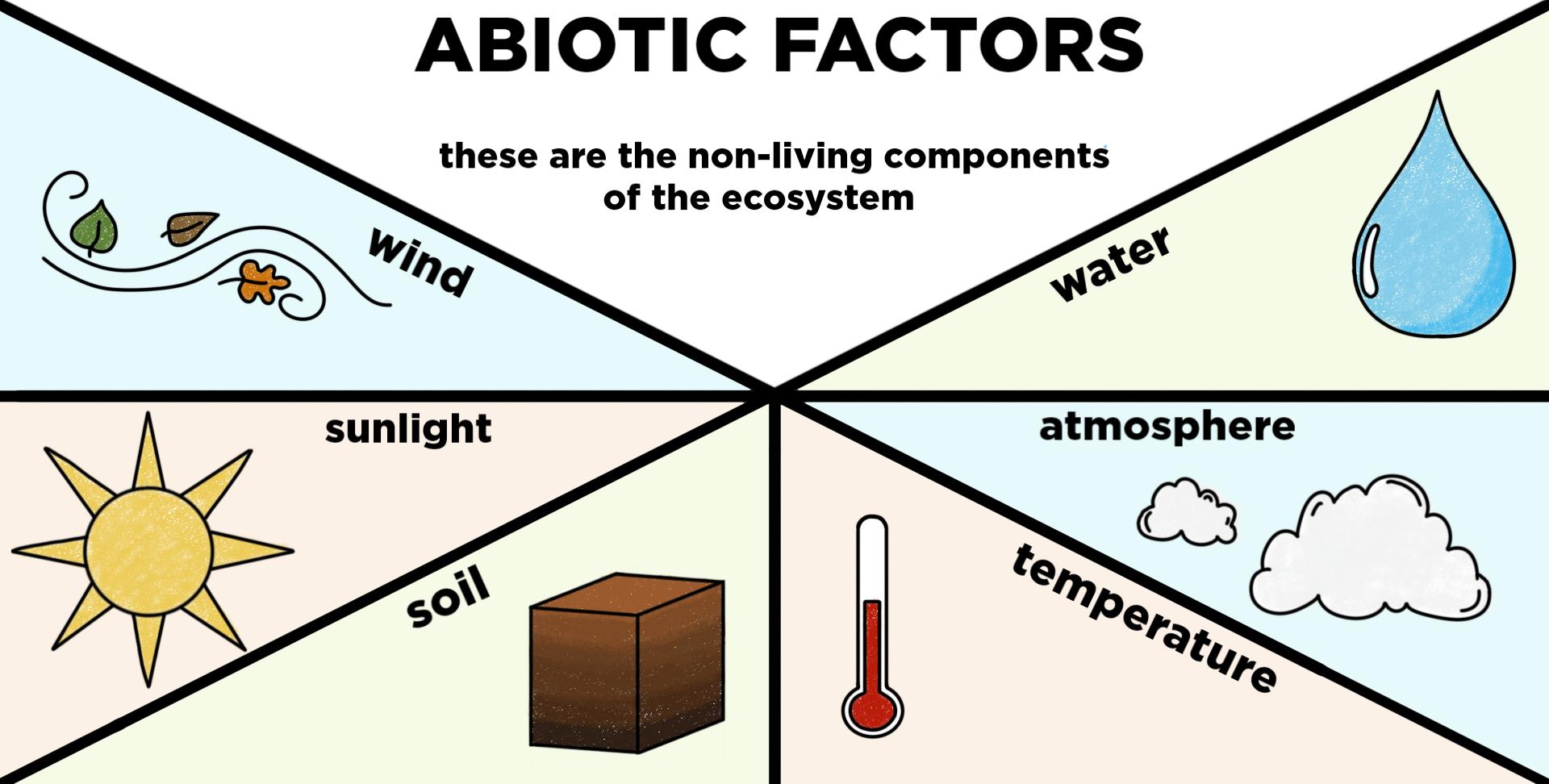
Types of Abiotic Factors: Light, Temperature, Water, and Soil
Abiotic factors are crucial components of the environment that influence the structure and function of ecosystems. Among these, light, temperature, water, and soil stand out as fundamental elements that affect both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Understanding how these factors interact helps us appreciate the complexity and dynamism of natural habitats.
- Light: Essential for photosynthesis, light determines plant growth rates, photosynthetic activity, and the distribution of plants and photosynthetic organisms. The availability of sunlight affects the energy flow through an ecosystem, influencing the productivity of the ecosystem.
- Temperature: Regulates the metabolic rates of organisms and affects their distribution. Extreme temperatures can limit the presence of living organisms in an area, while moderate temperatures may support a diverse range of life.
- Water: A critical factor for all living organisms, water availability influences species distribution, plant growth, and the types of habitats that can develop. Water quality and quantity are vital for sustaining life, shaping ecosystems like rivers, lakes, and wetlands.
- Soil: Composed of minerals, organic matter, air, and water, soil supports plant life and serves as a foundation for terrestrial ecosystems. The type, pH, and nutrient content of soil determine the species of plants that can thrive, which in turn influences the animals that depend on those plants for food and habitat.
Together, these abiotic factors create a unique environment that supports a wide array of life forms. Each factor contributes to the ecosystem"s overall health and productivity, demonstrating the interconnectedness of life and the non-living environment.
How Abiotic Factors Affect Biotic Components in Ecosystems
Abiotic factors, the non-living components of the environment, have a profound impact on the living, or biotic, components of ecosystems. These factors influence the survival, reproduction, and distribution of organisms, thereby shaping the composition and function of ecosystems. Understanding the relationship between abiotic and biotic components is essential for comprehending the dynamics of natural habitats.
- Regulation of Metabolic Processes: Temperature and water are critical in regulating the metabolic rates of organisms. For instance, enzymatic reactions in living organisms are highly temperature-sensitive, affecting growth and reproduction rates.
- Influence on Plant Growth: Light and soil quality directly impact plant growth. Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, while soil nutrients support plant health. These factors determine plant distribution, which in turn influences the availability of food for herbivores and other trophic levels.
- Water Availability: Water availability shapes ecosystems by determining the types of organisms that can survive in a given environment. Aquatic environments are influenced by factors such as salinity and pH, which affect the species composition of these habitats.
- Habitat Formation: The physical landscape, shaped by factors like soil type and water flow, creates diverse habitats. These habitats provide the necessary conditions for different life forms to thrive, from forests and grasslands to wetlands and deserts.
- Species Distribution and Diversity: The combination of abiotic factors such as temperature, light, and soil conditions dictates the distribution of species and the biodiversity within ecosystems. Extreme conditions may limit species diversity, while varied habitats can support a wide range of organisms.
Abiotic factors and biotic components are intricately linked, with changes in non-living elements often leading to significant effects on ecosystem structure and function. These interactions underline the importance of maintaining environmental balance to support biodiversity and ecosystem health.

Role of Climate and Weather as Abiotic Factors
Climate and weather are significant abiotic factors that have a profound impact on ecosystems. They shape the physical environment and influence the life cycles, distribution, and behavior of organisms. Understanding the role of climate and weather helps in comprehending the dynamics of natural ecosystems and the challenges faced by living organisms.
- Climate: Refers to the long-term patterns of temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation in an area. Climate determines the types of ecosystems that can exist in a region, influencing the diversity of species found there. For example, tropical climates support rainforests, while polar climates are home to tundra ecosystems.
- Weather: Represents the short-term variations in these same factors. Daily or seasonal weather changes can significantly affect the availability of resources, such as water and food, and can influence the reproductive patterns and survival of organisms.
Climate and weather affect ecosystems in several ways:
- Temperature and Precipitation: Govern plant growth, distribution, and the availability of water, thereby affecting the entire food web.
- Extreme Weather Events: Such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts, can reshape landscapes, alter habitats, and trigger changes in population dynamics.
- Seasonal Changes: Drive migration patterns, breeding seasons, and dormancy periods in various species.
Through these mechanisms, climate and weather play a crucial role in the structuring of ecosystems. They not only influence the physical characteristics of the environment but also affect the interactions among different biotic components, thereby shaping the biodiversity and productivity of ecosystems.
Influence of Abiotic Factors on Ecosystem Diversity and Productivity
Abiotic factors, the non-living components of an ecosystem, significantly influence its diversity and productivity. These factors, such as sunlight, temperature, water, and soil quality, create the physical environment in which organisms live. Their variability determines the types of habitats available and the species that can thrive in those habitats.
- Sunlight: It is the primary source of energy for ecosystems, driving photosynthesis in plants and determining the energy available for other organisms in the food web. Sunlight intensity and duration can influence plant growth patterns and, subsequently, the diversity of herbivores and predators.
- Temperature: Affects the physiological processes of organisms. Temperature variations define the geographical distribution of species and influence the rates of ecosystem processes, such as nutrient cycling and decomposition.
- Water: Availability is crucial for all living organisms and shapes ecosystems. Water scarcity or abundance affects species composition, plant growth, and the ability of animals to find hydration. Aquatic ecosystems" productivity is directly linked to water quality and temperature.
- Soil: The characteristics of soil, including its texture, nutrient content, and moisture, dictate the types of plants that can grow, influencing the entire food chain. Rich, fertile soil supports higher plant diversity, leading to greater overall biodiversity.
These abiotic factors interact in complex ways to influence ecosystem diversity and productivity. Changes in one factor can lead to shifts in the balance of ecosystems, affecting the variety of species and their populations. Understanding the role of abiotic factors is essential for conservation efforts, sustainable management of natural resources, and predicting the impacts of climate change on biodiversity.

Abiotic Factors in Ecosystems: Water
Water: Discover the mesmerizing beauty and power of water in this captivating video! Witness stunning ocean waves, serene waterfalls, and calming rain showers that will leave you in awe of nature\'s liquid wonders. Dive into this visually stunning journey and let the soothing sounds of water transport you to a state of tranquility.
Abiotic Factors in Ecosystems: Sunlight
Sunlight: Let the warm embrace of sunlight fill your senses as you embark on an enchanting visual adventure. This extraordinary video showcases the vibrant rays of the sun, casting a magical glow on nature\'s wonders. Immerse yourself in the golden hues of sunrise, bask in the serene glow of a sunset, and experience the rejuvenating power of sunlight like never before.
Adaptations of Organisms to Abiotic Environmental Stresses
Organisms have evolved a variety of adaptations to survive and thrive in the face of abiotic environmental stresses. These adaptations allow them to cope with challenges such as extreme temperatures, limited water supply, high salinity, and intense sunlight. Understanding these adaptations provides insight into the resilience of life in diverse ecosystems.
- Temperature Adaptations: Organisms living in extremely hot or cold environments have developed mechanisms to regulate their body temperature. For example, some desert animals are nocturnal to avoid daytime heat, while Arctic animals have thick fur and fat layers for insulation.
- Water Conservation: In arid environments, plants and animals have adaptations to minimize water loss. Plants may have waxy leaves to reduce transpiration, and animals like camels can tolerate dehydration and store water efficiently.
- Salinity Tolerance: Organisms in saline environments, such as salt marshes, have developed ways to excrete excess salt or to prevent its uptake. This includes specialized glands in animals and salt excretion mechanisms in plants.
- Light Adaptations: Plants in areas with varying light intensities have adapted by altering their leaf size, orientation, and pigment concentration to optimize photosynthesis. For instance, shade-tolerant species can photosynthesize efficiently at low light levels.
These adaptations are not only crucial for the survival of individual species but also influence the structure and function of the ecosystems they inhabit. By understanding how organisms adapt to abiotic stresses, we can better appreciate the complexity of life on Earth and the importance of conserving diverse habitats.
Human Impact on Abiotic Factors and Ecosystem Health
Human activities have a profound impact on abiotic factors, influencing ecosystem health and stability. From altering the climate to reshaping the landscape, our actions affect the fundamental components that support life on Earth. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing sustainable practices and mitigating negative consequences on ecosystems.
- Climate Change: The release of greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels increases global temperatures, altering weather patterns and affecting ecosystems worldwide. Changes in temperature and precipitation affect the distribution of species and the timing of biological events.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and urbanization introduce harmful substances into ecosystems. These pollutants can degrade habitat quality, reduce water availability, and harm organisms through toxic exposure.
- Land Use Change: Deforestation, urban expansion, and agriculture modify the landscape, reducing natural habitats and increasing soil erosion. Such changes impact water cycles, soil fertility, and the availability of resources for wildlife and humans.
- Water Management: Overuse of freshwater resources for agriculture, industry, and personal consumption alters hydrological systems. Dams, irrigation, and water diversion projects can lead to habitat destruction, reduced water quality, and changes in sediment transport.
These human-driven changes underscore the need for conservation efforts and sustainable management of abiotic factors. By understanding and mitigating our impact, we can preserve ecosystem health and ensure the continued provision of essential services that support life on Earth.

Monitoring and Managing Abiotic Factors for Conservation
Effective conservation efforts require a comprehensive understanding of the abiotic factors that influence ecosystem health and biodiversity. Monitoring and managing these non-living components are crucial for maintaining ecological balance and supporting sustainable habitats. Here are some strategies and considerations in the conservation of abiotic factors:
- Climate Monitoring: Regular observation of climate patterns helps in predicting and mitigating the adverse effects of climate change on ecosystems. This includes tracking changes in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events.
- Water Quality Management: Ensuring the cleanliness and chemical balance of water bodies is essential for the survival of aquatic life and the health of terrestrial ecosystems that depend on them. Measures include pollution control, restoration of natural water courses, and sustainable water use practices.
- Soil Conservation: Protecting soil from erosion, contamination, and degradation is key to preserving fertile land for agriculture and natural vegetation. Practices such as crop rotation, controlled grazing, and reforestation help maintain soil health and prevent land degradation.
- Light Pollution Reduction: Minimizing light pollution in natural habitats can protect nocturnal wildlife and maintain natural rhythms of ecosystems. This can be achieved through better planning of urban lighting and promoting awareness of its ecological impacts.
- Temperature Regulation: Mitigating the urban heat island effect through green infrastructure, such as planting trees and creating green spaces, can help regulate local temperatures and support urban biodiversity.
By actively monitoring and managing these abiotic factors, conservationists can help ensure the resilience of ecosystems against environmental stresses and human impacts. These efforts contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the sustainable use of natural resources, benefiting both nature and human societies.
READ MORE:
Future Challenges in Understanding the Impact of Abiotic Factors
As ecosystems worldwide face unprecedented changes due to human activity and climate change, understanding the impact of abiotic factors on these systems presents ongoing and emerging challenges. The complexity of ecosystems, coupled with the intricate interplay between abiotic and biotic components, necessitates a multidisciplinary approach to predict and mitigate the effects of these changes.
- Climate Change: One of the most pressing challenges is predicting how alterations in climate variables—such as temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events—will affect ecosystem structure and function. These changes can alter the distribution of species, the timing of biological events, and the productivity of ecosystems.
- Pollution: The increasing levels of pollutants in soil, water, and air from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources can drastically alter the quality and availability of abiotic factors, impacting ecosystem health and biodiversity.
- Land Use Change: Human activities that change the land surface, including deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture, can lead to the loss of habitats, changes in soil composition, and alterations in water cycles, further stressing ecosystems.
- Technological and Methodological Advances: There is a need for advanced monitoring techniques and models to accurately predict the responses of ecosystems to changes in abiotic factors. This includes developing remote sensing technologies, data analysis tools, and ecological models that can integrate complex environmental data.
- Global Cooperation and Policy Making: Addressing the global nature of environmental change requires international collaboration and effective policy frameworks that can adapt to new scientific findings and incorporate sustainable management practices for abiotic resources.
Addressing these challenges requires an integrated approach that combines research, technology, and policy to enhance our understanding of ecosystem dynamics. By fostering global collaboration and investing in science and education, we can develop strategies to mitigate the impacts of changing abiotic factors and safeguard the health and diversity of the planet"s ecosystems.
Exploring the intricate role of abiotic factors unveils the complexity of ecosystems and highlights the urgent need for sustainable interactions between humans and the natural world, fostering a deeper appreciation and proactive conservation efforts.